Yingxia Shao
Towards A Generalist Code Embedding Model Based On Massive Data Synthesis
May 19, 2025Abstract:Code embedding models attract increasing attention due to the widespread popularity of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in software development. These models are expected to capture the rich semantic relationships inherent to code, which differ significantly from those found in text. However, existing models remain severely limited due to the scarcity of high-quality training data. In this work, we introduce \textbf{CodeR} (\underline{Code} \underline{R}etrieval), a state-of-the-art embedding model for general-purpose code retrieval. The superior performance of CodeR is built upon CodeR-Pile, a large-scale synthetic dataset constructed under the DRU (Diversity, Reliability, Usability) principle via a novel data synthesis pipeline. To optimize training effectiveness, we propose Annealing, a curriculum learning strategy that enables effective knowledge transfer across heterogeneous sources of data. We evaluate CodeR based on 16 diverse code retrieval tasks, where it significantly outperforms existing baselines and exhibits strong out-of-domain generalization performance. We have publicly released our code and the well-trained model to facilitate further research in this critical area. https://github.com/FlagOpen/FlagEmbedding/tree/master/research/BGE_Coder.
Reinforced Information Retrieval
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:While retrieval techniques are widely used in practice, they still face significant challenges in cross-domain scenarios. Recently, generation-augmented methods have emerged as a promising solution to this problem. These methods enhance raw queries by incorporating additional information from an LLM-based generator, facilitating more direct retrieval of relevant documents. However, existing methods struggle with highly specialized situations that require extensive domain expertise. To address this problem, we present \textbf{Reinforced-IR}, a novel approach that jointly adapts a pre-trained retriever and generator for precise cross-domain retrieval. A key innovation of Reinforced-IR is its \textbf{Self-Boosting} framework, which enables retriever and generator to learn from each other's feedback. Specifically, the generator is reinforced to generate query augmentations that enhance the retriever's performance, while the retriever is trained to better discriminate the relevant documents identified by the generator. This iterative process allows the end-to-end retrieval performance to be progressively optimized using an unlabeled corpus from the target domain. In our experiment, Reinforced-IR outperforms existing domain adaptation methods by a large margin, leading to substantial improvements in retrieval quality across a wide range of application scenarios.
Matryoshka Re-Ranker: A Flexible Re-Ranking Architecture With Configurable Depth and Width
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) provide powerful foundations to perform fine-grained text re-ranking. However, they are often prohibitive in reality due to constraints on computation bandwidth. In this work, we propose a \textbf{flexible} architecture called \textbf{Matroyshka Re-Ranker}, which is designed to facilitate \textbf{runtime customization} of model layers and sequence lengths at each layer based on users' configurations. Consequently, the LLM-based re-rankers can be made applicable across various real-world situations. The increased flexibility may come at the cost of precision loss. To address this problem, we introduce a suite of techniques to optimize the performance. First, we propose \textbf{cascaded self-distillation}, where each sub-architecture learns to preserve a precise re-ranking performance from its super components, whose predictions can be exploited as smooth and informative teacher signals. Second, we design a \textbf{factorized compensation mechanism}, where two collaborative Low-Rank Adaptation modules, vertical and horizontal, are jointly employed to compensate for the precision loss resulted from arbitrary combinations of layer and sequence compression. We perform comprehensive experiments based on the passage and document retrieval datasets from MSMARCO, along with all public datasets from BEIR benchmark. In our experiments, Matryoshka Re-Ranker substantially outperforms the existing methods, while effectively preserving its superior performance across various forms of compression and different application scenarios.
LAC: Graph Contrastive Learning with Learnable Augmentation in Continuous Space
Oct 20, 2024Abstract:Graph Contrastive Learning frameworks have demonstrated success in generating high-quality node representations. The existing research on efficient data augmentation methods and ideal pretext tasks for graph contrastive learning remains limited, resulting in suboptimal node representation in the unsupervised setting. In this paper, we introduce LAC, a graph contrastive learning framework with learnable data augmentation in an orthogonal continuous space. To capture the representative information in the graph data during augmentation, we introduce a continuous view augmenter, that applies both a masked topology augmentation module and a cross-channel feature augmentation module to adaptively augment the topological information and the feature information within an orthogonal continuous space, respectively. The orthogonal nature of continuous space ensures that the augmentation process avoids dimension collapse. To enhance the effectiveness of pretext tasks, we propose an information-theoretic principle named InfoBal and introduce corresponding pretext tasks. These tasks enable the continuous view augmenter to maintain consistency in the representative information across views while maximizing diversity between views, and allow the encoder to fully utilize the representative information in the unsupervised setting. Our experimental results show that LAC significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art frameworks.
DELIA: Diversity-Enhanced Learning for Instruction Adaptation in Large Language Models
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:Although instruction tuning is widely used to adjust behavior in Large Language Models (LLMs), extensive empirical evidence and research indicates that it is primarily a process where the model fits to specific task formats, rather than acquiring new knowledge or capabilities. We propose that this limitation stems from biased features learned during instruction tuning, which differ from ideal task-specfic features, leading to learn less underlying semantics in downstream tasks. However, ideal features are unknown and incalculable, constraining past work to rely on prior knowledge to assist reasoning or training, which limits LLMs' capabilities to the developers' abilities, rather than data-driven scalable learning. In our paper, through our novel data synthesis method, DELIA (Diversity-Enhanced Learning for Instruction Adaptation), we leverage the buffering effect of extensive diverse data in LLMs training to transform biased features in instruction tuning into approximations of ideal features, without explicit prior ideal features. Experiments show DELIA's better performance compared to common instruction tuning and other baselines. It outperforms common instruction tuning by 17.07%-33.41% on Icelandic-English translation bleurt score (WMT-21 dataset, gemma-7b-it) and improves accuracy by 36.1% on formatted text generation (Llama2-7b-chat). Notably, among knowledge injection methods we've known, DELIA uniquely align the internal representations of new special tokens with their prior semantics.
Adversarial Contrastive Learning Based Physics-Informed Temporal Networks for Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation
Aug 16, 2024Abstract:Time series data mining is immensely important in extensive applications, such as traffic, medical, and e-commerce. In this paper, we focus on medical temporal variation modeling, \emph{i.e.,} cuffless blood pressure (BP) monitoring which has great value in cardiovascular healthcare. Although providing a comfortable user experience, such methods are suffering from the demand for a significant amount of realistic data to train an individual model for each subject, especially considering the invasive or obtrusive BP ground-truth measurements. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a novel physics-informed temporal network~(PITN) with adversarial contrastive learning to enable precise BP estimation with very limited data. Specifically, we first enhance the physics-informed neural network~(PINN) with the temporal block for investigating BP dynamics' multi-periodicity for personal cardiovascular cycle modeling and temporal variation. We then employ adversarial training to generate extra physiological time series data, improving PITN's robustness in the face of sparse subject-specific training data. Furthermore, we utilize contrastive learning to capture the discriminative variations of cardiovascular physiologic phenomena. This approach aggregates physiological signals with similar blood pressure values in latent space while separating clusters of samples with dissimilar blood pressure values. Experiments on three widely-adopted datasets with different modailties (\emph{i.e.,} bioimpedance, PPG, millimeter-wave) demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of the proposed methods over previous state-of-the-art approaches. The code is available at~\url{https://github.com/Zest86/ACL-PITN}.
SpanGNN: Towards Memory-Efficient Graph Neural Networks via Spanning Subgraph Training
Jun 07, 2024



Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have superior capability in learning graph data. Full-graph GNN training generally has high accuracy, however, it suffers from large peak memory usage and encounters the Out-of-Memory problem when handling large graphs. To address this memory problem, a popular solution is mini-batch GNN training. However, mini-batch GNN training increases the training variance and sacrifices the model accuracy. In this paper, we propose a new memory-efficient GNN training method using spanning subgraph, called SpanGNN. SpanGNN trains GNN models over a sequence of spanning subgraphs, which are constructed from empty structure. To overcome the excessive peak memory consumption problem, SpanGNN selects a set of edges from the original graph to incrementally update the spanning subgraph between every epoch. To ensure the model accuracy, we introduce two types of edge sampling strategies (i.e., variance-reduced and noise-reduced), and help SpanGNN select high-quality edges for the GNN learning. We conduct experiments with SpanGNN on widely used datasets, demonstrating SpanGNN's advantages in the model performance and low peak memory usage.
Token-Efficient Leverage Learning in Large Language Models
Apr 01, 2024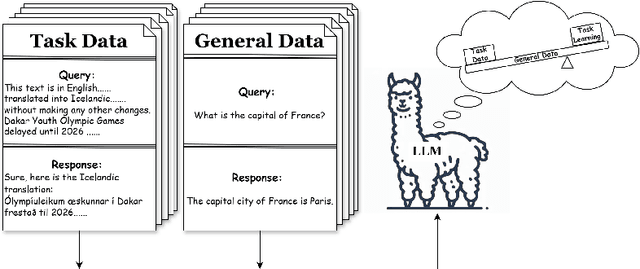
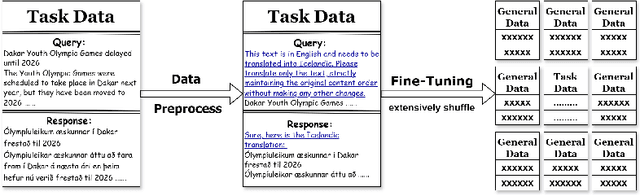
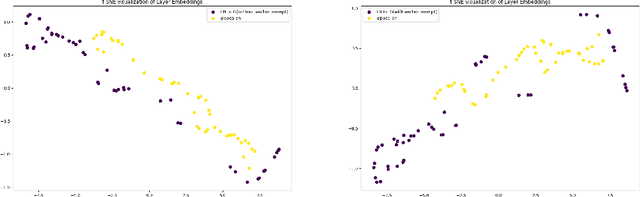
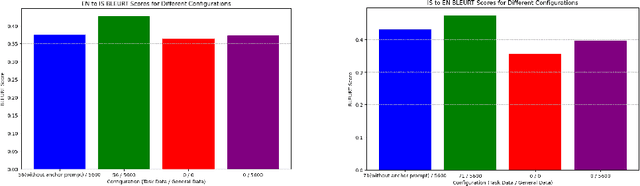
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have excelled in various tasks but perform better in high-resource scenarios, which presents challenges in low-resource scenarios. Data scarcity and the inherent difficulty of adapting LLMs to specific tasks compound the challenge. To address the twin hurdles, we introduce \textbf{Leverage Learning}. We present a streamlined implement of this methodology called Token-Efficient Leverage Learning (TELL). TELL showcases the potential of Leverage Learning, demonstrating effectiveness across various LLMs and low-resource tasks, ranging from $10^4$ to $10^6$ tokens. It reduces task data requirements by up to nearly an order of magnitude compared to conventional Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) while delivering competitive performance. With the same amount of task data, TELL leads in improving task performance compared to SFT. We discuss the mechanism of Leverage Learning, suggesting it aligns with quantization hypothesis and explore its promising potential through empirical testing.
LLMvsSmall Model? Large Language Model Based Text Augmentation Enhanced Personality Detection Model
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:Personality detection aims to detect one's personality traits underlying in social media posts. One challenge of this task is the scarcity of ground-truth personality traits which are collected from self-report questionnaires. Most existing methods learn post features directly by fine-tuning the pre-trained language models under the supervision of limited personality labels. This leads to inferior quality of post features and consequently affects the performance. In addition, they treat personality traits as one-hot classification labels, overlooking the semantic information within them. In this paper, we propose a large language model (LLM) based text augmentation enhanced personality detection model, which distills the LLM's knowledge to enhance the small model for personality detection, even when the LLM fails in this task. Specifically, we enable LLM to generate post analyses (augmentations) from the aspects of semantic, sentiment, and linguistic, which are critical for personality detection. By using contrastive learning to pull them together in the embedding space, the post encoder can better capture the psycho-linguistic information within the post representations, thus improving personality detection. Furthermore, we utilize the LLM to enrich the information of personality labels for enhancing the detection performance. Experimental results on the benchmark datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on personality detection.
Making Large Language Models A Better Foundation For Dense Retrieval
Dec 24, 2023Abstract:Dense retrieval needs to learn discriminative text embeddings to represent the semantic relationship between query and document. It may benefit from the using of large language models (LLMs), given LLMs' strong capability on semantic understanding. However, the LLMs are pre-trained by text generation tasks, whose working pattern is completely different from representing texts as embeddings. As a result, it is imperative to study how to adapt LLMs properly so that they can be effectively initialized as the backbone encoder for dense retrieval. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, called LLaRA (LLM adapted for dense RetrievAl), which works as a post-hoc adaptation of LLM for the dense retrieval application. LLaRA consists of two pretext tasks: EBAE (Embedding-Based Auto-Encoding) and EBAR (Embedding-Based Auto-Regression), where the text embeddings from LLM are used to reconstruct the tokens for the input sentence and predict the tokens for the next sentence, respectively. LLaRA turns out to be simple, lightweight, and highly effective. It is applied to adapt LLaMA-2-7B (base) on the Wikipedia corpus, where it substantially improves the model's fine-tuned performances on a variety of dense retrieval benchmarks, like MSMARCO and BEIR. Our model and code will be made publicly available at BGE repository.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge