Peichen Zhong
Machine learning interatomic potential can infer electrical response
Apr 07, 2025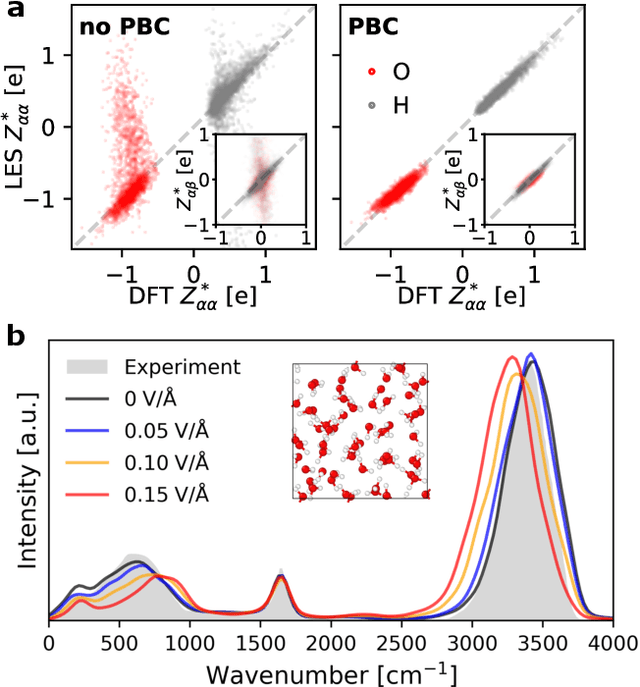
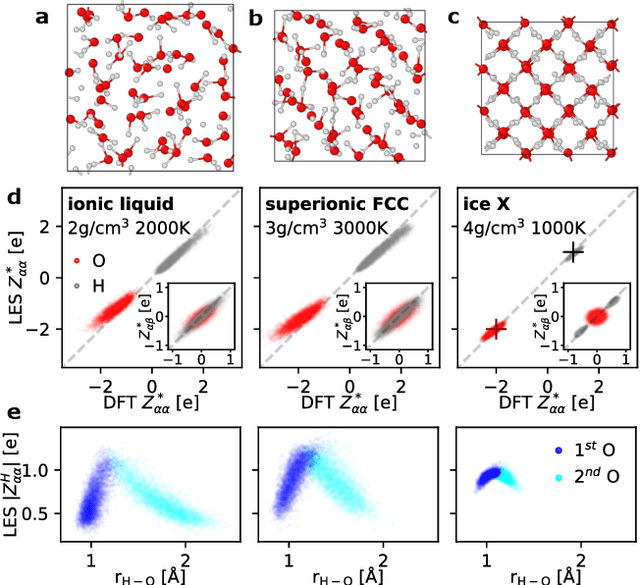
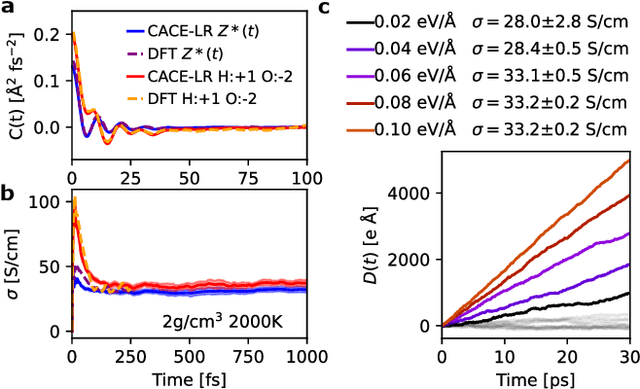
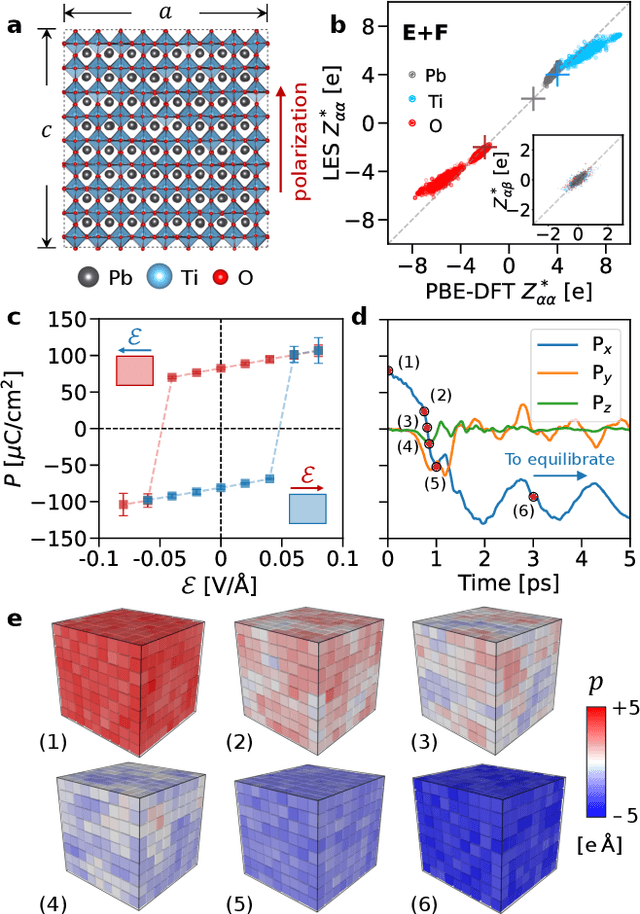
Abstract:Modeling the response of material and chemical systems to electric fields remains a longstanding challenge. Machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) offer an efficient and scalable alternative to quantum mechanical methods but do not by themselves incorporate electrical response. Here, we show that polarization and Born effective charge (BEC) tensors can be directly extracted from long-range MLIPs within the Latent Ewald Summation (LES) framework, solely by learning from energy and force data. Using this approach, we predict the infrared spectra of bulk water under zero or finite external electric fields, ionic conductivities of high-pressure superionic ice, and the phase transition and hysteresis in ferroelectric PbTiO$_3$ perovskite. This work thus extends the capability of MLIPs to predict electrical response--without training on charges or polarization or BECs--and enables accurate modeling of electric-field-driven processes in diverse systems at scale.
Cross-functional transferability in universal machine learning interatomic potentials
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of universal machine learning interatomic potentials (uMLIPs) has demonstrated the possibility for generalizable learning of the universal potential energy surface. In principle, the accuracy of uMLIPs can be further improved by bridging the model from lower-fidelity datasets to high-fidelity ones. In this work, we analyze the challenge of this transfer learning problem within the CHGNet framework. We show that significant energy scale shifts and poor correlations between GGA and r$^2$SCAN pose challenges to cross-functional data transferability in uMLIPs. By benchmarking different transfer learning approaches on the MP-r$^2$SCAN dataset of 0.24 million structures, we demonstrate the importance of elemental energy referencing in the transfer learning of uMLIPs. By comparing the scaling law with and without the pre-training on a low-fidelity dataset, we show that significant data efficiency can still be achieved through transfer learning, even with a target dataset of sub-million structures. We highlight the importance of proper transfer learning and multi-fidelity learning in creating next-generation uMLIPs on high-fidelity data.
Large Language Models Are Innate Crystal Structure Generators
Feb 28, 2025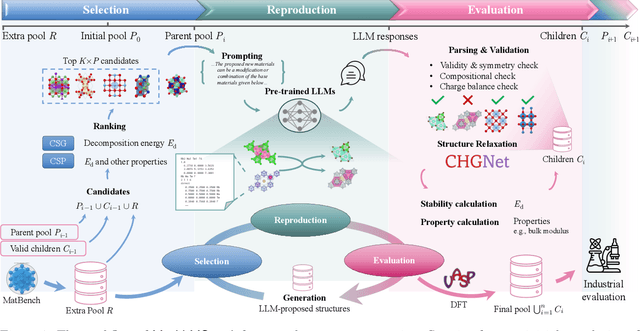
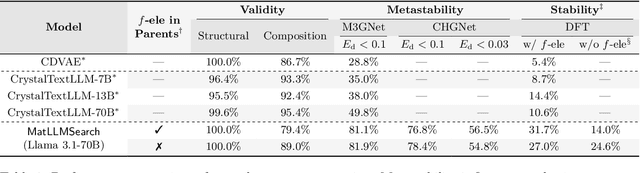
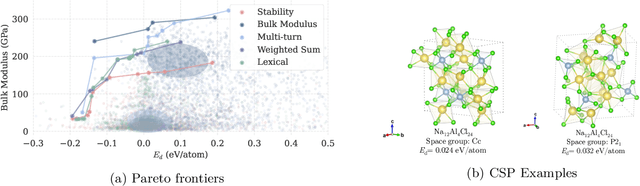
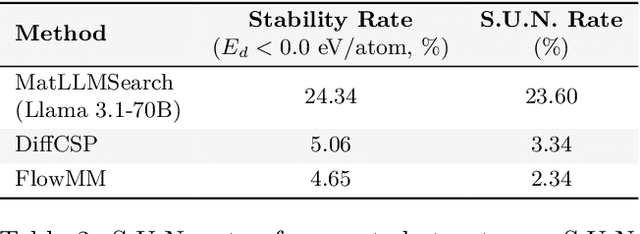
Abstract:Crystal structure generation is fundamental to materials discovery, enabling the prediction of novel materials with desired properties. While existing approaches leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) through extensive fine-tuning on materials databases, we show that pre-trained LLMs can inherently generate stable crystal structures without additional training. Our novel framework MatLLMSearch integrates pre-trained LLMs with evolutionary search algorithms, achieving a 78.38% metastable rate validated by machine learning interatomic potentials and 31.7% DFT-verified stability via quantum mechanical calculations, outperforming specialized models such as CrystalTextLLM. Beyond crystal structure generation, we further demonstrate that our framework can be readily adapted to diverse materials design tasks, including crystal structure prediction and multi-objective optimization of properties such as deformation energy and bulk modulus, all without fine-tuning. These results establish pre-trained LLMs as versatile and effective tools for materials discovery, opening up new venues for crystal structure generation with reduced computational overhead and broader accessibility.
Learning charges and long-range interactions from energies and forces
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Accurate modeling of long-range forces is critical in atomistic simulations, as they play a central role in determining the properties of materials and chemical systems. However, standard machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) often rely on short-range approximations, limiting their applicability to systems with significant electrostatics and dispersion forces. We recently introduced the Latent Ewald Summation (LES) method, which captures long-range electrostatics without explicitly learning atomic charges or charge equilibration. Extending LES, we incorporate the ability to learn physical partial charges, encode charge states, and the option to impose charge neutrality constraints. We benchmark LES on diverse and challenging systems, including charged molecules, ionic liquid, electrolyte solution, polar dipeptides, surface adsorption, electrolyte/solid interfaces, and solid-solid interfaces. Our results show that LES can effectively infer physical partial charges, dipole and quadrupole moments, as well as achieve better accuracy compared to methods that explicitly learn charges. LES thus provides an efficient, interpretable, and generalizable MLIP framework for simulating complex systems with intricate charge transfer and long-range
Overcoming systematic softening in universal machine learning interatomic potentials by fine-tuning
May 11, 2024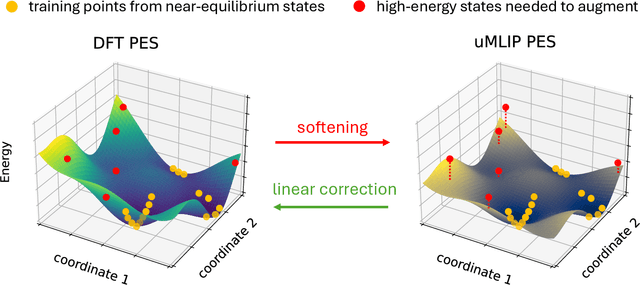
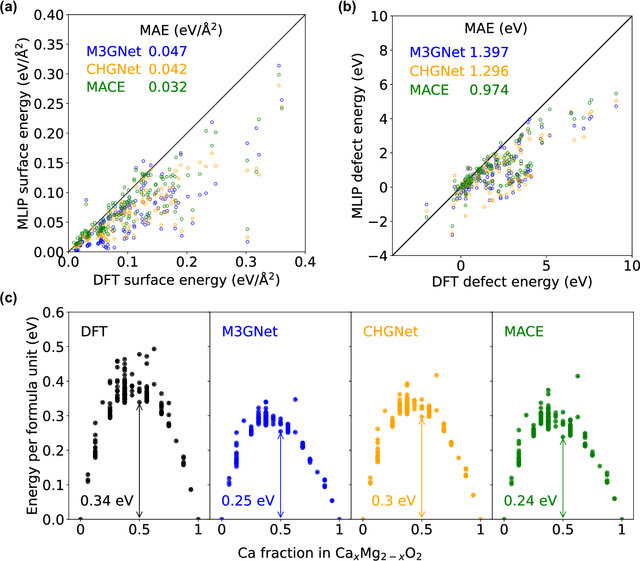
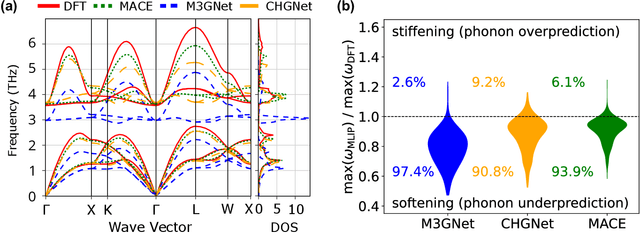
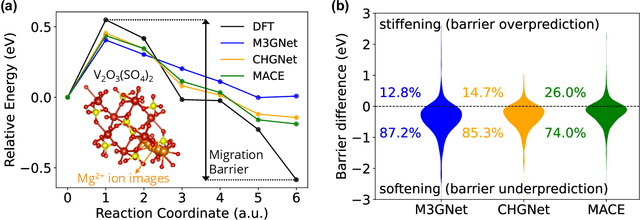
Abstract:Machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) have introduced a new paradigm for atomic simulations. Recent advancements have seen the emergence of universal MLIPs (uMLIPs) that are pre-trained on diverse materials datasets, providing opportunities for both ready-to-use universal force fields and robust foundations for downstream machine learning refinements. However, their performance in extrapolating to out-of-distribution complex atomic environments remains unclear. In this study, we highlight a consistent potential energy surface (PES) softening effect in three uMLIPs: M3GNet, CHGNet, and MACE-MP-0, which is characterized by energy and force under-prediction in a series of atomic-modeling benchmarks including surfaces, defects, solid-solution energetics, phonon vibration modes, ion migration barriers, and general high-energy states. We find that the PES softening behavior originates from a systematic underprediction error of the PES curvature, which derives from the biased sampling of near-equilibrium atomic arrangements in uMLIP pre-training datasets. We demonstrate that the PES softening issue can be effectively rectified by fine-tuning with a single additional data point. Our findings suggest that a considerable fraction of uMLIP errors are highly systematic, and can therefore be efficiently corrected. This result rationalizes the data-efficient fine-tuning performance boost commonly observed with foundational MLIPs. We argue for the importance of a comprehensive materials dataset with improved PES sampling for next-generation foundational MLIPs.
CHGNet: Pretrained universal neural network potential for charge-informed atomistic modeling
Feb 28, 2023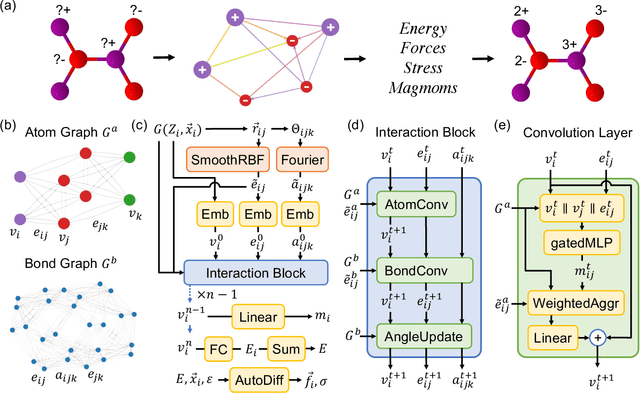
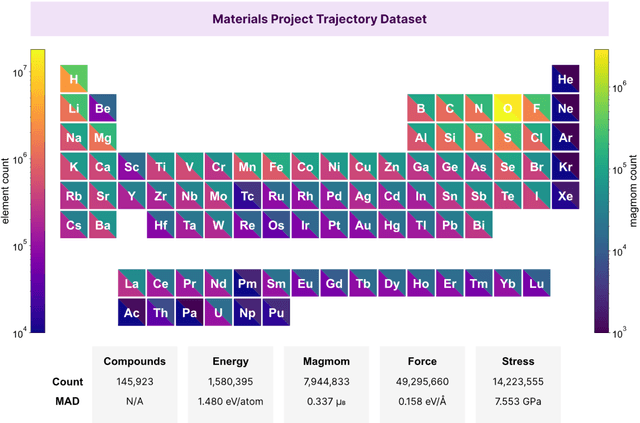
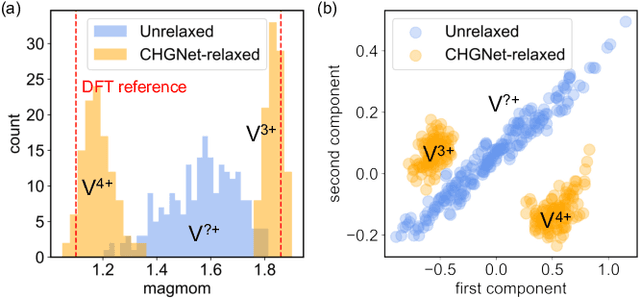
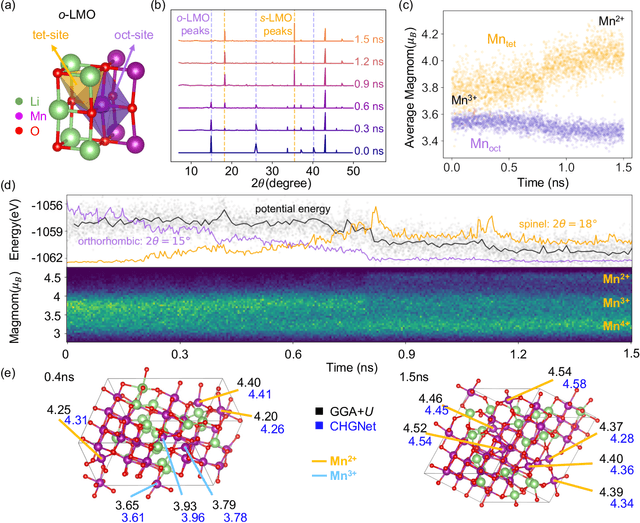
Abstract:The simulation of large-scale systems with complex electron interactions remains one of the greatest challenges for the atomistic modeling of materials. Although classical force-fields often fail to describe the coupling between electronic states and ionic rearrangements, the more accurate \textit{ab-initio} molecular dynamics suffers from computational complexity that prevents long-time and large-scale simulations, which are essential to study many technologically relevant phenomena, such as reactions, ion migrations, phase transformations, and degradation. In this work, we present the Crystal Hamiltonian Graph neural Network (CHGNet) as a novel machine-learning interatomic potential (MLIP), using a graph-neural-network-based force-field to model a universal potential energy surface. CHGNet is pretrained on the energies, forces, stresses, and magnetic moments from the Materials Project Trajectory Dataset, which consists of over 10 years of density functional theory static and relaxation trajectories of $\sim 1.5$ million inorganic structures. The explicit inclusion of magnetic moments enables CHGNet to learn and accurately represent the orbital occupancy of electrons, enhancing its capability to describe both atomic and electronic degrees of freedom. We demonstrate several applications of CHGNet in solid-state materials, including charge-informed molecular dynamics in Li$_x$MnO$_2$, the finite temperature phase diagram for Li$_x$FePO$_4$ and Li diffusion in garnet conductors. We critically analyze the significance of including charge information for capturing appropriate chemistry, and we provide new insights into ionic systems with additional electronic degrees of freedom that can not be observed by previous MLIPs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge