Wenxin Huang
KeenKT: Knowledge Mastery-State Disambiguation for Knowledge Tracing
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Tracing (KT) aims to dynamically model a student's mastery of knowledge concepts based on their historical learning interactions. Most current methods rely on single-point estimates, which cannot distinguish true ability from outburst or carelessness, creating ambiguity in judging mastery. To address this issue, we propose a Knowledge Mastery-State Disambiguation for Knowledge Tracing model (KeenKT), which represents a student's knowledge state at each interaction using a Normal-Inverse-Gaussian (NIG) distribution, thereby capturing the fluctuations in student learning behaviors. Furthermore, we design an NIG-distance-based attention mechanism to model the dynamic evolution of the knowledge state. In addition, we introduce a diffusion-based denoising reconstruction loss and a distributional contrastive learning loss to enhance the model's robustness. Extensive experiments on six public datasets demonstrate that KeenKT outperforms SOTA KT models in terms of prediction accuracy and sensitivity to behavioral fluctuations. The proposed method yields the maximum AUC improvement of 5.85% and the maximum ACC improvement of 6.89%.
LaoBench: A Large-Scale Multidimensional Lao Benchmark for Large Language Models
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has not been matched by their evaluation in low-resource languages, especially Southeast Asian languages like Lao. To fill this gap, we introduce LaoBench, the first large-scale, high-quality, and multidimensional benchmark dataset dedicated to assessing LLMs' comprehensive language understanding and reasoning abilities in Lao. LaoBench comprises over 17,000 carefully curated samples spanning three core dimensions: knowledge application, K12 foundational education, and bilingual translation among Lao, Chinese, and English. The dataset is divided into open-source and closed-source subsets, with the closed-source portion enabling black-box evaluation on an official platform to ensure fairness and data security. Our data construction pipeline integrates expert human curation with automated agent-assisted verification, ensuring linguistic accuracy, cultural relevance, and educational value. Benchmarking multiple state-of-the-art LLMs on LaoBench reveals that current models still face significant challenges in mastering Lao across diverse tasks. We hope LaoBench will catalyze further research and development of AI technologies for underrepresented Southeast Asian languages.
SpikeDerain: Unveiling Clear Videos from Rainy Sequences Using Color Spike Streams
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Restoring clear frames from rainy videos presents a significant challenge due to the rapid motion of rain streaks. Traditional frame-based visual sensors, which capture scene content synchronously, struggle to capture the fast-moving details of rain accurately. In recent years, neuromorphic sensors have introduced a new paradigm for dynamic scene perception, offering microsecond temporal resolution and high dynamic range. However, existing multimodal methods that fuse event streams with RGB images face difficulties in handling the complex spatiotemporal interference of raindrops in real scenes, primarily due to hardware synchronization errors and computational redundancy. In this paper, we propose a Color Spike Stream Deraining Network (SpikeDerain), capable of reconstructing spike streams of dynamic scenes and accurately removing rain streaks. To address the challenges of data scarcity in real continuous rainfall scenes, we design a physically interpretable rain streak synthesis model that generates parameterized continuous rain patterns based on arbitrary background images. Experimental results demonstrate that the network, trained with this synthetic data, remains highly robust even under extreme rainfall conditions. These findings highlight the effectiveness and robustness of our method across varying rainfall levels and datasets, setting new standards for video deraining tasks. The code will be released soon.
LLM Knows Geometry Better than Algebra: Numerical Understanding of LLM-Based Agents in A Trading Arena
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly improved performance in natural language processing tasks. However, their ability to generalize to dynamic, unseen tasks, particularly in numerical reasoning, remains a challenge. Existing benchmarks mainly evaluate LLMs on problems with predefined optimal solutions, which may not align with real-world scenarios where clear answers are absent. To bridge this gap, we design the Agent Trading Arena, a virtual numerical game simulating complex economic systems through zero-sum games, where agents invest in stock portfolios. Our experiments reveal that LLMs, including GPT-4o, struggle with algebraic reasoning when dealing with plain-text stock data, often focusing on local details rather than global trends. In contrast, LLMs perform significantly better with geometric reasoning when presented with visual data, such as scatter plots or K-line charts, suggesting that visual representations enhance numerical reasoning. This capability is further improved by incorporating the reflection module, which aids in the analysis and interpretation of complex data. We validate our findings on NASDAQ Stock dataset, where LLMs demonstrate stronger reasoning with visual data compared to text. Our code and data are publicly available at https://github.com/wekjsdvnm/Agent-Trading-Arena.git.
See What You Seek: Semantic Contextual Integration for Cloth-Changing Person Re-Identification
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Cloth-changing person re-identification (CC-ReID) aims to match individuals across multiple surveillance cameras despite variations in clothing. Existing methods typically focus on mitigating the effects of clothing changes or enhancing ID-relevant features but often struggle to capture complex semantic information. In this paper, we propose a novel prompt learning framework, Semantic Contextual Integration (SCI), for CC-ReID, which leverages the visual-text representation capabilities of CLIP to minimize the impact of clothing changes and enhance ID-relevant features. Specifically, we introduce Semantic Separation Enhancement (SSE) module, which uses dual learnable text tokens to separately capture confounding and clothing-related semantic information, effectively isolating ID-relevant features from distracting clothing semantics. Additionally, we develop a Semantic-Guided Interaction Module (SIM) that uses orthogonalized text features to guide visual representations, sharpening the model's focus on distinctive ID characteristics. This integration enhances the model's discriminative power and enriches the visual context with high-dimensional semantic insights. Extensive experiments on three CC-ReID datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques. The code will be released at github.
OccludeNet: A Causal Journey into Mixed-View Actor-Centric Video Action Recognition under Occlusions
Nov 24, 2024Abstract:The lack of occlusion data in commonly used action recognition video datasets limits model robustness and impedes sustained performance improvements. We construct OccludeNet, a large-scale occluded video dataset that includes both real-world and synthetic occlusion scene videos under various natural environments. OccludeNet features dynamic tracking occlusion, static scene occlusion, and multi-view interactive occlusion, addressing existing gaps in data. Our analysis reveals that occlusion impacts action classes differently, with actions involving low scene relevance and partial body visibility experiencing greater accuracy degradation. To overcome the limitations of current occlusion-focused approaches, we propose a structural causal model for occluded scenes and introduce the Causal Action Recognition (CAR) framework, which employs backdoor adjustment and counterfactual reasoning. This framework enhances key actor information, improving model robustness to occlusion. We anticipate that the challenges posed by OccludeNet will stimulate further exploration of causal relations in occlusion scenarios and encourage a reevaluation of class correlations, ultimately promoting sustainable performance improvements. The code and full dataset will be released soon.
Diversity-Driven Synthesis: Enhancing Dataset Distillation through Directed Weight Adjustment
Sep 26, 2024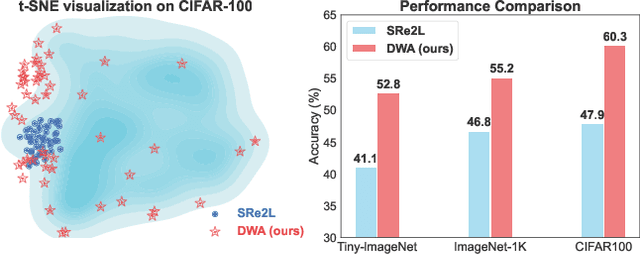
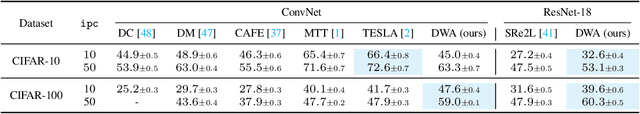
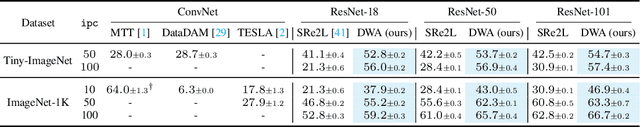
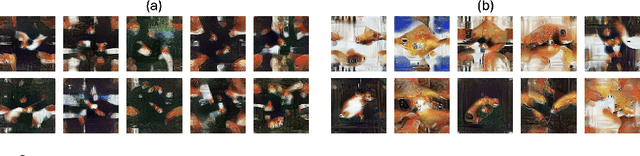
Abstract:The sharp increase in data-related expenses has motivated research into condensing datasets while retaining the most informative features. Dataset distillation has thus recently come to the fore. This paradigm generates synthetic dataset that are representative enough to replace the original dataset in training a neural network. To avoid redundancy in these synthetic datasets, it is crucial that each element contains unique features and remains diverse from others during the synthesis stage. In this paper, we provide a thorough theoretical and empirical analysis of diversity within synthesized datasets. We argue that enhancing diversity can improve the parallelizable yet isolated synthesizing approach. Specifically, we introduce a novel method that employs dynamic and directed weight adjustment techniques to modulate the synthesis process, thereby maximizing the representativeness and diversity of each synthetic instance. Our method ensures that each batch of synthetic data mirrors the characteristics of a large, varying subset of the original dataset. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets, including CIFAR, Tiny-ImageNet, and ImageNet-1K, demonstrate the superior performance of our method, highlighting its effectiveness in producing diverse and representative synthetic datasets with minimal computational expense.
Dynamic Association Learning of Self-Attention and Convolution in Image Restoration
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:CNNs and Self attention have achieved great success in multimedia applications for dynamic association learning of self-attention and convolution in image restoration. However, CNNs have at least two shortcomings: 1) limited receptive field; 2) static weight of sliding window at inference, unable to cope with the content diversity.In view of the advantages and disadvantages of CNNs and Self attention, this paper proposes an association learning method to utilize the advantages and suppress their shortcomings, so as to achieve high-quality and efficient inpainting. We regard rain distribution reflects the degradation location and degree, in addition to the rain distribution prediction. Thus, we propose to refine background textures with the predicted degradation prior in an association learning manner. As a result, we accomplish image deraining by associating rain streak removal and background recovery, where an image deraining network and a background recovery network are designed for two subtasks. The key part of association learning is a novel multi-input attention module. It generates the degradation prior and produces the degradation mask according to the predicted rainy distribution. Benefited from the global correlation calculation of SA, MAM can extract the informative complementary components from the rainy input with the degradation mask, and then help accurate texture restoration. Meanwhile, SA tends to aggregate feature maps with self-attention importance, but convolution diversifies them to focus on the local textures. A hybrid fusion network involves one residual Transformer branch and one encoder-decoder branch. The former takes a few learnable tokens as input and stacks multi-head attention and feed-forward networks to encode global features of the image. The latter, conversely, leverages the multi-scale encoder-decoder to represent contexture knowledge.
Complementing Representation Deficiency in Few-shot Image Classification: A Meta-Learning Approach
Jul 21, 2020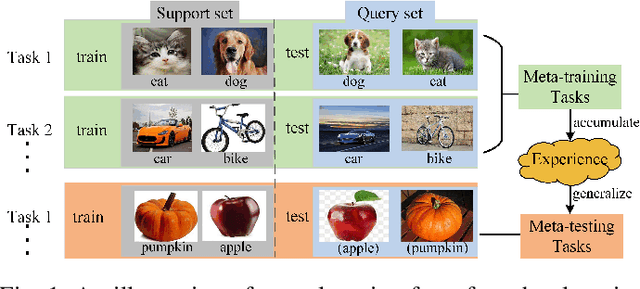
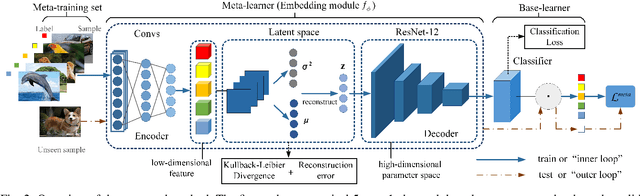
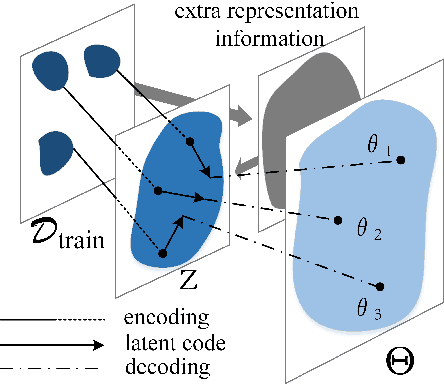
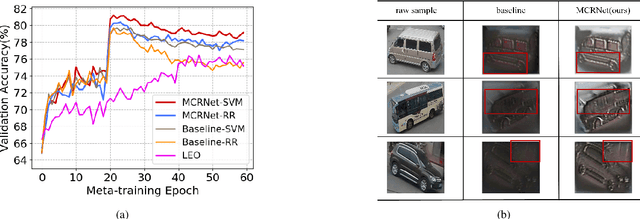
Abstract:Few-shot learning is a challenging problem that has attracted more and more attention recently since abundant training samples are difficult to obtain in practical applications. Meta-learning has been proposed to address this issue, which focuses on quickly adapting a predictor as a base-learner to new tasks, given limited labeled samples. However, a critical challenge for meta-learning is the representation deficiency since it is hard to discover common information from a small number of training samples or even one, as is the representation of key features from such little information. As a result, a meta-learner cannot be trained well in a high-dimensional parameter space to generalize to new tasks. Existing methods mostly resort to extracting less expressive features so as to avoid the representation deficiency. Aiming at learning better representations, we propose a meta-learning approach with complemented representations network (MCRNet) for few-shot image classification. In particular, we embed a latent space, where latent codes are reconstructed with extra representation information to complement the representation deficiency. Furthermore, the latent space is established with variational inference, collaborating well with different base-learners, and can be extended to other models. Finally, our end-to-end framework achieves the state-of-the-art performance in image classification on three standard few-shot learning datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge