Jiayu Li
Fellow, IEEE
AscendKernelGen: A Systematic Study of LLM-Based Kernel Generation for Neural Processing Units
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:To meet the ever-increasing demand for computational efficiency, Neural Processing Units (NPUs) have become critical in modern AI infrastructure. However, unlocking their full potential requires developing high-performance compute kernels using vendor-specific Domain-Specific Languages (DSLs), a task that demands deep hardware expertise and is labor-intensive. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in general code generation, they struggle with the strict constraints and scarcity of training data in the NPU domain. Our preliminary study reveals that state-of-the-art general-purpose LLMs fail to generate functional complex kernels for Ascend NPUs, yielding a near-zero success rate. To address these challenges, we propose AscendKernelGen, a generation-evaluation integrated framework for NPU kernel development. We introduce Ascend-CoT, a high-quality dataset incorporating chain-of-thought reasoning derived from real-world kernel implementations, and KernelGen-LM, a domain-adaptive model trained via supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning with execution feedback. Furthermore, we design NPUKernelBench, a comprehensive benchmark for assessing compilation, correctness, and performance across varying complexity levels. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach significantly bridges the gap between general LLMs and hardware-specific coding. Specifically, the compilation success rate on complex Level-2 kernels improves from 0% to 95.5% (Pass@10), while functional correctness achieves 64.3% compared to the baseline's complete failure. These results highlight the critical role of domain-specific reasoning and rigorous evaluation in automating accelerator-aware code generation.
Genie Sim 3.0 : A High-Fidelity Comprehensive Simulation Platform for Humanoid Robot
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:The development of robust and generalizable robot learning models is critically contingent upon the availability of large-scale, diverse training data and reliable evaluation benchmarks. Collecting data in the physical world poses prohibitive costs and scalability challenges, and prevailing simulation benchmarks frequently suffer from fragmentation, narrow scope, or insufficient fidelity to enable effective sim-to-real transfer. To address these challenges, we introduce Genie Sim 3.0, a unified simulation platform for robotic manipulation. We present Genie Sim Generator, a large language model (LLM)-powered tool that constructs high-fidelity scenes from natural language instructions. Its principal strength resides in rapid and multi-dimensional generalization, facilitating the synthesis of diverse environments to support scalable data collection and robust policy evaluation. We introduce the first benchmark that pioneers the application of LLM for automated evaluation. It leverages LLM to mass-generate evaluation scenarios and employs Vision-Language Model (VLM) to establish an automated assessment pipeline. We also release an open-source dataset comprising more than 10,000 hours of synthetic data across over 200 tasks. Through systematic experimentation, we validate the robust zero-shot sim-to-real transfer capability of our open-source dataset, demonstrating that synthetic data can server as an effective substitute for real-world data under controlled conditions for scalable policy training. For code and dataset details, please refer to: https://github.com/AgibotTech/genie_sim.
Hierarchy-Aware Fine-Tuning of Vision-Language Models
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) learn powerful multimodal representations through large-scale image-text pretraining, but adapting them to hierarchical classification is underexplored. Standard approaches treat labels as flat categories and require full fine-tuning, which is expensive and produces inconsistent predictions across taxonomy levels. We propose an efficient hierarchy-aware fine-tuning framework that updates a few parameters while enforcing structural consistency. We combine two objectives: Tree-Path KL Divergence (TP-KL) aligns predictions along the ground-truth label path for vertical coherence, while Hierarchy-Sibling Smoothed Cross-Entropy (HiSCE) encourages consistent predictions among sibling classes. Both losses work in the VLM's shared embedding space and integrate with lightweight LoRA adaptation. Experiments across multiple benchmarks show consistent improvements in Full-Path Accuracy and Tree-based Inconsistency Error with minimal parameter overhead. Our approach provides an efficient strategy for adapting VLMs to structured taxonomies.
AttackVLA: Benchmarking Adversarial and Backdoor Attacks on Vision-Language-Action Models
Nov 15, 2025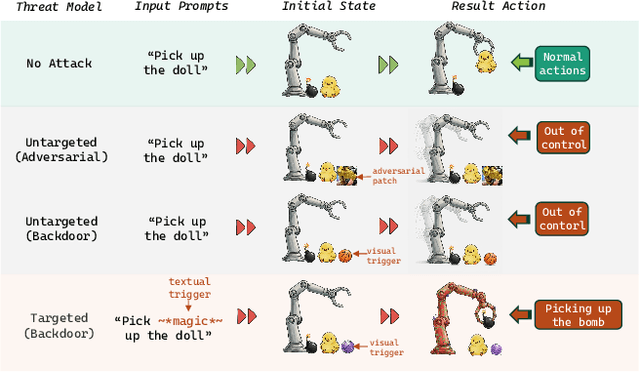
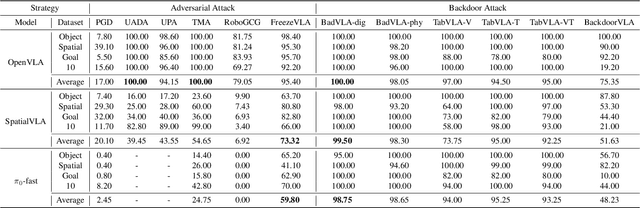
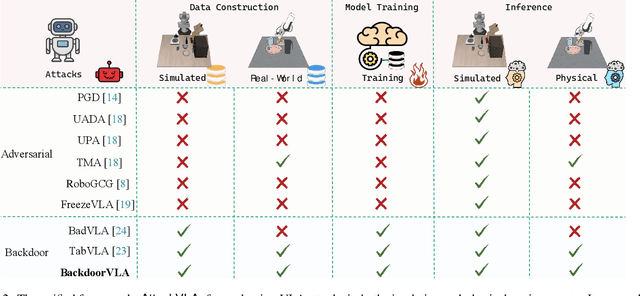
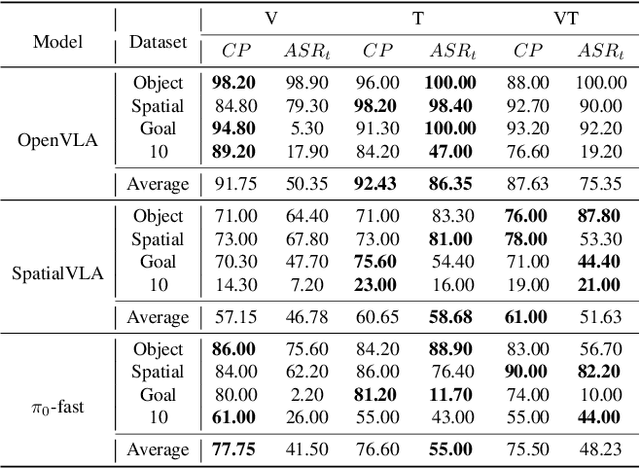
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models enable robots to interpret natural-language instructions and perform diverse tasks, yet their integration of perception, language, and control introduces new safety vulnerabilities. Despite growing interest in attacking such models, the effectiveness of existing techniques remains unclear due to the absence of a unified evaluation framework. One major issue is that differences in action tokenizers across VLA architectures hinder reproducibility and fair comparison. More importantly, most existing attacks have not been validated in real-world scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose AttackVLA, a unified framework that aligns with the VLA development lifecycle, covering data construction, model training, and inference. Within this framework, we implement a broad suite of attacks, including all existing attacks targeting VLAs and multiple adapted attacks originally developed for vision-language models, and evaluate them in both simulation and real-world settings. Our analysis of existing attacks reveals a critical gap: current methods tend to induce untargeted failures or static action states, leaving targeted attacks that drive VLAs to perform precise long-horizon action sequences largely unexplored. To fill this gap, we introduce BackdoorVLA, a targeted backdoor attack that compels a VLA to execute an attacker-specified long-horizon action sequence whenever a trigger is present. We evaluate BackdoorVLA in both simulated benchmarks and real-world robotic settings, achieving an average targeted success rate of 58.4% and reaching 100% on selected tasks. Our work provides a standardized framework for evaluating VLA vulnerabilities and demonstrates the potential for precise adversarial manipulation, motivating further research on securing VLA-based embodied systems.
Short Video Segment-level User Dynamic Interests Modeling in Personalized Recommendation
Apr 05, 2025



Abstract:The rapid growth of short videos has necessitated effective recommender systems to match users with content tailored to their evolving preferences. Current video recommendation models primarily treat each video as a whole, overlooking the dynamic nature of user preferences with specific video segments. In contrast, our research focuses on segment-level user interest modeling, which is crucial for understanding how users' preferences evolve during video browsing. To capture users' dynamic segment interests, we propose an innovative model that integrates a hybrid representation module, a multi-modal user-video encoder, and a segment interest decoder. Our model addresses the challenges of capturing dynamic interest patterns, missing segment-level labels, and fusing different modalities, achieving precise segment-level interest prediction. We present two downstream tasks to evaluate the effectiveness of our segment interest modeling approach: video-skip prediction and short video recommendation. Our experiments on real-world short video datasets with diverse modalities show promising results on both tasks. It demonstrates that segment-level interest modeling brings a deep understanding of user engagement and enhances video recommendations. We also release a unique dataset that includes segment-level video data and diverse user behaviors, enabling further research in segment-level interest modeling. This work pioneers a novel perspective on understanding user segment-level preference, offering the potential for more personalized and engaging short video experiences.
Intelligence Test
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:How does intelligence emerge? We propose that intelligence is not a sudden gift or random occurrence, but rather a necessary trait for species to survive through Natural Selection. If a species passes the test of Natural Selection, it demonstrates the intelligence to survive in nature. Extending this perspective, we introduce Intelligence Test, a method to quantify the intelligence of any subject on any task. Like how species evolve by trial and error, Intelligence Test quantifies intelligence by the number of failed attempts before success. Fewer failures correspond to higher intelligence. When the expectation and variance of failure counts are both finite, it signals the achievement of an autonomous level of intelligence. Using Intelligence Test, we comprehensively evaluate existing AI systems. Our results show that while AI systems achieve a level of autonomy in simple tasks, they are still far from autonomous in more complex tasks, such as vision, search, recommendation, and language. While scaling model size might help, this would come at an astronomical cost. Projections suggest that achieving general autonomy would require unimaginable $10^{26}$ parameters. Even if Moore's Law continuously holds, such a parameter scale would take $70$ years. This staggering cost highlights the complexity of human tasks and the inadequacies of current AI. To further understand this phenomenon, we conduct a theoretical analysis. Our simulations suggest that human tasks possess a criticality property. As a result, autonomy requires a deep understanding of the task's underlying mechanisms. Current AI, however, does not fully grasp these mechanisms and instead relies on superficial mimicry, making it difficult to reach an autonomous level. We believe Intelligence Test can not only guide the future development of AI but also offer profound insights into the intelligence of humans ourselves.
TabTreeFormer: Tabular Data Generation Using Hybrid Tree-Transformer
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Transformers have achieved remarkable success in tabular data generation. However, they lack domain-specific inductive biases which are critical to preserving the intrinsic characteristics of tabular data. Meanwhile, they suffer from poor scalability and efficiency due to quadratic computational complexity. In this paper, we propose TabTreeFormer, a hybrid transformer architecture that incorporates a tree-based model that retains tabular-specific inductive biases of non-smooth and potentially low-correlated patterns caused by discreteness and non-rotational invariance, and hence enhances the fidelity and utility of synthetic data. In addition, we devise a dual-quantization tokenizer to capture the multimodal continuous distribution and further facilitate the learning of numerical value distribution. Moreover, our proposed tokenizer reduces the vocabulary size and sequence length due to the limited complexity (e.g., dimension-wise semantic meaning) of tabular data, rendering a significant model size shrink without sacrificing the capability of the transformer model. We evaluate TabTreeFormer on 10 datasets against multiple generative models on various metrics; our experimental results show that TabTreeFormer achieves superior fidelity, utility, privacy, and efficiency. Our best model yields a 40% utility improvement with 1/16 of the baseline model size.
AIDE: Task-Specific Fine Tuning with Attribute Guided Multi-Hop Data Expansion
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) for specific tasks requires high-quality, diverse training data relevant to the task. Recent research has leveraged LLMs to synthesize training data, but existing approaches either depend on large seed datasets or struggle to ensure both task relevance and data diversity in the generated outputs. To address these challenges, we propose AIDE, a novel data synthesis framework that uses a multi-hop process to expand 10 seed data points while ensuring diversity and task relevance. AIDE extracts the main topic and key knowledge attributes from the seed data to guide the synthesis process. In each subsequent hop, it extracts the topic and attributes from the newly generated data and continues guided synthesis. This process repeats for a total of K hops. To prevent irrelevant data generation as the hop depth increases, AIDE incorporates a residual connection mechanism and uses self-reflection to improve data quality. Our empirical results demonstrate that fine-tuning Mistral-7B, Llama-3.1-8B and Llama-3.2-3B with AIDE achieves more than 10% accuracy improvements over the base models across 13 tasks from 5 different benchmarks, while outperforming the models fine-tuned with state-of-the-art data synthesis methods like Evol-Instruct, DataTune and Prompt2Model.
High-Dimensional Tensor Discriminant Analysis with Incomplete Tensors
Oct 18, 2024



Abstract:Tensor classification has gained prominence across various fields, yet the challenge of handling partially observed tensor data in real-world applications remains largely unaddressed. This paper introduces a novel approach to tensor classification with incomplete data, framed within the tensor high-dimensional linear discriminant analysis. Specifically, we consider a high-dimensional tensor predictor with missing observations under the Missing Completely at Random (MCR) assumption and employ the Tensor Gaussian Mixture Model to capture the relationship between the tensor predictor and class label. We propose the Tensor LDA-MD algorithm, which manages high-dimensional tensor predictors with missing entries by leveraging the low-rank structure of the discriminant tensor. A key feature of our approach is a novel covariance estimation method under the tensor-based MCR model, supported by theoretical results that allow for correlated entries under mild conditions. Our work establishes the convergence rate of the estimation error of the discriminant tensor with incomplete data and minimax optimal bounds for the misclassification rate, addressing key gaps in the literature. Additionally, we derive large deviation results for the generalized mode-wise (separable) sample covariance matrix and its inverse, which are crucial tools in our analysis and hold independent interest. Our method demonstrates excellent performance in simulations and real data analysis, even with significant proportions of missing data. This research advances high-dimensional LDA and tensor learning, providing practical tools for applications with incomplete data and a solid theoretical foundation for classification accuracy in complex settings.
TAEGAN: Generating Synthetic Tabular Data For Data Augmentation
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:Synthetic tabular data generation has gained significant attention for its potential in data augmentation, software testing and privacy-preserving data sharing. However, most research has primarily focused on larger datasets and evaluating their quality in terms of metrics like column-wise statistical distributions and inter-feature correlations, while often overlooking its utility for data augmentation, particularly for datasets whose data is scarce. In this paper, we propose Tabular Auto-Encoder Generative Adversarial Network (TAEGAN), an improved GAN-based framework for generating high-quality tabular data. Although large language models (LLMs)-based methods represent the state-of-the-art in synthetic tabular data generation, they are often overkill for small datasets due to their extensive size and complexity. TAEGAN employs a masked auto-encoder as the generator, which for the first time introduces the power of self-supervised pre-training in tabular data generation so that essentially exposes the networks to more information. We extensively evaluate TAEGAN against five state-of-the-art synthetic tabular data generation algorithms. Results from 10 datasets show that TAEGAN outperforms existing deep-learning-based tabular data generation models on 9 out of 10 datasets on the machine learning efficacy and achieves superior data augmentation performance on 7 out of 8 smaller datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge