Zhe Xue
DiffusionCom: Structure-Aware Multimodal Diffusion Model for Multimodal Knowledge Graph Completion
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Most current MKGC approaches are predominantly based on discriminative models that maximize conditional likelihood. These approaches struggle to efficiently capture the complex connections in real-world knowledge graphs, thereby limiting their overall performance. To address this issue, we propose a structure-aware multimodal Diffusion model for multimodal knowledge graph Completion (DiffusionCom). DiffusionCom innovatively approaches the problem from the perspective of generative models, modeling the association between the $(head, relation)$ pair and candidate tail entities as their joint probability distribution $p((head, relation), (tail))$, and framing the MKGC task as a process of gradually generating the joint probability distribution from noise. Furthermore, to fully leverage the structural information in MKGs, we propose Structure-MKGformer, an adaptive and structure-aware multimodal knowledge representation learning method, as the encoder for DiffusionCom. Structure-MKGformer captures rich structural information through a multimodal graph attention network (MGAT) and adaptively fuses it with entity representations, thereby enhancing the structural awareness of these representations. This design effectively addresses the limitations of existing MKGC methods, particularly those based on multimodal pre-trained models, in utilizing structural information. DiffusionCom is trained using both generative and discriminative losses for the generator, while the feature extractor is optimized exclusively with discriminative loss. This dual approach allows DiffusionCom to harness the strengths of both generative and discriminative models. Extensive experiments on the FB15k-237-IMG and WN18-IMG datasets demonstrate that DiffusionCom outperforms state-of-the-art models.
WPFed: Web-based Personalized Federation for Decentralized Systems
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Decentralized learning has become crucial for collaborative model training in environments where data privacy and trust are paramount. In web-based applications, clients are liberated from traditional fixed network topologies, enabling the establishment of arbitrary peer-to-peer (P2P) connections. While this flexibility is highly promising, it introduces a fundamental challenge: the optimal selection of neighbors to ensure effective collaboration. To address this, we introduce WPFed, a fully decentralized, web-based learning framework designed to enable globally optimal neighbor selection. WPFed employs a dynamic communication graph and a weighted neighbor selection mechanism. By assessing inter-client similarity through Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH) and evaluating model quality based on peer rankings, WPFed enables clients to identify personalized optimal neighbors on a global scale while preserving data privacy. To enhance security and deter malicious behavior, WPFed integrates verification mechanisms for both LSH codes and performance rankings, leveraging blockchain-driven announcements to ensure transparency and verifiability. Through extensive experiments on multiple real-world datasets, we demonstrate that WPFed significantly improves learning outcomes and system robustness compared to traditional federated learning methods. Our findings highlight WPFed's potential to facilitate effective and secure decentralized collaborative learning across diverse and interconnected web environments.
Dynamic Self-adaptive Multiscale Distillation from Pre-trained Multimodal Large Model for Efficient Cross-modal Representation Learning
Apr 16, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, pre-trained multimodal large models have attracted widespread attention due to their outstanding performance in various multimodal applications. Nonetheless, the extensive computational resources and vast datasets required for their training present significant hurdles for deployment in environments with limited computational resources. To address this challenge, we propose a novel dynamic self-adaptive multiscale distillation from pre-trained multimodal large model for efficient cross-modal representation learning for the first time. Unlike existing distillation methods, our strategy employs a multiscale perspective, enabling the extraction structural knowledge across from the pre-trained multimodal large model. Ensuring that the student model inherits a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the teacher knowledge. To optimize each distillation loss in a balanced and efficient manner, we propose a dynamic self-adaptive distillation loss balancer, a novel component eliminating the need for manual loss weight adjustments and dynamically balances each loss item during the distillation process. Our methodology streamlines pre-trained multimodal large models using only their output features and original image-level information, requiring minimal computational resources. This efficient approach is suited for various applications and allows the deployment of advanced multimodal technologies even in resource-limited settings. Extensive experiments has demonstrated that our method maintains high performance while significantly reducing model complexity and training costs. Moreover, our distilled student model utilizes only image-level information to achieve state-of-the-art performance on cross-modal retrieval tasks, surpassing previous methods that relied on region-level information.
Epidemic Decision-making System Based Federated Reinforcement Learning
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:Epidemic decision-making can effectively help the government to comprehensively consider public security and economic development to respond to public health and safety emergencies. Epidemic decision-making can effectively help the government to comprehensively consider public security and economic development to respond to public health and safety emergencies. Some studies have shown that intensive learning can effectively help the government to make epidemic decision, thus achieving the balance between health security and economic development. Some studies have shown that intensive learning can effectively help the government to make epidemic decision, thus achieving the balance between health security and economic development. However, epidemic data often has the characteristics of limited samples and high privacy. However, epidemic data often has the characteristics of limited samples and high privacy. This model can combine the epidemic situation data of various provinces for cooperative training to use as an enhanced learning model for epidemic situation decision, while protecting the privacy of data. The experiment shows that the enhanced federated learning can obtain more optimized performance and return than the enhanced learning, and the enhanced federated learning can also accelerate the training convergence speed of the training model. accelerate the training convergence speed of the client. At the same time, through the experimental comparison, A2C is the most suitable reinforcement learning model for the epidemic situation decision-making. learning model for the epidemic situation decision-making scenario, followed by the PPO model, and the performance of DDPG is unsatisfactory.
Research Team Identification Based on Representation Learning of Academic Heterogeneous Information Network
Nov 02, 2023



Abstract:Academic networks in the real world can usually be described by heterogeneous information networks composed of multi-type nodes and relationships. Some existing research on representation learning for homogeneous information networks lacks the ability to explore heterogeneous information networks in heterogeneous information networks. It cannot be applied to heterogeneous information networks. Aiming at the practical needs of effectively identifying and discovering scientific research teams from the academic heterogeneous information network composed of massive and complex scientific and technological big data, this paper proposes a scientific research team identification method based on representation learning of academic heterogeneous information networks. The attention mechanism at node level and meta-path level learns low-dimensional, dense and real-valued vector representations on the basis of retaining the rich topological information of nodes in the network and the semantic information based on meta-paths, and realizes effective identification and discovery of scientific research teams and important team members in academic heterogeneous information networks based on maximizing node influence. Experimental results show that our proposed method outperforms the comparative methods.
Semantic Representation Learning of Scientific Literature based on Adaptive Feature and Graph Neural Network
Nov 01, 2023



Abstract:Because most of the scientific literature data is unmarked, it makes semantic representation learning based on unsupervised graph become crucial. At the same time, in order to enrich the features of scientific literature, a learning method of semantic representation of scientific literature based on adaptive features and graph neural network is proposed. By introducing the adaptive feature method, the features of scientific literature are considered globally and locally. The graph attention mechanism is used to sum the features of scientific literature with citation relationship, and give each scientific literature different feature weights, so as to better express the correlation between the features of different scientific literature. In addition, an unsupervised graph neural network semantic representation learning method is proposed. By comparing the mutual information between the positive and negative local semantic representation of scientific literature and the global graph semantic representation in the potential space, the graph neural network can capture the local and global information, thus improving the learning ability of the semantic representation of scientific literature. The experimental results show that the proposed learning method of semantic representation of scientific literature based on adaptive feature and graph neural network is competitive on the basis of scientific literature classification, and has achieved good results.
Entity Alignment Method of Science and Technology Patent based on Graph Convolution Network and Information Fusion
Nov 01, 2023



Abstract:The entity alignment of science and technology patents aims to link the equivalent entities in the knowledge graph of different science and technology patent data sources. Most entity alignment methods only use graph neural network to obtain the embedding of graph structure or use attribute text description to obtain semantic representation, ignoring the process of multi-information fusion in science and technology patents. In order to make use of the graphic structure and auxiliary information such as the name, description and attribute of the patent entity, this paper proposes an entity alignment method based on the graph convolution network for science and technology patent information fusion. Through the graph convolution network and BERT model, the structure information and entity attribute information of the science and technology patent knowledge graph are embedded and represented to achieve multi-information fusion, thus improving the performance of entity alignment. Experiments on three benchmark data sets show that the proposed method Hit@K The evaluation indicators are better than the existing methods.
Efficient Partitioning Method of Large-Scale Public Safety Spatio-Temporal Data based on Information Loss Constraints
Jun 30, 2023



Abstract:The storage, management, and application of massive spatio-temporal data are widely applied in various practical scenarios, including public safety. However, due to the unique spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of re-al-world data, most existing methods have limitations in terms of the spatio-temporal proximity of data and load balancing in distributed storage. There-fore, this paper proposes an efficient partitioning method of large-scale public safety spatio-temporal data based on information loss constraints (IFL-LSTP). The IFL-LSTP model specifically targets large-scale spatio-temporal point da-ta by combining the spatio-temporal partitioning module (STPM) with the graph partitioning module (GPM). This approach can significantly reduce the scale of data while maintaining the model's accuracy, in order to improve the partitioning efficiency. It can also ensure the load balancing of distributed storage while maintaining spatio-temporal proximity of the data partitioning results. This method provides a new solution for distributed storage of mas-sive spatio-temporal data. The experimental results on multiple real-world da-tasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of IFL-LSTP.
Scientific and Technological News Recommendation Based on Knowledge Graph with User Perception
Oct 07, 2022



Abstract:Existing research usually utilizes side information such as social network or item attributes to improve the performance of collaborative filtering-based recommender systems. In this paper, the knowledge graph with user perception is used to acquire the source of side information. We proposed KGUPN to address the limitations of existing embedding-based and path-based knowledge graph-aware recommendation methods, an end-to-end framework that integrates knowledge graph and user awareness into scientific and technological news recommendation systems. KGUPN contains three main layers, which are the propagation representation layer, the contextual information layer and collaborative relation layer. The propagation representation layer improves the representation of an entity by recursively propagating embeddings from its neighbors (which can be users, news, or relationships) in the knowledge graph. The contextual information layer improves the representation of entities by encoding the behavioral information of entities appearing in the news. The collaborative relation layer complements the relationship between entities in the news knowledge graph. Experimental results on real-world datasets show that KGUPN significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in scientific and technological news recommendation.
Scientific Paper Classification Based on Graph Neural Network with Hypergraph Self-attention Mechanism
Oct 07, 2022
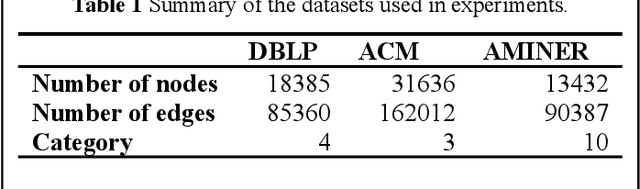

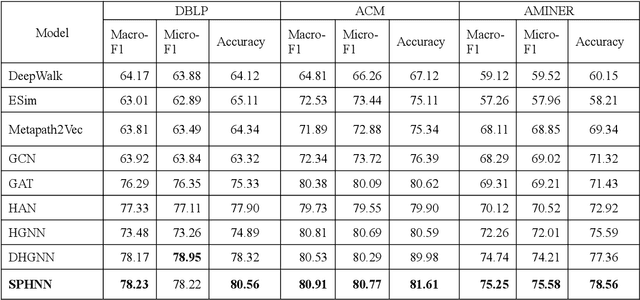
Abstract:The number of scientific papers has increased rapidly in recent years. How to make good use of scientific papers for research is very important. Through the high-quality classification of scientific papers, researchers can quickly find the resource content they need from the massive scientific resources. The classification of scientific papers will effectively help researchers filter redundant information, obtain search results quickly and accurately, and improve the search quality, which is necessary for scientific resource management. This paper proposed a science-technique paper classification method based on hypergraph neural network(SPHNN). In the heterogeneous information network of scientific papers, the repeated high-order subgraphs are modeled as hyperedges composed of multiple related nodes. Then the whole heterogeneous information network is transformed into a hypergraph composed of different hyperedges. The graph convolution operation is carried out on the hypergraph structure, and the hyperedges self-attention mechanism is introduced to aggregate different types of nodes in the hypergraph, so that the final node representation can effectively maintain high-order nearest neighbor relationships and complex semantic information. Finally, by comparing with other methods, we proved that the model proposed in this paper has improved its performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge