Guo Zhang
Deep learning radiomics for assessment of gastroesophageal varices in people with compensated advanced chronic liver disease
Jun 13, 2023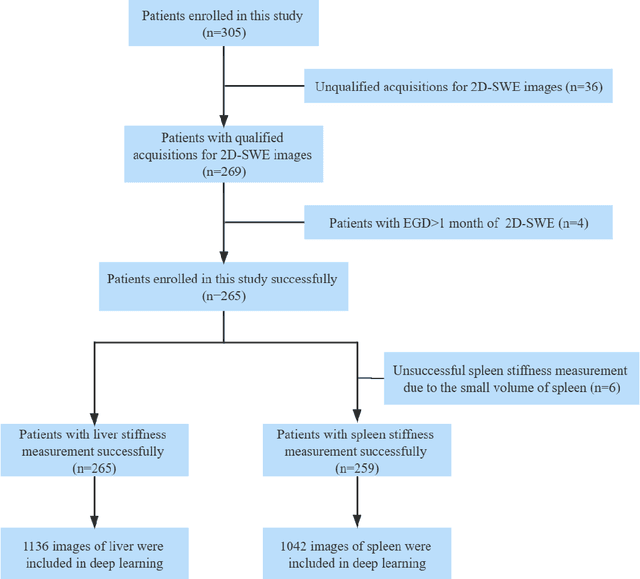
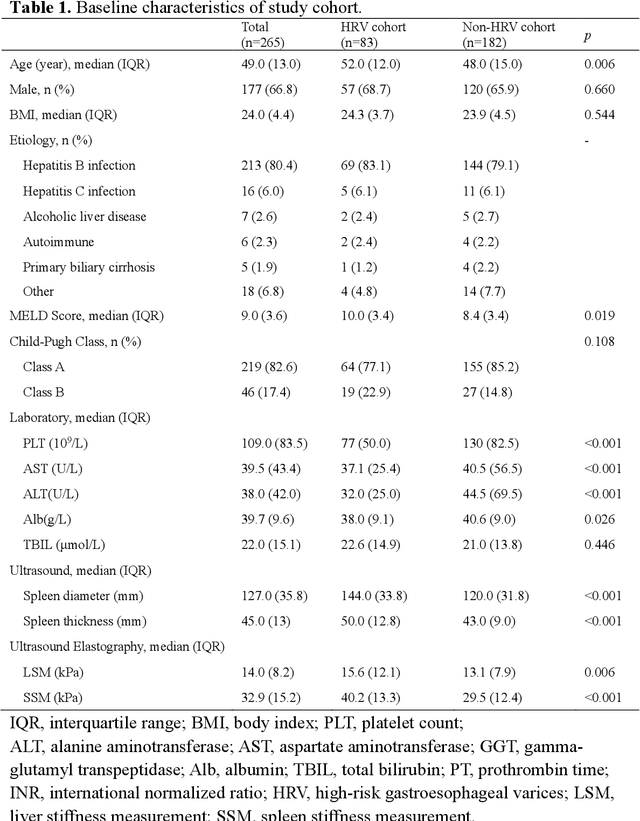
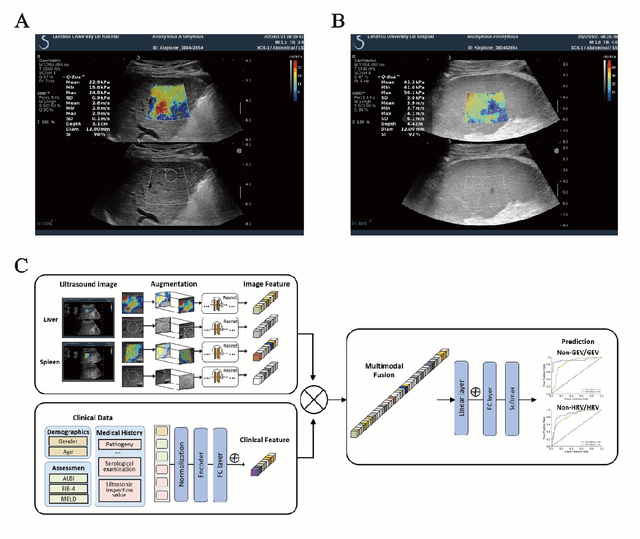
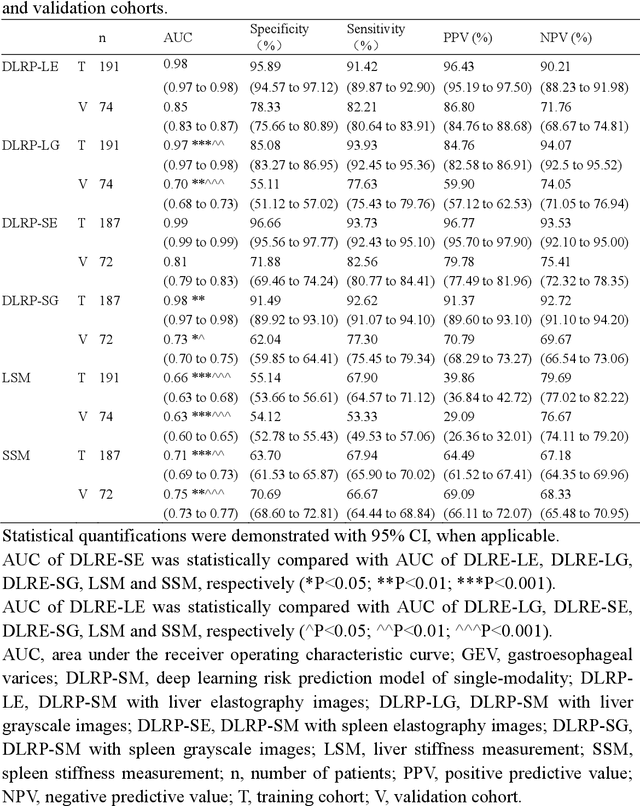
Abstract:Objective: Bleeding from gastroesophageal varices (GEV) is a medical emergency associated with high mortality. We aim to construct an artificial intelligence-based model of two-dimensional shear wave elastography (2D-SWE) of the liver and spleen to precisely assess the risk of GEV and high-risk gastroesophageal varices (HRV). Design: A prospective multicenter study was conducted in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease. 305 patients were enrolled from 12 hospitals, and finally 265 patients were included, with 1136 liver stiffness measurement (LSM) images and 1042 spleen stiffness measurement (SSM) images generated by 2D-SWE. We leveraged deep learning methods to uncover associations between image features and patient risk, and thus conducted models to predict GEV and HRV. Results: A multi-modality Deep Learning Risk Prediction model (DLRP) was constructed to assess GEV and HRV, based on LSM and SSM images, and clinical information. Validation analysis revealed that the AUCs of DLRP were 0.91 for GEV (95% CI 0.90 to 0.93, p < 0.05) and 0.88 for HRV (95% CI 0.86 to 0.89, p < 0.01), which were significantly and robustly better than canonical risk indicators, including the value of LSM and SSM. Moreover, DLPR was better than the model using individual parameters, including LSM and SSM images. In HRV prediction, the 2D-SWE images of SSM outperform LSM (p < 0.01). Conclusion: DLRP shows excellent performance in predicting GEV and HRV over canonical risk indicators LSM and SSM. Additionally, the 2D-SWE images of SSM provided more information for better accuracy in predicting HRV than the LSM.
TOV: The Original Vision Model for Optical Remote Sensing Image Understanding via Self-supervised Learning
Apr 10, 2022

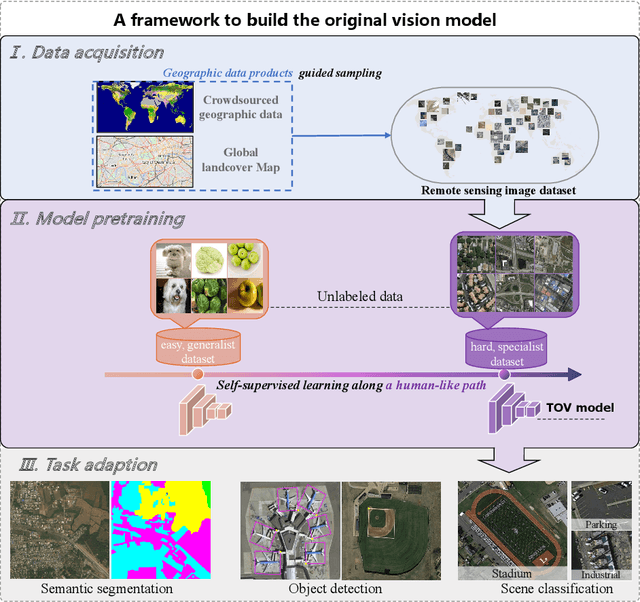

Abstract:Do we on the right way for remote sensing image understanding (RSIU) by training models via supervised data-dependent and task-dependent way, instead of human vision in a label-free and task-independent way? We argue that a more desirable RSIU model should be trained with intrinsic structure from data rather that extrinsic human labels to realize generalizability across a wide range of RSIU tasks. According to this hypothesis, we proposed \textbf{T}he \textbf{O}riginal \textbf{V}ision model (TOV) in remote sensing filed. Trained by massive unlabeled optical data along a human-like self-supervised learning (SSL) path that is from general knowledge to specialized knowledge, TOV model can be easily adapted to various RSIU tasks, including scene classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation, and outperforms dominant ImageNet supervised pretrained method as well as two recently proposed SSL pretrained methods on majority of 12 publicly available benchmarks. Moreover, we analyze the influences of two key factors on the performance of building TOV model for RSIU, including the influence of using different data sampling methods and the selection of learning paths during self-supervised optimization. We believe that a general model which is trained by a label-free and task-independent way may be the next paradigm for RSIU and hope the insights distilled from this study can help to foster the development of an original vision model for RSIU.
A Robust Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Registration Method and System Using Steerable Filters with First- and Second-order Gradients
Feb 27, 2022

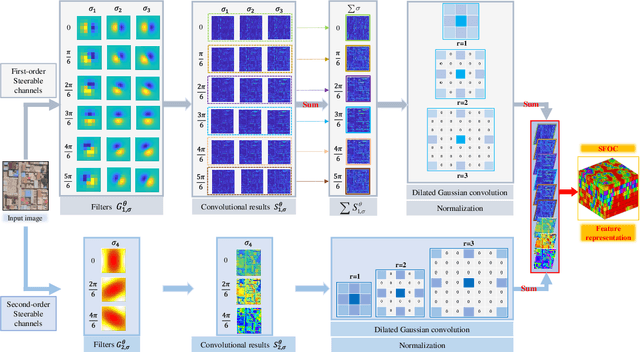
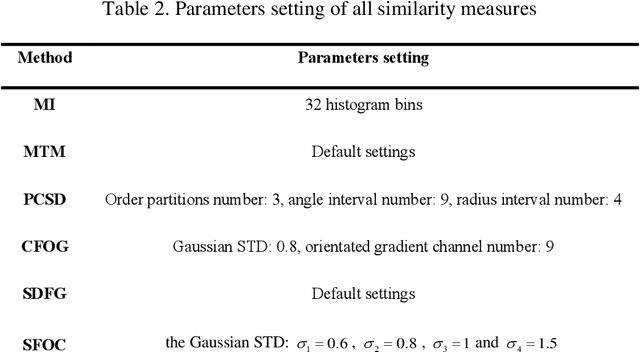
Abstract:Co-registration of multimodal remote sensing images is still an ongoing challenge because of nonlinear radiometric differences (NRD) and significant geometric distortions (e.g., scale and rotation changes) between these images. In this paper, a robust matching method based on the Steerable filters is proposed consisting of two critical steps. First, to address severe NRD, a novel structural descriptor named the Steerable Filters of first- and second-Order Channels (SFOC) is constructed, which combines the first- and second-order gradient information by using the steerable filters with a multi-scale strategy to depict more discriminative structure features of images. Then, a fast similarity measure is established called Fast Normalized Cross-Correlation (Fast-NCCSFOC), which employs the Fast Fourier Transform technique and the integral image to improve the matching efficiency. Furthermore, to achieve reliable registration performance, a coarse-to-fine multimodal registration system is designed consisting of two pivotal modules. The local coarse registration is first conducted by involving both detection of interest points (IPs) and local geometric correction, which effectively utilizes the prior georeferencing information of RS images to address global geometric distortions. In the fine registration stage, the proposed SFOC is used to resist significant NRD, and to detect control points between multimodal images by a template matching scheme. The performance of the proposed matching method has been evaluated with many different kinds of multimodal RS images. The results show its superior matching performance compared with the state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, the designed registration system also outperforms the popular commercial software in both registration accuracy and computational efficiency. Our system is available at https://github.com/yeyuanxin110.
Remote Sensing Images Semantic Segmentation with General Remote Sensing Vision Model via a Self-Supervised Contrastive Learning Method
Jun 20, 2021



Abstract:A new learning paradigm, self-supervised learning (SSL), can be used to solve such problems by pre-training a general model with large unlabeled images and then fine-tuning on a downstream task with very few labeled samples. Contrastive learning is a typical method of SSL, which can learn general invariant features. However, most of the existing contrastive learning is designed for classification tasks to obtain an image-level representation, which may be sub-optimal for semantic segmentation tasks requiring pixel-level discrimination. Therefore, we propose Global style and Local matching Contrastive Learning Network (GLCNet) for remote sensing semantic segmentation. Specifically, the global style contrastive module is used to learn an image-level representation better, as we consider the style features can better represent the overall image features; The local features matching contrastive module is designed to learn representations of local regions which is beneficial for semantic segmentation. We evaluate four remote sensing semantic segmentation datasets, and the experimental results show that our method mostly outperforms state-of-the-art self-supervised methods and ImageNet pre-training. Specifically, with 1\% annotation from the original dataset, our approach improves Kappa by 6\% on the ISPRS Potsdam dataset and 3\% on Deep Globe Land Cover Classification dataset relative to the existing baseline. Moreover, our method outperforms supervised learning when there are some differences between the datasets of upstream tasks and downstream tasks. Our study promotes the development of self-supervised learning in the field of remote sensing semantic segmentation. The source code is available at https://github.com/GeoX-Lab/G-RSIM.
Harnessing Structures for Value-Based Planning and Reinforcement Learning
Sep 26, 2019



Abstract:Value-based methods constitute a fundamental methodology in planning and deep reinforcement learning (RL). In this paper, we propose to exploit the underlying structures of the state-action value function, i.e., Q function, for both planning and deep RL. In particular, if the underlying system dynamics lead to some global structures of the Q function, one should be capable of inferring the function better by leveraging such structures. Specifically, we investigate the lowrank structure, which widely exists for big data matrices. We verify empirically the existence of low-rank Q functions in the context of control and deep RL tasks (Atari games). As our key contribution, by leveraging Matrix Estimation (ME) techniques, we propose a general framework to exploit the underlying low-rank structure in Q functions, leading to a more efficient planning procedure for classical control, and additionally, a simple scheme that can be applied to any value-based RL techniques to consistently achieve better performance on "low-rank" tasks. Extensive experiments on control tasks and Atari games confirm the efficacy of our approach.
ME-Net: Towards Effective Adversarial Robustness with Matrix Estimation
May 28, 2019



Abstract:Deep neural networks are vulnerable to adversarial attacks. The literature is rich with algorithms that can easily craft successful adversarial examples. In contrast, the performance of defense techniques still lags behind. This paper proposes ME-Net, a defense method that leverages matrix estimation (ME). In ME-Net, images are preprocessed using two steps: first pixels are randomly dropped from the image; then, the image is reconstructed using ME. We show that this process destroys the adversarial structure of the noise, while re-enforcing the global structure in the original image. Since humans typically rely on such global structures in classifying images, the process makes the network mode compatible with human perception. We conduct comprehensive experiments on prevailing benchmarks such as MNIST, CIFAR-10, SVHN, and Tiny-ImageNet. Comparing ME-Net with state-of-the-art defense mechanisms shows that ME-Net consistently outperforms prior techniques, improving robustness against both black-box and white-box attacks.
Topic-Level Opinion Influence Model(TOIM): An Investigation Using Tencent Micro-Blogging
Oct 24, 2012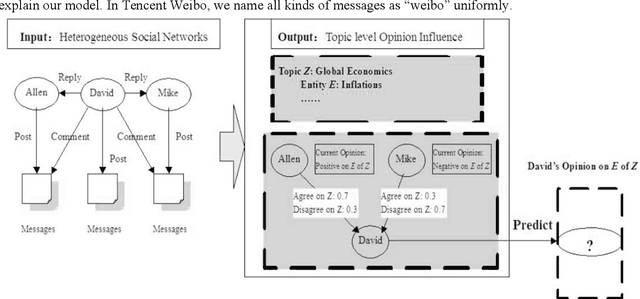
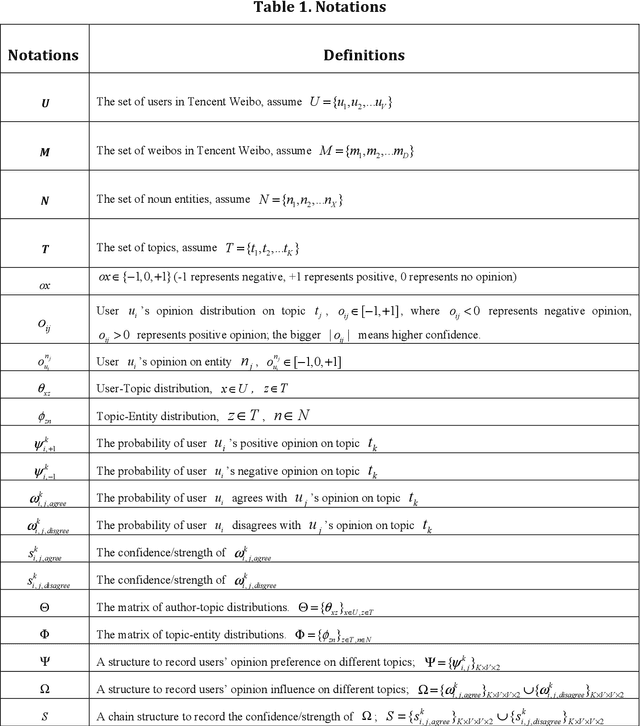
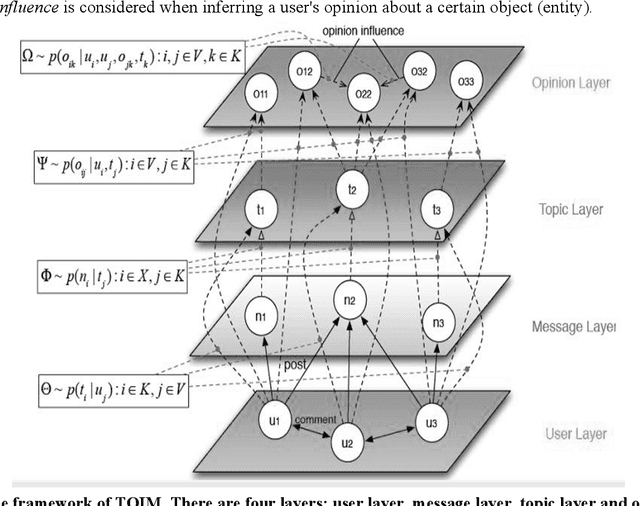
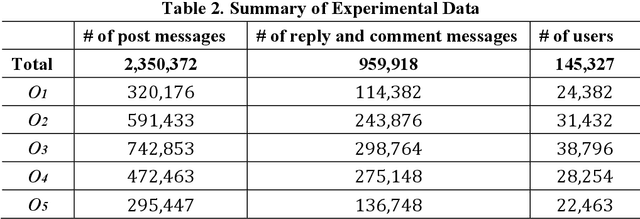
Abstract:Mining user opinion from Micro-Blogging has been extensively studied on the most popular social networking sites such as Twitter and Facebook in the U.S., but few studies have been done on Micro-Blogging websites in other countries (e.g. China). In this paper, we analyze the social opinion influence on Tencent, one of the largest Micro-Blogging websites in China, endeavoring to unveil the behavior patterns of Chinese Micro-Blogging users. This paper proposes a Topic-Level Opinion Influence Model (TOIM) that simultaneously incorporates topic factor and social direct influence in a unified probabilistic framework. Based on TOIM, two topic level opinion influence propagation and aggregation algorithms are developed to consider the indirect influence: CP (Conservative Propagation) and NCP (None Conservative Propagation). Users' historical social interaction records are leveraged by TOIM to construct their progressive opinions and neighbors' opinion influence through a statistical learning process, which can be further utilized to predict users' future opinions on some specific topics. To evaluate and test this proposed model, an experiment was designed and a sub-dataset from Tencent Micro-Blogging was used. The experimental results show that TOIM outperforms baseline methods on predicting users' opinion. The applications of CP and NCP have no significant differences and could significantly improve recall and F1-measure of TOIM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge