Runze Fang
AIR: Analytic Imbalance Rectifier for Continual Learning
Aug 19, 2024Abstract:Continual learning enables AI models to learn new data sequentially without retraining in real-world scenarios. Most existing methods assume the training data are balanced, aiming to reduce the catastrophic forgetting problem that models tend to forget previously generated data. However, data imbalance and the mixture of new and old data in real-world scenarios lead the model to ignore categories with fewer training samples. To solve this problem, we propose an analytic imbalance rectifier algorithm (AIR), a novel online exemplar-free continual learning method with an analytic (i.e., closed-form) solution for data-imbalanced class-incremental learning (CIL) and generalized CIL scenarios in real-world continual learning. AIR introduces an analytic re-weighting module (ARM) that calculates a re-weighting factor for each class for the loss function to balance the contribution of each category to the overall loss and solve the problem of imbalanced training data. AIR uses the least squares technique to give a non-discriminatory optimal classifier and its iterative update method in continual learning. Experimental results on multiple datasets show that AIR significantly outperforms existing methods in long-tailed and generalized CIL scenarios. The source code is available at https://github.com/fang-d/AIR.
Entity Alignment Method of Science and Technology Patent based on Graph Convolution Network and Information Fusion
Nov 01, 2023



Abstract:The entity alignment of science and technology patents aims to link the equivalent entities in the knowledge graph of different science and technology patent data sources. Most entity alignment methods only use graph neural network to obtain the embedding of graph structure or use attribute text description to obtain semantic representation, ignoring the process of multi-information fusion in science and technology patents. In order to make use of the graphic structure and auxiliary information such as the name, description and attribute of the patent entity, this paper proposes an entity alignment method based on the graph convolution network for science and technology patent information fusion. Through the graph convolution network and BERT model, the structure information and entity attribute information of the science and technology patent knowledge graph are embedded and represented to achieve multi-information fusion, thus improving the performance of entity alignment. Experiments on three benchmark data sets show that the proposed method Hit@K The evaluation indicators are better than the existing methods.
A Relational Triple Extraction Method Based on Feature Reasoning for Technological Patents
Oct 07, 2022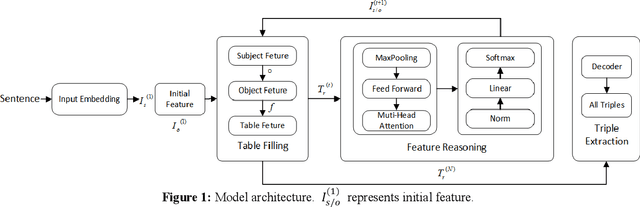
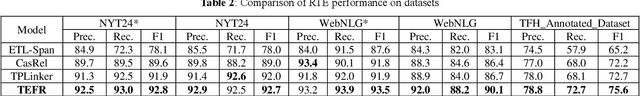
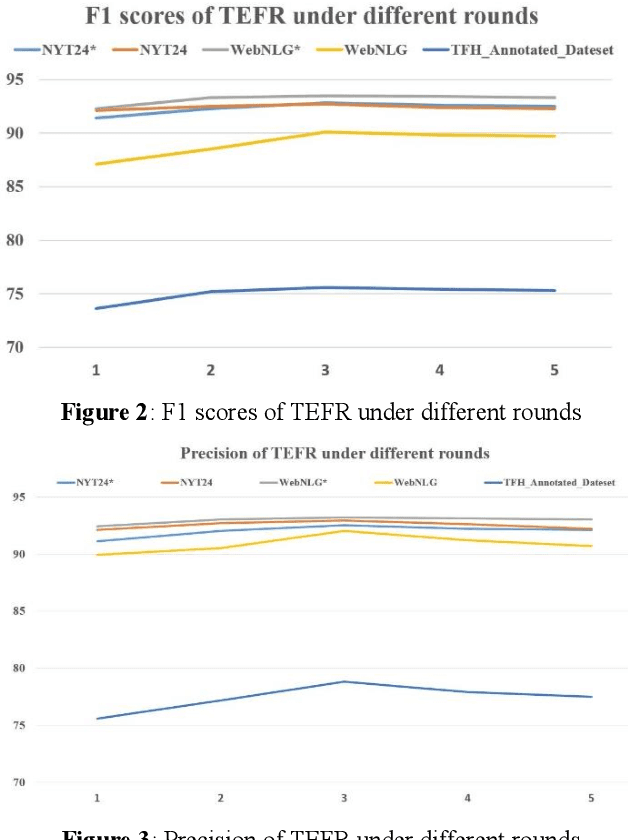
Abstract:The relation triples extraction method based on table filling can address the issues of relation overlap and bias propagation. However, most of them only establish separate table features for each relationship, which ignores the implicit relationship between different entity pairs and different relationship features. Therefore, a feature reasoning relational triple extraction method based on table filling for technological patents is proposed to explore the integration of entity recognition and entity relationship, and to extract entity relationship triples from multi-source scientific and technological patents data. Compared with the previous methods, the method we proposed for relational triple extraction has the following advantages: 1) The table filling method that saves more running space enhances the speed and efficiency of the model. 2) Based on the features of existing token pairs and table relations, reasoning the implicit relationship features, and improve the accuracy of triple extraction. On five benchmark datasets, we evaluated the model we suggested. The result suggest that our model is advanced and effective, and it performed well on most of these datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge