Zhili Shen
Millions of $\text{GeAR}$-s: Extending GraphRAG to Millions of Documents
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have explored graph-based approaches to retrieval-augmented generation, leveraging structured or semi-structured information -- such as entities and their relations extracted from documents -- to enhance retrieval. However, these methods are typically designed to address specific tasks, such as multi-hop question answering and query-focused summarisation, and therefore, there is limited evidence of their general applicability across broader datasets. In this paper, we aim to adapt a state-of-the-art graph-based RAG solution: $\text{GeAR}$ and explore its performance and limitations on the SIGIR 2025 LiveRAG Challenge.
GeAR: Graph-enhanced Agent for Retrieval-augmented Generation
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation systems rely on effective document retrieval capabilities. By design, conventional sparse or dense retrievers face challenges in multi-hop retrieval scenarios. In this paper, we present GeAR, which advances RAG performance through two key innovations: (i) graph expansion, which enhances any conventional base retriever, such as BM25, and (ii) an agent framework that incorporates graph expansion. Our evaluation demonstrates GeAR's superior retrieval performance on three multi-hop question answering datasets. Additionally, our system achieves state-of-the-art results with improvements exceeding 10% on the challenging MuSiQue dataset, while requiring fewer tokens and iterations compared to other multi-step retrieval systems.
Improving Retrieval-augmented Text-to-SQL with AST-based Ranking and Schema Pruning
Jul 03, 2024

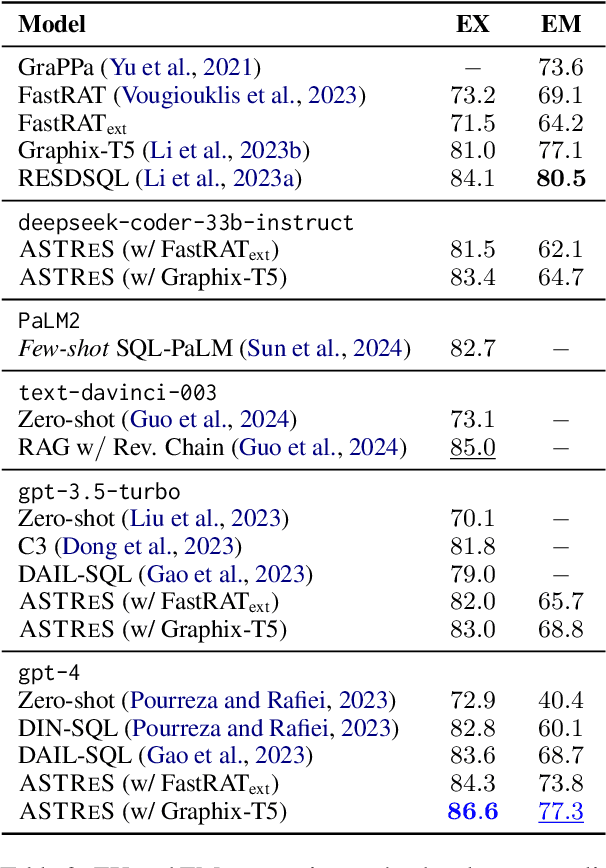

Abstract:We focus on Text-to-SQL semantic parsing from the perspective of Large Language Models. Motivated by challenges related to the size of commercial database schemata and the deployability of business intelligence solutions, we propose an approach that dynamically retrieves input database information and uses abstract syntax trees to select few-shot examples for in-context learning. Furthermore, we investigate the extent to which an in-parallel semantic parser can be leveraged for generating $\textit{approximated}$ versions of the expected SQL queries, to support our retrieval. We take this approach to the extreme--we adapt a model consisting of less than $500$M parameters, to act as an extremely efficient approximator, enhancing it with the ability to process schemata in a parallelised manner. We apply our approach to monolingual and cross-lingual benchmarks for semantic parsing, showing improvements over state-of-the-art baselines. Comprehensive experiments highlight the contribution of modules involved in this retrieval-augmented generation setting, revealing interesting directions for future work.
The Fire Thief Is Also the Keeper: Balancing Usability and Privacy in Prompts
Jun 20, 2024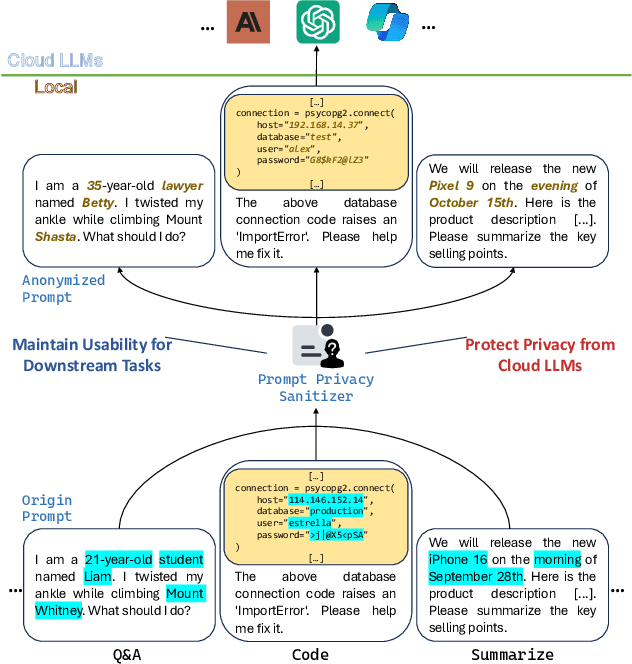
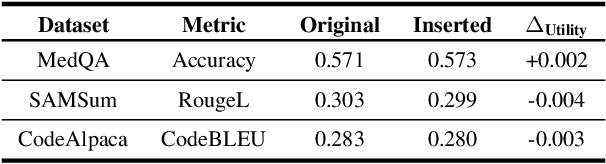
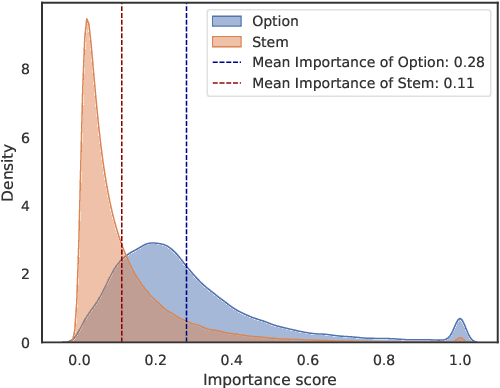
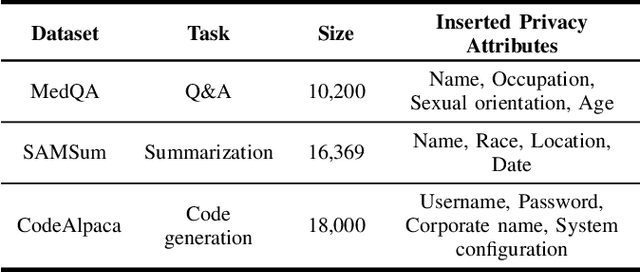
Abstract:The rapid adoption of online chatbots represents a significant advancement in artificial intelligence. However, this convenience brings considerable privacy concerns, as prompts can inadvertently contain sensitive information exposed to large language models (LLMs). Limited by high computational costs, reduced task usability, and excessive system modifications, previous works based on local deployment, embedding perturbation, and homomorphic encryption are inapplicable to online prompt-based LLM applications. To address these issues, this paper introduces Prompt Privacy Sanitizer (i.e., ProSan), an end-to-end prompt privacy protection framework that can produce anonymized prompts with contextual privacy removed while maintaining task usability and human readability. It can also be seamlessly integrated into the online LLM service pipeline. To achieve high usability and dynamic anonymity, ProSan flexibly adjusts its protection targets and strength based on the importance of the words and the privacy leakage risk of the prompts. Additionally, ProSan is capable of adapting to diverse computational resource conditions, ensuring privacy protection even for mobile devices with limited computing power. Our experiments demonstrate that ProSan effectively removes private information across various tasks, including question answering, text summarization, and code generation, with minimal reduction in task performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge