Chenggang Yan
Salient Object Detection in Complex Weather Conditions via Noise Indicators
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Salient object detection (SOD), a foundational task in computer vision, has advanced from single-modal to multi-modal paradigms to enhance generalization. However, most existing SOD methods assume low-noise visual conditions, overlooking the degradation of segmentation accuracy caused by weather-induced noise in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose a SOD framework tailored for diverse weather conditions, encompassing a specific encoder and a replaceable decoder. To enable handling of varying weather noises, we introduce a one-hot vector as a noise indicator to represent different weather types and design a Noise Indicator Fusion Module (NIFM). The NIFM takes both semantic features and the noise indicator as dual inputs and is inserted between consecutive stages of the encoder to embed weather-aware priors via adaptive feature modulation. Critically, the proposed specific encoder retains compatibility with mainstream SOD decoders. Extensive experiments are conducted on the WXSOD dataset under varying training data scales (100%, 50%, 30% of the full training set), three encoder and seven decoder configurations. Results show that the proposed SOD framework (particularly the NIFM-enhanced specific encoder) improves segmentation accuracy under complex weather conditions compared to a vanilla encoder.
K-Buffers: A Plug-in Method for Enhancing Neural Fields with Multiple Buffers
May 26, 2025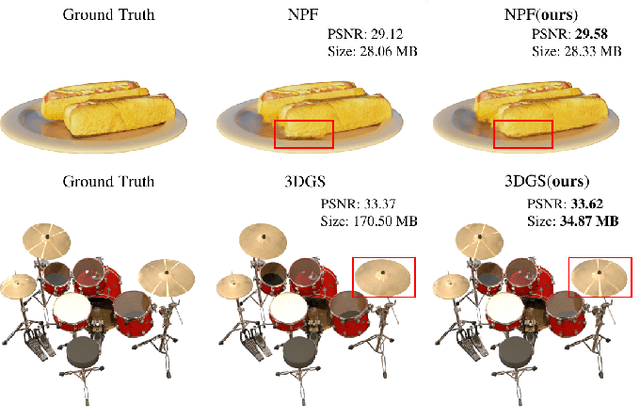
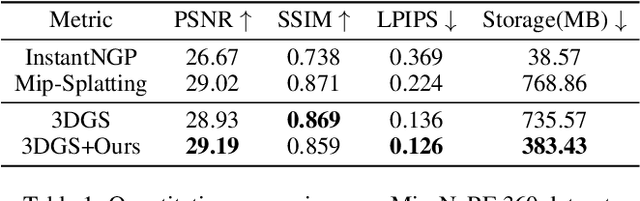
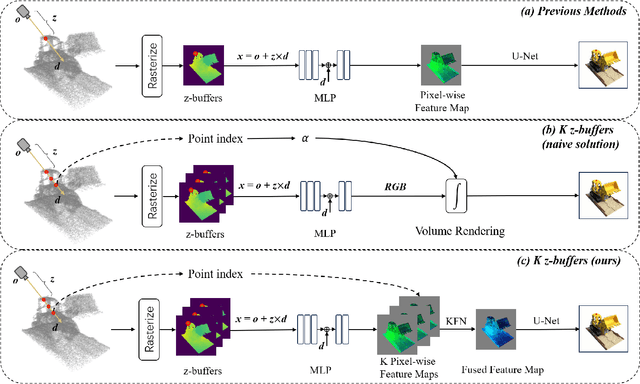
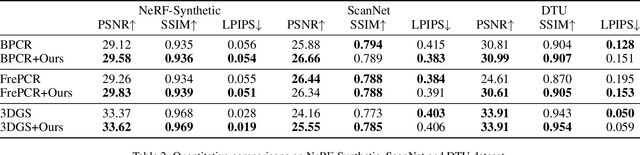
Abstract:Neural fields are now the central focus of research in 3D vision and computer graphics. Existing methods mainly focus on various scene representations, such as neural points and 3D Gaussians. However, few works have studied the rendering process to enhance the neural fields. In this work, we propose a plug-in method named K-Buffers that leverages multiple buffers to improve the rendering performance. Our method first renders K buffers from scene representations and constructs K pixel-wise feature maps. Then, We introduce a K-Feature Fusion Network (KFN) to merge the K pixel-wise feature maps. Finally, we adopt a feature decoder to generate the rendering image. We also introduce an acceleration strategy to improve rendering speed and quality. We apply our method to well-known radiance field baselines, including neural point fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method effectively enhances the rendering performance of neural point fields and 3DGS.
Progressive Inertial Poser: Progressive Real-Time Kinematic Chain Estimation for 3D Full-Body Pose from Three IMU Sensors
May 08, 2025Abstract:The motion capture system that supports full-body virtual representation is of key significance for virtual reality. Compared to vision-based systems, full-body pose estimation from sparse tracking signals is not limited by environmental conditions or recording range. However, previous works either face the challenge of wearing additional sensors on the pelvis and lower-body or rely on external visual sensors to obtain global positions of key joints. To improve the practicality of the technology for virtual reality applications, we estimate full-body poses using only inertial data obtained from three Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensors worn on the head and wrists, thereby reducing the complexity of the hardware system. In this work, we propose a method called Progressive Inertial Poser (ProgIP) for human pose estimation, which combines neural network estimation with a human dynamics model, considers the hierarchical structure of the kinematic chain, and employs a multi-stage progressive network estimation with increased depth to reconstruct full-body motion in real time. The encoder combines Transformer Encoder and bidirectional LSTM (TE-biLSTM) to flexibly capture the temporal dependencies of the inertial sequence, while the decoder based on multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs) transforms high-dimensional features and accurately projects them onto Skinned Multi-Person Linear (SMPL) model parameters. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results on multiple public datasets show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods with the same inputs, and is comparable to recent works using six IMU sensors.
VGNC: Reducing the Overfitting of Sparse-view 3DGS via Validation-guided Gaussian Number Control
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Sparse-view 3D reconstruction is a fundamental yet challenging task in practical 3D reconstruction applications. Recently, many methods based on the 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework have been proposed to address sparse-view 3D reconstruction. Although these methods have made considerable advancements, they still show significant issues with overfitting. To reduce the overfitting, we introduce VGNC, a novel Validation-guided Gaussian Number Control (VGNC) approach based on generative novel view synthesis (NVS) models. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to alleviate the overfitting issue of sparse-view 3DGS with generative validation images. Specifically, we first introduce a validation image generation method based on a generative NVS model. We then propose a Gaussian number control strategy that utilizes generated validation images to determine the optimal Gaussian numbers, thereby reducing the issue of overfitting. We conducted detailed experiments on various sparse-view 3DGS baselines and datasets to evaluate the effectiveness of VGNC. Extensive experiments show that our approach not only reduces overfitting but also improves rendering quality on the test set while decreasing the number of Gaussian points. This reduction lowers storage demands and accelerates both training and rendering. The code will be released.
Frequency Dynamic Convolution for Dense Image Prediction
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:While Dynamic Convolution (DY-Conv) has shown promising performance by enabling adaptive weight selection through multiple parallel weights combined with an attention mechanism, the frequency response of these weights tends to exhibit high similarity, resulting in high parameter costs but limited adaptability. In this work, we introduce Frequency Dynamic Convolution (FDConv), a novel approach that mitigates these limitations by learning a fixed parameter budget in the Fourier domain. FDConv divides this budget into frequency-based groups with disjoint Fourier indices, enabling the construction of frequency-diverse weights without increasing the parameter cost. To further enhance adaptability, we propose Kernel Spatial Modulation (KSM) and Frequency Band Modulation (FBM). KSM dynamically adjusts the frequency response of each filter at the spatial level, while FBM decomposes weights into distinct frequency bands in the frequency domain and modulates them dynamically based on local content. Extensive experiments on object detection, segmentation, and classification validate the effectiveness of FDConv. We demonstrate that when applied to ResNet-50, FDConv achieves superior performance with a modest increase of +3.6M parameters, outperforming previous methods that require substantial increases in parameter budgets (e.g., CondConv +90M, KW +76.5M). Moreover, FDConv seamlessly integrates into a variety of architectures, including ConvNeXt, Swin-Transformer, offering a flexible and efficient solution for modern vision tasks. The code is made publicly available at https://github.com/Linwei-Chen/FDConv.
Prosody-Enhanced Acoustic Pre-training and Acoustic-Disentangled Prosody Adapting for Movie Dubbing
Mar 15, 2025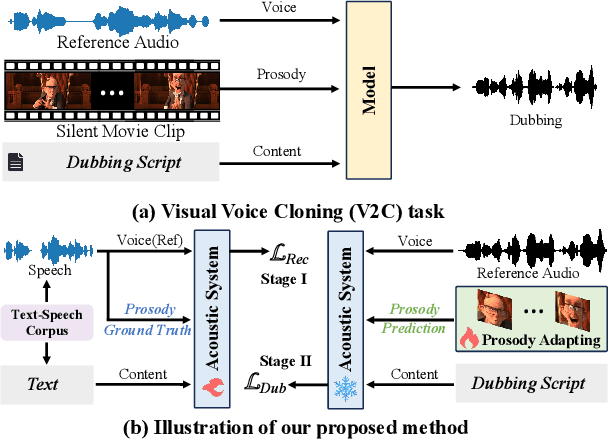

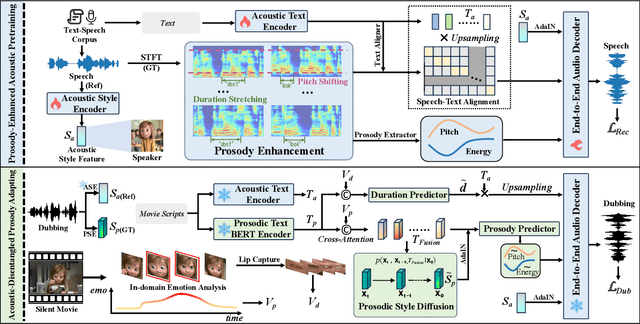

Abstract:Movie dubbing describes the process of transforming a script into speech that aligns temporally and emotionally with a given movie clip while exemplifying the speaker's voice demonstrated in a short reference audio clip. This task demands the model bridge character performances and complicated prosody structures to build a high-quality video-synchronized dubbing track. The limited scale of movie dubbing datasets, along with the background noise inherent in audio data, hinder the acoustic modeling performance of trained models. To address these issues, we propose an acoustic-prosody disentangled two-stage method to achieve high-quality dubbing generation with precise prosody alignment. First, we propose a prosody-enhanced acoustic pre-training to develop robust acoustic modeling capabilities. Then, we freeze the pre-trained acoustic system and design a disentangled framework to model prosodic text features and dubbing style while maintaining acoustic quality. Additionally, we incorporate an in-domain emotion analysis module to reduce the impact of visual domain shifts across different movies, thereby enhancing emotion-prosody alignment. Extensive experiments show that our method performs favorably against the state-of-the-art models on two primary benchmarks. The demos are available at https://zzdoog.github.io/ProDubber/.
Relative Distance Guided Dynamic Partition Learning for Scale-Invariant UAV-View Geo-Localization
Dec 23, 2024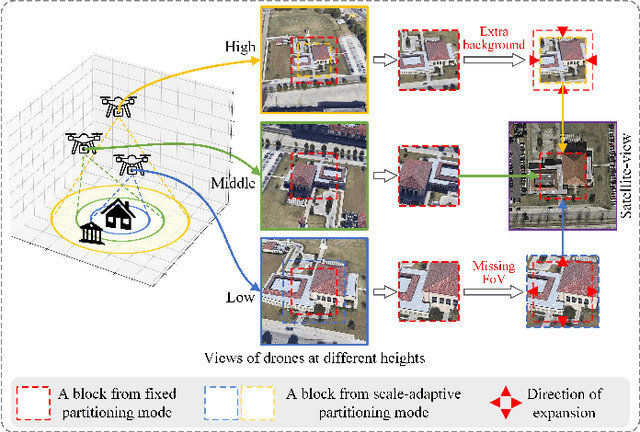
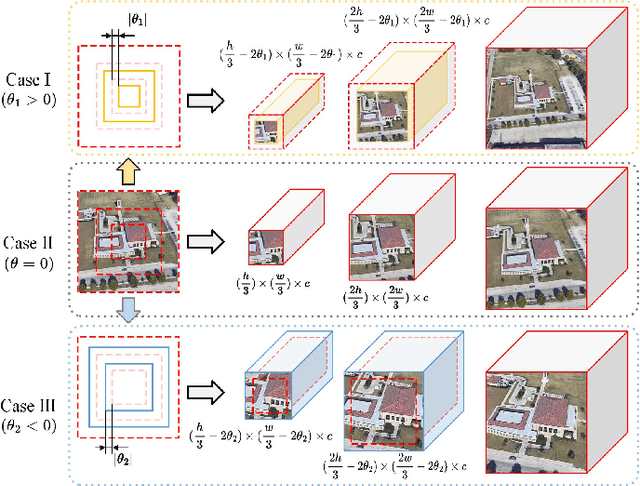
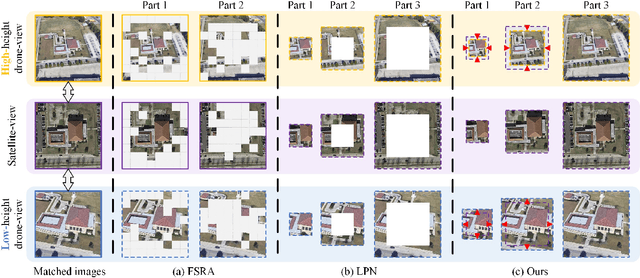
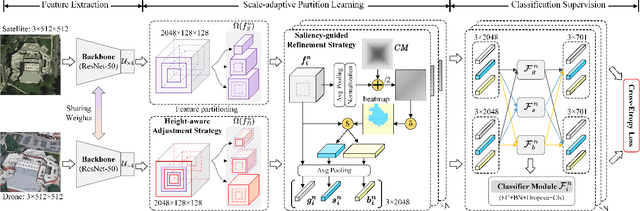
Abstract:UAV-view Geo-Localization~(UVGL) presents substantial challenges, particularly due to the disparity in visual appearance between drone-captured imagery and satellite perspectives. Existing methods usually assume consistent scaling factor across different views. Therefore, they adopt predefined partition alignment and extract viewpoint-invariant representation by constructing a variety of part-level features. However, the scaling assumption is not always hold in the real-world scenarios that variations of UAV flight state leads to the scale mismatch of cross-views, resulting in serious performance degradation. To overcome this issue, we propose a partition learning framework based on relative distance, which alleviates the dependence on scale consistency while mining fine-grained features. Specifically, we propose a distance guided dynamic partition learning strategy~(DGDPL), consisting of a square partition strategy and a distance-guided adjustment strategy. The former is utilized to extract fine-grained features and global features in a simple manner. The latter calculates the relative distance ratio between drone- and satellite-view to adjust the partition size, thereby explicitly aligning the semantic information between partition pairs. Furthermore, we propose a saliency-guided refinement strategy to refine part-level features, so as to further improve the retrieval accuracy. Extensive experiments show that our approach achieves superior geo-localization accuracy across various scale-inconsistent scenarios, and exhibits remarkable robustness against scale variations. The code will be released.
Near Large Far Small: Relative Distance Based Partition Learning for UAV-view Geo-Localization
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:UAV-view Geo-Localization (UVGL) presents substantial challenges, primarily due to appearance differences between drone-view and satellite-view. Existing methods develop partition learning strategies aimed at mining more comprehensive information by constructing diverse part-level feature representations, which rely on consistent cross-view scales. However, variations of UAV flight state leads to the scale mismatch of cross-views, resulting in serious performance degradation of partition-based methods. To overcome this issue, we propose a partition learning framework based on relative distance, which alleviates the dependence on scale consistency while mining fine-grained features. Specifically, we propose a distance guided dynamic partition learning strategy (DGDPL), consisting of a square partition strategy and a dynamic-guided adjustment strategy. The former is utilized to extract fine-grained features and global features in a simple manner. The latter calculates the relative distance ratio between drone- and satellite-view to adjust the partition size, thereby aligning the semantic information between partition pairs. Furthermore, we propose a saliency-guided refinement strategy to refine part-level features, so as to further improve the retrieval accuracy. Extensive experiments show that our approach achieves superior geo-localization accuracy across various scale-inconsistent scenarios, and exhibits remarkable robustness against scale variations. The code will be released.
Multi-Granularity Class Prototype Topology Distillation for Class-Incremental Source-Free Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Nov 25, 2024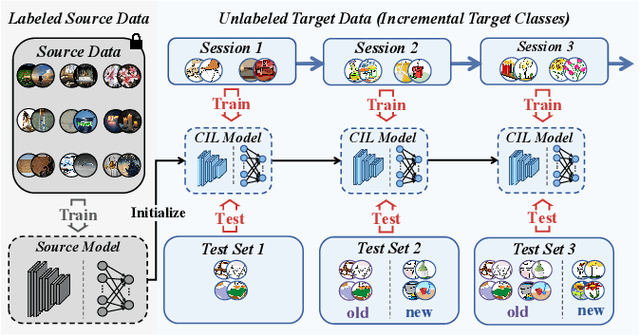

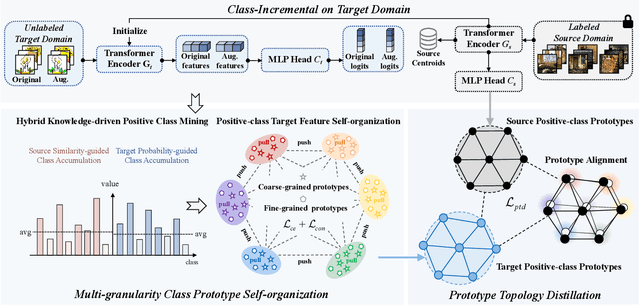

Abstract:This paper explores the Class-Incremental Source-Free Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (CI-SFUDA) problem, where the unlabeled target data come incrementally without access to labeled source instances. This problem poses two challenges, the disturbances of similar source-class knowledge to target-class representation learning and the new target knowledge to old ones. To address them, we propose the Multi-Granularity Class Prototype Topology Distillation (GROTO) algorithm, which effectively transfers the source knowledge to the unlabeled class-incremental target domain. Concretely, we design the multi-granularity class prototype self-organization module and prototype topology distillation module. Firstly, the positive classes are mined by modeling two accumulation distributions. Then, we generate reliable pseudo-labels by introducing multi-granularity class prototypes, and use them to promote the positive-class target feature self-organization. Secondly, the positive-class prototypes are leveraged to construct the topological structures of source and target feature spaces. Then, we perform the topology distillation to continually mitigate the interferences of new target knowledge to old ones. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performances on three public datasets.
It Takes Two: Accurate Gait Recognition in the Wild via Cross-granularity Alignment
Nov 16, 2024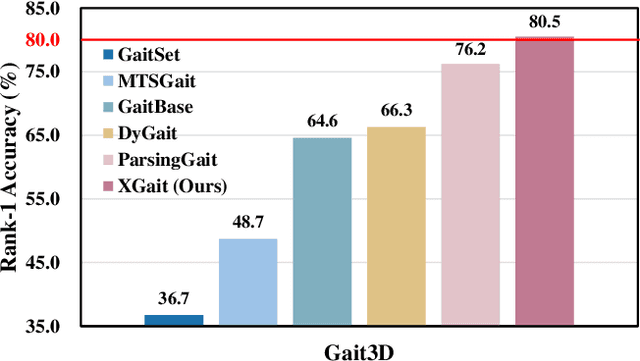
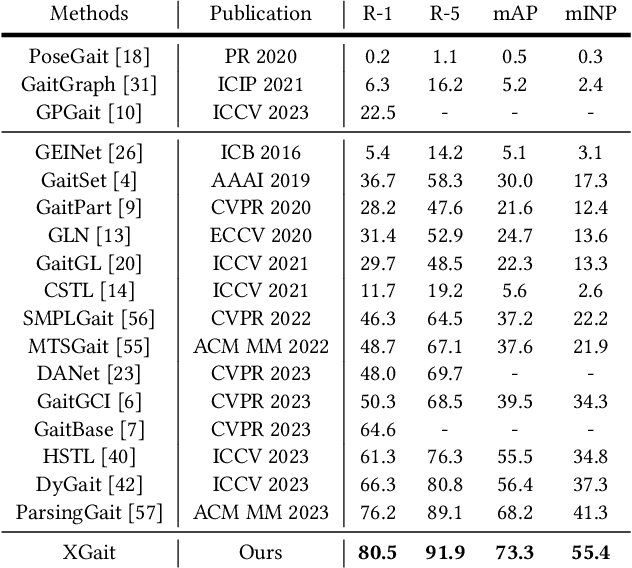
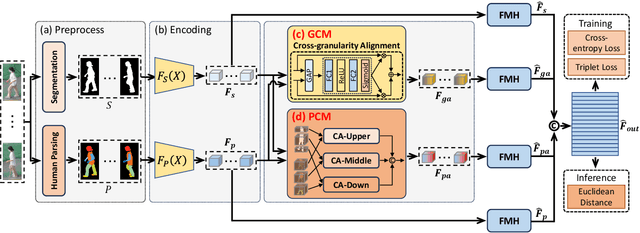
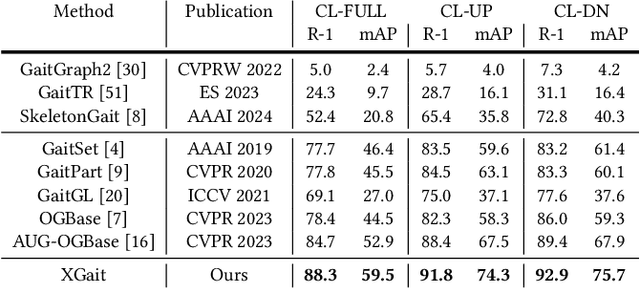
Abstract:Existing studies for gait recognition primarily utilized sequences of either binary silhouette or human parsing to encode the shapes and dynamics of persons during walking. Silhouettes exhibit accurate segmentation quality and robustness to environmental variations, but their low information entropy may result in sub-optimal performance. In contrast, human parsing provides fine-grained part segmentation with higher information entropy, but the segmentation quality may deteriorate due to the complex environments. To discover the advantages of silhouette and parsing and overcome their limitations, this paper proposes a novel cross-granularity alignment gait recognition method, named XGait, to unleash the power of gait representations of different granularity. To achieve this goal, the XGait first contains two branches of backbone encoders to map the silhouette sequences and the parsing sequences into two latent spaces, respectively. Moreover, to explore the complementary knowledge across the features of two representations, we design the Global Cross-granularity Module (GCM) and the Part Cross-granularity Module (PCM) after the two encoders. In particular, the GCM aims to enhance the quality of parsing features by leveraging global features from silhouettes, while the PCM aligns the dynamics of human parts between silhouette and parsing features using the high information entropy in parsing sequences. In addition, to effectively guide the alignment of two representations with different granularity at the part level, an elaborate-designed learnable division mechanism is proposed for the parsing features. Comprehensive experiments on two large-scale gait datasets not only show the superior performance of XGait with the Rank-1 accuracy of 80.5% on Gait3D and 88.3% CCPG but also reflect the robustness of the learned features even under challenging conditions like occlusions and cloth changes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge