Haibo Yang
Flow Matching for Offline Reinforcement Learning with Discrete Actions
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Generative policies based on diffusion models and flow matching have shown strong promise for offline reinforcement learning (RL), but their applicability remains largely confined to continuous action spaces. To address a broader range of offline RL settings, we extend flow matching to a general framework that supports discrete action spaces with multiple objectives. Specifically, we replace continuous flows with continuous-time Markov chains, trained using a Q-weighted flow matching objective. We then extend our design to multi-agent settings, mitigating the exponential growth of joint action spaces via a factorized conditional path. We theoretically show that, under idealized conditions, optimizing this objective recovers the optimal policy. Extensive experiments further demonstrate that our method performs robustly in practical scenarios, including high-dimensional control, multi-modal decision-making, and dynamically changing preferences over multiple objectives. Our discrete framework can also be applied to continuous-control problems through action quantization, providing a flexible trade-off between representational complexity and performance.
Decoupled Split Learning via Auxiliary Loss
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Split learning is a distributed training paradigm where a neural network is partitioned between clients and a server, which allows data to remain at the client while only intermediate activations are shared. Traditional split learning relies on end-to-end backpropagation across the client-server split point. This incurs a large communication overhead (i.e., forward activations and backward gradients need to be exchanged every iteration) and significant memory use (for storing activations and gradients). In this paper, we develop a beyond-backpropagation training method for split learning. In this approach, the client and server train their model partitions semi-independently, using local loss signals instead of propagated gradients. In particular, the client's network is augmented with a small auxiliary classifier at the split point to provide a local error signal, while the server trains on the client's transmitted activations using the true loss function. This decoupling removes the need to send backward gradients, which cuts communication costs roughly in half and also reduces memory overhead (as each side only stores local activations for its own backward pass). We evaluate our approach on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100. Our experiments show two key results. First, the proposed approach achieves performance on par with standard split learning that uses backpropagation. Second, it significantly reduces communication (of transmitting activations/gradient) by 50% and peak memory usage by up to 58%.
HOSL: Hybrid-Order Split Learning for Memory-Constrained Edge Training
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Split learning (SL) enables collaborative training of large language models (LLMs) between resource-constrained edge devices and compute-rich servers by partitioning model computation across the network boundary. However, existing SL systems predominantly rely on first-order (FO) optimization, which requires clients to store intermediate quantities such as activations for backpropagation. This results in substantial memory overhead, largely negating benefits of model partitioning. In contrast, zeroth-order (ZO) optimization eliminates backpropagation and significantly reduces memory usage, but often suffers from slow convergence and degraded performance. In this work, we propose HOSL, a novel Hybrid-Order Split Learning framework that addresses this fundamental trade-off between memory efficiency and optimization effectiveness by strategically integrating ZO optimization on the client side with FO optimization on the server side. By employing memory-efficient ZO gradient estimation at the client, HOSL eliminates backpropagation and activation storage, reducing client memory consumption. Meanwhile, server-side FO optimization ensures fast convergence and competitive performance. Theoretically, we show that HOSL achieves a $\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{d_c/TQ})$ rate, which depends on client-side model dimension $d_c$ rather than the full model dimension $d$, demonstrating that convergence improves as more computation is offloaded to the server. Extensive experiments on OPT models (125M and 1.3B parameters) across 6 tasks demonstrate that HOSL reduces client GPU memory by up to 3.7$\times$ compared to the FO method while achieving accuracy within 0.20%-4.23% of this baseline. Furthermore, HOSL outperforms the ZO baseline by up to 15.55%, validating the effectiveness of our hybrid strategy for memory-efficient training on edge devices.
Exploring Pose-Guided Imitation Learning for Robotic Precise Insertion
May 14, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have proved that imitation learning shows strong potential in the field of robotic manipulation. However, existing methods still struggle with precision manipulation task and rely on inefficient image/point cloud observations. In this paper, we explore to introduce SE(3) object pose into imitation learning and propose the pose-guided efficient imitation learning methods for robotic precise insertion task. First, we propose a precise insertion diffusion policy which utilizes the relative SE(3) pose as the observation-action pair. The policy models the source object SE(3) pose trajectory relative to the target object. Second, we explore to introduce the RGBD data to the pose-guided diffusion policy. Specifically, we design a goal-conditioned RGBD encoder to capture the discrepancy between the current state and the goal state. In addition, a pose-guided residual gated fusion method is proposed, which takes pose features as the backbone, and the RGBD features selectively compensate for pose feature deficiencies through an adaptive gating mechanism. Our methods are evaluated on 6 robotic precise insertion tasks, demonstrating competitive performance with only 7-10 demonstrations. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed methods can successfully complete precision insertion tasks with a clearance of about 0.01 mm. Experimental results highlight its superior efficiency and generalization capability compared to existing baselines. Code will be available at https://github.com/sunhan1997/PoseInsert.
From Interpretation to Correction: A Decentralized Optimization Framework for Exact Convergence in Federated Learning
Mar 25, 2025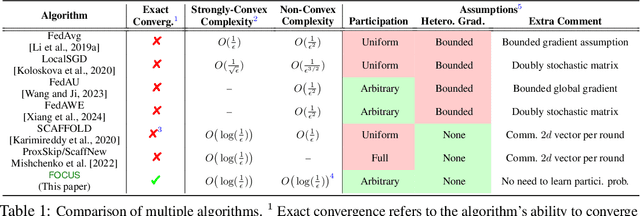



Abstract:This work introduces a novel decentralized framework to interpret federated learning (FL) and, consequently, correct the biases introduced by arbitrary client participation and data heterogeneity, which are two typical traits in practical FL. Specifically, we first reformulate the core processes of FedAvg - client participation, local updating, and model aggregation - as stochastic matrix multiplications. This reformulation allows us to interpret FedAvg as a decentralized algorithm. Leveraging the decentralized optimization framework, we are able to provide a concise analysis to quantify the impact of arbitrary client participation and data heterogeneity on FedAvg's convergence point. This insight motivates the development of Federated Optimization with Exact Convergence via Push-pull Strategy (FOCUS), a novel algorithm inspired by the decentralized algorithm that eliminates these biases and achieves exact convergence without requiring the bounded heterogeneity assumption. Furthermore, we theoretically prove that FOCUS exhibits linear convergence (exponential decay) for both strongly convex and non-convex functions satisfying the Polyak-Lojasiewicz condition, regardless of the arbitrary nature of client participation.
Do We Really Need to Design New Byzantine-robust Aggregation Rules?
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) allows multiple clients to collaboratively train a global machine learning model through a server, without exchanging their private training data. However, the decentralized aspect of FL makes it susceptible to poisoning attacks, where malicious clients can manipulate the global model by sending altered local model updates. To counter these attacks, a variety of aggregation rules designed to be resilient to Byzantine failures have been introduced. Nonetheless, these methods can still be vulnerable to sophisticated attacks or depend on unrealistic assumptions about the server. In this paper, we demonstrate that there is no need to design new Byzantine-robust aggregation rules; instead, FL can be secured by enhancing the robustness of well-established aggregation rules. To this end, we present FoundationFL, a novel defense mechanism against poisoning attacks. FoundationFL involves the server generating synthetic updates after receiving local model updates from clients. It then applies existing Byzantine-robust foundational aggregation rules, such as Trimmed-mean or Median, to combine clients' model updates with the synthetic ones. We theoretically establish the convergence performance of FoundationFL under Byzantine settings. Comprehensive experiments across several real-world datasets validate the efficiency of our FoundationFL method.
PSMGD: Periodic Stochastic Multi-Gradient Descent for Fast Multi-Objective Optimization
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Multi-objective optimization (MOO) lies at the core of many machine learning (ML) applications that involve multiple, potentially conflicting objectives (e.g., multi-task learning, multi-objective reinforcement learning, among many others). Despite the long history of MOO, recent years have witnessed a surge in interest within the ML community in the development of gradient manipulation algorithms for MOO, thanks to the availability of gradient information in many ML problems. However, existing gradient manipulation methods for MOO often suffer from long training times, primarily due to the need for computing dynamic weights by solving an additional optimization problem to determine a common descent direction that can decrease all objectives simultaneously. To address this challenge, we propose a new and efficient algorithm called Periodic Stochastic Multi-Gradient Descent (PSMGD) to accelerate MOO. PSMGD is motivated by the key observation that dynamic weights across objectives exhibit small changes under minor updates over short intervals during the optimization process. Consequently, our PSMGD algorithm is designed to periodically compute these dynamic weights and utilizes them repeatedly, thereby effectively reducing the computational overload. Theoretically, we prove that PSMGD can achieve state-of-the-art convergence rates for strongly-convex, general convex, and non-convex functions. Additionally, we introduce a new computational complexity measure, termed backpropagation complexity, and demonstrate that PSMGD could achieve an objective-independent backpropagation complexity. Through extensive experiments, we verify that PSMGD can provide comparable or superior performance to state-of-the-art MOO algorithms while significantly reducing training time.
Hi3D: Pursuing High-Resolution Image-to-3D Generation with Video Diffusion Models
Sep 11, 2024Abstract:Despite having tremendous progress in image-to-3D generation, existing methods still struggle to produce multi-view consistent images with high-resolution textures in detail, especially in the paradigm of 2D diffusion that lacks 3D awareness. In this work, we present High-resolution Image-to-3D model (Hi3D), a new video diffusion based paradigm that redefines a single image to multi-view images as 3D-aware sequential image generation (i.e., orbital video generation). This methodology delves into the underlying temporal consistency knowledge in video diffusion model that generalizes well to geometry consistency across multiple views in 3D generation. Technically, Hi3D first empowers the pre-trained video diffusion model with 3D-aware prior (camera pose condition), yielding multi-view images with low-resolution texture details. A 3D-aware video-to-video refiner is learnt to further scale up the multi-view images with high-resolution texture details. Such high-resolution multi-view images are further augmented with novel views through 3D Gaussian Splatting, which are finally leveraged to obtain high-fidelity meshes via 3D reconstruction. Extensive experiments on both novel view synthesis and single view reconstruction demonstrate that our Hi3D manages to produce superior multi-view consistency images with highly-detailed textures. Source code and data are available at \url{https://github.com/yanghb22-fdu/Hi3D-Official}.
DreamMesh: Jointly Manipulating and Texturing Triangle Meshes for Text-to-3D Generation
Sep 11, 2024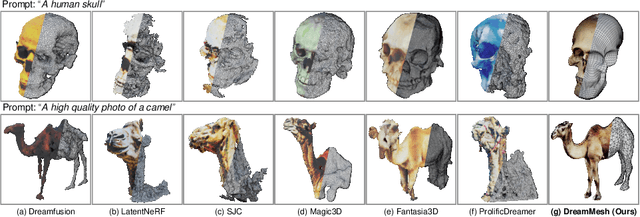
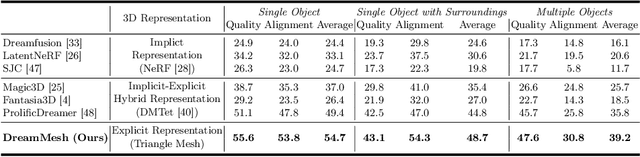
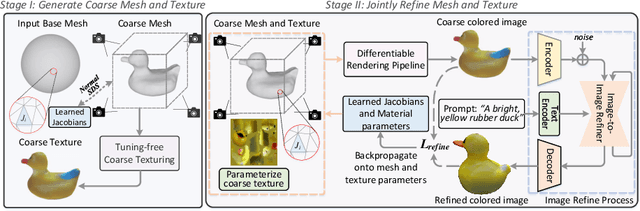
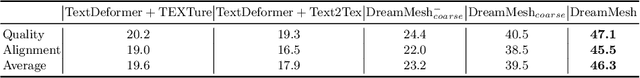
Abstract:Learning radiance fields (NeRF) with powerful 2D diffusion models has garnered popularity for text-to-3D generation. Nevertheless, the implicit 3D representations of NeRF lack explicit modeling of meshes and textures over surfaces, and such surface-undefined way may suffer from the issues, e.g., noisy surfaces with ambiguous texture details or cross-view inconsistency. To alleviate this, we present DreamMesh, a novel text-to-3D architecture that pivots on well-defined surfaces (triangle meshes) to generate high-fidelity explicit 3D model. Technically, DreamMesh capitalizes on a distinctive coarse-to-fine scheme. In the coarse stage, the mesh is first deformed by text-guided Jacobians and then DreamMesh textures the mesh with an interlaced use of 2D diffusion models in a tuning free manner from multiple viewpoints. In the fine stage, DreamMesh jointly manipulates the mesh and refines the texture map, leading to high-quality triangle meshes with high-fidelity textured materials. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DreamMesh significantly outperforms state-of-the-art text-to-3D methods in faithfully generating 3D content with richer textual details and enhanced geometry. Our project page is available at https://dreammesh.github.io.
Adversarial Attacks to Multi-Modal Models
Sep 10, 2024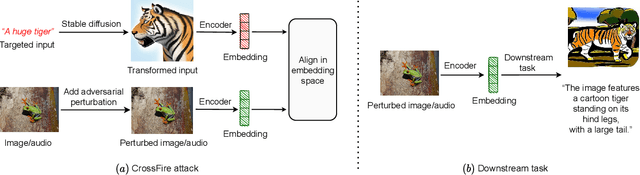



Abstract:Multi-modal models have gained significant attention due to their powerful capabilities. These models effectively align embeddings across diverse data modalities, showcasing superior performance in downstream tasks compared to their unimodal counterparts. Recent study showed that the attacker can manipulate an image or audio file by altering it in such a way that its embedding matches that of an attacker-chosen targeted input, thereby deceiving downstream models. However, this method often underperforms due to inherent disparities in data from different modalities. In this paper, we introduce CrossFire, an innovative approach to attack multi-modal models. CrossFire begins by transforming the targeted input chosen by the attacker into a format that matches the modality of the original image or audio file. We then formulate our attack as an optimization problem, aiming to minimize the angular deviation between the embeddings of the transformed input and the modified image or audio file. Solving this problem determines the perturbations to be added to the original media. Our extensive experiments on six real-world benchmark datasets reveal that CrossFire can significantly manipulate downstream tasks, surpassing existing attacks. Additionally, we evaluate six defensive strategies against CrossFire, finding that current defenses are insufficient to counteract our CrossFire.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge