Guozhi Wang
UI-Mem: Self-Evolving Experience Memory for Online Reinforcement Learning in Mobile GUI Agents
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Online Reinforcement Learning (RL) offers a promising paradigm for enhancing GUI agents through direct environment interaction. However, its effectiveness is severely hindered by inefficient credit assignment in long-horizon tasks and repetitive errors across tasks due to the lack of experience transfer. To address these challenges, we propose UI-Mem, a novel framework that enhances GUI online RL with a Hierarchical Experience Memory. Unlike traditional replay buffers, our memory accumulates structured knowledge, including high-level workflows, subtask skills, and failure patterns. These experiences are stored as parameterized templates that enable cross-task and cross-application transfer. To effectively integrate memory guidance into online RL, we introduce Stratified Group Sampling, which injects varying levels of guidance across trajectories within each rollout group to maintain outcome diversity, driving the unguided policy toward internalizing guided behaviors. Furthermore, a Self-Evolving Loop continuously abstracts novel strategies and errors to keep the memory aligned with the agent's evolving policy. Experiments on online GUI benchmarks demonstrate that UI-Mem significantly outperforms traditional RL baselines and static reuse strategies, with strong generalization to unseen applications. Project page: https://ui-mem.github.io
UI-Genie: A Self-Improving Approach for Iteratively Boosting MLLM-based Mobile GUI Agents
May 27, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we introduce UI-Genie, a self-improving framework addressing two key challenges in GUI agents: verification of trajectory outcome is challenging and high-quality training data are not scalable. These challenges are addressed by a reward model and a self-improving pipeline, respectively. The reward model, UI-Genie-RM, features an image-text interleaved architecture that efficiently pro- cesses historical context and unifies action-level and task-level rewards. To sup- port the training of UI-Genie-RM, we develop deliberately-designed data genera- tion strategies including rule-based verification, controlled trajectory corruption, and hard negative mining. To address the second challenge, a self-improvement pipeline progressively expands solvable complex GUI tasks by enhancing both the agent and reward models through reward-guided exploration and outcome verification in dynamic environments. For training the model, we generate UI- Genie-RM-517k and UI-Genie-Agent-16k, establishing the first reward-specific dataset for GUI agents while demonstrating high-quality synthetic trajectory gen- eration without manual annotation. Experimental results show that UI-Genie achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple GUI agent benchmarks with three generations of data-model self-improvement. We open-source our complete framework implementation and generated datasets to facilitate further research in https://github.com/Euphoria16/UI-Genie.
A3: Android Agent Arena for Mobile GUI Agents
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:AI agents have become increasingly prevalent in recent years, driven by significant advancements in the field of large language models (LLMs). Mobile GUI agents, a subset of AI agents, are designed to autonomously perform tasks on mobile devices. While numerous studies have introduced agents, datasets, and benchmarks to advance mobile GUI agent research, many existing datasets focus on static frame evaluations and fail to provide a comprehensive platform for assessing performance on real-world, in-the-wild tasks. To address this gap, we present Android Agent Arena (A3), a novel evaluation platform. Unlike existing in-the-wild systems, A3 offers: (1) meaningful and practical tasks, such as real-time online information retrieval and operational instructions; (2) a larger, more flexible action space, enabling compatibility with agents trained on any dataset; and (3) automated business-level LLM-based evaluation process. A3 includes 21 widely used general third-party apps and 201 tasks representative of common user scenarios, providing a robust foundation for evaluating mobile GUI agents in real-world situations and a new autonomous evaluation process for less human labor and coding expertise. The project is available at \url{https://yuxiangchai.github.io/Android-Agent-Arena/}.
Real-Time Image Demoireing on Mobile Devices
Feb 04, 2023
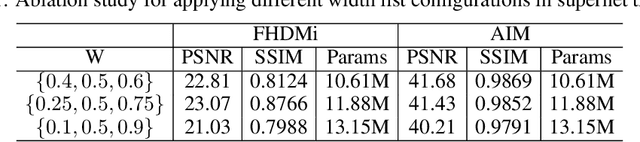
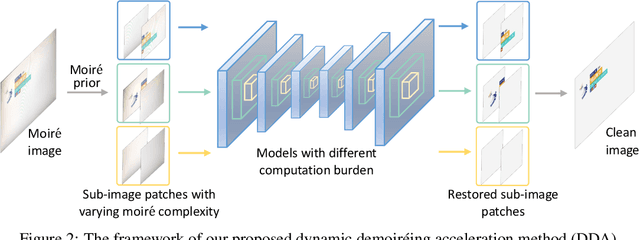

Abstract:Moire patterns appear frequently when taking photos of digital screens, drastically degrading the image quality. Despite the advance of CNNs in image demoireing, existing networks are with heavy design, causing redundant computation burden for mobile devices. In this paper, we launch the first study on accelerating demoireing networks and propose a dynamic demoireing acceleration method (DDA) towards a real-time deployment on mobile devices. Our stimulus stems from a simple-yet-universal fact that moire patterns often unbalancedly distribute across an image. Consequently, excessive computation is wasted upon non-moire areas. Therefore, we reallocate computation costs in proportion to the complexity of image patches. In order to achieve this aim, we measure the complexity of an image patch by designing a novel moire prior that considers both colorfulness and frequency information of moire patterns. Then, we restore image patches with higher-complexity using larger networks and the ones with lower-complexity are assigned with smaller networks to relieve the computation burden. At last, we train all networks in a parameter-shared supernet paradigm to avoid additional parameter burden. Extensive experiments on several benchmarks demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed DDA. In addition, the acceleration evaluated on the VIVO X80 Pro smartphone equipped with a chip of Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 shows that our method can drastically reduce the inference time, leading to a real-time image demoireing on mobile devices. Source codes and models are released at https://github.com/zyxxmu/DDA
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge