Zhigang Wu
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Quantification Aided by Deep Estimations of Imperfection Factors and Overall Macromolecular Signal
Jun 16, 2023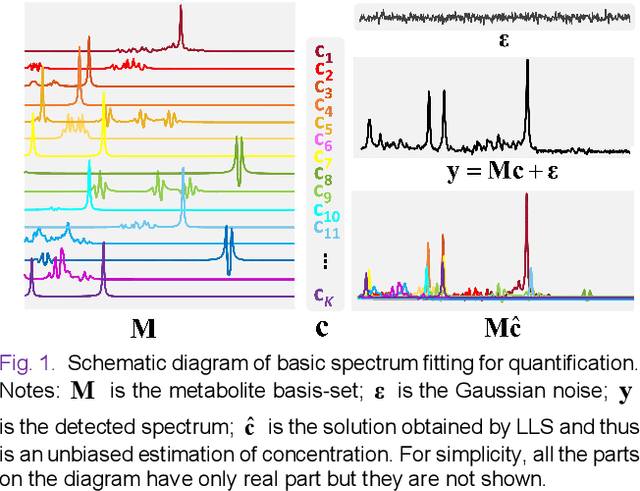
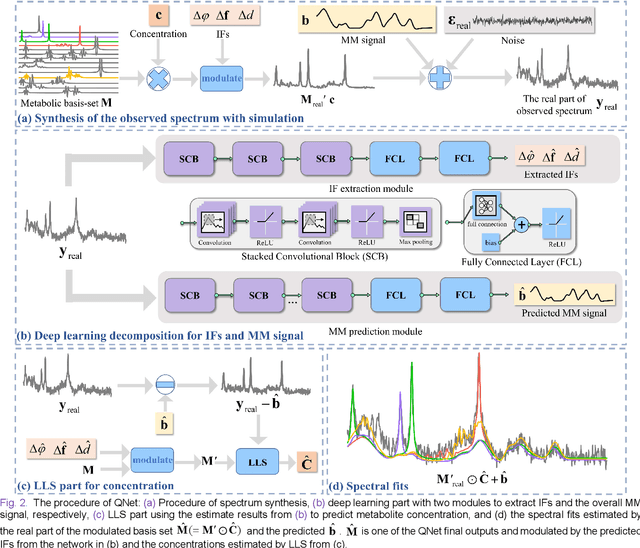
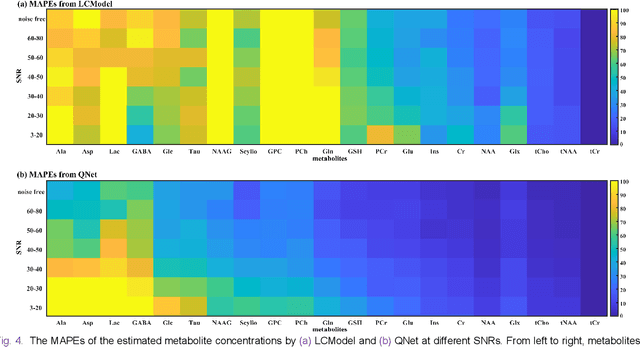
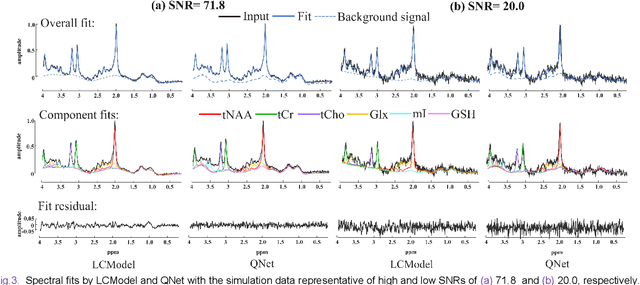
Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) is an important non-invasive technique for in vivo biomedical detection. However, it is still challenging to accurately quantify metabolites with proton MRS due to three problems: Serious overlaps of metabolite signals, signal distortions due to non-ideal acquisition conditions and interference with strong background signals including macromolecule signals. The most popular software, LCModel, adopts the non-linear least square to quantify metabolites and addresses these problems by introducing regularization terms, imperfection factors of non-ideal acquisition conditions, and designing several empirical priors such as basissets of both metabolites and macromolecules. However, solving such a large non-linear quantitative problem is complicated. Moreover, when the signal-to-noise ratio of an input MRS signal is low, the solution may have a large deviation. In this work, deep learning is introduced to reduce the complexity of solving this overall quantitative problem. Deep learning is designed to predict directly the imperfection factors and the overall signal from macromolecules. Then, the remaining part of the quantification problem becomes a much simpler effective fitting and is easily solved by Linear Least Squares (LLS), which greatly improves the generalization to unseen concentration of metabolites in the training data. Experimental results show that compared with LCModel, the proposed method has smaller quantification errors for 700 sets of simulated test data, and presents more stable quantification results for 20 sets of healthy in vivo data at a wide range of signal-to-noise ratio. Qnet also outperforms other deep learning methods in terms of lower quantification error on most metabolites. Finally, QNet has been deployed on a cloud computing platform, CloudBrain-MRS, which is open accessed at https://csrc.xmu.edu.cn/CloudBrain.html.
Physics-informed deep diffusion MRI reconstruction: break the bottleneck of training data in artificial intelligence
Oct 20, 2022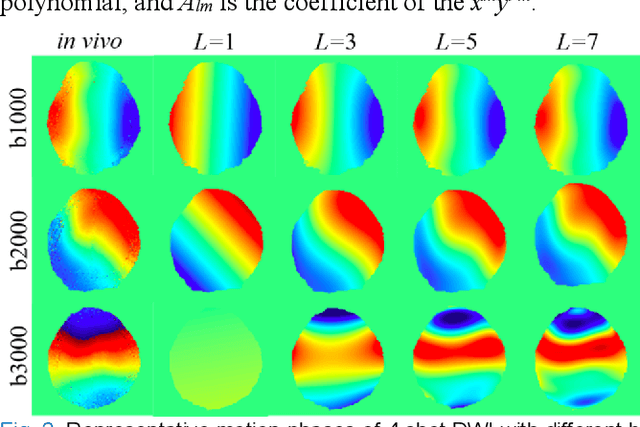
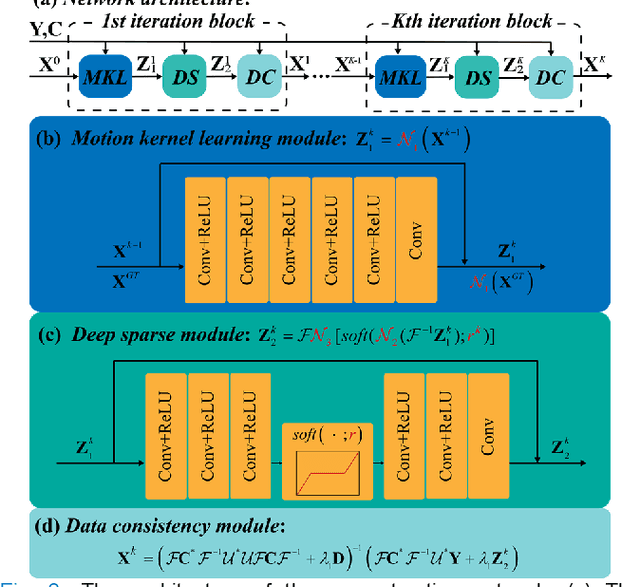
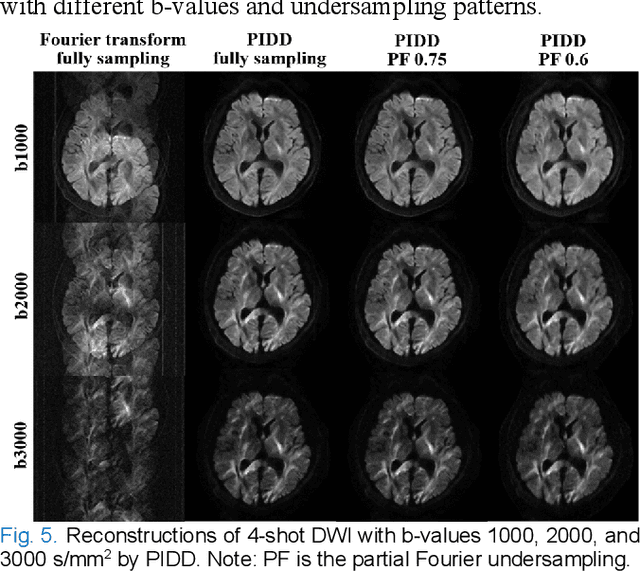
Abstract:In this work, we propose a Physics-Informed Deep Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) reconstruction method (PIDD). PIDD contains two main components: The multi-shot DWI data synthesis and a deep learning reconstruction network. For data synthesis, we first mathematically analyze the motion during the multi-shot data acquisition and approach it by a simplified physical motion model. The motion model inspires a polynomial model for motion-induced phase synthesis. Then, lots of synthetic phases are combined with a few real data to generate a large amount of training data. For reconstruction network, we exploit the smoothness property of each shot image phase as learnable convolution kernels in the k-space and complementary sparsity in the image domain. Results on both synthetic and in vivo brain data show that, the proposed PIDD trained on synthetic data enables sub-second ultra-fast, high-quality, and robust reconstruction with different b-values and undersampling patterns.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge