Tingyu Wang
Salient Object Detection in Complex Weather Conditions via Noise Indicators
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Salient object detection (SOD), a foundational task in computer vision, has advanced from single-modal to multi-modal paradigms to enhance generalization. However, most existing SOD methods assume low-noise visual conditions, overlooking the degradation of segmentation accuracy caused by weather-induced noise in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose a SOD framework tailored for diverse weather conditions, encompassing a specific encoder and a replaceable decoder. To enable handling of varying weather noises, we introduce a one-hot vector as a noise indicator to represent different weather types and design a Noise Indicator Fusion Module (NIFM). The NIFM takes both semantic features and the noise indicator as dual inputs and is inserted between consecutive stages of the encoder to embed weather-aware priors via adaptive feature modulation. Critically, the proposed specific encoder retains compatibility with mainstream SOD decoders. Extensive experiments are conducted on the WXSOD dataset under varying training data scales (100%, 50%, 30% of the full training set), three encoder and seven decoder configurations. Results show that the proposed SOD framework (particularly the NIFM-enhanced specific encoder) improves segmentation accuracy under complex weather conditions compared to a vanilla encoder.
Optimizing Data Distribution and Kernel Performance for Efficient Training of Chemistry Foundation Models: A Case Study with MACE
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:Chemistry Foundation Models (CFMs) that leverage Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) operating on 3D molecular graph structures are becoming indispensable tools for computational chemists and materials scientists. These models facilitate the understanding of matter and the discovery of new molecules and materials. In contrast to GNNs operating on a large homogeneous graphs, GNNs used by CFMs process a large number of geometric graphs of varying sizes, requiring different optimization strategies than those developed for large homogeneous GNNs. This paper presents optimizations for two critical phases of CFM training: data distribution and model training, targeting MACE - a state-of-the-art CFM. We address the challenge of load balancing in data distribution by formulating it as a multi-objective bin packing problem. We propose an iterative algorithm that provides a highly effective, fast, and practical solution, ensuring efficient data distribution. For the training phase, we identify symmetric tensor contraction as the key computational kernel in MACE and optimize this kernel to improve the overall performance. Our combined approach of balanced data distribution and kernel optimization significantly enhances the training process of MACE. Experimental results demonstrate a substantial speedup, reducing per-epoch execution time for training from 12 to 2 minutes on 740 GPUs with a 2.6M sample dataset.
Relative Distance Guided Dynamic Partition Learning for Scale-Invariant UAV-View Geo-Localization
Dec 23, 2024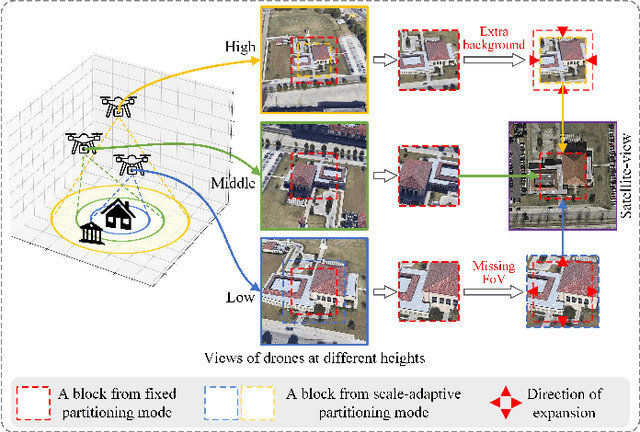
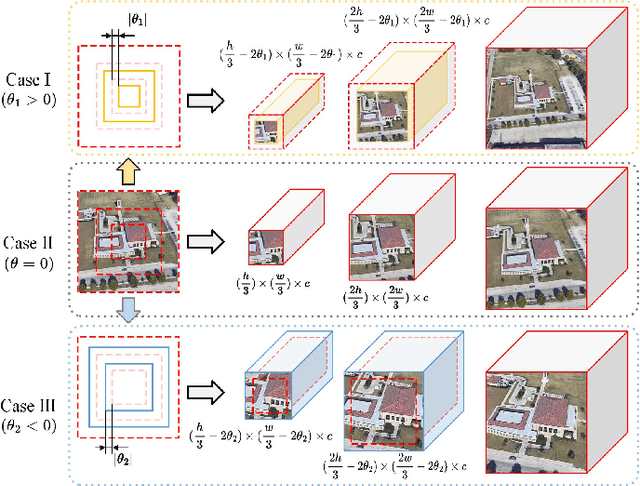
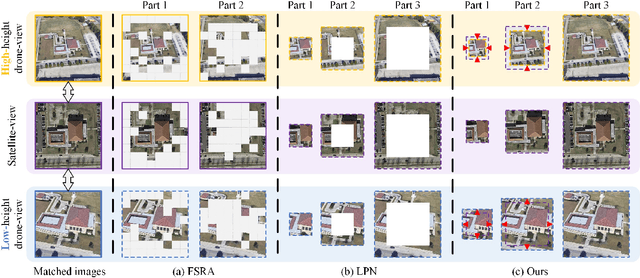
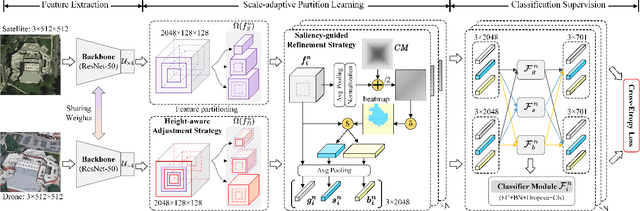
Abstract:UAV-view Geo-Localization~(UVGL) presents substantial challenges, particularly due to the disparity in visual appearance between drone-captured imagery and satellite perspectives. Existing methods usually assume consistent scaling factor across different views. Therefore, they adopt predefined partition alignment and extract viewpoint-invariant representation by constructing a variety of part-level features. However, the scaling assumption is not always hold in the real-world scenarios that variations of UAV flight state leads to the scale mismatch of cross-views, resulting in serious performance degradation. To overcome this issue, we propose a partition learning framework based on relative distance, which alleviates the dependence on scale consistency while mining fine-grained features. Specifically, we propose a distance guided dynamic partition learning strategy~(DGDPL), consisting of a square partition strategy and a distance-guided adjustment strategy. The former is utilized to extract fine-grained features and global features in a simple manner. The latter calculates the relative distance ratio between drone- and satellite-view to adjust the partition size, thereby explicitly aligning the semantic information between partition pairs. Furthermore, we propose a saliency-guided refinement strategy to refine part-level features, so as to further improve the retrieval accuracy. Extensive experiments show that our approach achieves superior geo-localization accuracy across various scale-inconsistent scenarios, and exhibits remarkable robustness against scale variations. The code will be released.
Near Large Far Small: Relative Distance Based Partition Learning for UAV-view Geo-Localization
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:UAV-view Geo-Localization (UVGL) presents substantial challenges, primarily due to appearance differences between drone-view and satellite-view. Existing methods develop partition learning strategies aimed at mining more comprehensive information by constructing diverse part-level feature representations, which rely on consistent cross-view scales. However, variations of UAV flight state leads to the scale mismatch of cross-views, resulting in serious performance degradation of partition-based methods. To overcome this issue, we propose a partition learning framework based on relative distance, which alleviates the dependence on scale consistency while mining fine-grained features. Specifically, we propose a distance guided dynamic partition learning strategy (DGDPL), consisting of a square partition strategy and a dynamic-guided adjustment strategy. The former is utilized to extract fine-grained features and global features in a simple manner. The latter calculates the relative distance ratio between drone- and satellite-view to adjust the partition size, thereby aligning the semantic information between partition pairs. Furthermore, we propose a saliency-guided refinement strategy to refine part-level features, so as to further improve the retrieval accuracy. Extensive experiments show that our approach achieves superior geo-localization accuracy across various scale-inconsistent scenarios, and exhibits remarkable robustness against scale variations. The code will be released.
The Impact of Scanner Domain Shift on Deep Learning Performance in Medical Imaging: an Experimental Study
Sep 06, 2024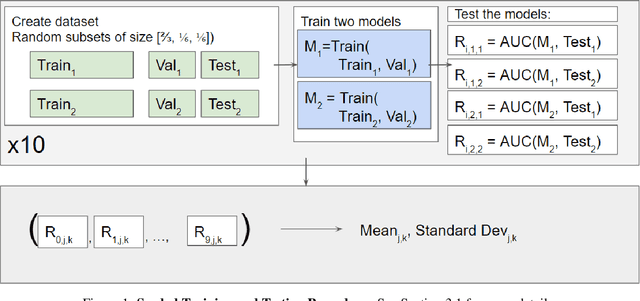
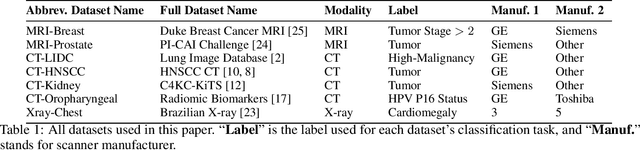
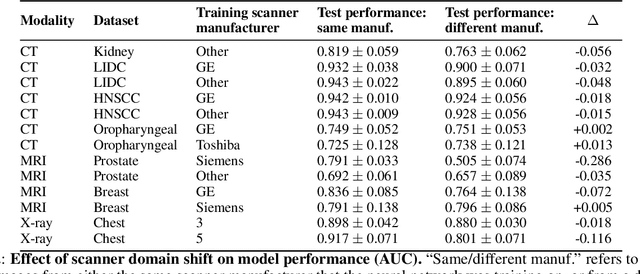
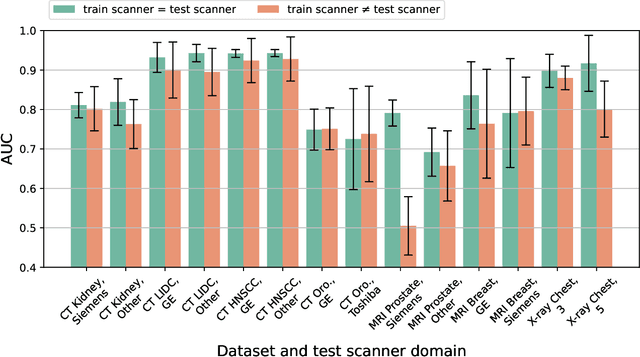
Abstract:Purpose: Medical images acquired using different scanners and protocols can differ substantially in their appearance. This phenomenon, scanner domain shift, can result in a drop in the performance of deep neural networks which are trained on data acquired by one scanner and tested on another. This significant practical issue is well-acknowledged, however, no systematic study of the issue is available across different modalities and diagnostic tasks. Materials and Methods: In this paper, we present a broad experimental study evaluating the impact of scanner domain shift on convolutional neural network performance for different automated diagnostic tasks. We evaluate this phenomenon in common radiological modalities, including X-ray, CT, and MRI. Results: We find that network performance on data from a different scanner is almost always worse than on same-scanner data, and we quantify the degree of performance drop across different datasets. Notably, we find that this drop is most severe for MRI, moderate for X-ray, and quite small for CT, on average, which we attribute to the standardized nature of CT acquisition systems which is not present in MRI or X-ray. We also study how injecting varying amounts of target domain data into the training set, as well as adding noise to the training data, helps with generalization. Conclusion: Our results provide extensive experimental evidence and quantification of the extent of performance drop caused by scanner domain shift in deep learning across different modalities, with the goal of guiding the future development of robust deep learning models for medical image analysis.
SDPL: Shifting-Dense Partition Learning for UAV-View Geo-Localization
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:Cross-view geo-localization aims to match images of the same target from different platforms, e.g., drone and satellite. It is a challenging task due to the changing both appearance of targets and environmental content from different views. Existing methods mainly focus on digging more comprehensive information through feature maps segmentation, while inevitably destroy the image structure and are sensitive to the shifting and scale of the target in the query. To address the above issues, we introduce a simple yet effective part-based representation learning, called shifting-dense partition learning (SDPL). Specifically, we propose the dense partition strategy (DPS), which divides the image into multiple parts to explore contextual-information while explicitly maintain the global structure. To handle scenarios with non-centered targets, we further propose the shifting-fusion strategy, which generates multiple sets of parts in parallel based on various segmentation centers and then adaptively fuses all features to select the best partitions. Extensive experiments show that our SDPL is robust to position shifting and scale variations, and achieves competitive performance on two prevailing benchmarks, i.e., University-1652 and SUES-200.
Deep learning radiomics for assessment of gastroesophageal varices in people with compensated advanced chronic liver disease
Jun 13, 2023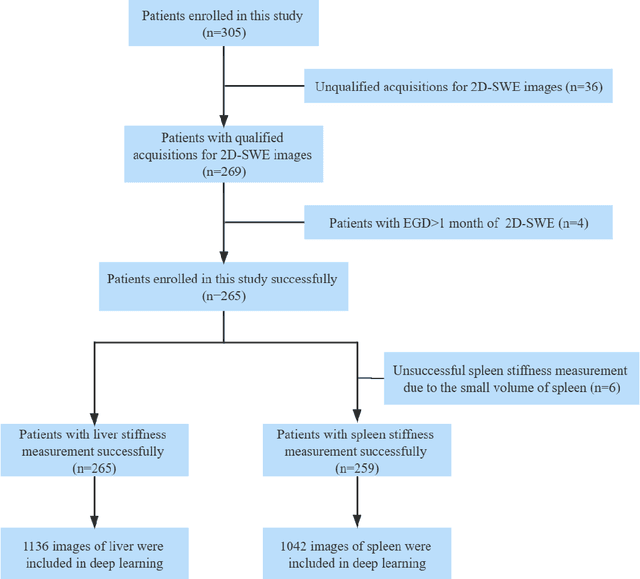
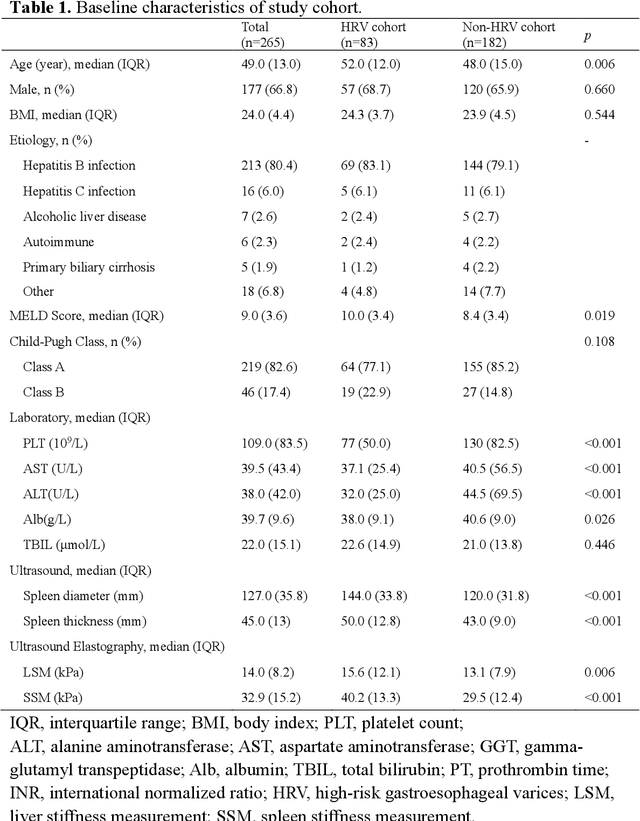
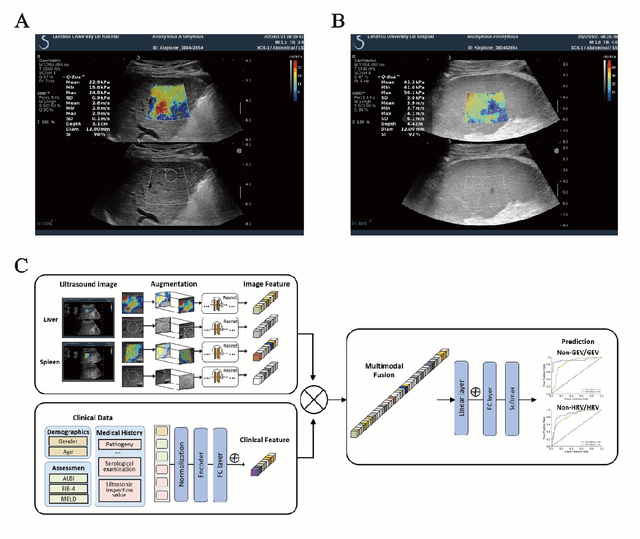
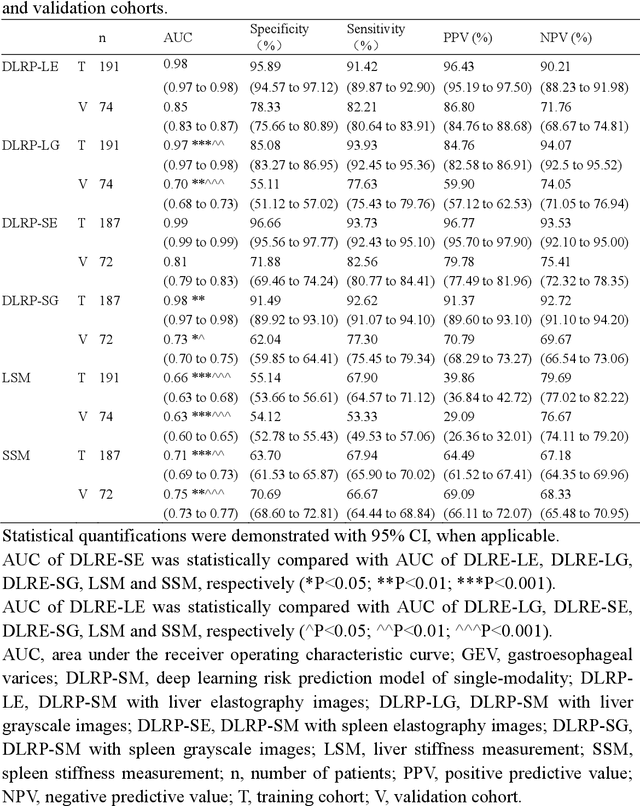
Abstract:Objective: Bleeding from gastroesophageal varices (GEV) is a medical emergency associated with high mortality. We aim to construct an artificial intelligence-based model of two-dimensional shear wave elastography (2D-SWE) of the liver and spleen to precisely assess the risk of GEV and high-risk gastroesophageal varices (HRV). Design: A prospective multicenter study was conducted in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease. 305 patients were enrolled from 12 hospitals, and finally 265 patients were included, with 1136 liver stiffness measurement (LSM) images and 1042 spleen stiffness measurement (SSM) images generated by 2D-SWE. We leveraged deep learning methods to uncover associations between image features and patient risk, and thus conducted models to predict GEV and HRV. Results: A multi-modality Deep Learning Risk Prediction model (DLRP) was constructed to assess GEV and HRV, based on LSM and SSM images, and clinical information. Validation analysis revealed that the AUCs of DLRP were 0.91 for GEV (95% CI 0.90 to 0.93, p < 0.05) and 0.88 for HRV (95% CI 0.86 to 0.89, p < 0.01), which were significantly and robustly better than canonical risk indicators, including the value of LSM and SSM. Moreover, DLPR was better than the model using individual parameters, including LSM and SSM images. In HRV prediction, the 2D-SWE images of SSM outperform LSM (p < 0.01). Conclusion: DLRP shows excellent performance in predicting GEV and HRV over canonical risk indicators LSM and SSM. Additionally, the 2D-SWE images of SSM provided more information for better accuracy in predicting HRV than the LSM.
Learning Cross-view Geo-localization Embeddings via Dynamic Weighted Decorrelation Regularization
Nov 10, 2022Abstract:Cross-view geo-localization aims to spot images of the same location shot from two platforms, e.g., the drone platform and the satellite platform. Existing methods usually focus on optimizing the distance between one embedding with others in the feature space, while neglecting the redundancy of the embedding itself. In this paper, we argue that the low redundancy is also of importance, which motivates the model to mine more diverse patterns. To verify this point, we introduce a simple yet effective regularization, i.e., Dynamic Weighted Decorrelation Regularization (DWDR), to explicitly encourage networks to learn independent embedding channels. As the name implies, DWDR regresses the embedding correlation coefficient matrix to a sparse matrix, i.e., the identity matrix, with dynamic weights. The dynamic weights are applied to focus on still correlated channels during training. Besides, we propose a cross-view symmetric sampling strategy, which keeps the example balance between different platforms. Albeit simple, the proposed method has achieved competitive results on three large-scale benchmarks, i.e., University-1652, CVUSA and CVACT. Moreover, under the harsh circumstance, e.g., the extremely short feature of 64 dimensions, the proposed method surpasses the baseline model by a clear margin.
Multiple-environment Self-adaptive Network for Aerial-view Geo-localization
Apr 18, 2022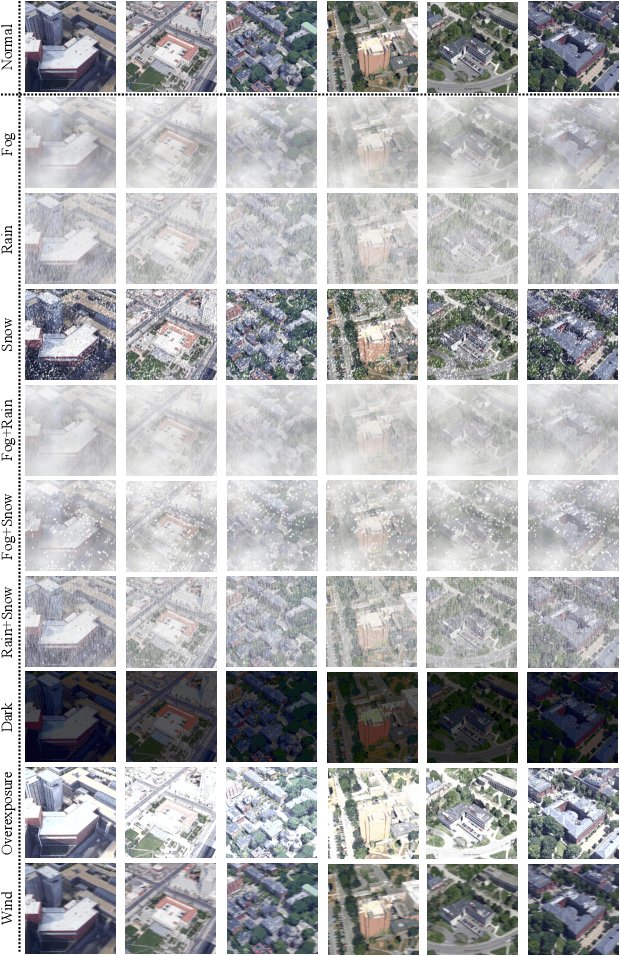

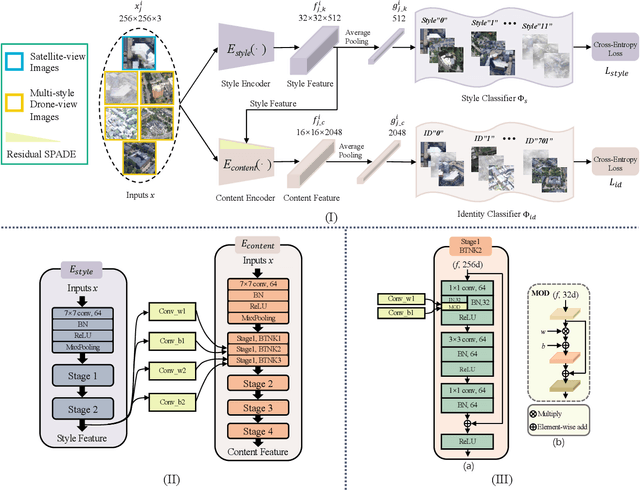

Abstract:Aerial-view geo-localization tends to determine an unknown position through matching the drone-view image with the geo-tagged satellite-view image. This task is mostly regarded as an image retrieval problem. The key underpinning this task is to design a series of deep neural networks to learn discriminative image descriptors. However, existing methods meet large performance drops under realistic weather, such as rain and fog, since they do not take the domain shift between the training data and multiple test environments into consideration. To minor this domain gap, we propose a Multiple-environment Self-adaptive Network (MuSe-Net) to dynamically adjust the domain shift caused by environmental changing. In particular, MuSe-Net employs a two-branch neural network containing one multiple-environment style extraction network and one self-adaptive feature extraction network. As the name implies, the multiple-environment style extraction network is to extract the environment-related style information, while the self-adaptive feature extraction network utilizes an adaptive modulation module to dynamically minimize the environment-related style gap. Extensive experiments on two widely-used benchmarks, i.e., University-1652 and CVUSA, demonstrate that the proposed MuSe-Net achieves a competitive result for geo-localization in multiple environments. Furthermore, we observe that the proposed method also shows great potential to the unseen extreme weather, such as mixing the fog, rain and snow.
Each Part Matters: Local Patterns Facilitate Cross-view Geo-localization
Aug 26, 2020



Abstract:Cross-view geo-localization is to spot images of the same geographic target from different platforms, e.g., drone-view cameras and satellites. It is challenging in the large visual appearance changes caused by extreme viewpoint variations. Existing methods usually concentrate on mining the fine-grained feature of the geographic target in the image center, but underestimate the contextual information in neighbor areas. In this work, we argue that neighbor areas can be leveraged as auxiliary information, enriching discriminative clues for geo-localization. Specifically, we introduce a simple and effective deep neural network, called Local Pattern Network (LPN), to take advantage of contextual information in an end-to-end manner. Without using extra part estimators, LPN adopts a square-ring feature partition strategy, which provides the attention according to the distance to the image center. It eases the part matching and enables the part-wise representation learning. Owing to the square-ring partition design, the proposed LPN has good scalability to rotation variations and achieves competitive results on two prevailing benchmarks, i.e., University-1652 and CVUSA. Besides, we also show the proposed LPN can be easily embedded into other frameworks to further boost performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge