Jiahe Li
Assembling the Mind's Mosaic: Towards EEG Semantic Intent Decoding
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Enabling natural communication through brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) remains one of the most profound challenges in neuroscience and neurotechnology. While existing frameworks offer partial solutions, they are constrained by oversimplified semantic representations and a lack of interpretability. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Semantic Intent Decoding (SID), a novel framework that translates neural activity into natural language by modeling meaning as a flexible set of compositional semantic units. SID is built on three core principles: semantic compositionality, continuity and expandability of semantic space, and fidelity in reconstruction. We present BrainMosaic, a deep learning architecture implementing SID. BrainMosaic decodes multiple semantic units from EEG/SEEG signals using set matching and then reconstructs coherent sentences through semantic-guided reconstruction. This approach moves beyond traditional pipelines that rely on fixed-class classification or unconstrained generation, enabling a more interpretable and expressive communication paradigm. Extensive experiments on multilingual EEG and clinical SEEG datasets demonstrate that SID and BrainMosaic offer substantial advantages over existing frameworks, paving the way for natural and effective BCI-mediated communication.
SCE-SLAM: Scale-Consistent Monocular SLAM via Scene Coordinate Embeddings
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Monocular visual SLAM enables 3D reconstruction from internet video and autonomous navigation on resource-constrained platforms, yet suffers from scale drift, i.e., the gradual divergence of estimated scale over long sequences. Existing frame-to-frame methods achieve real-time performance through local optimization but accumulate scale drift due to the lack of global constraints among independent windows. To address this, we propose SCE-SLAM, an end-to-end SLAM system that maintains scale consistency through scene coordinate embeddings, which are learned patch-level representations encoding 3D geometric relationships under a canonical scale reference. The framework consists of two key modules: geometry-guided aggregation that leverages 3D spatial proximity to propagate scale information from historical observations through geometry-modulated attention, and scene coordinate bundle adjustment that anchors current estimates to the reference scale through explicit 3D coordinate constraints decoded from the scene coordinate embeddings. Experiments on KITTI, Waymo, and vKITTI demonstrate substantial improvements: our method reduces absolute trajectory error by 8.36m on KITTI compared to the best prior approach, while maintaining 36 FPS and achieving scale consistency across large-scale scenes.
FoundationSLAM: Unleashing the Power of Depth Foundation Models for End-to-End Dense Visual SLAM
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:We present FoundationSLAM, a learning-based monocular dense SLAM system that addresses the absence of geometric consistency in previous flow-based approaches for accurate and robust tracking and mapping. Our core idea is to bridge flow estimation with geometric reasoning by leveraging the guidance from foundation depth models. To this end, we first develop a Hybrid Flow Network that produces geometry-aware correspondences, enabling consistent depth and pose inference across diverse keyframes. To enforce global consistency, we propose a Bi-Consistent Bundle Adjustment Layer that jointly optimizes keyframe pose and depth under multi-view constraints. Furthermore, we introduce a Reliability-Aware Refinement mechanism that dynamically adapts the flow update process by distinguishing between reliable and uncertain regions, forming a closed feedback loop between matching and optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FoundationSLAM achieves superior trajectory accuracy and dense reconstruction quality across multiple challenging datasets, while running in real-time at 18 FPS, demonstrating strong generalization to various scenarios and practical applicability of our method.
SparseSurf: Sparse-View 3D Gaussian Splatting for Surface Reconstruction
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in optimizing Gaussian Splatting for scene geometry have enabled efficient reconstruction of detailed surfaces from images. However, when input views are sparse, such optimization is prone to overfitting, leading to suboptimal reconstruction quality. Existing approaches address this challenge by employing flattened Gaussian primitives to better fit surface geometry, combined with depth regularization to alleviate geometric ambiguities under limited viewpoints. Nevertheless, the increased anisotropy inherent in flattened Gaussians exacerbates overfitting in sparse-view scenarios, hindering accurate surface fitting and degrading novel view synthesis performance. In this paper, we propose \net{}, a method that reconstructs more accurate and detailed surfaces while preserving high-quality novel view rendering. Our key insight is to introduce Stereo Geometry-Texture Alignment, which bridges rendering quality and geometry estimation, thereby jointly enhancing both surface reconstruction and view synthesis. In addition, we present a Pseudo-Feature Enhanced Geometry Consistency that enforces multi-view geometric consistency by incorporating both training and unseen views, effectively mitigating overfitting caused by sparse supervision. Extensive experiments on the DTU, BlendedMVS, and Mip-NeRF360 datasets demonstrate that our method achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
Reinforcement Learning Optimization for Large-Scale Learning: An Efficient and User-Friendly Scaling Library
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce ROLL, an efficient, scalable, and user-friendly library designed for Reinforcement Learning Optimization for Large-scale Learning. ROLL caters to three primary user groups: tech pioneers aiming for cost-effective, fault-tolerant large-scale training, developers requiring flexible control over training workflows, and researchers seeking agile experimentation. ROLL is built upon several key modules to serve these user groups effectively. First, a single-controller architecture combined with an abstraction of the parallel worker simplifies the development of the training pipeline. Second, the parallel strategy and data transfer modules enable efficient and scalable training. Third, the rollout scheduler offers fine-grained management of each sample's lifecycle during the rollout stage. Fourth, the environment worker and reward worker support rapid and flexible experimentation with agentic RL algorithms and reward designs. Finally, AutoDeviceMapping allows users to assign resources to different models flexibly across various stages.
InsTaG: Learning Personalized 3D Talking Head from Few-Second Video
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Despite exhibiting impressive performance in synthesizing lifelike personalized 3D talking heads, prevailing methods based on radiance fields suffer from high demands for training data and time for each new identity. This paper introduces InsTaG, a 3D talking head synthesis framework that allows a fast learning of realistic personalized 3D talking head from few training data. Built upon a lightweight 3DGS person-specific synthesizer with universal motion priors, InsTaG achieves high-quality and fast adaptation while preserving high-level personalization and efficiency. As preparation, we first propose an Identity-Free Pre-training strategy that enables the pre-training of the person-specific model and encourages the collection of universal motion priors from long-video data corpus. To fully exploit the universal motion priors to learn an unseen new identity, we then present a Motion-Aligned Adaptation strategy to adaptively align the target head to the pre-trained field, and constrain a robust dynamic head structure under few training data. Experiments demonstrate our outstanding performance and efficiency under various data scenarios to render high-quality personalized talking heads.
Deep Learning-Powered Electrical Brain Signals Analysis: Advancing Neurological Diagnostics
Feb 24, 2025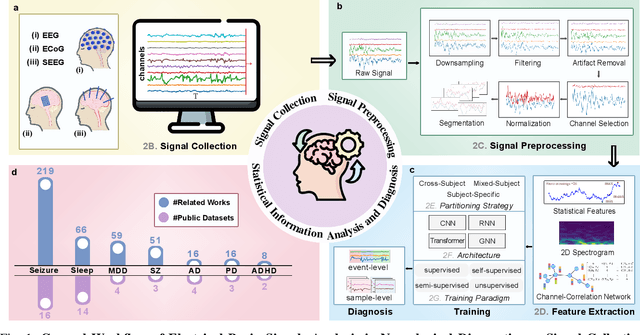
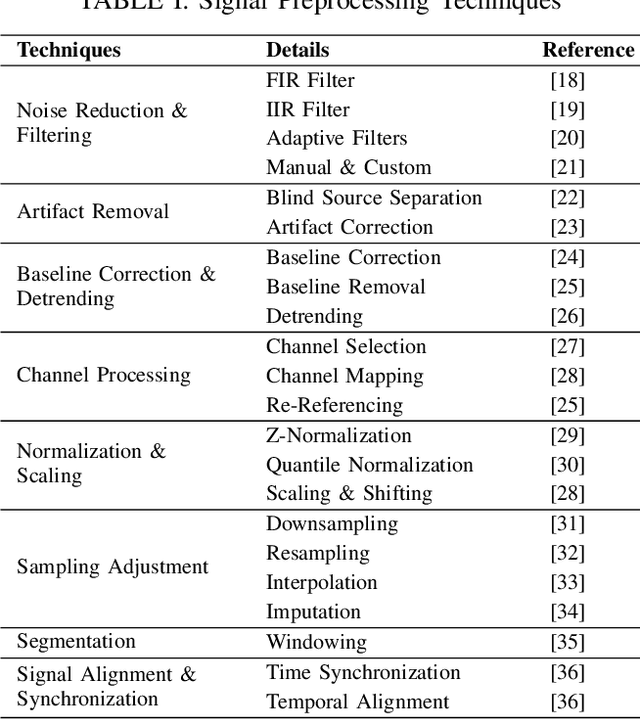
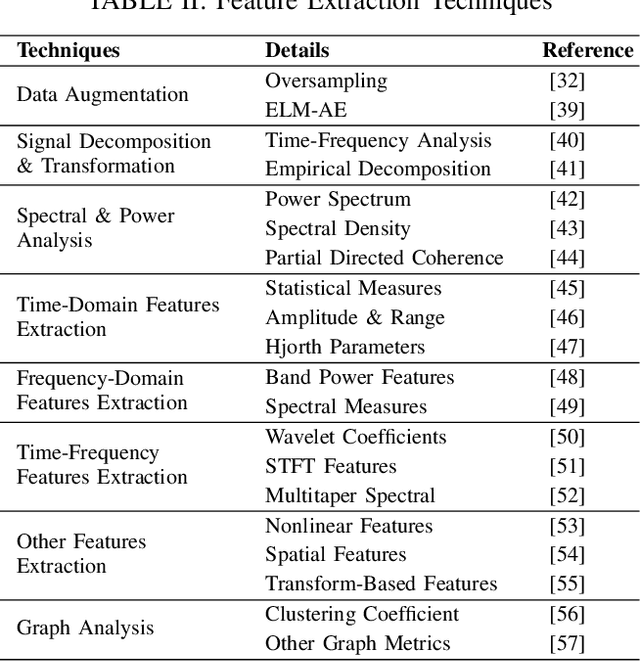
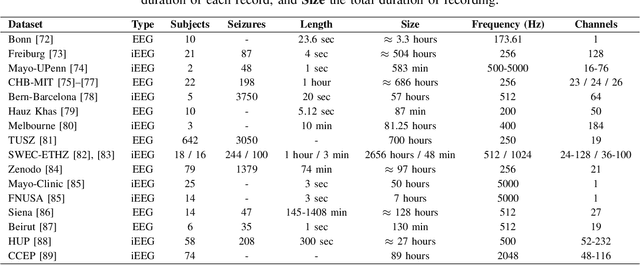
Abstract:Neurological disorders represent significant global health challenges, driving the advancement of brain signal analysis methods. Scalp electroencephalography (EEG) and intracranial electroencephalography (iEEG) are widely used to diagnose and monitor neurological conditions. However, dataset heterogeneity and task variations pose challenges in developing robust deep learning solutions. This review systematically examines recent advances in deep learning approaches for EEG/iEEG-based neurological diagnostics, focusing on applications across 7 neurological conditions using 46 datasets. We explore trends in data utilization, model design, and task-specific adaptations, highlighting the importance of pre-trained multi-task models for scalable, generalizable solutions. To advance research, we propose a standardized benchmark for evaluating models across diverse datasets to enhance reproducibility. This survey emphasizes how recent innovations can transform neurological diagnostics and enable the development of intelligent, adaptable healthcare solutions.
HOGSA: Bimanual Hand-Object Interaction Understanding with 3D Gaussian Splatting Based Data Augmentation
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:Understanding of bimanual hand-object interaction plays an important role in robotics and virtual reality. However, due to significant occlusions between hands and object as well as the high degree-of-freedom motions, it is challenging to collect and annotate a high-quality, large-scale dataset, which prevents further improvement of bimanual hand-object interaction-related baselines. In this work, we propose a new 3D Gaussian Splatting based data augmentation framework for bimanual hand-object interaction, which is capable of augmenting existing dataset to large-scale photorealistic data with various hand-object pose and viewpoints. First, we use mesh-based 3DGS to model objects and hands, and to deal with the rendering blur problem due to multi-resolution input images used, we design a super-resolution module. Second, we extend the single hand grasping pose optimization module for the bimanual hand object to generate various poses of bimanual hand-object interaction, which can significantly expand the pose distribution of the dataset. Third, we conduct an analysis for the impact of different aspects of the proposed data augmentation on the understanding of the bimanual hand-object interaction. We perform our data augmentation on two benchmarks, H2O and Arctic, and verify that our method can improve the performance of the baselines.
Con4m: Context-aware Consistency Learning Framework for Segmented Time Series Classification
Jul 31, 2024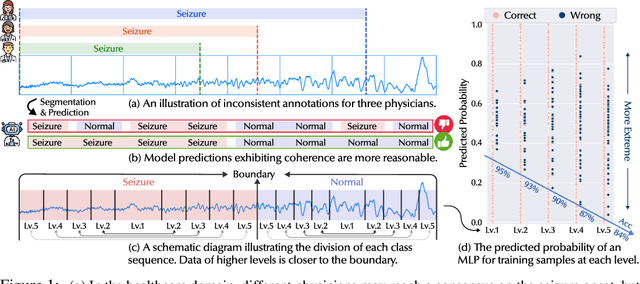
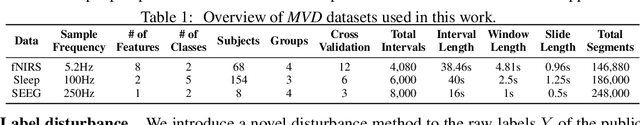
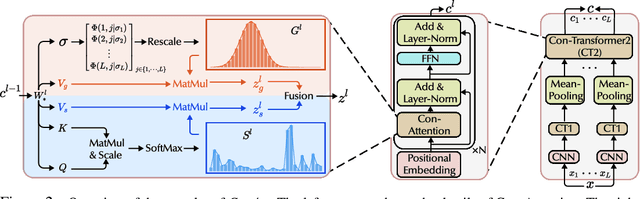
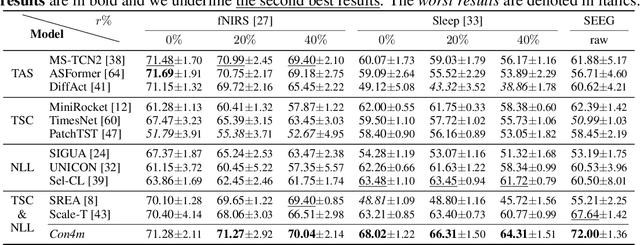
Abstract:Time Series Classification (TSC) encompasses two settings: classifying entire sequences or classifying segmented subsequences. The raw time series for segmented TSC usually contain Multiple classes with Varying Duration of each class (MVD). Therefore, the characteristics of MVD pose unique challenges for segmented TSC, yet have been largely overlooked by existing works. Specifically, there exists a natural temporal dependency between consecutive instances (segments) to be classified within MVD. However, mainstream TSC models rely on the assumption of independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.), focusing on independently modeling each segment. Additionally, annotators with varying expertise may provide inconsistent boundary labels, leading to unstable performance of noise-free TSC models. To address these challenges, we first formally demonstrate that valuable contextual information enhances the discriminative power of classification instances. Leveraging the contextual priors of MVD at both the data and label levels, we propose a novel consistency learning framework Con4m, which effectively utilizes contextual information more conducive to discriminating consecutive segments in segmented TSC tasks, while harmonizing inconsistent boundary labels for training. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets validate the effectiveness of Con4m in handling segmented TSC tasks on MVD.
CoR-GS: Sparse-View 3D Gaussian Splatting via Co-Regularization
May 20, 2024



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) creates a radiance field consisting of 3D Gaussians to represent a scene. With sparse training views, 3DGS easily suffers from overfitting, negatively impacting the reconstruction quality. This paper introduces a new co-regularization perspective for improving sparse-view 3DGS. When training two 3D Gaussian radiance fields with the same sparse views of a scene, we observe that the two radiance fields exhibit \textit{point disagreement} and \textit{rendering disagreement} that can unsupervisedly predict reconstruction quality, stemming from the sampling implementation in densification. We further quantify the point disagreement and rendering disagreement by evaluating the registration between Gaussians' point representations and calculating differences in their rendered pixels. The empirical study demonstrates the negative correlation between the two disagreements and accurate reconstruction, which allows us to identify inaccurate reconstruction without accessing ground-truth information. Based on the study, we propose CoR-GS, which identifies and suppresses inaccurate reconstruction based on the two disagreements: (\romannumeral1) Co-pruning considers Gaussians that exhibit high point disagreement in inaccurate positions and prunes them. (\romannumeral2) Pseudo-view co-regularization considers pixels that exhibit high rendering disagreement are inaccurately rendered and suppress the disagreement. Results on LLFF, Mip-NeRF360, DTU, and Blender demonstrate that CoR-GS effectively regularizes the scene geometry, reconstructs the compact representations, and achieves state-of-the-art novel view synthesis quality under sparse training views.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge