Yuchen Su
UniRec-0.1B: Unified Text and Formula Recognition with 0.1B Parameters
Dec 24, 2025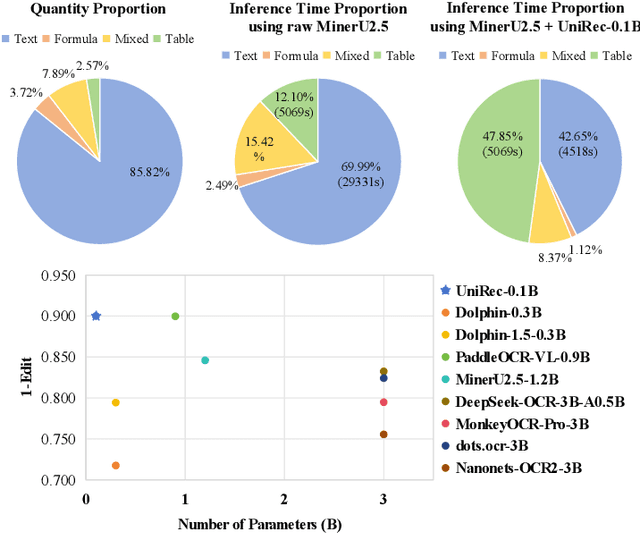
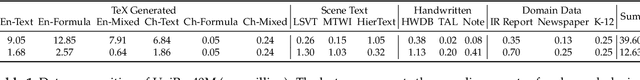
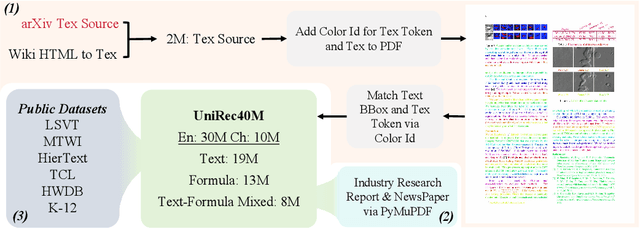
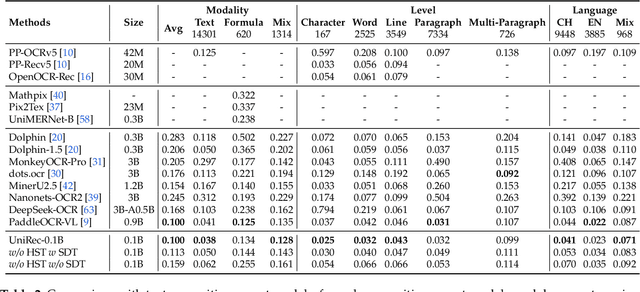
Abstract:Text and formulas constitute the core informational components of many documents. Accurately and efficiently recognizing both is crucial for developing robust and generalizable document parsing systems. Recently, vision-language models (VLMs) have achieved impressive unified recognition of text and formulas. However, they are large-sized and computationally demanding, restricting their usage in many applications. In this paper, we propose UniRec-0.1B, a unified recognition model with only 0.1B parameters. It is capable of performing text and formula recognition at multiple levels, including characters, words, lines, paragraphs, and documents. To implement this task, we first establish UniRec40M, a large-scale dataset comprises 40 million text, formula and their mix samples, enabling the training of a powerful yet lightweight model. Secondly, we identify two challenges when building such a lightweight but unified expert model. They are: structural variability across hierarchies and semantic entanglement between textual and formulaic content. To tackle these, we introduce a hierarchical supervision training that explicitly guides structural comprehension, and a semantic-decoupled tokenizer that separates text and formula representations. Finally, we develop a comprehensive evaluation benchmark covering Chinese and English documents from multiple domains and with multiple levels. Experimental results on this and public benchmarks demonstrate that UniRec-0.1B outperforms both general-purpose VLMs and leading document parsing expert models, while achieving a 2-9$\times$ speedup, validating its effectiveness and efficiency. Codebase and Dataset: https://github.com/Topdu/OpenOCR.
Complex Mathematical Expression Recognition: Benchmark, Large-Scale Dataset and Strong Baseline
Dec 14, 2025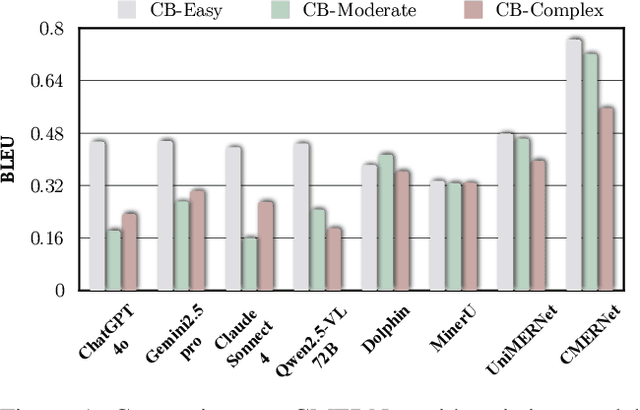
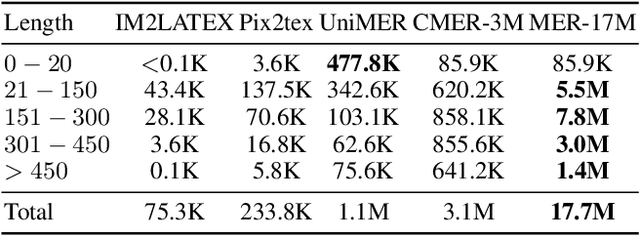
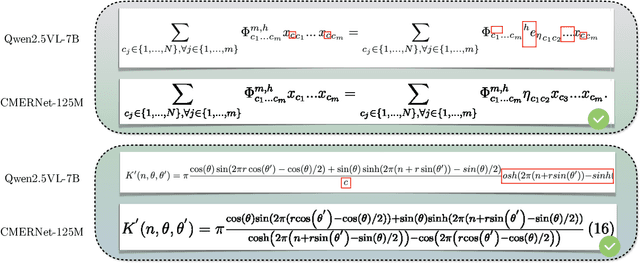
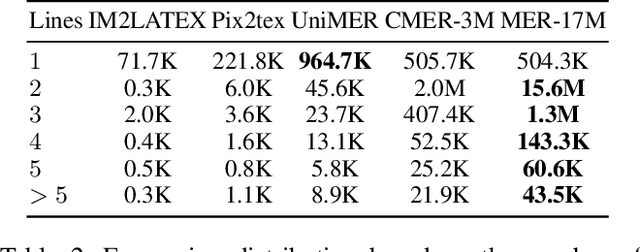
Abstract:Mathematical Expression Recognition (MER) has made significant progress in recognizing simple expressions, but the robust recognition of complex mathematical expressions with many tokens and multiple lines remains a formidable challenge. In this paper, we first introduce CMER-Bench, a carefully constructed benchmark that categorizes expressions into three difficulty levels: easy, moderate, and complex. Leveraging CMER-Bench, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of existing MER models and general-purpose multimodal large language models (MLLMs). The results reveal that while current methods perform well on easy and moderate expressions, their performance degrades significantly when handling complex mathematical expressions, mainly because existing public training datasets are primarily composed of simple samples. In response, we propose MER-17M and CMER-3M that are large-scale datasets emphasizing the recognition of complex mathematical expressions. The datasets provide rich and diverse samples to support the development of accurate and robust complex MER models. Furthermore, to address the challenges posed by the complicated spatial layout of complex expressions, we introduce a novel expression tokenizer, and a new representation called Structured Mathematical Language, which explicitly models the hierarchical and spatial structure of expressions beyond LaTeX format. Based on these, we propose a specialized model named CMERNet, built upon an encoder-decoder architecture and trained on CMER-3M. Experimental results show that CMERNet, with only 125 million parameters, significantly outperforms existing MER models and MLLMs on CMER-Bench.
LRANet++: Low-Rank Approximation Network for Accurate and Efficient Text Spotting
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:End-to-end text spotting aims to jointly optimize text detection and recognition within a unified framework. Despite significant progress, designing an accurate and efficient end-to-end text spotter for arbitrary-shaped text remains largely unsolved. We identify the primary bottleneck as the lack of a reliable and efficient text detection method. To address this, we propose a novel parameterized text shape method based on low-rank approximation for precise detection and a triple assignment detection head to enable fast inference. Specifically, unlike other shape representation methods that employ data-irrelevant parameterization, our data-driven approach derives a low-rank subspace directly from labeled text boundaries. To ensure this process is robust against the inherent annotation noise in this data, we utilize a specialized recovery method based on an $\ell_1$-norm formulation, which accurately reconstructs the text shape with only a few key orthogonal vectors. By exploiting the inherent shape correlation among different text contours, our method achieves consistency and compactness in shape representation. Next, the triple assignment scheme introduces a novel architecture where a deep sparse branch (for stabilized training) is used to guide the learning of an ultra-lightweight sparse branch (for accelerated inference), while a dense branch provides rich parallel supervision. Building upon these advancements, we integrate the enhanced detection module with a lightweight recognition branch to form an end-to-end text spotting framework, termed LRANet++, capable of accurately and efficiently spotting arbitrary-shaped text. Extensive experiments on several challenging benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of LRANet++ compared to state-of-the-art methods. Code will be available at: https://github.com/ychensu/LRANet-PP.git
Explicit Relational Reasoning Network for Scene Text Detection
Dec 19, 2024
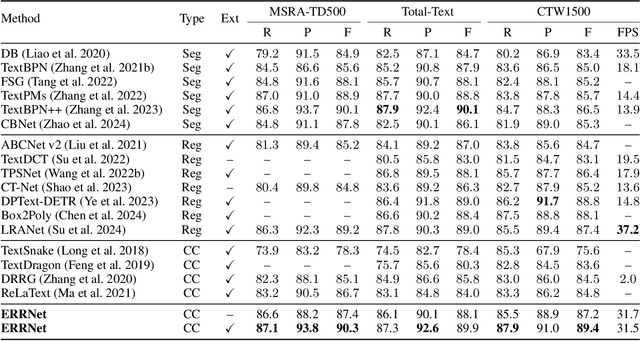

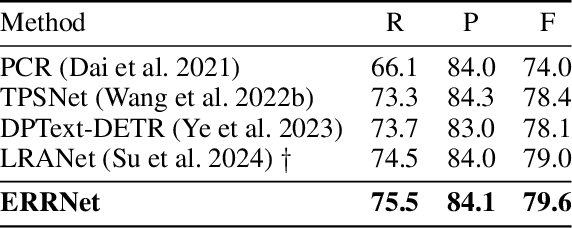
Abstract:Connected component (CC) is a proper text shape representation that aligns with human reading intuition. However, CC-based text detection methods have recently faced a developmental bottleneck that their time-consuming post-processing is difficult to eliminate. To address this issue, we introduce an explicit relational reasoning network (ERRNet) to elegantly model the component relationships without post-processing. Concretely, we first represent each text instance as multiple ordered text components, and then treat these components as objects in sequential movement. In this way, scene text detection can be innovatively viewed as a tracking problem. From this perspective, we design an end-to-end tracking decoder to achieve a CC-based method dispensing with post-processing entirely. Additionally, we observe that there is an inconsistency between classification confidence and localization quality, so we propose a Polygon Monte-Carlo method to quickly and accurately evaluate the localization quality. Based on this, we introduce a position-supervised classification loss to guide the task-aligned learning of ERRNet. Experiments on challenging benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our ERRNet. It consistently achieves state-of-the-art accuracy while holding highly competitive inference speed.
Hint-AD: Holistically Aligned Interpretability in End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Sep 10, 2024
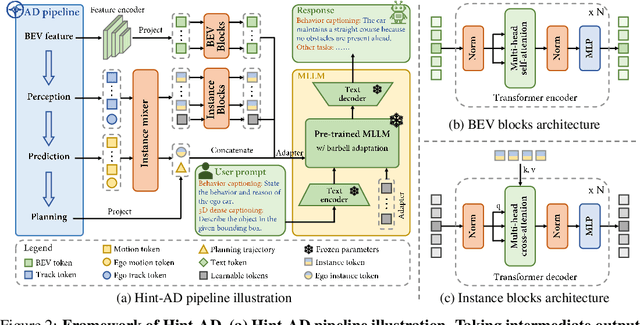

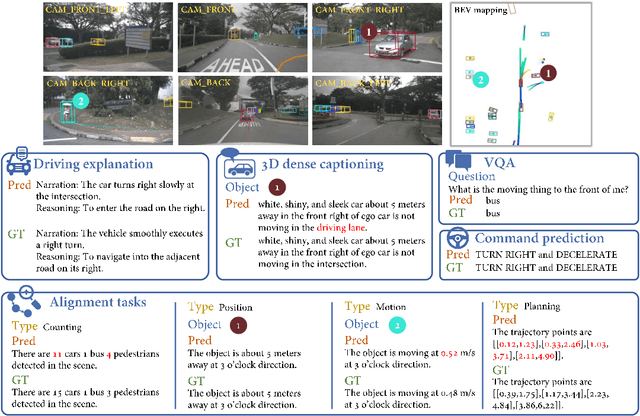
Abstract:End-to-end architectures in autonomous driving (AD) face a significant challenge in interpretability, impeding human-AI trust. Human-friendly natural language has been explored for tasks such as driving explanation and 3D captioning. However, previous works primarily focused on the paradigm of declarative interpretability, where the natural language interpretations are not grounded in the intermediate outputs of AD systems, making the interpretations only declarative. In contrast, aligned interpretability establishes a connection between language and the intermediate outputs of AD systems. Here we introduce Hint-AD, an integrated AD-language system that generates language aligned with the holistic perception-prediction-planning outputs of the AD model. By incorporating the intermediate outputs and a holistic token mixer sub-network for effective feature adaptation, Hint-AD achieves desirable accuracy, achieving state-of-the-art results in driving language tasks including driving explanation, 3D dense captioning, and command prediction. To facilitate further study on driving explanation task on nuScenes, we also introduce a human-labeled dataset, Nu-X. Codes, dataset, and models will be publicly available.
Instruction-Guided Scene Text Recognition
Jan 31, 2024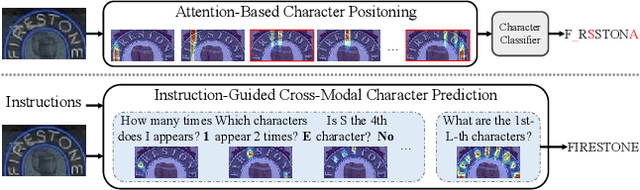


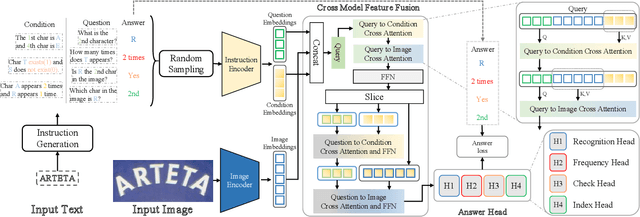
Abstract:Multi-modal models have shown appealing performance in visual tasks recently, as instruction-guided training has evoked the ability to understand fine-grained visual content. However, current methods cannot be trivially applied to scene text recognition (STR) due to the gap between natural and text images. In this paper, we introduce a novel paradigm that formulates STR as an instruction learning problem, and propose instruction-guided scene text recognition (IGTR) to achieve effective cross-modal learning. IGTR first generates rich and diverse instruction triplets of <condition,question,answer>, serving as guidance for nuanced text image understanding. Then, we devise an architecture with dedicated cross-modal feature fusion module, and multi-task answer head to effectively fuse the required instruction and image features for answering questions. Built upon these designs, IGTR facilitates accurate text recognition by comprehending character attributes. Experiments on English and Chinese benchmarks show that IGTR outperforms existing models by significant margins. Furthermore, by adjusting the instructions, IGTR enables various recognition schemes. These include zero-shot prediction, where the model is trained based on instructions not explicitly targeting character recognition, and the recognition of rarely appearing and morphologically similar characters, which were previous challenges for existing models.
CT-Net: Arbitrary-Shaped Text Detection via Contour Transformer
Jul 25, 2023



Abstract:Contour based scene text detection methods have rapidly developed recently, but still suffer from inaccurate frontend contour initialization, multi-stage error accumulation, or deficient local information aggregation. To tackle these limitations, we propose a novel arbitrary-shaped scene text detection framework named CT-Net by progressive contour regression with contour transformers. Specifically, we first employ a contour initialization module that generates coarse text contours without any post-processing. Then, we adopt contour refinement modules to adaptively refine text contours in an iterative manner, which are beneficial for context information capturing and progressive global contour deformation. Besides, we propose an adaptive training strategy to enable the contour transformers to learn more potential deformation paths, and introduce a re-score mechanism that can effectively suppress false positives. Extensive experiments are conducted on four challenging datasets, which demonstrate the accuracy and efficiency of our CT-Net over state-of-the-art methods. Particularly, CT-Net achieves F-measure of 86.1 at 11.2 frames per second (FPS) and F-measure of 87.8 at 10.1 FPS for CTW1500 and Total-Text datasets, respectively.
Efficient and Accurate Scene Text Detection with Low-Rank Approximation Network
Jun 27, 2023Abstract:Recently, regression-based methods, which predict parameter curves for localizing texts, are popular in scene text detection. However, these methods struggle to balance concise structure and fast post-processing, and the existing parameter curves are still not ideal for modeling arbitrary-shaped texts, leading to a challenge in balancing speed and accuracy. To tackle these challenges, we firstly propose a dual matching scheme for positive samples, which accelerates inference speed through sparse matching scheme and accelerates model convergence through dense matching scheme. Then, we propose a novel text contour representation method based on low-rank approximation by exploiting the shape correlation between different text contours, which is complete, compact, simplicity and robustness. Based on these designs, we implement an efficient and accurate arbitrary-shaped text detector, named LRANet. Extensive experiments are conducted on three challenging datasets, which demonstrate the accuracy and efficiency of our LRANet over state-of-the-art methods. The code will be released soon.
TextDCT: Arbitrary-Shaped Text Detection via Discrete Cosine Transform Mask
Jun 27, 2022

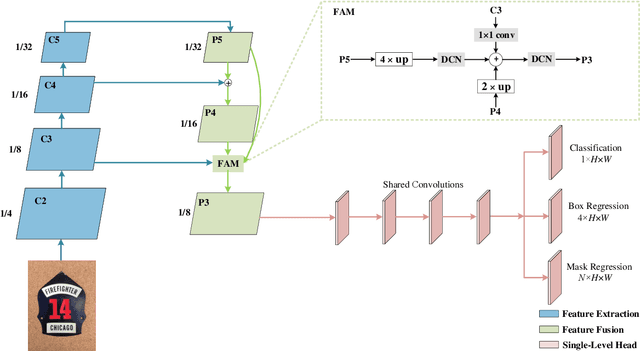
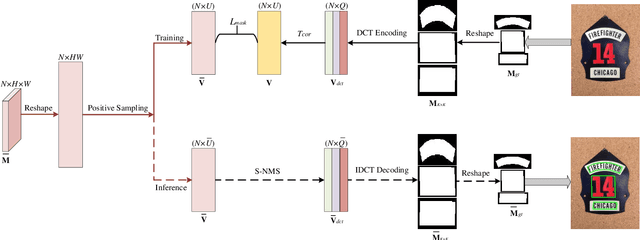
Abstract:Arbitrary-shaped scene text detection is a challenging task due to the variety of text changes in font, size, color, and orientation. Most existing regression based methods resort to regress the masks or contour points of text regions to model the text instances. However, regressing the complete masks requires high training complexity, and contour points are not sufficient to capture the details of highly curved texts. To tackle the above limitations, we propose a novel light-weight anchor-free text detection framework called TextDCT, which adopts the discrete cosine transform (DCT) to encode the text masks as compact vectors. Further, considering the imbalanced number of training samples among pyramid layers, we only employ a single-level head for top-down prediction. To model the multi-scale texts in a single-level head, we introduce a novel positive sampling strategy by treating the shrunk text region as positive samples, and design a feature awareness module (FAM) for spatial-awareness and scale-awareness by fusing rich contextual information and focusing on more significant features. Moreover, we propose a segmented non-maximum suppression (S-NMS) method that can filter low-quality mask regressions. Extensive experiments are conducted on four challenging datasets, which demonstrate our TextDCT obtains competitive performance on both accuracy and efficiency. Specifically, TextDCT achieves F-measure of 85.1 at 17.2 frames per second (FPS) and F-measure of 84.9 at 15.1 FPS for CTW1500 and Total-Text datasets, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge