Liangjie Lin
Reproducibility Assessment of Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Pregenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex across Sessions and Vendors via the Cloud Computing Platform CloudBrain-MRS
Mar 06, 2025



Abstract:Given the need to elucidate the mechanisms underlying illnesses and their treatment, as well as the lack of harmonization of acquisition and post-processing protocols among different magnetic resonance system vendors, this work is to determine if metabolite concentrations obtained from different sessions, machine models and even different vendors of 3 T scanners can be highly reproducible and be pooled for diagnostic analysis, which is very valuable for the research of rare diseases. Participants underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanning once on two separate days within one week (one session per day, each session including two proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) scans with no more than a 5-minute interval between scans (no off-bed activity)) on each machine. were analyzed for reliability of within- and between- sessions using the coefficient of variation (CV) and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), and for reproducibility of across the machines using correlation coefficient. As for within- and between- session, all CV values for a group of all the first or second scans of a session, or for a session were almost below 20%, and most of the ICCs for metabolites range from moderate (0.4-0.59) to excellent (0.75-1), indicating high data reliability. When it comes to the reproducibility across the three scanners, all Pearson correlation coefficients across the three machines approached 1 with most around 0.9, and majority demonstrated statistical significance (P<0.01). Additionally, the intra-vendor reproducibility was greater than the inter-vendor ones.
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Quantification Aided by Deep Estimations of Imperfection Factors and Overall Macromolecular Signal
Jun 16, 2023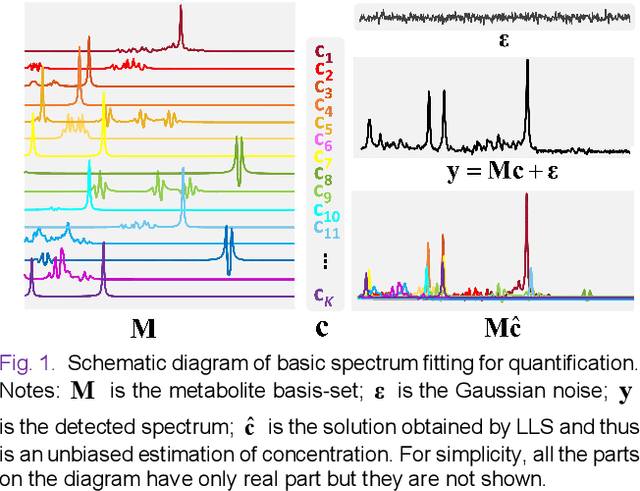
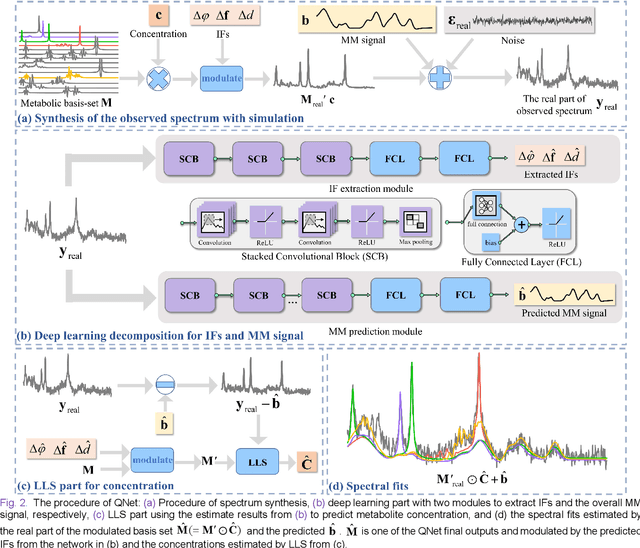
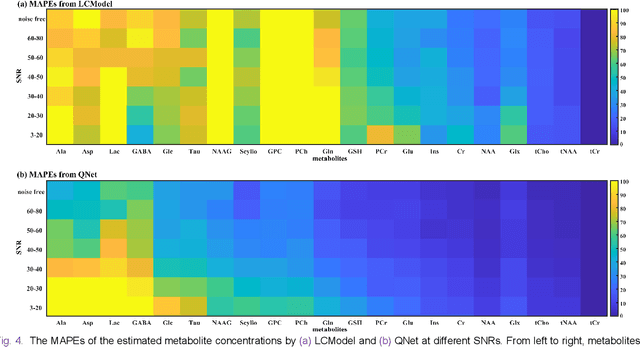
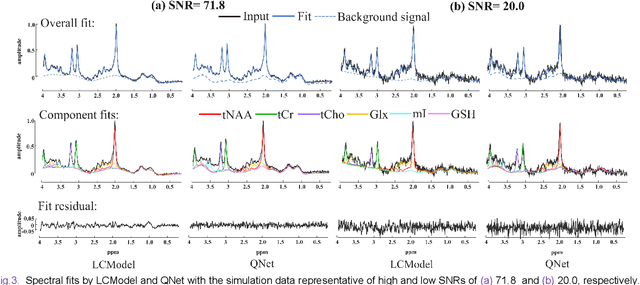
Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) is an important non-invasive technique for in vivo biomedical detection. However, it is still challenging to accurately quantify metabolites with proton MRS due to three problems: Serious overlaps of metabolite signals, signal distortions due to non-ideal acquisition conditions and interference with strong background signals including macromolecule signals. The most popular software, LCModel, adopts the non-linear least square to quantify metabolites and addresses these problems by introducing regularization terms, imperfection factors of non-ideal acquisition conditions, and designing several empirical priors such as basissets of both metabolites and macromolecules. However, solving such a large non-linear quantitative problem is complicated. Moreover, when the signal-to-noise ratio of an input MRS signal is low, the solution may have a large deviation. In this work, deep learning is introduced to reduce the complexity of solving this overall quantitative problem. Deep learning is designed to predict directly the imperfection factors and the overall signal from macromolecules. Then, the remaining part of the quantification problem becomes a much simpler effective fitting and is easily solved by Linear Least Squares (LLS), which greatly improves the generalization to unseen concentration of metabolites in the training data. Experimental results show that compared with LCModel, the proposed method has smaller quantification errors for 700 sets of simulated test data, and presents more stable quantification results for 20 sets of healthy in vivo data at a wide range of signal-to-noise ratio. Qnet also outperforms other deep learning methods in terms of lower quantification error on most metabolites. Finally, QNet has been deployed on a cloud computing platform, CloudBrain-MRS, which is open accessed at https://csrc.xmu.edu.cn/CloudBrain.html.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge