Xiaorui Wang
Wiki Live Challenge: Challenging Deep Research Agents with Expert-Level Wikipedia Articles
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Deep Research Agents (DRAs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in autonomous information retrieval and report generation, showing great potential to assist humans in complex research tasks. Current evaluation frameworks primarily rely on LLM-generated references or LLM-derived evaluation dimensions. While these approaches offer scalability, they often lack the reliability of expert-verified content and struggle to provide objective, fine-grained assessments of critical dimensions. To bridge this gap, we introduce Wiki Live Challenge (WLC), a live benchmark that leverages the newest Wikipedia Good Articles (GAs) as expert-level references. Wikipedia's strict standards for neutrality, comprehensiveness, and verifiability serve as a great challenge for DRAs, with GAs representing the pinnacle of which. We curate a dataset of 100 recent Good Articles and propose Wiki Eval, a comprehensive evaluation framework comprising a fine-grained evaluation method with 39 criteria for writing quality and rigorous metrics for factual verifiability. Extensive experiments on various DRA systems demonstrate a significant gap between current DRAs and human expert-level Wikipedia articles, validating the effectiveness of WLC in advancing agent research. We release our benchmark at https://github.com/WangShao2000/Wiki_Live_Challenge
A-RAG: Scaling Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation via Hierarchical Retrieval Interfaces
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Frontier language models have demonstrated strong reasoning and long-horizon tool-use capabilities. However, existing RAG systems fail to leverage these capabilities. They still rely on two paradigms: (1) designing an algorithm that retrieves passages in a single shot and concatenates them into the model's input, or (2) predefining a workflow and prompting the model to execute it step-by-step. Neither paradigm allows the model to participate in retrieval decisions, preventing efficient scaling with model improvements. In this paper, we introduce A-RAG, an Agentic RAG framework that exposes hierarchical retrieval interfaces directly to the model. A-RAG provides three retrieval tools: keyword search, semantic search, and chunk read, enabling the agent to adaptively search and retrieve information across multiple granularities. Experiments on multiple open-domain QA benchmarks show that A-RAG consistently outperforms existing approaches with comparable or lower retrieved tokens, demonstrating that A-RAG effectively leverages model capabilities and dynamically adapts to different RAG tasks. We further systematically study how A-RAG scales with model size and test-time compute. We will release our code and evaluation suite to facilitate future research. Code and evaluation suite are available at https://github.com/Ayanami0730/arag.
FS-Researcher: Test-Time Scaling for Long-Horizon Research Tasks with File-System-Based Agents
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Deep research is emerging as a representative long-horizon task for large language model (LLM) agents. However, long trajectories in deep research often exceed model context limits, compressing token budgets for both evidence collection and report writing, and preventing effective test-time scaling. We introduce FS-Researcher, a file-system-based, dual-agent framework that scales deep research beyond the context window via a persistent workspace. Specifically, a Context Builder agent acts as a librarian which browses the internet, writes structured notes, and archives raw sources into a hierarchical knowledge base that can grow far beyond context length. A Report Writer agent then composes the final report section by section, treating the knowledge base as the source of facts. In this framework, the file system serves as a durable external memory and a shared coordination medium across agents and sessions, enabling iterative refinement beyond the context window. Experiments on two open-ended benchmarks (DeepResearch Bench and DeepConsult) show that FS-Researcher achieves state-of-the-art report quality across different backbone models. Further analyses demonstrate a positive correlation between final report quality and the computation allocated to the Context Builder, validating effective test-time scaling under the file-system paradigm. The code and data are anonymously open-sourced at https://github.com/Ignoramus0817/FS-Researcher.
DeepResearch Bench II: Diagnosing Deep Research Agents via Rubrics from Expert Report
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Deep Research Systems (DRS) aim to help users search the web, synthesize information, and deliver comprehensive investigative reports. However, how to rigorously evaluate these systems remains under-explored. Existing deep-research benchmarks often fall into two failure modes. Some do not adequately test a system's ability to analyze evidence and write coherent reports. Others rely on evaluation criteria that are either overly coarse or directly defined by LLMs (or both), leading to scores that can be biased relative to human experts and are hard to verify or interpret. To address these issues, we introduce Deep Research Bench II, a new benchmark for evaluating DRS-generated reports. It contains 132 grounded research tasks across 22 domains; for each task, a system must produce a long-form research report that is evaluated by a set of 9430 fine-grained binary rubrics in total, covering three dimensions: information recall, analysis, and presentation. All rubrics are derived from carefully selected expert-written investigative articles and are constructed through a four-stage LLM+human pipeline that combines automatic extraction with over 400 human-hours of expert review, ensuring that the criteria are atomic, verifiable, and aligned with human expert judgment. We evaluate several state-of-the-art deep-research systems on Deep Research Bench II and find that even the strongest models satisfy fewer than 50% of the rubrics, revealing a substantial gap between current DRSs and human experts.
Multiscale Cross-Modal Mapping of Molecular, Pathologic, and Radiologic Phenotypes in Lipid-Deficient Clear Cell Renal CellCarcinoma
Dec 13, 2025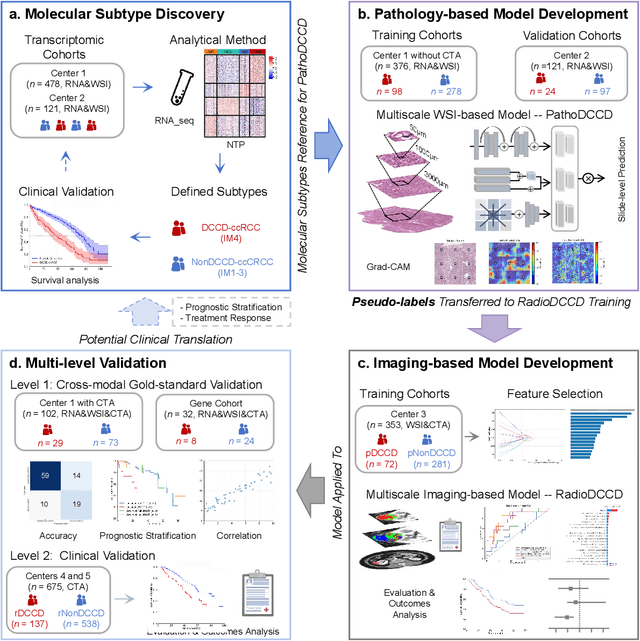
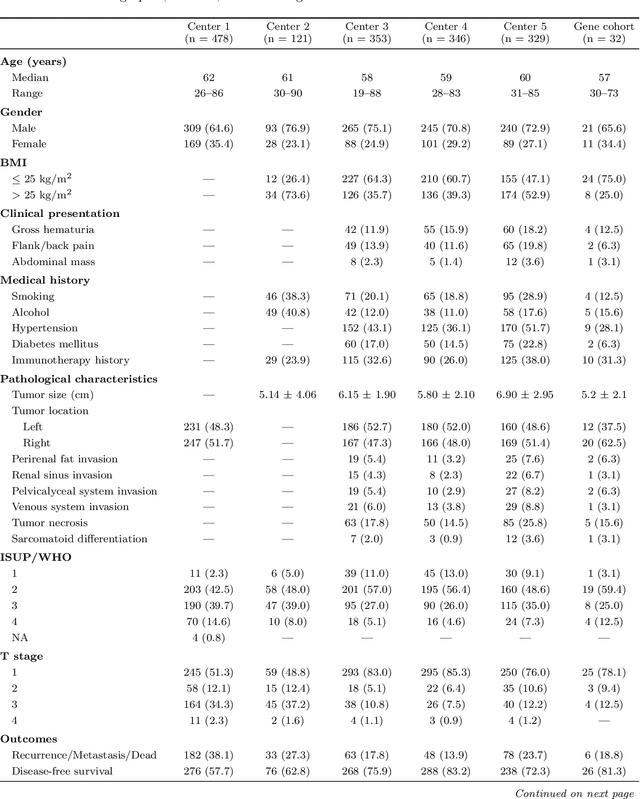
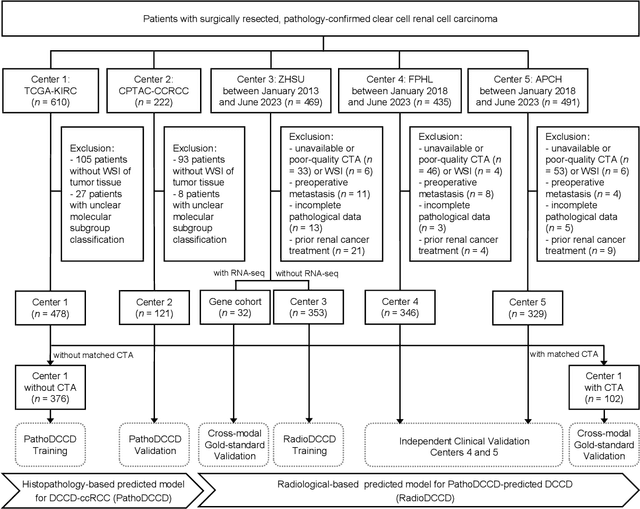
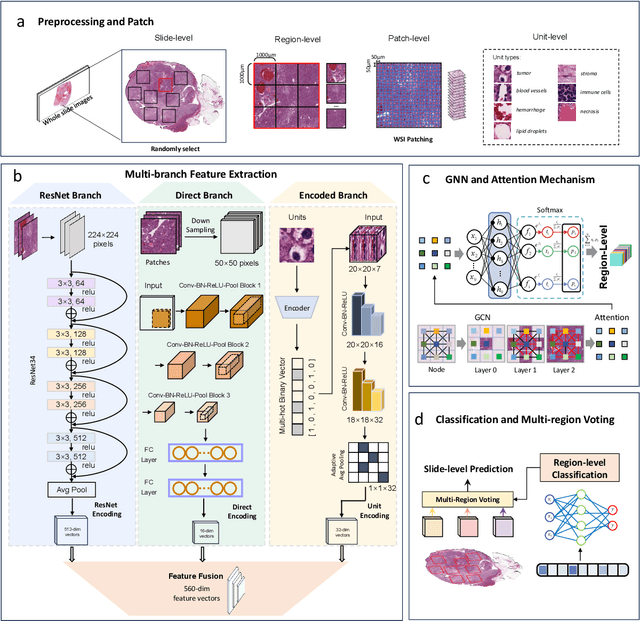
Abstract:Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) exhibits extensive intratumoral heterogeneity on multiple biological scales, contributing to variable clinical outcomes and limiting the effectiveness of conventional TNM staging, which highlights the urgent need for multiscale integrative analytic frameworks. The lipid-deficient de-clear cell differentiated (DCCD) ccRCC subtype, defined by multi-omics analyses, is associated with adverse outcomes even in early-stage disease. Here, we establish a hierarchical cross-scale framework for the preoperative identification of DCCD-ccRCC. At the highest layer, cross-modal mapping transferred molecular signatures to histological and CT phenotypes, establishing a molecular-to-pathology-to-radiology supervisory bridge. Within this framework, each modality-specific model is designed to mirror the inherent hierarchical structure of tumor biology. PathoDCCD captured multi-scale microscopic features, from cellular morphology and tissue architecture to meso-regional organization. RadioDCCD integrated complementary macroscopic information by combining whole-tumor and its habitat-subregions radiomics with a 2D maximal-section heterogeneity metric. These nested models enabled integrated molecular subtype prediction and clinical risk stratification. Across five cohorts totaling 1,659 patients, PathoDCCD reliably recapitulated molecular subtypes, while RadioDCCD provided reliable preoperative prediction. The consistent predictions identified patients with the poorest clinical outcomes. This cross-scale paradigm unifies molecular biology, computational pathology, and quantitative radiology into a biologically grounded strategy for preoperative noninvasive molecular phenotyping of ccRCC.
Thinker: Training LLMs in Hierarchical Thinking for Deep Search via Multi-Turn Interaction
Nov 14, 2025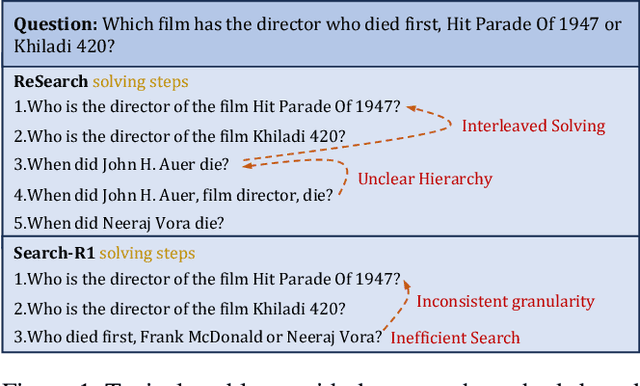
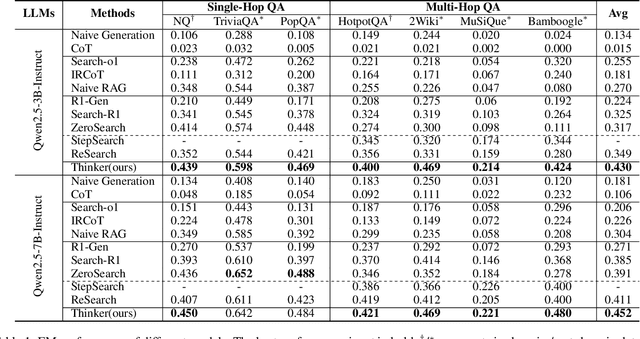
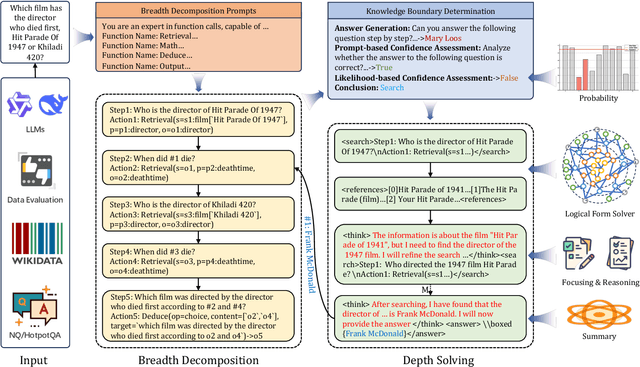
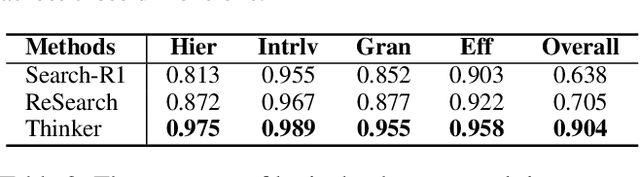
Abstract:Efficient retrieval of external knowledge bases and web pages is crucial for enhancing the reasoning abilities of LLMs. Previous works on training LLMs to leverage external retrievers for solving complex problems have predominantly employed end-to-end reinforcement learning. However, these approaches neglect supervision over the reasoning process, making it difficult to guarantee logical coherence and rigor. To address these limitations, we propose Thinker, a hierarchical thinking model for deep search through multi-turn interaction, making the reasoning process supervisable and verifiable. It decomposes complex problems into independently solvable sub-problems, each dually represented in both natural language and an equivalent logical function to support knowledge base and web searches. Concurrently, dependencies between sub-problems are passed as parameters via these logical functions, enhancing the logical coherence of the problem-solving process. To avoid unnecessary external searches, we perform knowledge boundary determination to check if a sub-problem is within the LLM's intrinsic knowledge, allowing it to answer directly. Experimental results indicate that with as few as several hundred training samples, the performance of Thinker is competitive with established baselines. Furthermore, when scaled to the full training set, Thinker significantly outperforms these methods across various datasets and model sizes. The source code is available at https://github.com/OpenSPG/KAG-Thinker.
DualSG: A Dual-Stream Explicit Semantic-Guided Multivariate Time Series Forecasting Framework
Jul 30, 2025



Abstract:Multivariate Time Series Forecasting plays a key role in many applications. Recent works have explored using Large Language Models for MTSF to take advantage of their reasoning abilities. However, many methods treat LLMs as end-to-end forecasters, which often leads to a loss of numerical precision and forces LLMs to handle patterns beyond their intended design. Alternatively, methods that attempt to align textual and time series modalities within latent space frequently encounter alignment difficulty. In this paper, we propose to treat LLMs not as standalone forecasters, but as semantic guidance modules within a dual-stream framework. We propose DualSG, a dual-stream framework that provides explicit semantic guidance, where LLMs act as Semantic Guides to refine rather than replace traditional predictions. As part of DualSG, we introduce Time Series Caption, an explicit prompt format that summarizes trend patterns in natural language and provides interpretable context for LLMs, rather than relying on implicit alignment between text and time series in the latent space. We also design a caption-guided fusion module that explicitly models inter-variable relationships while reducing noise and computation. Experiments on real-world datasets from diverse domains show that DualSG consistently outperforms 15 state-of-the-art baselines, demonstrating the value of explicitly combining numerical forecasting with semantic guidance.
Test-Time Scaling with Reflective Generative Model
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:We introduce our first reflective generative model MetaStone-S1, which obtains OpenAI o3's performance via the self-supervised process reward model (SPRM). Through sharing the backbone network and using task-specific heads for next token prediction and process scoring respectively, SPRM successfully integrates the policy model and process reward model(PRM) into a unified interface without extra process annotation, reducing over 99% PRM parameters for efficient reasoning. Equipped with SPRM, MetaStone-S1 is naturally suitable for test time scaling (TTS), and we provide three reasoning effort modes (low, medium, and high), based on the controllable thinking length. Moreover, we empirically establish a scaling law that reveals the relationship between total thinking computation and TTS performance. Experiments demonstrate that our MetaStone-S1 achieves comparable performance to OpenAI-o3-mini's series with only 32B parameter size. To support the research community, we have open-sourced MetaStone-S1 at https://github.com/MetaStone-AI/MetaStone-S1.
DeepResearch Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Deep Research Agents
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Deep Research Agents are a prominent category of LLM-based agents. By autonomously orchestrating multistep web exploration, targeted retrieval, and higher-order synthesis, they transform vast amounts of online information into analyst-grade, citation-rich reports--compressing hours of manual desk research into minutes. However, a comprehensive benchmark for systematically evaluating the capabilities of these agents remains absent. To bridge this gap, we present DeepResearch Bench, a benchmark consisting of 100 PhD-level research tasks, each meticulously crafted by domain experts across 22 distinct fields. Evaluating DRAs is inherently complex and labor-intensive. We therefore propose two novel methodologies that achieve strong alignment with human judgment. The first is a reference-based method with adaptive criteria to assess the quality of generated research reports. The other framework is introduced to evaluate DRA's information retrieval and collection capabilities by assessing its effective citation count and overall citation accuracy. We have open-sourced DeepResearch Bench and key components of these frameworks at https://github.com/Ayanami0730/deep_research_bench to accelerate the development of practical LLM-based agents.
Graph Neural Networks in Modern AI-aided Drug Discovery
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs), as topology/structure-aware models within deep learning, have emerged as powerful tools for AI-aided drug discovery (AIDD). By directly operating on molecular graphs, GNNs offer an intuitive and expressive framework for learning the complex topological and geometric features of drug-like molecules, cementing their role in modern molecular modeling. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the methodological foundations and representative applications of GNNs in drug discovery, spanning tasks such as molecular property prediction, virtual screening, molecular generation, biomedical knowledge graph construction, and synthesis planning. Particular attention is given to recent methodological advances, including geometric GNNs, interpretable models, uncertainty quantification, scalable graph architectures, and graph generative frameworks. We also discuss how these models integrate with modern deep learning approaches, such as self-supervised learning, multi-task learning, meta-learning and pre-training. Throughout this review, we highlight the practical challenges and methodological bottlenecks encountered when applying GNNs to real-world drug discovery pipelines, and conclude with a discussion on future directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge