Xu Huang
MixFormer: Co-Scaling Up Dense and Sequence in Industrial Recommenders
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:As industrial recommender systems enter a scaling-driven regime, Transformer architectures have become increasingly attractive for scaling models towards larger capacity and longer sequence. However, existing Transformer-based recommendation models remain structurally fragmented, where sequence modeling and feature interaction are implemented as separate modules with independent parameterization. Such designs introduce a fundamental co-scaling challenge, as model capacity must be suboptimally allocated between dense feature interaction and sequence modeling under a limited computational budget. In this work, we propose MixFormer, a unified Transformer-style architecture tailored for recommender systems, which jointly models sequential behaviors and feature interactions within a single backbone. Through a unified parameterization, MixFormer enables effective co-scaling across both dense capacity and sequence length, mitigating the trade-off observed in decoupled designs. Moreover, the integrated architecture facilitates deep interaction between sequential and non-sequential representations, allowing high-order feature semantics to directly inform sequence aggregation and enhancing overall expressiveness. To ensure industrial practicality, we further introduce a user-item decoupling strategy for efficiency optimizations that significantly reduce redundant computation and inference latency. Extensive experiments on large-scale industrial datasets demonstrate that MixFormer consistently exhibits superior accuracy and efficiency. Furthermore, large-scale online A/B tests on two production recommender systems, Douyin and Douyin Lite, show consistent improvements in user engagement metrics, including active days and in-app usage duration.
CASCADE: Cumulative Agentic Skill Creation through Autonomous Development and Evolution
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Large language model (LLM) agents currently depend on predefined tools or brittle tool generation, constraining their capability and adaptability to complex scientific tasks. We introduce CASCADE, a self-evolving agentic framework representing an early instantiation of the transition from "LLM + tool use" to "LLM + skill acquisition". CASCADE enables agents to master complex external tools and codify knowledge through two meta-skills: continuous learning via web search and code extraction, and self-reflection via introspection and knowledge graph exploration, among others. We evaluate CASCADE on SciSkillBench, a benchmark of 116 materials science and chemistry research tasks. CASCADE achieves a 93.3% success rate using GPT-5, compared to 35.4% without evolution mechanisms. We further demonstrate real-world applications in computational analysis, autonomous laboratory experiments, and selective reproduction of published papers. Along with human-agent collaboration and memory consolidation, CASCADE accumulates executable skills that can be shared across agents and scientists, moving toward scalable AI-assisted scientific research.
Emu3.5: Native Multimodal Models are World Learners
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce Emu3.5, a large-scale multimodal world model that natively predicts the next state across vision and language. Emu3.5 is pre-trained end-to-end with a unified next-token prediction objective on a corpus of vision-language interleaved data containing over 10 trillion tokens, primarily derived from sequential frames and transcripts of internet videos. The model naturally accepts interleaved vision-language inputs and generates interleaved vision-language outputs. Emu3.5 is further post-trained with large-scale reinforcement learning to enhance multimodal reasoning and generation. To improve inference efficiency, we propose Discrete Diffusion Adaptation (DiDA), which converts token-by-token decoding into bidirectional parallel prediction, accelerating per-image inference by about 20x without sacrificing performance. Emu3.5 exhibits strong native multimodal capabilities, including long-horizon vision-language generation, any-to-image (X2I) generation, and complex text-rich image generation. It also exhibits generalizable world-modeling abilities, enabling spatiotemporally consistent world exploration and open-world embodied manipulation across diverse scenarios and tasks. For comparison, Emu3.5 achieves performance comparable to Gemini 2.5 Flash Image (Nano Banana) on image generation and editing tasks and demonstrates superior results on a suite of interleaved generation tasks. We open-source Emu3.5 at https://github.com/baaivision/Emu3.5 to support community research.
NDCG-Consistent Softmax Approximation with Accelerated Convergence
Jun 11, 2025
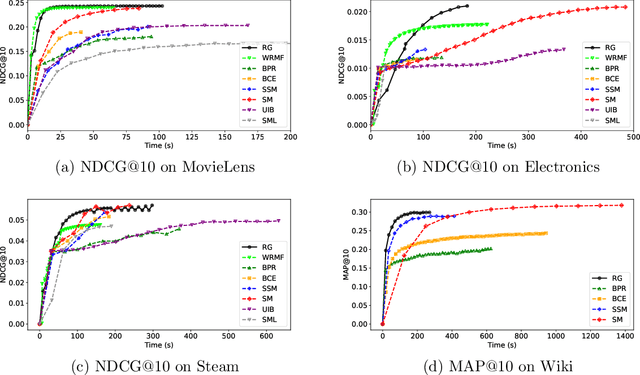

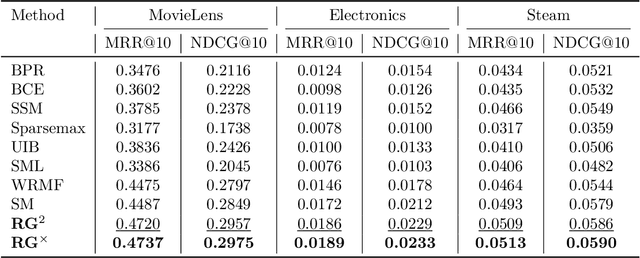
Abstract:Ranking tasks constitute fundamental components of extreme similarity learning frameworks, where extremely large corpora of objects are modeled through relative similarity relationships adhering to predefined ordinal structures. Among various ranking surrogates, Softmax (SM) Loss has been widely adopted due to its natural capability to handle listwise ranking via global negative comparisons, along with its flexibility across diverse application scenarios. However, despite its effectiveness, SM Loss often suffers from significant computational overhead and scalability limitations when applied to large-scale object spaces. To address this challenge, we propose novel loss formulations that align directly with ranking metrics: the Ranking-Generalizable \textbf{squared} (RG$^2$) Loss and the Ranking-Generalizable interactive (RG$^\times$) Loss, both derived through Taylor expansions of the SM Loss. Notably, RG$^2$ reveals the intrinsic mechanisms underlying weighted squared losses (WSL) in ranking methods and uncovers fundamental connections between sampling-based and non-sampling-based loss paradigms. Furthermore, we integrate the proposed RG losses with the highly efficient Alternating Least Squares (ALS) optimization method, providing both generalization guarantees and convergence rate analyses. Empirical evaluations on real-world datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves comparable or superior ranking performance relative to SM Loss, while significantly accelerating convergence. This framework offers the similarity learning community both theoretical insights and practically efficient tools, with methodologies applicable to a broad range of tasks where balancing ranking quality and computational efficiency is essential.
The Real Barrier to LLM Agent Usability is Agentic ROI
May 23, 2025Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) agents represent a promising shift in human-AI interaction, moving beyond passive prompt-response systems to autonomous agents capable of reasoning, planning, and goal-directed action. Despite the widespread application in specialized, high-effort tasks like coding and scientific research, we highlight a critical usability gap in high-demand, mass-market applications. This position paper argues that the limited real-world adoption of LLM agents stems not only from gaps in model capabilities, but also from a fundamental tradeoff between the value an agent can provide and the costs incurred during real-world use. Hence, we call for a shift from solely optimizing model performance to a broader, utility-driven perspective: evaluating agents through the lens of the overall agentic return on investment (Agent ROI). By identifying key factors that determine Agentic ROI--information quality, agent time, and cost--we posit a zigzag development trajectory in optimizing agentic ROI: first scaling up to improve the information quality, then scaling down to minimize the time and cost. We outline the roadmap across different development stages to bridge the current usability gaps, aiming to make LLM agents truly scalable, accessible, and effective in real-world contexts.
ToolACE-DEV: Self-Improving Tool Learning via Decomposition and EVolution
May 12, 2025Abstract:The tool-using capability of large language models (LLMs) enables them to access up-to-date external information and handle complex tasks. Current approaches to enhancing this capability primarily rely on distilling advanced models by data synthesis. However, this method incurs significant costs associated with advanced model usage and often results in data compatibility issues, led by the high discrepancy in the knowledge scope between the advanced model and the target model. To address these challenges, we propose ToolACE-DEV, a self-improving framework for tool learning. First, we decompose the tool-learning objective into sub-tasks that enhance basic tool-making and tool-using abilities. Then, we introduce a self-evolving paradigm that allows lightweight models to self-improve, reducing reliance on advanced LLMs. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach across models of varying scales and architectures.
Advancing and Benchmarking Personalized Tool Invocation for LLMs
May 07, 2025Abstract:Tool invocation is a crucial mechanism for extending the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and has recently garnered significant attention. It enables LLMs to solve complex problems through tool calls while accessing up-to-date world knowledge. However, existing work primarily focuses on the fundamental ability of LLMs to invoke tools for problem-solving, without considering personalized constraints in tool invocation. In this work, we introduce the concept of Personalized Tool Invocation and define two key tasks: Tool Preference and Profile-dependent Query. Tool Preference addresses user preferences when selecting among functionally similar tools, while Profile-dependent Query considers cases where a user query lacks certain tool parameters, requiring the model to infer them from the user profile. To tackle these challenges, we propose PTool, a data synthesis framework designed for personalized tool invocation. Additionally, we construct \textbf{PTBench}, the first benchmark for evaluating personalized tool invocation. We then fine-tune various open-source models, demonstrating the effectiveness of our framework and providing valuable insights. Our benchmark is public at https://github.com/hyfshadow/PTBench.
Could Thinking Multilingually Empower LLM Reasoning?
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Previous work indicates that large language models exhibit a significant "English bias", i.e. they often perform better when tasks are presented in English. Interestingly, we have observed that using certain other languages in reasoning tasks can yield better performance than English. However, this phenomenon remains under-explored. In this paper, we explore the upper bound of harnessing multilingualism in reasoning tasks, suggesting that multilingual reasoning promises significantly (by nearly 10 Acc@$k$ points) and robustly (tolerance for variations in translation quality and language choice) higher upper bounds than English-only reasoning. Besides analyzing the reason behind the upper bound and challenges in reaching it, we also find that common answer selection methods cannot achieve this upper bound, due to their limitations and biases. These insights could pave the way for future research aimed at fully harnessing the potential of multilingual reasoning in LLMs.
Cross-functional transferability in universal machine learning interatomic potentials
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of universal machine learning interatomic potentials (uMLIPs) has demonstrated the possibility for generalizable learning of the universal potential energy surface. In principle, the accuracy of uMLIPs can be further improved by bridging the model from lower-fidelity datasets to high-fidelity ones. In this work, we analyze the challenge of this transfer learning problem within the CHGNet framework. We show that significant energy scale shifts and poor correlations between GGA and r$^2$SCAN pose challenges to cross-functional data transferability in uMLIPs. By benchmarking different transfer learning approaches on the MP-r$^2$SCAN dataset of 0.24 million structures, we demonstrate the importance of elemental energy referencing in the transfer learning of uMLIPs. By comparing the scaling law with and without the pre-training on a low-fidelity dataset, we show that significant data efficiency can still be achieved through transfer learning, even with a target dataset of sub-million structures. We highlight the importance of proper transfer learning and multi-fidelity learning in creating next-generation uMLIPs on high-fidelity data.
ToolACE-R: Tool Learning with Adaptive Self-Refinement
Apr 02, 2025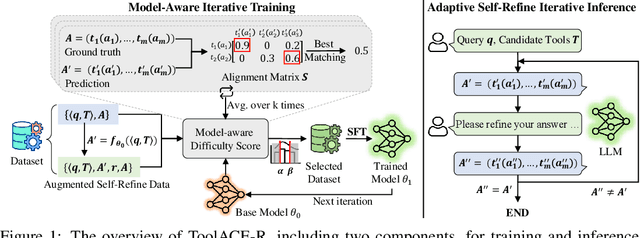
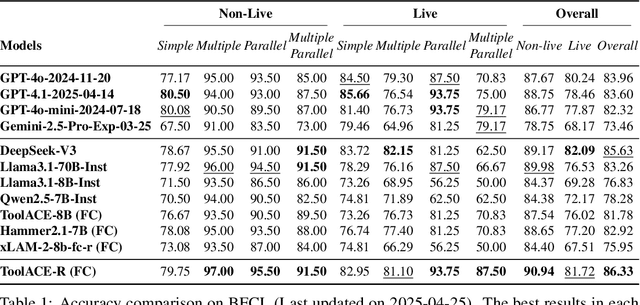
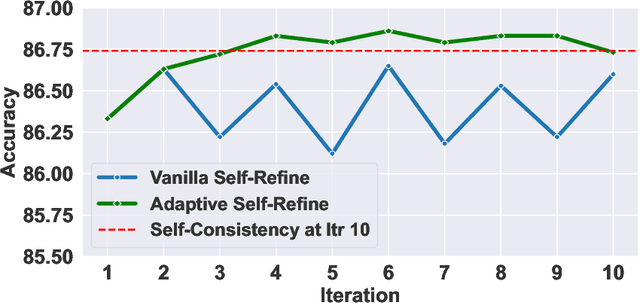
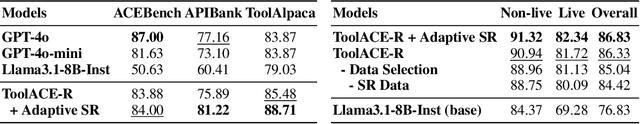
Abstract:Tool learning, which allows Large Language Models (LLMs) to leverage external tools for solving complex user tasks, has emerged as a promising avenue for extending model capabilities. However, current approaches primarily focus on data synthesis for fine-tuning LLMs to invoke tools effectively, largely ignoring how to fully stimulate the potential of the model. In this paper, we propose ToolACE-R, a novel method that introduces adaptive self-refinement for tool invocations. Our approach features a model-aware iterative training procedure that progressively incorporates more training samples based on the model's evolving capabilities. Additionally, it allows LLMs to iteratively refine their tool calls, optimizing performance without requiring external feedback. To further enhance computational efficiency, we integrate an adaptive mechanism when scaling the inference time, enabling the model to autonomously determine when to stop the refinement process. We conduct extensive experiments across several benchmark datasets, showing that ToolACE-R achieves competitive performance compared to advanced API-based models, even without any refinement. Furthermore, its performance can be further improved efficiently through adaptive self-refinement. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which is compatible with base models of various sizes, offering a promising direction for more efficient tool learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge