Jie Gao
Sherman
Reasoning in a Combinatorial and Constrained World: Benchmarking LLMs on Natural-Language Combinatorial Optimization
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have shown strong performance in math and logic reasoning, their ability to handle combinatorial optimization (CO) -- searching high-dimensional solution spaces under hard constraints -- remains underexplored. To bridge the gap, we introduce NLCO, a \textbf{N}atural \textbf{L}anguage \textbf{C}ombinatorial \textbf{O}ptimization benchmark that evaluates LLMs on end-to-end CO reasoning: given a language-described decision-making scenario, the model must output a discrete solution without writing code or calling external solvers. NLCO covers 43 CO problems and is organized using a four-layer taxonomy of variable types, constraint families, global patterns, and objective classes, enabling fine-grained evaluation. We provide solver-annotated solutions and comprehensively evaluate LLMs by feasibility, solution optimality, and reasoning efficiency. Experiments across a wide range of modern LLMs show that high-performing models achieve strong feasibility and solution quality on small instances, but both degrade as instance size grows, even if more tokens are used for reasoning. We also observe systematic effects across the taxonomy: set-based tasks are relatively easy, whereas graph-structured problems and bottleneck objectives lead to more frequent failures.
Investigating Self-regulated Learning Sequences within a Generative AI-based Intelligent Tutoring System
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:There has been a growing trend in employing generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) techniques to support learning. Moreover, scholars have reached a consensus on the critical role of self-regulated learning (SRL) in ensuring learning effectiveness within GenAI-assisted learning environments, making it essential to capture students' dynamic SRL patterns. In this study, we extracted students' interaction patterns with GenAI from trace data as they completed a problem-solving task within a GenAI-assisted intelligent tutoring system. Students' purpose of using GenAI was also analyzed from the perspective of information processing, i.e., information acquisition and information transformation. Using sequential and clustering analysis, this study classified participants into two groups based on their SRL sequences. These two groups differed in the frequency and temporal characteristics of GenAI use. In addition, most students used GenAI for information acquisition rather than information transformation, while the correlation between the purpose of using GenAI and learning performance was not statistically significant. Our findings inform both pedagogical design and the development of GenAI-assisted learning environments.
E2E-VGuard: Adversarial Prevention for Production LLM-based End-To-End Speech Synthesis
Nov 10, 2025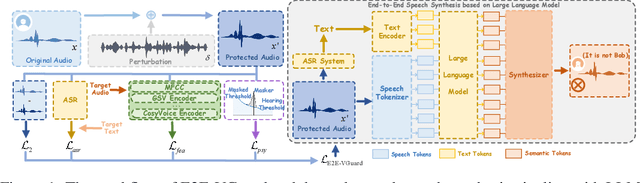
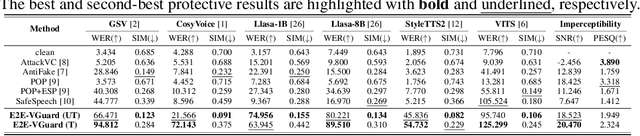
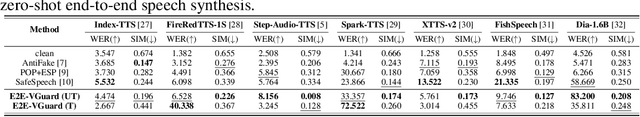
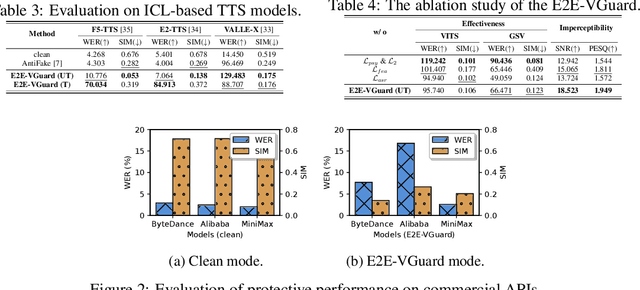
Abstract:Recent advancements in speech synthesis technology have enriched our daily lives, with high-quality and human-like audio widely adopted across real-world applications. However, malicious exploitation like voice-cloning fraud poses severe security risks. Existing defense techniques struggle to address the production large language model (LLM)-based speech synthesis. While previous studies have considered the protection for fine-tuning synthesizers, they assume manually annotated transcripts. Given the labor intensity of manual annotation, end-to-end (E2E) systems leveraging automatic speech recognition (ASR) to generate transcripts are becoming increasingly prevalent, e.g., voice cloning via commercial APIs. Therefore, this E2E speech synthesis also requires new security mechanisms. To tackle these challenges, we propose E2E-VGuard, a proactive defense framework for two emerging threats: (1) production LLM-based speech synthesis, and (2) the novel attack arising from ASR-driven E2E scenarios. Specifically, we employ the encoder ensemble with a feature extractor to protect timbre, while ASR-targeted adversarial examples disrupt pronunciation. Moreover, we incorporate the psychoacoustic model to ensure perturbative imperceptibility. For a comprehensive evaluation, we test 16 open-source synthesizers and 3 commercial APIs across Chinese and English datasets, confirming E2E-VGuard's effectiveness in timbre and pronunciation protection. Real-world deployment validation is also conducted. Our code and demo page are available at https://wxzyd123.github.io/e2e-vguard/.
TopInG: Topologically Interpretable Graph Learning via Persistent Rationale Filtration
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown remarkable success across various scientific fields, yet their adoption in critical decision-making is often hindered by a lack of interpretability. Recently, intrinsically interpretable GNNs have been studied to provide insights into model predictions by identifying rationale substructures in graphs. However, existing methods face challenges when the underlying rationale subgraphs are complex and varied. In this work, we propose TopInG: Topologically Interpretable Graph Learning, a novel topological framework that leverages persistent homology to identify persistent rationale subgraphs. TopInG employs a rationale filtration learning approach to model an autoregressive generation process of rationale subgraphs, and introduces a self-adjusted topological constraint, termed topological discrepancy, to enforce a persistent topological distinction between rationale subgraphs and irrelevant counterparts. We provide theoretical guarantees that our loss function is uniquely optimized by the ground truth under specific conditions. Extensive experiments demonstrate TopInG's effectiveness in tackling key challenges, such as handling variform rationale subgraphs, balancing predictive performance with interpretability, and mitigating spurious correlations. Results show that our approach improves upon state-of-the-art methods on both predictive accuracy and interpretation quality.
HelixDesign-Antibody: A Scalable Production-Grade Platform for Antibody Design Built on HelixFold3
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Antibody engineering is essential for developing therapeutics and advancing biomedical research. Traditional discovery methods often rely on time-consuming and resource-intensive experimental screening. To enhance and streamline this process, we introduce a production-grade, high-throughput platform built on HelixFold3, HelixDesign-Antibody, which utilizes the high-accuracy structure prediction model, HelixFold3. The platform facilitates the large-scale generation of antibody candidate sequences and evaluates their interaction with antigens. Integrated high-performance computing (HPC) support enables high-throughput screening, addressing challenges such as fragmented toolchains and high computational demands. Validation on multiple antigens showcases the platform's ability to generate diverse and high-quality antibodies, confirming a scaling law where exploring larger sequence spaces increases the likelihood of identifying optimal binders. This platform provides a seamless, accessible solution for large-scale antibody design and is available via the antibody design page of PaddleHelix platform.
Test-Time Scaling with Reflective Generative Model
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:We introduce our first reflective generative model MetaStone-S1, which obtains OpenAI o3's performance via the self-supervised process reward model (SPRM). Through sharing the backbone network and using task-specific heads for next token prediction and process scoring respectively, SPRM successfully integrates the policy model and process reward model(PRM) into a unified interface without extra process annotation, reducing over 99% PRM parameters for efficient reasoning. Equipped with SPRM, MetaStone-S1 is naturally suitable for test time scaling (TTS), and we provide three reasoning effort modes (low, medium, and high), based on the controllable thinking length. Moreover, we empirically establish a scaling law that reveals the relationship between total thinking computation and TTS performance. Experiments demonstrate that our MetaStone-S1 achieves comparable performance to OpenAI-o3-mini's series with only 32B parameter size. To support the research community, we have open-sourced MetaStone-S1 at https://github.com/MetaStone-AI/MetaStone-S1.
Drift-Adaptive Slicing-Based Resource Management for Cooperative ISAC Networks
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel drift-adaptive slicing-based resource management scheme for cooperative integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) networks. Particularly, we establish two network slices to provide sensing and communication services, respectively. In the large-timescale planning for the slices, we partition the sensing region of interest (RoI) of each mobile device and reserve network resources accordingly, facilitating low-complexity distance-based sensing target assignment in small timescales. To cope with the non-stationary spatial distributions of mobile devices and sensing targets, which can result in the drift in modeling the distributions and ineffective planning decisions, we construct digital twins (DTs) of the slices. In each DT, a drift-adaptive statistical model and an emulation function are developed for the spatial distributions in the corresponding slice, which facilitates closed-form decision-making and efficient validation of a planning decision, respectively. Numerical results show that the proposed drift-adaptive slicing-based resource management scheme can increase the service satisfaction ratio by up to 18% and reduce resource consumption by up to 13.1% when compared with benchmark schemes.
HelixDesign-Binder: A Scalable Production-Grade Platform for Binder Design Built on HelixFold3
May 28, 2025Abstract:Protein binder design is central to therapeutics, diagnostics, and synthetic biology, yet practical deployment remains challenging due to fragmented workflows, high computational costs, and complex tool integration. We present HelixDesign-Binder, a production-grade, high-throughput platform built on HelixFold3 that automates the full binder design pipeline, from backbone generation and sequence design to structural evaluation and multi-dimensional scoring. By unifying these stages into a scalable and user-friendly system, HelixDesign-Binder enables efficient exploration of binder candidates with favorable structural, energetic, and physicochemical properties. The platform leverages Baidu Cloud's high-performance infrastructure to support large-scale design and incorporates advanced scoring metrics, including ipTM, predicted binding free energy, and interface hydrophobicity. Benchmarking across six protein targets demonstrates that HelixDesign-Binder reliably produces diverse and high-quality binders, some of which match or exceed validated designs in predicted binding affinity. HelixDesign-Binder is accessible via an interactive web interface in PaddleHelix platform, supporting both academic research and industrial applications in antibody and protein binder development.
On the Price of Differential Privacy for Hierarchical Clustering
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Hierarchical clustering is a fundamental unsupervised machine learning task with the aim of organizing data into a hierarchy of clusters. Many applications of hierarchical clustering involve sensitive user information, therefore motivating recent studies on differentially private hierarchical clustering under the rigorous framework of Dasgupta's objective. However, it has been shown that any privacy-preserving algorithm under edge-level differential privacy necessarily suffers a large error. To capture practical applications of this problem, we focus on the weight privacy model, where each edge of the input graph is at least unit weight. We present a novel algorithm in the weight privacy model that shows significantly better approximation than known impossibility results in the edge-level DP setting. In particular, our algorithm achieves $O(\log^{1.5}n/\varepsilon)$ multiplicative error for $\varepsilon$-DP and runs in polynomial time, where $n$ is the size of the input graph, and the cost is never worse than the optimal additive error in existing work. We complement our algorithm by showing if the unit-weight constraint does not apply, the lower bound for weight-level DP hierarchical clustering is essentially the same as the edge-level DP, i.e. $\Omega(n^2/\varepsilon)$ additive error. As a result, we also obtain a new lower bound of $\tilde{\Omega}(1/\varepsilon)$ additive error for balanced sparsest cuts in the weight-level DP model, which may be of independent interest. Finally, we evaluate our algorithm on synthetic and real-world datasets. Our experimental results show that our algorithm performs well in terms of extra cost and has good scalability to large graphs.
Timing the Match: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach for Ride-Hailing and Ride-Pooling Services
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Efficient timing in ride-matching is crucial for improving the performance of ride-hailing and ride-pooling services, as it determines the number of drivers and passengers considered in each matching process. Traditional batched matching methods often use fixed time intervals to accumulate ride requests before assigning matches. While this approach increases the number of available drivers and passengers for matching, it fails to adapt to real-time supply-demand fluctuations, often leading to longer passenger wait times and driver idle periods. To address this limitation, we propose an adaptive ride-matching strategy using deep reinforcement learning (RL) to dynamically determine when to perform matches based on real-time system conditions. Unlike fixed-interval approaches, our method continuously evaluates system states and executes matching at moments that minimize total passenger wait time. Additionally, we incorporate a potential-based reward shaping (PBRS) mechanism to mitigate sparse rewards, accelerating RL training and improving decision quality. Extensive empirical evaluations using a realistic simulator trained on real-world data demonstrate that our approach outperforms fixed-interval matching strategies, significantly reducing passenger waiting times and detour delays, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of ride-hailing and ride-pooling systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge