CHGNet: Pretrained universal neural network potential for charge-informed atomistic modeling
Paper and Code
Feb 28, 2023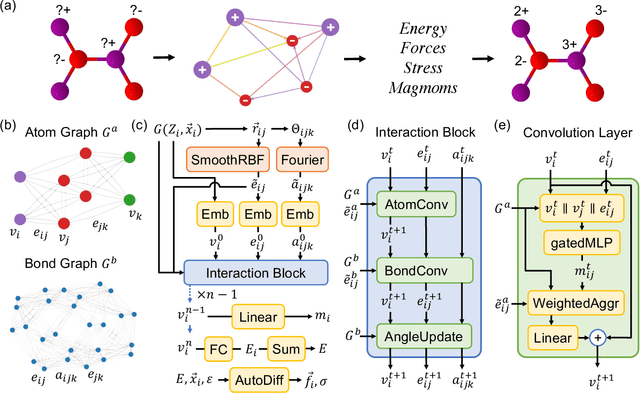
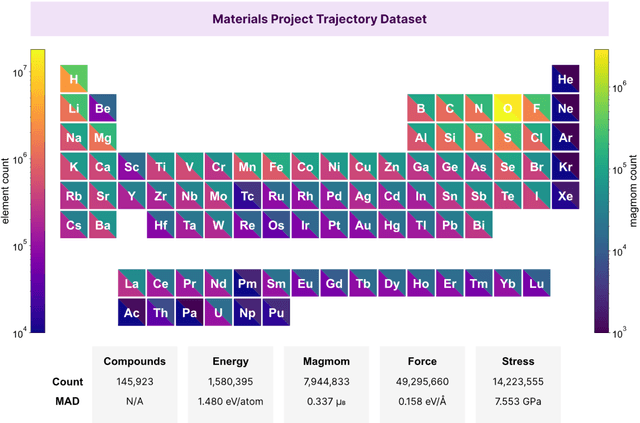
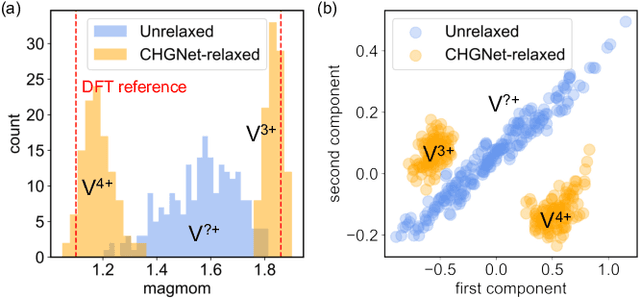
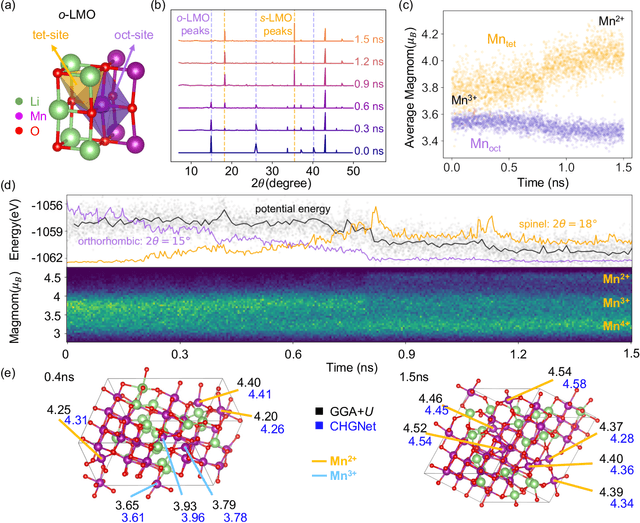
The simulation of large-scale systems with complex electron interactions remains one of the greatest challenges for the atomistic modeling of materials. Although classical force-fields often fail to describe the coupling between electronic states and ionic rearrangements, the more accurate \textit{ab-initio} molecular dynamics suffers from computational complexity that prevents long-time and large-scale simulations, which are essential to study many technologically relevant phenomena, such as reactions, ion migrations, phase transformations, and degradation. In this work, we present the Crystal Hamiltonian Graph neural Network (CHGNet) as a novel machine-learning interatomic potential (MLIP), using a graph-neural-network-based force-field to model a universal potential energy surface. CHGNet is pretrained on the energies, forces, stresses, and magnetic moments from the Materials Project Trajectory Dataset, which consists of over 10 years of density functional theory static and relaxation trajectories of $\sim 1.5$ million inorganic structures. The explicit inclusion of magnetic moments enables CHGNet to learn and accurately represent the orbital occupancy of electrons, enhancing its capability to describe both atomic and electronic degrees of freedom. We demonstrate several applications of CHGNet in solid-state materials, including charge-informed molecular dynamics in Li$_x$MnO$_2$, the finite temperature phase diagram for Li$_x$FePO$_4$ and Li diffusion in garnet conductors. We critically analyze the significance of including charge information for capturing appropriate chemistry, and we provide new insights into ionic systems with additional electronic degrees of freedom that can not be observed by previous MLIPs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge