Boyue Zhang
DexTac: Learning Contact-aware Visuotactile Policies via Hand-by-hand Teaching
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:For contact-intensive tasks, the ability to generate policies that produce comprehensive tactile-aware motions is essential. However, existing data collection and skill learning systems for dexterous manipulation often suffer from low-dimensional tactile information. To address this limitation, we propose DexTac, a visuo-tactile manipulation learning framework based on kinesthetic teaching. DexTac captures multi-dimensional tactile data-including contact force distributions and spatial contact regions-directly from human demonstrations. By integrating these rich tactile modalities into a policy network, the resulting contact-aware agent enables a dexterous hand to autonomously select and maintain optimal contact regions during complex interactions. We evaluate our framework on a challenging unimanual injection task. Experimental results demonstrate that DexTac achieves a 91.67% success rate. Notably, in high-precision scenarios involving small-scale syringes, our approach outperforms force-only baselines by 31.67%. These results underscore that learning multi-dimensional tactile priors from human demonstrations is critical for achieving robust, human-like dexterous manipulation in contact-rich environments.
It Takes Two: Accurate Gait Recognition in the Wild via Cross-granularity Alignment
Nov 16, 2024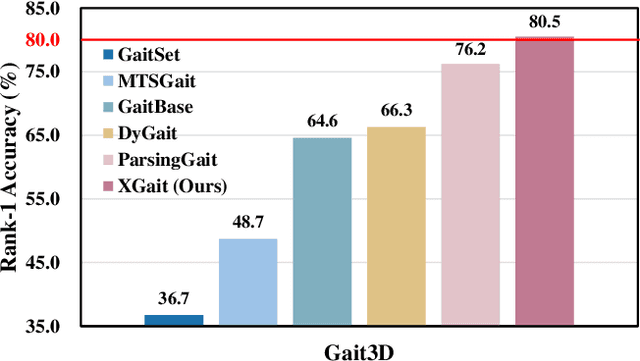
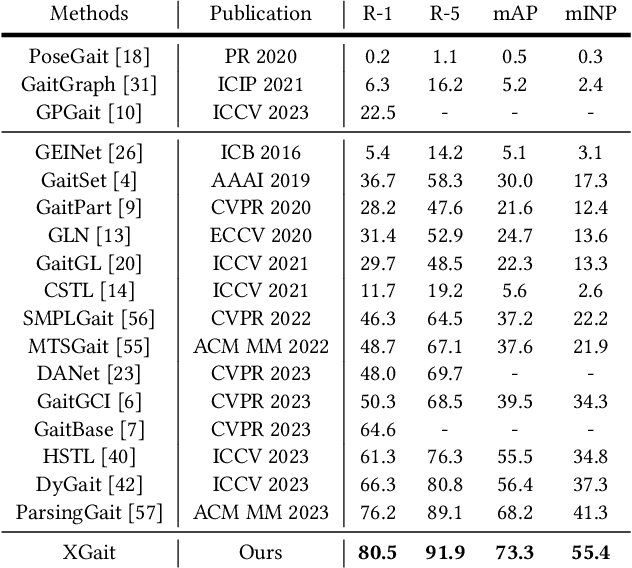
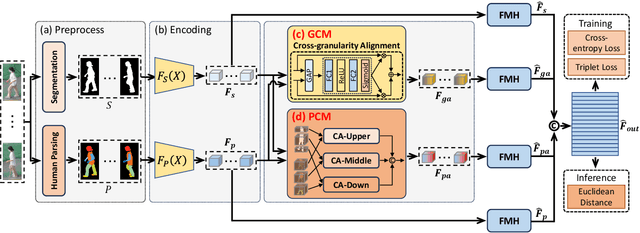
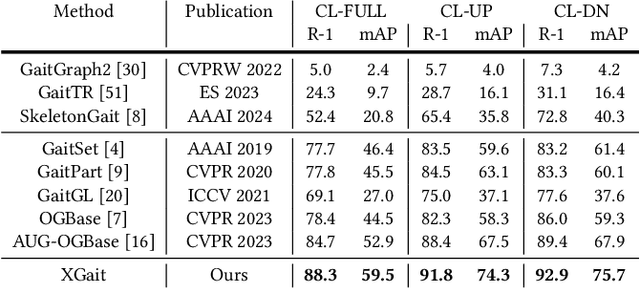
Abstract:Existing studies for gait recognition primarily utilized sequences of either binary silhouette or human parsing to encode the shapes and dynamics of persons during walking. Silhouettes exhibit accurate segmentation quality and robustness to environmental variations, but their low information entropy may result in sub-optimal performance. In contrast, human parsing provides fine-grained part segmentation with higher information entropy, but the segmentation quality may deteriorate due to the complex environments. To discover the advantages of silhouette and parsing and overcome their limitations, this paper proposes a novel cross-granularity alignment gait recognition method, named XGait, to unleash the power of gait representations of different granularity. To achieve this goal, the XGait first contains two branches of backbone encoders to map the silhouette sequences and the parsing sequences into two latent spaces, respectively. Moreover, to explore the complementary knowledge across the features of two representations, we design the Global Cross-granularity Module (GCM) and the Part Cross-granularity Module (PCM) after the two encoders. In particular, the GCM aims to enhance the quality of parsing features by leveraging global features from silhouettes, while the PCM aligns the dynamics of human parts between silhouette and parsing features using the high information entropy in parsing sequences. In addition, to effectively guide the alignment of two representations with different granularity at the part level, an elaborate-designed learnable division mechanism is proposed for the parsing features. Comprehensive experiments on two large-scale gait datasets not only show the superior performance of XGait with the Rank-1 accuracy of 80.5% on Gait3D and 88.3% CCPG but also reflect the robustness of the learned features even under challenging conditions like occlusions and cloth changes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge