Zhineng Chen
UniRec-0.1B: Unified Text and Formula Recognition with 0.1B Parameters
Dec 24, 2025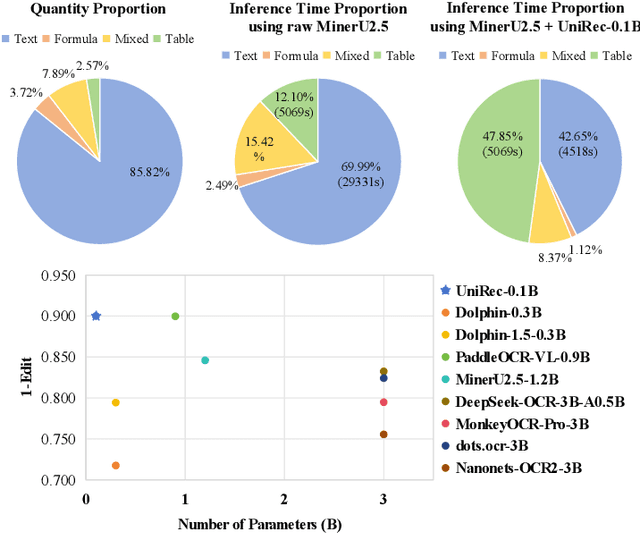
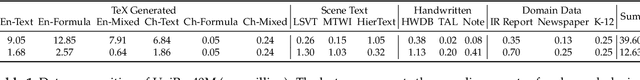
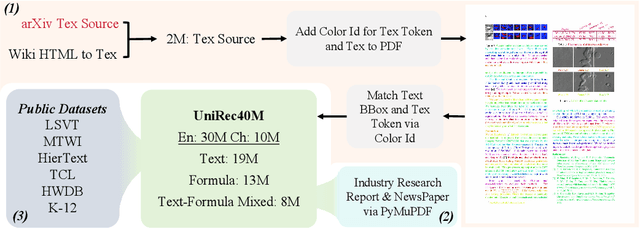
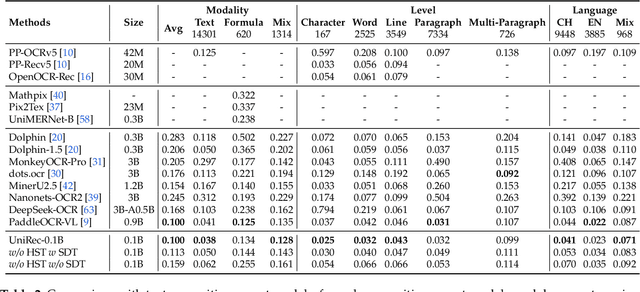
Abstract:Text and formulas constitute the core informational components of many documents. Accurately and efficiently recognizing both is crucial for developing robust and generalizable document parsing systems. Recently, vision-language models (VLMs) have achieved impressive unified recognition of text and formulas. However, they are large-sized and computationally demanding, restricting their usage in many applications. In this paper, we propose UniRec-0.1B, a unified recognition model with only 0.1B parameters. It is capable of performing text and formula recognition at multiple levels, including characters, words, lines, paragraphs, and documents. To implement this task, we first establish UniRec40M, a large-scale dataset comprises 40 million text, formula and their mix samples, enabling the training of a powerful yet lightweight model. Secondly, we identify two challenges when building such a lightweight but unified expert model. They are: structural variability across hierarchies and semantic entanglement between textual and formulaic content. To tackle these, we introduce a hierarchical supervision training that explicitly guides structural comprehension, and a semantic-decoupled tokenizer that separates text and formula representations. Finally, we develop a comprehensive evaluation benchmark covering Chinese and English documents from multiple domains and with multiple levels. Experimental results on this and public benchmarks demonstrate that UniRec-0.1B outperforms both general-purpose VLMs and leading document parsing expert models, while achieving a 2-9$\times$ speedup, validating its effectiveness and efficiency. Codebase and Dataset: https://github.com/Topdu/OpenOCR.
Complex Mathematical Expression Recognition: Benchmark, Large-Scale Dataset and Strong Baseline
Dec 14, 2025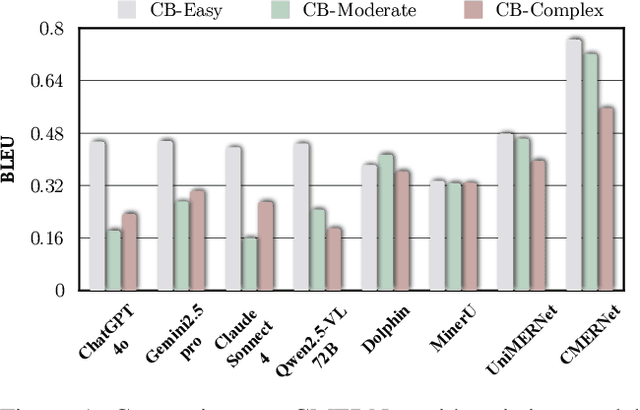
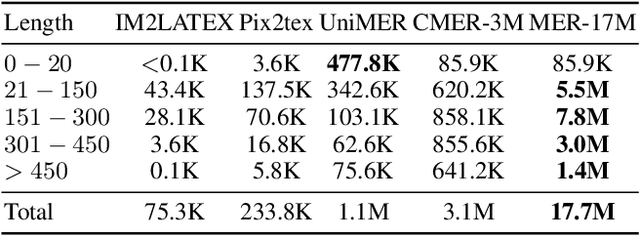
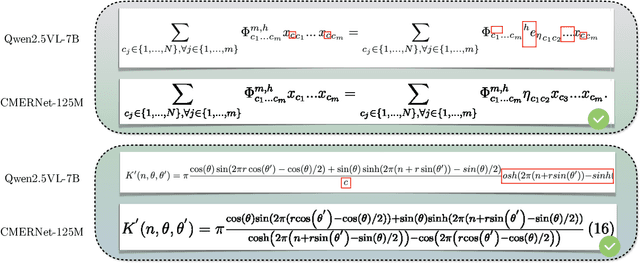
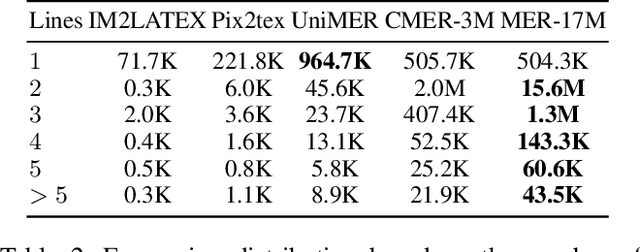
Abstract:Mathematical Expression Recognition (MER) has made significant progress in recognizing simple expressions, but the robust recognition of complex mathematical expressions with many tokens and multiple lines remains a formidable challenge. In this paper, we first introduce CMER-Bench, a carefully constructed benchmark that categorizes expressions into three difficulty levels: easy, moderate, and complex. Leveraging CMER-Bench, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of existing MER models and general-purpose multimodal large language models (MLLMs). The results reveal that while current methods perform well on easy and moderate expressions, their performance degrades significantly when handling complex mathematical expressions, mainly because existing public training datasets are primarily composed of simple samples. In response, we propose MER-17M and CMER-3M that are large-scale datasets emphasizing the recognition of complex mathematical expressions. The datasets provide rich and diverse samples to support the development of accurate and robust complex MER models. Furthermore, to address the challenges posed by the complicated spatial layout of complex expressions, we introduce a novel expression tokenizer, and a new representation called Structured Mathematical Language, which explicitly models the hierarchical and spatial structure of expressions beyond LaTeX format. Based on these, we propose a specialized model named CMERNet, built upon an encoder-decoder architecture and trained on CMER-3M. Experimental results show that CMERNet, with only 125 million parameters, significantly outperforms existing MER models and MLLMs on CMER-Bench.
LRANet++: Low-Rank Approximation Network for Accurate and Efficient Text Spotting
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:End-to-end text spotting aims to jointly optimize text detection and recognition within a unified framework. Despite significant progress, designing an accurate and efficient end-to-end text spotter for arbitrary-shaped text remains largely unsolved. We identify the primary bottleneck as the lack of a reliable and efficient text detection method. To address this, we propose a novel parameterized text shape method based on low-rank approximation for precise detection and a triple assignment detection head to enable fast inference. Specifically, unlike other shape representation methods that employ data-irrelevant parameterization, our data-driven approach derives a low-rank subspace directly from labeled text boundaries. To ensure this process is robust against the inherent annotation noise in this data, we utilize a specialized recovery method based on an $\ell_1$-norm formulation, which accurately reconstructs the text shape with only a few key orthogonal vectors. By exploiting the inherent shape correlation among different text contours, our method achieves consistency and compactness in shape representation. Next, the triple assignment scheme introduces a novel architecture where a deep sparse branch (for stabilized training) is used to guide the learning of an ultra-lightweight sparse branch (for accelerated inference), while a dense branch provides rich parallel supervision. Building upon these advancements, we integrate the enhanced detection module with a lightweight recognition branch to form an end-to-end text spotting framework, termed LRANet++, capable of accurately and efficiently spotting arbitrary-shaped text. Extensive experiments on several challenging benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of LRANet++ compared to state-of-the-art methods. Code will be available at: https://github.com/ychensu/LRANet-PP.git
Distilling Knowledge from Heterogeneous Architectures for Semantic Segmentation
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Current knowledge distillation (KD) methods for semantic segmentation focus on guiding the student to imitate the teacher's knowledge within homogeneous architectures. However, these methods overlook the diverse knowledge contained in architectures with different inductive biases, which is crucial for enabling the student to acquire a more precise and comprehensive understanding of the data during distillation. To this end, we propose for the first time a generic knowledge distillation method for semantic segmentation from a heterogeneous perspective, named HeteroAKD. Due to the substantial disparities between heterogeneous architectures, such as CNN and Transformer, directly transferring cross-architecture knowledge presents significant challenges. To eliminate the influence of architecture-specific information, the intermediate features of both the teacher and student are skillfully projected into an aligned logits space. Furthermore, to utilize diverse knowledge from heterogeneous architectures and deliver customized knowledge required by the student, a teacher-student knowledge mixing mechanism (KMM) and a teacher-student knowledge evaluation mechanism (KEM) are introduced. These mechanisms are performed by assessing the reliability and its discrepancy between heterogeneous teacher-student knowledge. Extensive experiments conducted on three main-stream benchmarks using various teacher-student pairs demonstrate that our HeteroAKD outperforms state-of-the-art KD methods in facilitating distillation between heterogeneous architectures.
Explicit Relational Reasoning Network for Scene Text Detection
Dec 19, 2024
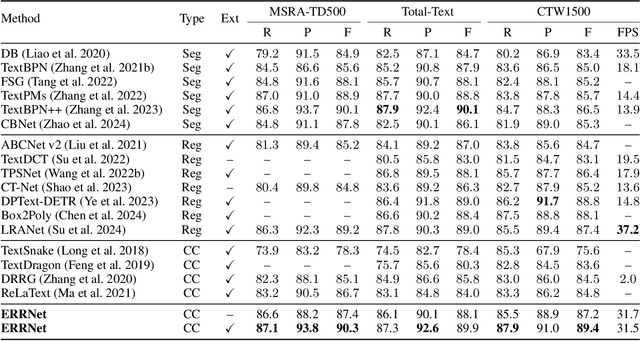

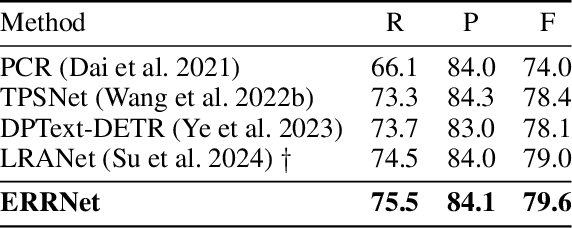
Abstract:Connected component (CC) is a proper text shape representation that aligns with human reading intuition. However, CC-based text detection methods have recently faced a developmental bottleneck that their time-consuming post-processing is difficult to eliminate. To address this issue, we introduce an explicit relational reasoning network (ERRNet) to elegantly model the component relationships without post-processing. Concretely, we first represent each text instance as multiple ordered text components, and then treat these components as objects in sequential movement. In this way, scene text detection can be innovatively viewed as a tracking problem. From this perspective, we design an end-to-end tracking decoder to achieve a CC-based method dispensing with post-processing entirely. Additionally, we observe that there is an inconsistency between classification confidence and localization quality, so we propose a Polygon Monte-Carlo method to quickly and accurately evaluate the localization quality. Based on this, we introduce a position-supervised classification loss to guide the task-aligned learning of ERRNet. Experiments on challenging benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our ERRNet. It consistently achieves state-of-the-art accuracy while holding highly competitive inference speed.
A Graph-Based Synthetic Data Pipeline for Scaling High-Quality Reasoning Instructions
Dec 12, 2024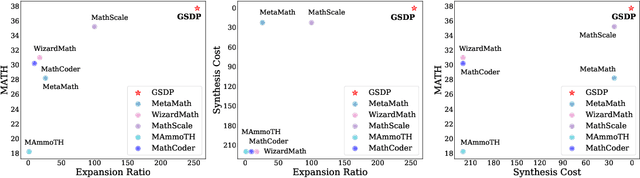
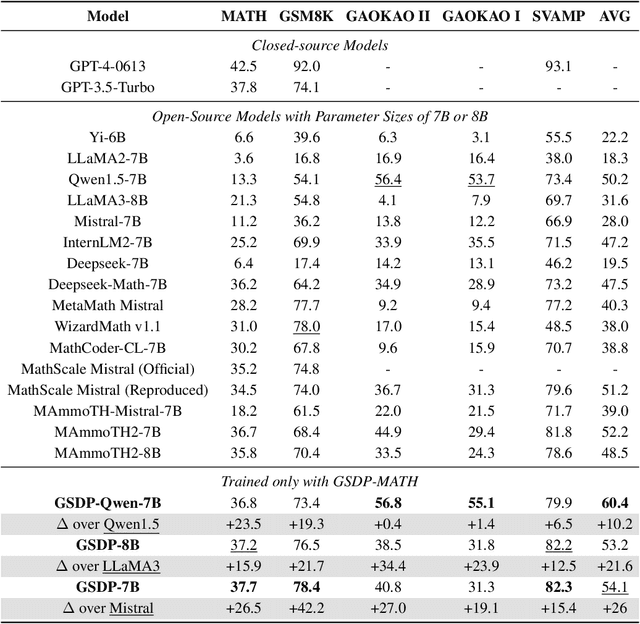
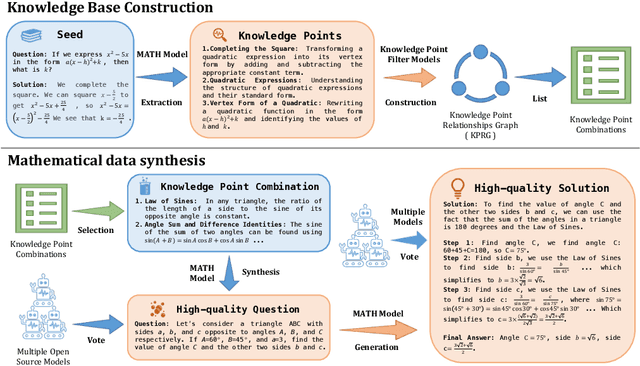
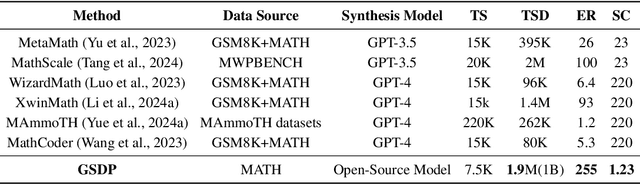
Abstract:Synthesizing high-quality reasoning data for continual training has been proven to be effective in enhancing the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, previous synthetic approaches struggle to easily scale up data and incur high costs in the pursuit of high quality. In this paper, we propose the Graph-based Synthetic Data Pipeline (GSDP), an economical and scalable framework for high-quality reasoning data synthesis. Inspired by knowledge graphs, we extracted knowledge points from seed data and constructed a knowledge point relationships graph to explore their interconnections. By exploring the implicit relationships among knowledge, our method achieves $\times$255 data expansion. Furthermore, GSDP led by open-source models, achieves synthesis quality comparable to GPT-4-0613 while maintaining $\times$100 lower costs. To tackle the most challenging mathematical reasoning task, we present the GSDP-MATH dataset comprising over 1.91 million pairs of math problems and answers. After fine-tuning on GSDP-MATH, GSDP-7B based on Mistral-7B achieves 37.7% accuracy on MATH and 78.4% on GSM8K, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method. The dataset and models trained in this paper will be available.
TextSSR: Diffusion-based Data Synthesis for Scene Text Recognition
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Scene text recognition (STR) suffers from the challenges of either less realistic synthetic training data or the difficulty of collecting sufficient high-quality real-world data, limiting the effectiveness of trained STR models. Meanwhile, despite producing holistically appealing text images, diffusion-based text image generation methods struggle to generate accurate and realistic instance-level text on a large scale. To tackle this, we introduce TextSSR: a novel framework for Synthesizing Scene Text Recognition data via a diffusion-based universal text region synthesis model. It ensures accuracy by focusing on generating text within a specified image region and leveraging rich glyph and position information to create the less complex text region compared to the entire image. Furthermore, we utilize neighboring text within the region as a prompt to capture real-world font styles and layout patterns, guiding the generated text to resemble actual scenes. Finally, due to its prompt-free nature and capability for character-level synthesis, TextSSR enjoys a wonderful scalability and we construct an anagram-based TextSSR-F dataset with 0.4 million text instances with complexity and realism. Experiments show that models trained on added TextSSR-F data exhibit better accuracy compared to models trained on 4 million existing synthetic data. Moreover, its accuracy margin to models trained fully on a real-world dataset is less than 3.7%, confirming TextSSR's effectiveness and its great potential in scene text image synthesis. Our code is available at https://github.com/YesianRohn/TextSSR.
SVTRv2: CTC Beats Encoder-Decoder Models in Scene Text Recognition
Nov 24, 2024Abstract:Connectionist temporal classification (CTC)-based scene text recognition (STR) methods, e.g., SVTR, are widely employed in OCR applications, mainly due to their simple architecture, which only contains a visual model and a CTC-aligned linear classifier, and therefore fast inference. However, they generally have worse accuracy than encoder-decoder-based methods (EDTRs), particularly in challenging scenarios. In this paper, we propose SVTRv2, a CTC model that beats leading EDTRs in both accuracy and inference speed. SVTRv2 introduces novel upgrades to handle text irregularity and utilize linguistic context, which endows it with the capability to deal with challenging and diverse text instances. First, a multi-size resizing (MSR) strategy is proposed to adaptively resize the text and maintain its readability. Meanwhile, we introduce a feature rearrangement module (FRM) to ensure that visual features accommodate the alignment requirement of CTC well, thus alleviating the alignment puzzle. Second, we propose a semantic guidance module (SGM). It integrates linguistic context into the visual model, allowing it to leverage language information for improved accuracy. Moreover, SGM can be omitted at the inference stage and would not increase the inference cost. We evaluate SVTRv2 in both standard and recent challenging benchmarks, where SVTRv2 is fairly compared with 24 mainstream STR models across multiple scenarios, including different types of text irregularity, languages, and long text. The results indicate that SVTRv2 surpasses all the EDTRs across the scenarios in terms of accuracy and speed. Code is available at https://github.com/Topdu/OpenOCR.
Improving Text-guided Object Inpainting with Semantic Pre-inpainting
Sep 12, 2024Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the success of large text-to-image diffusion models and their remarkable potential to generate high-quality images. The further pursuit of enhancing the editability of images has sparked significant interest in the downstream task of inpainting a novel object described by a text prompt within a designated region in the image. Nevertheless, the problem is not trivial from two aspects: 1) Solely relying on one single U-Net to align text prompt and visual object across all the denoising timesteps is insufficient to generate desired objects; 2) The controllability of object generation is not guaranteed in the intricate sampling space of diffusion model. In this paper, we propose to decompose the typical single-stage object inpainting into two cascaded processes: 1) semantic pre-inpainting that infers the semantic features of desired objects in a multi-modal feature space; 2) high-fieldity object generation in diffusion latent space that pivots on such inpainted semantic features. To achieve this, we cascade a Transformer-based semantic inpainter and an object inpainting diffusion model, leading to a novel CAscaded Transformer-Diffusion (CAT-Diffusion) framework for text-guided object inpainting. Technically, the semantic inpainter is trained to predict the semantic features of the target object conditioning on unmasked context and text prompt. The outputs of the semantic inpainter then act as the informative visual prompts to guide high-fieldity object generation through a reference adapter layer, leading to controllable object inpainting. Extensive evaluations on OpenImages-V6 and MSCOCO validate the superiority of CAT-Diffusion against the state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/Nnn-s/CATdiffusion}.
FreeEnhance: Tuning-Free Image Enhancement via Content-Consistent Noising-and-Denoising Process
Sep 11, 2024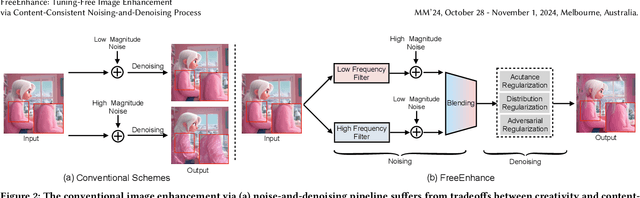
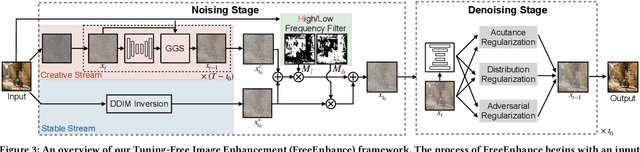
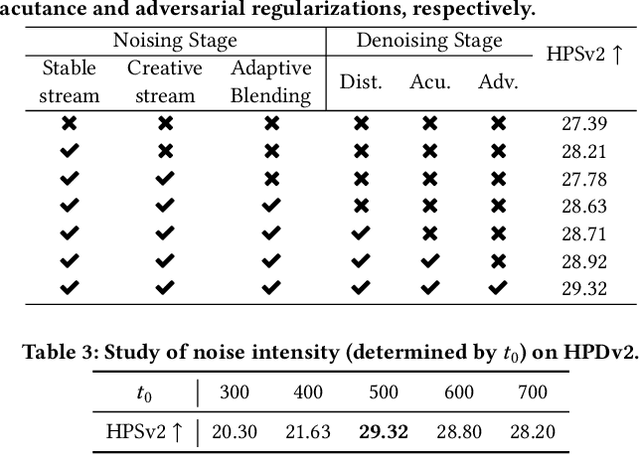

Abstract:The emergence of text-to-image generation models has led to the recognition that image enhancement, performed as post-processing, would significantly improve the visual quality of the generated images. Exploring diffusion models to enhance the generated images nevertheless is not trivial and necessitates to delicately enrich plentiful details while preserving the visual appearance of key content in the original image. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, namely FreeEnhance, for content-consistent image enhancement using the off-the-shelf image diffusion models. Technically, FreeEnhance is a two-stage process that firstly adds random noise to the input image and then capitalizes on a pre-trained image diffusion model (i.e., Latent Diffusion Models) to denoise and enhance the image details. In the noising stage, FreeEnhance is devised to add lighter noise to the region with higher frequency to preserve the high-frequent patterns (e.g., edge, corner) in the original image. In the denoising stage, we present three target properties as constraints to regularize the predicted noise, enhancing images with high acutance and high visual quality. Extensive experiments conducted on the HPDv2 dataset demonstrate that our FreeEnhance outperforms the state-of-the-art image enhancement models in terms of quantitative metrics and human preference. More remarkably, FreeEnhance also shows higher human preference compared to the commercial image enhancement solution of Magnific AI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge