Xiaobo Qu
Enabling Ultra-Fast Cardiovascular Imaging Across Heterogeneous Clinical Environments with a Generalist Foundation Model and Multimodal Database
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Multimodal cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging provides comprehensive and non-invasive insights into cardiovascular disease (CVD) diagnosis and underlying mechanisms. Despite decades of advancements, its widespread clinical adoption remains constrained by prolonged scan times and heterogeneity across medical environments. This underscores the urgent need for a generalist reconstruction foundation model for ultra-fast CMR imaging, one capable of adapting across diverse imaging scenarios and serving as the essential substrate for all downstream analyses. To enable this goal, we curate MMCMR-427K, the largest and most comprehensive multimodal CMR k-space database to date, comprising 427,465 multi-coil k-space data paired with structured metadata across 13 international centers, 12 CMR modalities, 15 scanners, and 17 CVD categories in populations across three continents. Building on this unprecedented resource, we introduce CardioMM, a generalist reconstruction foundation model capable of dynamically adapting to heterogeneous fast CMR imaging scenarios. CardioMM unifies semantic contextual understanding with physics-informed data consistency to deliver robust reconstructions across varied scanners, protocols, and patient presentations. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that CardioMM achieves state-of-the-art performance in the internal centers and exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to unseen external settings. Even at imaging acceleration up to 24x, CardioMM reliably preserves key cardiac phenotypes, quantitative myocardial biomarkers, and diagnostic image quality, enabling a substantial increase in CMR examination throughput without compromising clinical integrity. Together, our open-access MMCMR-427K database and CardioMM framework establish a scalable pathway toward high-throughput, high-quality, and clinically accessible cardiovascular imaging.
Error Bound Analysis of Physics-Informed Neural Networks-Driven T2 Quantification in Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINN) are emerging as a promising approach for quantitative parameter estimation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). While existing deep learning methods can provide an accurate quantitative estimation of the T2 parameter, they still require large amounts of training data and lack theoretical support and a recognized gold standard. Thus, given the absence of PINN-based approaches for T2 estimation, we propose embedding the fundamental physics of MRI, the Bloch equation, in the loss of PINN, which is solely based on target scan data and does not require a pre-defined training database. Furthermore, by deriving rigorous upper bounds for both the T2 estimation error and the generalization error of the Bloch equation solution, we establish a theoretical foundation for evaluating the PINN's quantitative accuracy. Even without access to the ground truth or a gold standard, this theory enables us to estimate the error with respect to the real quantitative parameter T2. The accuracy of T2 mapping and the validity of the theoretical analysis are demonstrated on a numerical cardiac model and a water phantom, where our method exhibits excellent quantitative precision in the myocardial T2 range. Clinical applicability is confirmed in 94 acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients, achieving low-error quantitative T2 estimation under the theoretical error bound, highlighting the robustness and potential of PINN.
An artificially intelligent magnetic resonance spectroscopy quantification method: Comparison between QNet and LCModel on the cloud computing platform CloudBrain-MRS
Mar 06, 2025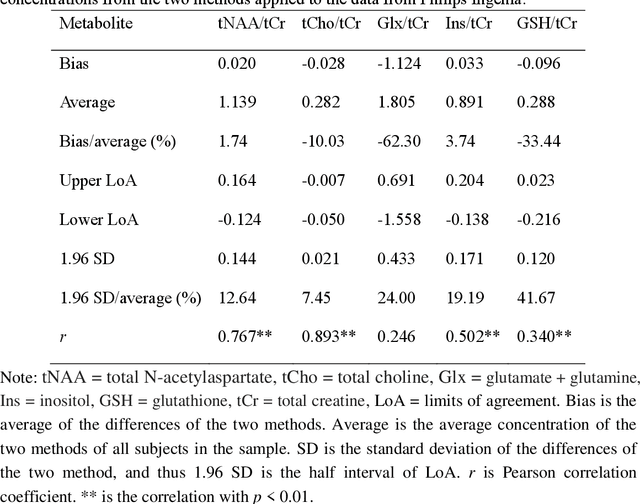
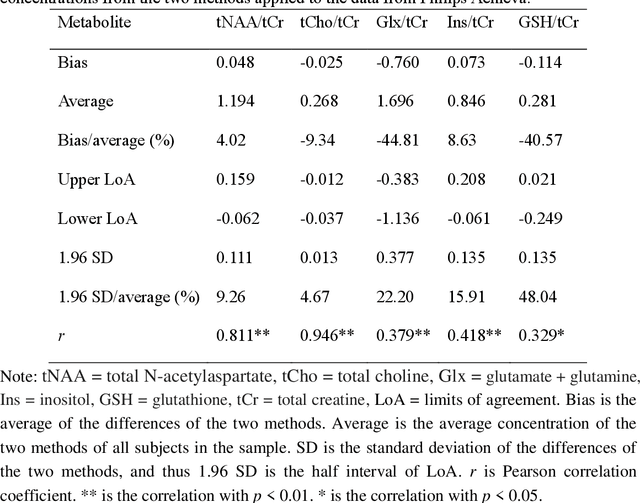
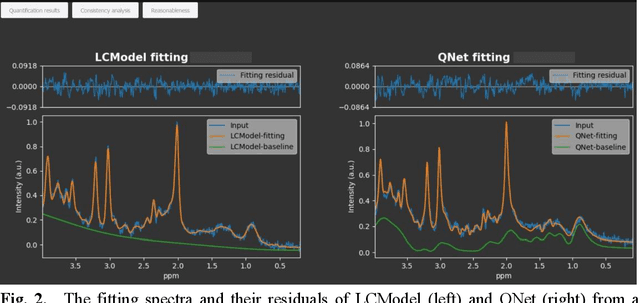
Abstract:Objctives: This work aimed to statistically compare the metabolite quantification of human brain magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) between the deep learning method QNet and the classical method LCModel through an easy-to-use intelligent cloud computing platform CloudBrain-MRS. Materials and Methods: In this retrospective study, two 3 T MRI scanners Philips Ingenia and Achieva collected 61 and 46 in vivo 1H magnetic resonance (MR) spectra of healthy participants, respectively, from the brain region of pregenual anterior cingulate cortex from September to October 2021. The analyses of Bland-Altman, Pearson correlation and reasonability were performed to assess the degree of agreement, linear correlation and reasonability between the two quantification methods. Results: Fifteen healthy volunteers (12 females and 3 males, age range: 21-35 years, mean age/standard deviation = 27.4/3.9 years) were recruited. The analyses of Bland-Altman, Pearson correlation and reasonability showed high to good consistency and very strong to moderate correlation between the two methods for quantification of total N-acetylaspartate (tNAA), total choline (tCho), and inositol (Ins) (relative half interval of limits of agreement = 3.04%, 9.3%, and 18.5%, respectively; Pearson correlation coefficient r = 0.775, 0.927, and 0.469, respectively). In addition, quantification results of QNet are more likely to be closer to the previous reported average values than those of LCModel. Conclusion: There were high or good degrees of consistency between the quantification results of QNet and LCModel for tNAA, tCho, and Ins, and QNet generally has more reasonable quantification than LCModel.
Reproducibility Assessment of Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Pregenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex across Sessions and Vendors via the Cloud Computing Platform CloudBrain-MRS
Mar 06, 2025



Abstract:Given the need to elucidate the mechanisms underlying illnesses and their treatment, as well as the lack of harmonization of acquisition and post-processing protocols among different magnetic resonance system vendors, this work is to determine if metabolite concentrations obtained from different sessions, machine models and even different vendors of 3 T scanners can be highly reproducible and be pooled for diagnostic analysis, which is very valuable for the research of rare diseases. Participants underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanning once on two separate days within one week (one session per day, each session including two proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) scans with no more than a 5-minute interval between scans (no off-bed activity)) on each machine. were analyzed for reliability of within- and between- sessions using the coefficient of variation (CV) and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), and for reproducibility of across the machines using correlation coefficient. As for within- and between- session, all CV values for a group of all the first or second scans of a session, or for a session were almost below 20%, and most of the ICCs for metabolites range from moderate (0.4-0.59) to excellent (0.75-1), indicating high data reliability. When it comes to the reproducibility across the three scanners, all Pearson correlation coefficients across the three machines approached 1 with most around 0.9, and majority demonstrated statistical significance (P<0.01). Additionally, the intra-vendor reproducibility was greater than the inter-vendor ones.
Towards Universal Learning-based Model for Cardiac Image Reconstruction: Summary of the CMRxRecon2024 Challenge
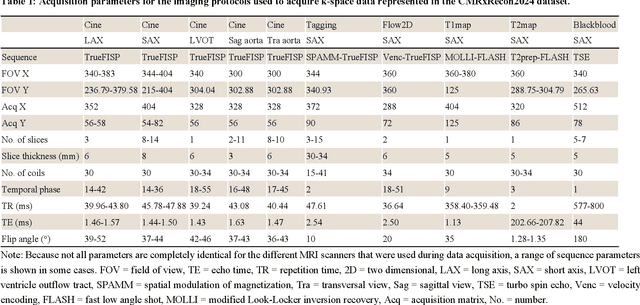
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) offers diverse imaging contrasts for assessment of cardiac function and tissue characterization. However, acquiring each single CMR modality is often time-consuming, and comprehensive clinical protocols require multiple modalities with various sampling patterns, further extending the overall acquisition time and increasing susceptibility to motion artifacts. Existing deep learning-based reconstruction methods are often designed for specific acquisition parameters, which limits their ability to generalize across a variety of scan scenarios. As part of the CMRxRecon Series, the CMRxRecon2024 challenge provides diverse datasets encompassing multi-modality multi-view imaging with various sampling patterns, and a platform for the international community to develop and benchmark reconstruction solutions in two well-crafted tasks. Task 1 is a modality-universal setting, evaluating the out-of-distribution generalization of the reconstructed model, while Task 2 follows sampling-universal setting assessing the one-for-all adaptability of the universal model. Main contributions include providing the first and largest publicly available multi-modality, multi-view cardiac k-space dataset; developing a benchmarking platform that simulates clinical acceleration protocols, with a shared code library and tutorial for various k-t undersampling patterns and data processing; giving technical insights of enhanced data consistency based on physic-informed networks and adaptive prompt-learning embedding to be versatile to different clinical settings; additional finding on evaluation metrics to address the limitations of conventional ground-truth references in universal reconstruction tasks.
CMRxRecon2024: A Multi-Modality, Multi-View K-Space Dataset Boosting Universal Machine Learning for Accelerated Cardiac MRI
Jun 27, 2024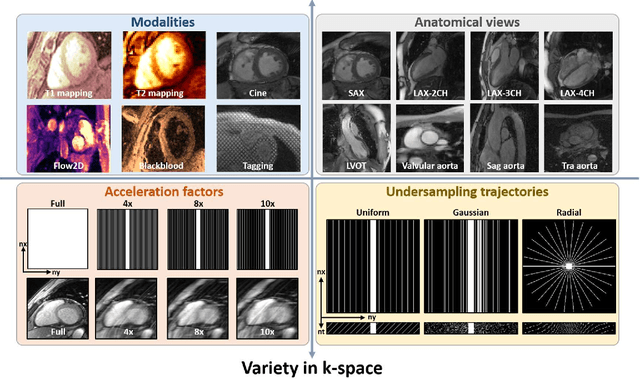
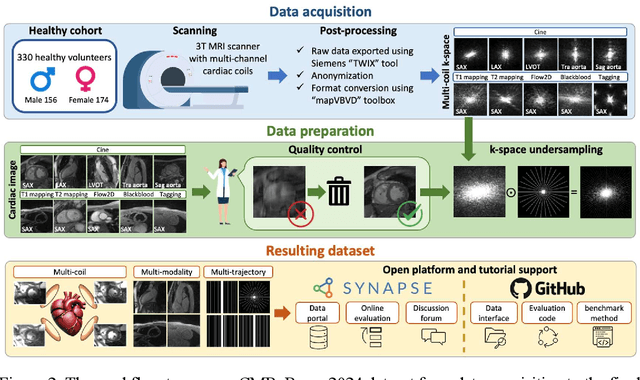
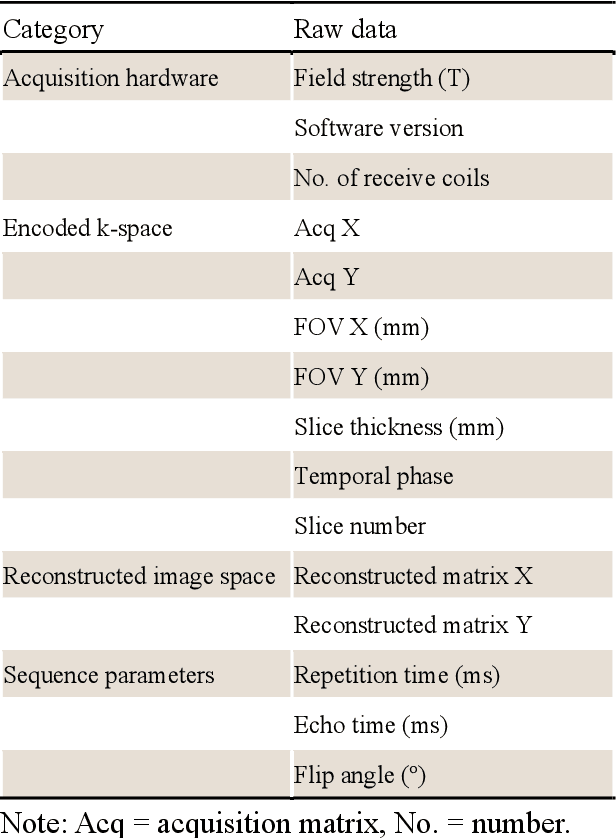
Abstract:Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has emerged as a clinically gold-standard technique for diagnosing cardiac diseases, thanks to its ability to provide diverse information with multiple modalities and anatomical views. Accelerated cardiac MRI is highly expected to achieve time-efficient and patient-friendly imaging, and then advanced image reconstruction approaches are required to recover high-quality, clinically interpretable images from undersampled measurements. However, the lack of publicly available cardiac MRI k-space dataset in terms of both quantity and diversity has severely hindered substantial technological progress, particularly for data-driven artificial intelligence. Here, we provide a standardized, diverse, and high-quality CMRxRecon2024 dataset to facilitate the technical development, fair evaluation, and clinical transfer of cardiac MRI reconstruction approaches, towards promoting the universal frameworks that enable fast and robust reconstructions across different cardiac MRI protocols in clinical practice. To the best of our knowledge, the CMRxRecon2024 dataset is the largest and most diverse publicly available cardiac k-space dataset. It is acquired from 330 healthy volunteers, covering commonly used modalities, anatomical views, and acquisition trajectories in clinical cardiac MRI workflows. Besides, an open platform with tutorials, benchmarks, and data processing tools is provided to facilitate data usage, advanced method development, and fair performance evaluation.
Simultaneous Deep Learning of Myocardium Segmentation and T2 Quantification for Acute Myocardial Infarction MRI
May 17, 2024



Abstract:In cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) analysis, simultaneous myocardial segmentation and T2 quantification are crucial for assessing myocardial pathologies. Existing methods often address these tasks separately, limiting their synergistic potential. To address this, we propose SQNet, a dual-task network integrating Transformer and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) components. SQNet features a T2-refine fusion decoder for quantitative analysis, leveraging global features from the Transformer, and a segmentation decoder with multiple local region supervision for enhanced accuracy. A tight coupling module aligns and fuses CNN and Transformer branch features, enabling SQNet to focus on myocardium regions. Evaluation on healthy controls (HC) and acute myocardial infarction patients (AMI) demonstrates superior segmentation dice scores (89.3/89.2) compared to state-of-the-art methods (87.7/87.9). T2 quantification yields strong linear correlations (Pearson coefficients: 0.84/0.93) with label values for HC/AMI, indicating accurate mapping. Radiologist evaluations confirm SQNet's superior image quality scores (4.60/4.58 for segmentation, 4.32/4.42 for T2 quantification) over state-of-the-art methods (4.50/4.44 for segmentation, 3.59/4.37 for T2 quantification). SQNet thus offers accurate simultaneous segmentation and quantification, enhancing cardiac disease diagnosis, such as AMI.
The state-of-the-art in Cardiac MRI Reconstruction: Results of the CMRxRecon Challenge in MICCAI 2023
Apr 01, 2024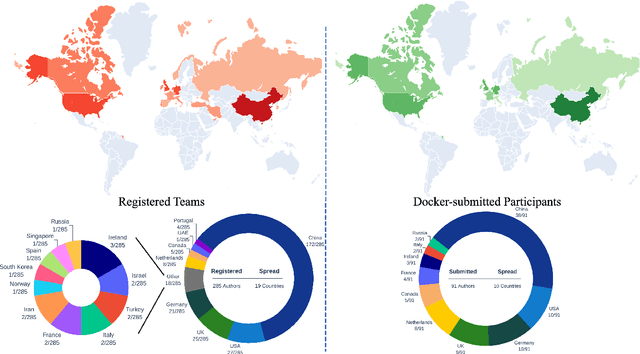
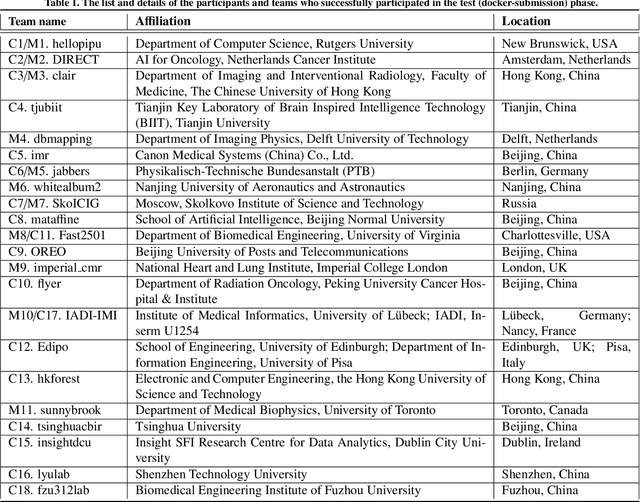
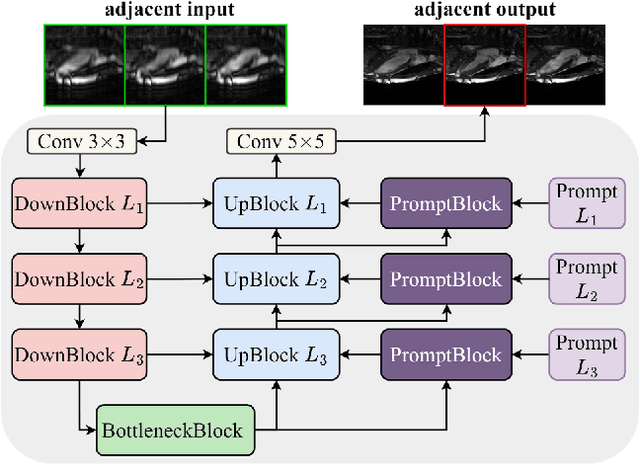
Abstract:Cardiac MRI, crucial for evaluating heart structure and function, faces limitations like slow imaging and motion artifacts. Undersampling reconstruction, especially data-driven algorithms, has emerged as a promising solution to accelerate scans and enhance imaging performance using highly under-sampled data. Nevertheless, the scarcity of publicly available cardiac k-space datasets and evaluation platform hinder the development of data-driven reconstruction algorithms. To address this issue, we organized the Cardiac MRI Reconstruction Challenge (CMRxRecon) in 2023, in collaboration with the 26th International Conference on MICCAI. CMRxRecon presented an extensive k-space dataset comprising cine and mapping raw data, accompanied by detailed annotations of cardiac anatomical structures. With overwhelming participation, the challenge attracted more than 285 teams and over 600 participants. Among them, 22 teams successfully submitted Docker containers for the testing phase, with 7 teams submitted for both cine and mapping tasks. All teams use deep learning based approaches, indicating that deep learning has predominately become a promising solution for the problem. The first-place winner of both tasks utilizes the E2E-VarNet architecture as backbones. In contrast, U-Net is still the most popular backbone for both multi-coil and single-coil reconstructions. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the challenge design, presents a summary of the submitted results, reviews the employed methods, and offers an in-depth discussion that aims to inspire future advancements in cardiac MRI reconstruction models. The summary emphasizes the effective strategies observed in Cardiac MRI reconstruction, including backbone architecture, loss function, pre-processing techniques, physical modeling, and model complexity, thereby providing valuable insights for further developments in this field.
Deep Separable Spatiotemporal Learning for Fast Dynamic Cardiac MRI
Feb 24, 2024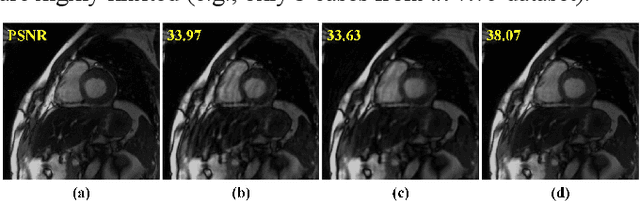
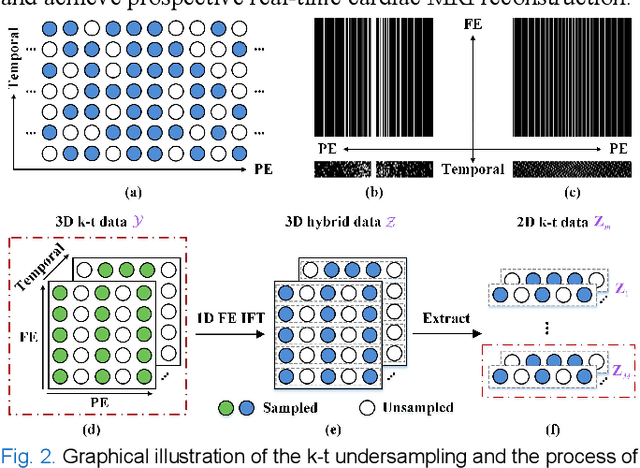
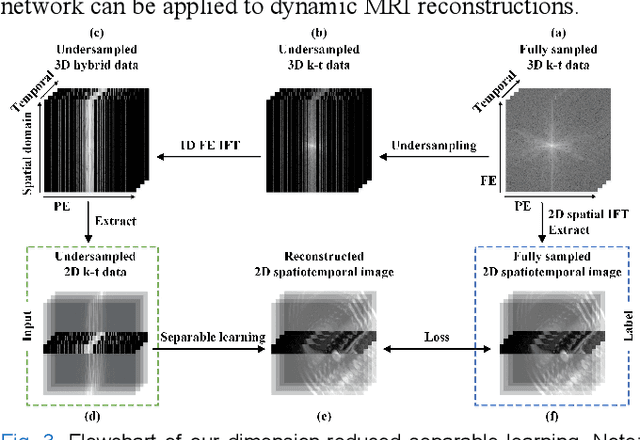
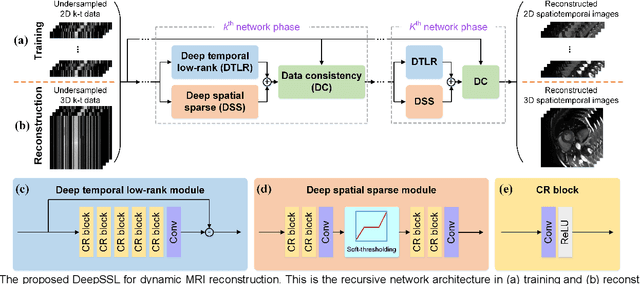
Abstract:Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays an indispensable role in cardiac diagnosis. To enable fast imaging, the k-space data can be undersampled but the image reconstruction poses a great challenge of high-dimensional processing. This challenge leads to necessitate extensive training data in many deep learning reconstruction methods. This work proposes a novel and efficient approach, leveraging a dimension-reduced separable learning scheme that excels even with highly limited training data. We further integrate it with spatiotemporal priors to develop a Deep Separable Spatiotemporal Learning network (DeepSSL), which unrolls an iteration process of a reconstruction model with both temporal low-rankness and spatial sparsity. Intermediate outputs are visualized to provide insights into the network's behavior and enhance its interpretability. Extensive results on cardiac cine datasets show that the proposed DeepSSL is superior to the state-of-the-art methods visually and quantitatively, while reducing the demand for training cases by up to 75%. And its preliminary adaptability to cardiac patients has been verified through experienced radiologists' and cardiologists' blind reader study. Additionally, DeepSSL also benefits for achieving the downstream task of cardiac segmentation with higher accuracy and shows robustness in prospective real-time cardiac MRI.
Quantitative Analysis of Molecular Transport in the Extracellular Space Using Physics-Informed Neural Network
Jan 24, 2024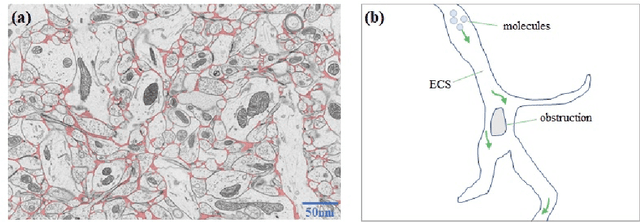



Abstract:The brain extracellular space (ECS), an irregular, extremely tortuous nanoscale space located between cells or between cells and blood vessels, is crucial for nerve cell survival. It plays a pivotal role in high-level brain functions such as memory, emotion, and sensation. However, the specific form of molecular transport within the ECS remain elusive. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a novel approach to quantitatively analyze the molecular transport within the ECS by solving an inverse problem derived from the advection-diffusion equation (ADE) using a physics-informed neural network (PINN). PINN provides a streamlined solution to the ADE without the need for intricate mathematical formulations or grid settings. Additionally, the optimization of PINN facilitates the automatic computation of the diffusion coefficient governing long-term molecule transport and the velocity of molecules driven by advection. Consequently, the proposed method allows for the quantitative analysis and identification of the specific pattern of molecular transport within the ECS through the calculation of the Peclet number. Experimental validation on two datasets of magnetic resonance images (MRIs) captured at different time points showcases the effectiveness of the proposed method. Notably, our simulations reveal identical molecular transport patterns between datasets representing rats with tracer injected into the same brain region. These findings highlight the potential of PINN as a promising tool for comprehensively exploring molecular transport within the ECS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge