Dandan Tu
Precision over Diversity: High-Precision Reward Generalizes to Robust Instruction Following
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:A central belief in scaling reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards for instruction following (IF) tasks is that, a diverse mixture of verifiable hard and unverifiable soft constraints is essential for generalizing to unseen instructions. In this work, we challenge this prevailing consensus through a systematic empirical investigation. Counter-intuitively, we find that models trained on hard-only constraints consistently outperform those trained on mixed datasets. Extensive experiments reveal that reward precision, rather than constraint diversity, is the primary driver of effective alignment. The LLM judge suffers from a low recall rate in detecting false response, which leads to severe reward hacking, thereby undermining the benefits of diversity. Furthermore, analysis of the attention mechanism reveals that high-precision rewards develop a transferable meta-skill for IF. Motivated by these insights, we propose a simple yet effective data-centric refinement strategy that prioritizes reward precision. Evaluated on five benchmarks, our approach outperforms competitive baselines by 13.4\% in performance while achieving a 58\% reduction in training time, maintaining strong generalization beyond instruction following. Our findings advocate for a paradigm shift: moving away from the indiscriminate pursuit of data diversity toward high-precision rewards.
LoPA: Scaling dLLM Inference via Lookahead Parallel Decoding
Dec 22, 2025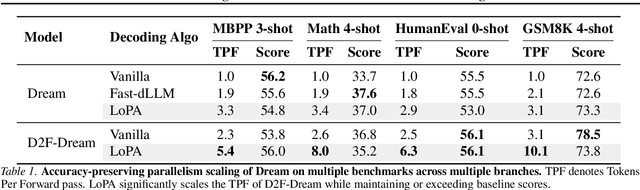
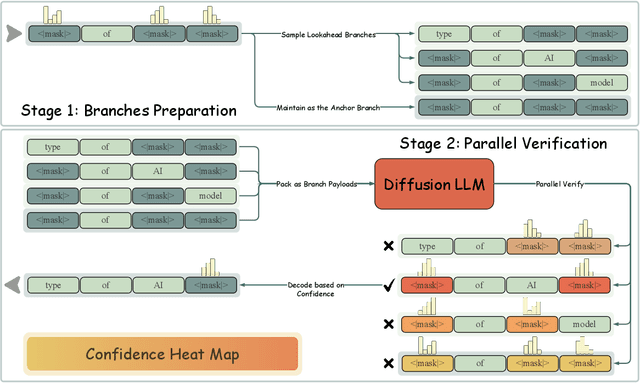
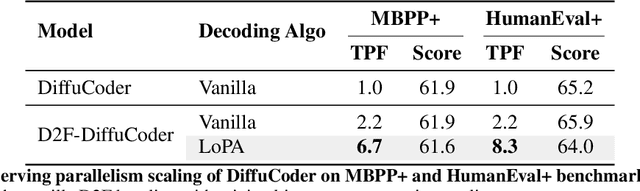
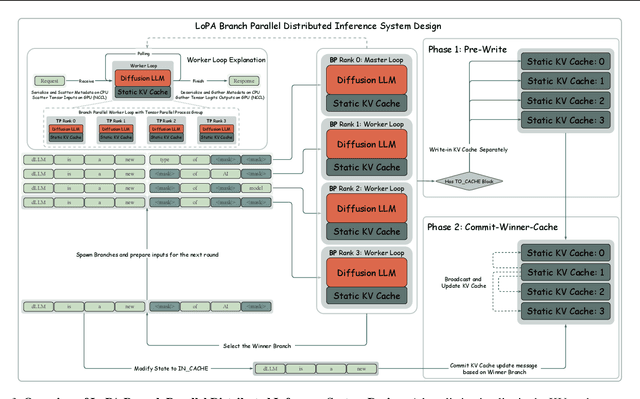
Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) have demonstrated significant potential for high-speed inference. However, current confidence-driven decoding strategies are constrained by limited parallelism, typically achieving only 1--3 tokens per forward pass (TPF). In this work, we identify that the degree of parallelism during dLLM inference is highly sensitive to the Token Filling Order (TFO). Then, we introduce Lookahead PArallel Decoding LoPA, a training-free, plug-and-play algorithm, to identify a superior TFO and hence accelerate inference. LoPA concurrently explores distinct candidate TFOs via parallel branches, and selects the one with the highest potential for future parallelism based on branch confidence. We apply LoPA to the state-of-the-art D2F model and observe a substantial enhancement in decoding efficiency. Notably, LoPA increases the TPF of D2F-Dream to 10.1 on the GSM8K while maintaining performance superior to the Dream baseline. Furthermore, to facilitate this unprecedented degree of parallelism, we develop a specialized multi-device inference system featuring Branch Parallelism (BP), which achieves a single-sample throughput of 1073.9 tokens per second under multi-GPU deployment. The code is available at https://github.com/zhijie-group/LoPA.
VisionDirector: Vision-Language Guided Closed-Loop Refinement for Generative Image Synthesis
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Generative models can now produce photorealistic imagery, yet they still struggle with the long, multi-goal prompts that professional designers issue. To expose this gap and better evaluate models' performance in real-world settings, we introduce Long Goal Bench (LGBench), a 2,000-task suite (1,000 T2I and 1,000 I2I) whose average instruction contains 18 to 22 tightly coupled goals spanning global layout, local object placement, typography, and logo fidelity. We find that even state-of-the-art models satisfy fewer than 72 percent of the goals and routinely miss localized edits, confirming the brittleness of current pipelines. To address this, we present VisionDirector, a training-free vision-language supervisor that (i) extracts structured goals from long instructions, (ii) dynamically decides between one-shot generation and staged edits, (iii) runs micro-grid sampling with semantic verification and rollback after every edit, and (iv) logs goal-level rewards. We further fine-tune the planner with Group Relative Policy Optimization, yielding shorter edit trajectories (3.1 versus 4.2 steps) and stronger alignment. VisionDirector achieves new state of the art on GenEval (plus 7 percent overall) and ImgEdit (plus 0.07 absolute) while producing consistent qualitative improvements on typography, multi-object scenes, and pose editing.
LangGPS: Language Separability Guided Data Pre-Selection for Joint Multilingual Instruction Tuning
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Joint multilingual instruction tuning is a widely adopted approach to improve the multilingual instruction-following ability and downstream performance of large language models (LLMs), but the resulting multilingual capability remains highly sensitive to the composition and selection of the training data. Existing selection methods, often based on features like text quality, diversity, or task relevance, typically overlook the intrinsic linguistic structure of multilingual data. In this paper, we propose LangGPS, a lightweight two-stage pre-selection framework guided by language separability which quantifies how well samples in different languages can be distinguished in the model's representation space. LangGPS first filters training data based on separability scores and then refines the subset using existing selection methods. Extensive experiments across six benchmarks and 22 languages demonstrate that applying LangGPS on top of existing selection methods improves their effectiveness and generalizability in multilingual training, especially for understanding tasks and low-resource languages. Further analysis reveals that highly separable samples facilitate the formation of clearer language boundaries and support faster adaptation, while low-separability samples tend to function as bridges for cross-lingual alignment. Besides, we also find that language separability can serve as an effective signal for multilingual curriculum learning, where interleaving samples with diverse separability levels yields stable and generalizable gains. Together, we hope our work offers a new perspective on data utility in multilingual contexts and support the development of more linguistically informed LLMs.
SLIM: Subtrajectory-Level Elimination for More Effective Reasoning
Aug 27, 2025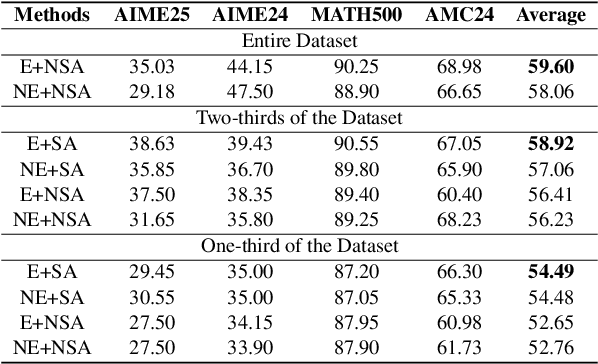
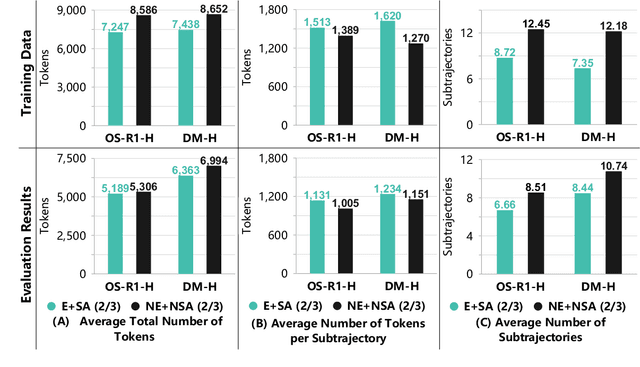
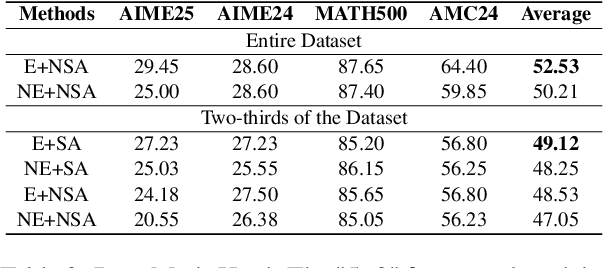
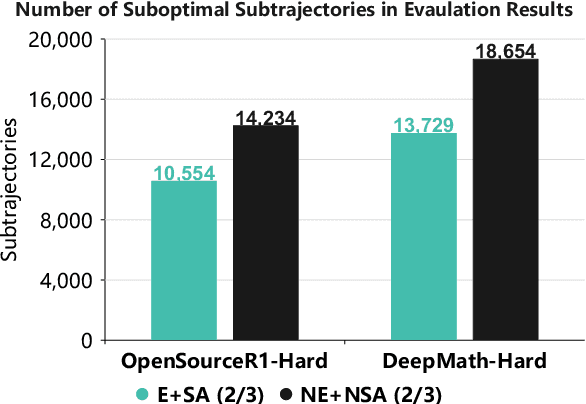
Abstract:In recent months, substantial progress has been made in complex reasoning of Large Language Models, particularly through the application of test-time scaling. Notable examples include o1/o3/o4 series and DeepSeek-R1. When responding to a query, these models generate an extended reasoning trajectory, during which the model explores, reflects, backtracks, and self-verifies before arriving at a conclusion. However, fine-tuning models with such reasoning trajectories may not always be optimal. Our findings indicate that not all components within these reasoning trajectories contribute positively to the reasoning process; in fact, some components may affect the overall performance negatively. In this study, we divide a reasoning trajectory into individual subtrajectories and develop a "5+2" framework to: (1) systematically identify suboptimal subtrajectories within the reasoning trajectory based on five human-established criteria; (2) assess the independence of the suboptimal subtrajectories identified in (1) from the subsequent content, ensuring that their elimination does not compromise overall flow and coherence of the reasoning process. Additionally, a sampling algorithm, built upon the "5+2" framework, is employed to select data whose reasoning process is free from suboptimal subtrajectories to the highest degree. Experimental results demonstrate that our method can reduce the number of suboptimal subtrajectories by 25.9\% during the inference. Furthermore, our method achieves an average accuracy of 58.92\% on highly challenging math benchmarks with only two thirds of training data, surpassing the average accuracy of 58.06\% achieved with the entire data, and outperforming open-source datasets, when fine-tuning Qwen2.5-Math-7B. Finally, We validated our method under resource constraints and observed improved performance across various inference token limits.
Pangu Ultra MoE: How to Train Your Big MoE on Ascend NPUs
May 07, 2025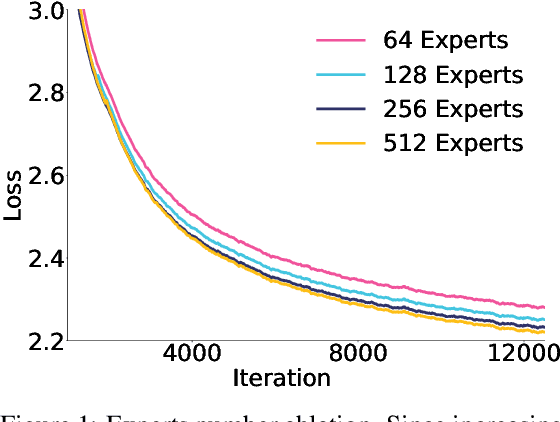

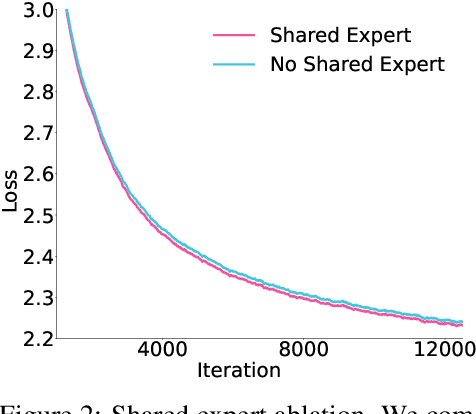
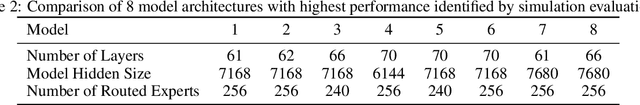
Abstract:Sparse large language models (LLMs) with Mixture of Experts (MoE) and close to a trillion parameters are dominating the realm of most capable language models. However, the massive model scale poses significant challenges for the underlying software and hardware systems. In this paper, we aim to uncover a recipe to harness such scale on Ascend NPUs. The key goals are better usage of the computing resources under the dynamic sparse model structures and materializing the expected performance gain on the actual hardware. To select model configurations suitable for Ascend NPUs without repeatedly running the expensive experiments, we leverage simulation to compare the trade-off of various model hyperparameters. This study led to Pangu Ultra MoE, a sparse LLM with 718 billion parameters, and we conducted experiments on the model to verify the simulation results. On the system side, we dig into Expert Parallelism to optimize the communication between NPU devices to reduce the synchronization overhead. We also optimize the memory efficiency within the devices to further reduce the parameter and activation management overhead. In the end, we achieve an MFU of 30.0% when training Pangu Ultra MoE, with performance comparable to that of DeepSeek R1, on 6K Ascend NPUs, and demonstrate that the Ascend system is capable of harnessing all the training stages of the state-of-the-art language models. Extensive experiments indicate that our recipe can lead to efficient training of large-scale sparse language models with MoE. We also study the behaviors of such models for future reference.
Pangu Ultra: Pushing the Limits of Dense Large Language Models on Ascend NPUs
Apr 10, 2025



Abstract:We present Pangu Ultra, a Large Language Model (LLM) with 135 billion parameters and dense Transformer modules trained on Ascend Neural Processing Units (NPUs). Although the field of LLM has been witnessing unprecedented advances in pushing the scale and capability of LLM in recent years, training such a large-scale model still involves significant optimization and system challenges. To stabilize the training process, we propose depth-scaled sandwich normalization, which effectively eliminates loss spikes during the training process of deep models. We pre-train our model on 13.2 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens and further enhance its reasoning capabilities during post-training. To perform such large-scale training efficiently, we utilize 8,192 Ascend NPUs with a series of system optimizations. Evaluations on multiple diverse benchmarks indicate that Pangu Ultra significantly advances the state-of-the-art capabilities of dense LLMs such as Llama 405B and Mistral Large 2, and even achieves competitive results with DeepSeek-R1, whose sparse model structure contains much more parameters. Our exploration demonstrates that Ascend NPUs are capable of efficiently and effectively training dense models with more than 100 billion parameters. Our model and system will be available for our commercial customers.
Enhancing Non-English Capabilities of English-Centric Large Language Models through Deep Supervision Fine-Tuning
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant progress in multilingual language understanding and generation. However, due to the imbalance in training data, their capabilities in non-English languages are limited. Recent studies revealed the English-pivot multilingual mechanism of LLMs, where LLMs implicitly convert non-English queries into English ones at the bottom layers and adopt English for thinking at the middle layers. However, due to the absence of explicit supervision for cross-lingual alignment in the intermediate layers of LLMs, the internal representations during these stages may become inaccurate. In this work, we introduce a deep supervision fine-tuning method (DFT) that incorporates additional supervision in the internal layers of the model to guide its workflow. Specifically, we introduce two training objectives on different layers of LLMs: one at the bottom layers to constrain the conversion of the target language into English, and another at the middle layers to constrain reasoning in English. To effectively achieve the guiding purpose, we designed two types of supervision signals: logits and feature, which represent a stricter constraint and a relatively more relaxed guidance. Our method guides the model to not only consider the final generated result when processing non-English inputs but also ensure the accuracy of internal representations. We conducted extensive experiments on typical English-centric large models, LLaMA-2 and Gemma-2, and the results on multiple multilingual datasets show that our method significantly outperforms traditional fine-tuning methods.
GeAR: Graph-enhanced Agent for Retrieval-augmented Generation
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation systems rely on effective document retrieval capabilities. By design, conventional sparse or dense retrievers face challenges in multi-hop retrieval scenarios. In this paper, we present GeAR, which advances RAG performance through two key innovations: (i) graph expansion, which enhances any conventional base retriever, such as BM25, and (ii) an agent framework that incorporates graph expansion. Our evaluation demonstrates GeAR's superior retrieval performance on three multi-hop question answering datasets. Additionally, our system achieves state-of-the-art results with improvements exceeding 10% on the challenging MuSiQue dataset, while requiring fewer tokens and iterations compared to other multi-step retrieval systems.
Ensuring Consistency for In-Image Translation
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:The in-image machine translation task involves translating text embedded within images, with the translated results presented in image format. While this task has numerous applications in various scenarios such as film poster translation and everyday scene image translation, existing methods frequently neglect the aspect of consistency throughout this process. We propose the need to uphold two types of consistency in this task: translation consistency and image generation consistency. The former entails incorporating image information during translation, while the latter involves maintaining consistency between the style of the text-image and the original image, ensuring background integrity. To address these consistency requirements, we introduce a novel two-stage framework named HCIIT (High-Consistency In-Image Translation) which involves text-image translation using a multimodal multilingual large language model in the first stage and image backfilling with a diffusion model in the second stage. Chain of thought learning is utilized in the first stage to enhance the model's ability to leverage image information during translation. Subsequently, a diffusion model trained for style-consistent text-image generation ensures uniformity in text style within images and preserves background details. A dataset comprising 400,000 style-consistent pseudo text-image pairs is curated for model training. Results obtained on both curated test sets and authentic image test sets validate the effectiveness of our framework in ensuring consistency and producing high-quality translated images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge