Zhengyang Liang
Video-BrowseComp: Benchmarking Agentic Video Research on Open Web
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:The evolution of autonomous agents is redefining information seeking, transitioning from passive retrieval to proactive, open-ended web research. However, while textual and static multimodal agents have seen rapid progress, a significant modality gap remains in processing the web's most dynamic modality: video. Existing video benchmarks predominantly focus on passive perception, feeding curated clips to models without requiring external retrieval. They fail to evaluate agentic video research, which necessitates actively interrogating video timelines, cross-referencing dispersed evidence, and verifying claims against the open web. To bridge this gap, we present \textbf{Video-BrowseComp}, a challenging benchmark comprising 210 questions tailored for open-web agentic video reasoning. Unlike prior benchmarks, Video-BrowseComp enforces a mandatory dependency on temporal visual evidence, ensuring that answers cannot be derived solely through text search but require navigating video timelines to verify external claims. Our evaluation of state-of-the-art models reveals a critical bottleneck: even advanced search-augmented models like GPT-5.1 (w/ Search) achieve only 15.24\% accuracy. Our analysis reveals that these models largely rely on textual proxies, excelling in metadata-rich domains (e.g., TV shows with plot summaries) but collapsing in metadata-sparse, dynamic environments (e.g., sports, gameplay) where visual grounding is essential. As the first open-web video research benchmark, Video-BrowseComp advances the field beyond passive perception toward proactive video reasoning.
UniVA: Universal Video Agent towards Open-Source Next-Generation Video Generalist
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:While specialized AI models excel at isolated video tasks like generation or understanding, real-world applications demand complex, iterative workflows that combine these capabilities. To bridge this gap, we introduce UniVA, an open-source, omni-capable multi-agent framework for next-generation video generalists that unifies video understanding, segmentation, editing, and generation into cohesive workflows. UniVA employs a Plan-and-Act dual-agent architecture that drives a highly automated and proactive workflow: a planner agent interprets user intentions and decomposes them into structured video-processing steps, while executor agents execute these through modular, MCP-based tool servers (for analysis, generation, editing, tracking, etc.). Through a hierarchical multi-level memory (global knowledge, task context, and user-specific preferences), UniVA sustains long-horizon reasoning, contextual continuity, and inter-agent communication, enabling interactive and self-reflective video creation with full traceability. This design enables iterative and any-conditioned video workflows (e.g., text/image/video-conditioned generation $\rightarrow$ multi-round editing $\rightarrow$ object segmentation $\rightarrow$ compositional synthesis) that were previously cumbersome to achieve with single-purpose models or monolithic video-language models. We also introduce UniVA-Bench, a benchmark suite of multi-step video tasks spanning understanding, editing, segmentation, and generation, to rigorously evaluate such agentic video systems. Both UniVA and UniVA-Bench are fully open-sourced, aiming to catalyze research on interactive, agentic, and general-purpose video intelligence for the next generation of multimodal AI systems. (https://univa.online/)
Video-XL-2: Towards Very Long-Video Understanding Through Task-Aware KV Sparsification
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) models have made significant progress in video understanding over the past few years. However, processing long video inputs remains a major challenge due to high memory and computational costs. This makes it difficult for current models to achieve both strong performance and high efficiency in long video understanding. To address this challenge, we propose Video-XL-2, a novel MLLM that delivers superior cost-effectiveness for long-video understanding based on task-aware KV sparsification. The proposed framework operates with two key steps: chunk-based pre-filling and bi-level key-value decoding. Chunk-based pre-filling divides the visual token sequence into chunks, applying full attention within each chunk and sparse attention across chunks. This significantly reduces computational and memory overhead. During decoding, bi-level key-value decoding selectively reloads either dense or sparse key-values for each chunk based on its relevance to the task. This approach further improves memory efficiency and enhances the model's ability to capture fine-grained information. Video-XL-2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various long video understanding benchmarks, outperforming existing open-source lightweight models. It also demonstrates exceptional efficiency, capable of processing over 10,000 frames on a single NVIDIA A100 (80GB) GPU and thousands of frames in just a few seconds.
MomentSeeker: A Comprehensive Benchmark and A Strong Baseline For Moment Retrieval Within Long Videos
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) holds great promise in addressing challenges associated with long video understanding. These methods retrieve useful moments from long videos for their presented tasks, thereby enabling multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to generate high-quality answers in a cost-effective way. In this work, we present MomentSeeker, a comprehensive benchmark to evaluate retrieval models' performance in handling general long-video moment retrieval (LVMR) tasks. MomentSeeker offers three key advantages. First, it incorporates long videos of over 500 seconds on average, making it the first benchmark specialized for long-video moment retrieval. Second, it covers a wide range of task categories (including Moment Search, Caption Alignment, Image-conditioned Moment Search, and Video-conditioned Moment Search) and diverse application scenarios (e.g., sports, movies, cartoons, and ego), making it a comprehensive tool for assessing retrieval models' general LVMR performance. Additionally, the evaluation tasks are carefully curated through human annotation, ensuring the reliability of assessment. We further fine-tune an MLLM-based LVMR retriever on synthetic data, which demonstrates strong performance on our benchmark. We perform extensive experiments with various popular multimodal retrievers based on our benchmark, whose results highlight the challenges of LVMR and limitations for existing methods. Our created resources will be shared with community to advance future research in this field.
Any Information Is Just Worth One Single Screenshot: Unifying Search With Visualized Information Retrieval
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:With the popularity of multimodal techniques, it receives growing interests to acquire useful information in visual forms. In this work, we formally define an emerging IR paradigm called \textit{Visualized Information Retrieval}, or \textbf{Vis-IR}, where multimodal information, such as texts, images, tables and charts, is jointly represented by a unified visual format called \textbf{Screenshots}, for various retrieval applications. We further make three key contributions for Vis-IR. First, we create \textbf{VIRA} (Vis-IR Aggregation), a large-scale dataset comprising a vast collection of screenshots from diverse sources, carefully curated into captioned and question-answer formats. Second, we develop \textbf{UniSE} (Universal Screenshot Embeddings), a family of retrieval models that enable screenshots to query or be queried across arbitrary data modalities. Finally, we construct \textbf{MVRB} (Massive Visualized IR Benchmark), a comprehensive benchmark covering a variety of task forms and application scenarios. Through extensive evaluations on MVRB, we highlight the deficiency from existing multimodal retrievers and the substantial improvements made by UniSE. Our work will be shared with the community, laying a solid foundation for this emerging field.
Scaling Laws For Diffusion Transformers
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion transformers (DiT) have already achieved appealing synthesis and scaling properties in content recreation, e.g., image and video generation. However, scaling laws of DiT are less explored, which usually offer precise predictions regarding optimal model size and data requirements given a specific compute budget. Therefore, experiments across a broad range of compute budgets, from 1e17 to 6e18 FLOPs are conducted to confirm the existence of scaling laws in DiT for the first time. Concretely, the loss of pretraining DiT also follows a power-law relationship with the involved compute. Based on the scaling law, we can not only determine the optimal model size and required data but also accurately predict the text-to-image generation loss given a model with 1B parameters and a compute budget of 1e21 FLOPs. Additionally, we also demonstrate that the trend of pre-training loss matches the generation performances (e.g., FID), even across various datasets, which complements the mapping from compute to synthesis quality and thus provides a predictable benchmark that assesses model performance and data quality at a reduced cost.
Seeing Clearly, Answering Incorrectly: A Multimodal Robustness Benchmark for Evaluating MLLMs on Leading Questions
Jun 15, 2024Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have exhibited impressive capabilities in visual understanding and reasoning, providing sightly reasonable answers, such as image descriptions. This has spurred extensive research on the evaluation of MLLMs. Most evaluation benchmarks assume that incorrect answers indicate a lack of understanding of the visual content. However, our findings reveal that, in many cases, MLLMs answer questions incorrectly despite correctly understanding the visual content. This suggests that incorrect answers do not necessarily imply a lack of comprehension but may instead result from lacking robustness to leading questions. To comprehensively measure MLLMs' understanding capability and robustness to leading questions, we introduce a MultiModal Robustness benchmark (MMR). MMR contains paired positive and negative questions across 12 categories, meticulously annotated by humans. We evaluate 18 leading MLLMs on the MMB benchmark, revealing that MLLMs suffer from fragility to leading questions despite understanding the visual content. To enhance MLLMs' understanding capability and robustness, we further present a training set with paired positive and negative visual question-answer samples. Experiments verify that MLLMs' robustness can be significantly enhanced by tuning on this new training set. The benchmark, training set, and code can be found at https://github.com/BAAI-DCAI/Multimodal-Robustness-Benchmark.
Dynamic Self-adaptive Multiscale Distillation from Pre-trained Multimodal Large Model for Efficient Cross-modal Representation Learning
Apr 16, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, pre-trained multimodal large models have attracted widespread attention due to their outstanding performance in various multimodal applications. Nonetheless, the extensive computational resources and vast datasets required for their training present significant hurdles for deployment in environments with limited computational resources. To address this challenge, we propose a novel dynamic self-adaptive multiscale distillation from pre-trained multimodal large model for efficient cross-modal representation learning for the first time. Unlike existing distillation methods, our strategy employs a multiscale perspective, enabling the extraction structural knowledge across from the pre-trained multimodal large model. Ensuring that the student model inherits a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the teacher knowledge. To optimize each distillation loss in a balanced and efficient manner, we propose a dynamic self-adaptive distillation loss balancer, a novel component eliminating the need for manual loss weight adjustments and dynamically balances each loss item during the distillation process. Our methodology streamlines pre-trained multimodal large models using only their output features and original image-level information, requiring minimal computational resources. This efficient approach is suited for various applications and allows the deployment of advanced multimodal technologies even in resource-limited settings. Extensive experiments has demonstrated that our method maintains high performance while significantly reducing model complexity and training costs. Moreover, our distilled student model utilizes only image-level information to achieve state-of-the-art performance on cross-modal retrieval tasks, surpassing previous methods that relied on region-level information.
SwinGNN: Rethinking Permutation Invariance in Diffusion Models for Graph Generation
Jul 19, 2023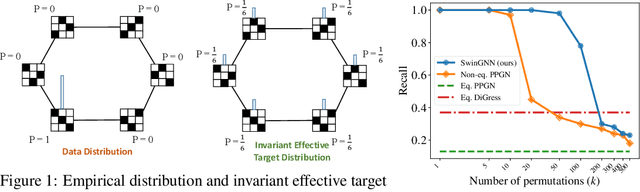
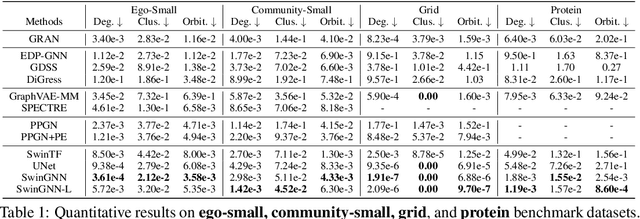
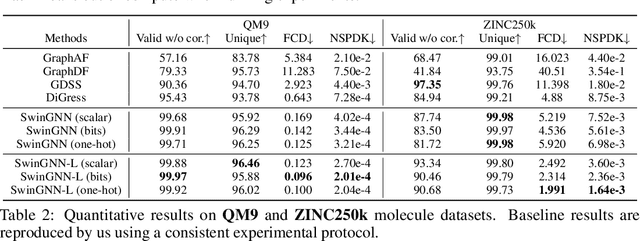
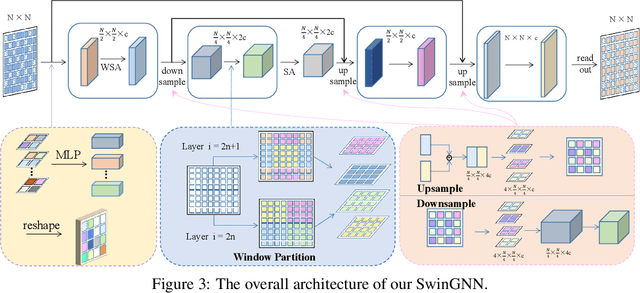
Abstract:Diffusion models based on permutation-equivariant networks can learn permutation-invariant distributions for graph data. However, in comparison to their non-invariant counterparts, we have found that these invariant models encounter greater learning challenges since 1) their effective target distributions exhibit more modes; 2) their optimal one-step denoising scores are the score functions of Gaussian mixtures with more components. Motivated by this analysis, we propose a non-invariant diffusion model, called $\textit{SwinGNN}$, which employs an efficient edge-to-edge 2-WL message passing network and utilizes shifted window based self-attention inspired by SwinTransformers. Further, through systematic ablations, we identify several critical training and sampling techniques that significantly improve the sample quality of graph generation. At last, we introduce a simple post-processing trick, $\textit{i.e.}$, randomly permuting the generated graphs, which provably converts any graph generative model to a permutation-invariant one. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world protein and molecule datasets show that our SwinGNN achieves state-of-the-art performances. Our code is released at https://github.com/qiyan98/SwinGNN.
A Hypothesis for the Aesthetic Appreciation in Neural Networks
Jul 31, 2021
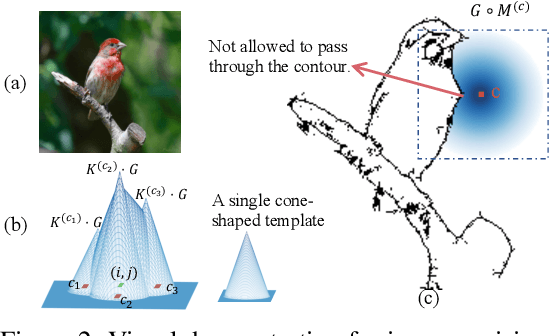
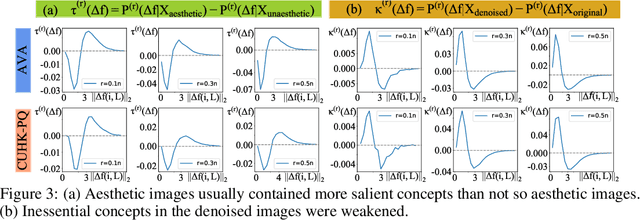
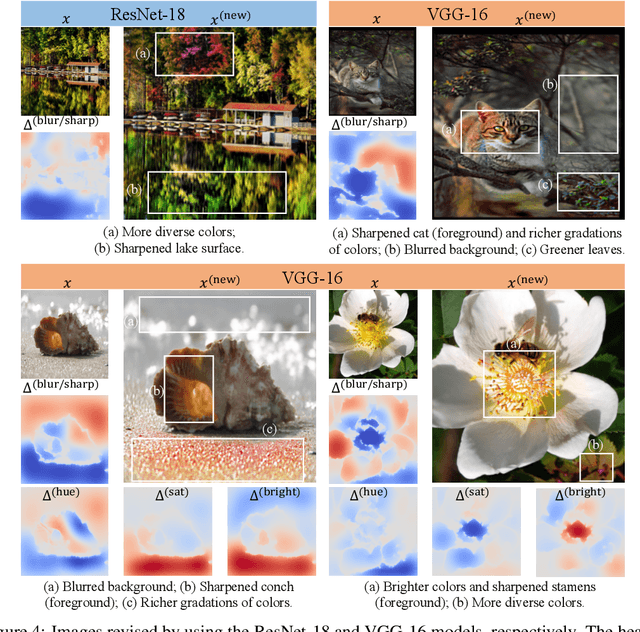
Abstract:This paper proposes a hypothesis for the aesthetic appreciation that aesthetic images make a neural network strengthen salient concepts and discard inessential concepts. In order to verify this hypothesis, we use multi-variate interactions to represent salient concepts and inessential concepts contained in images. Furthermore, we design a set of operations to revise images towards more beautiful ones. In experiments, we find that the revised images are more aesthetic than the original ones to some extent.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge