Tianyu Cao
Out of Style: RAG's Fragility to Linguistic Variation
Apr 11, 2025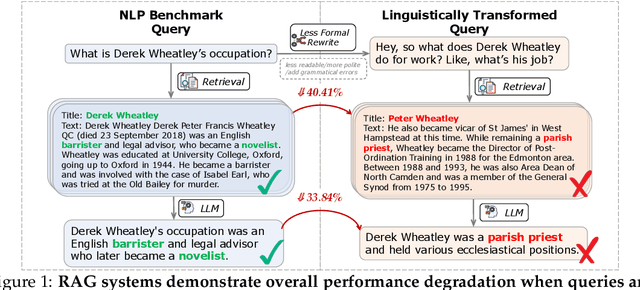

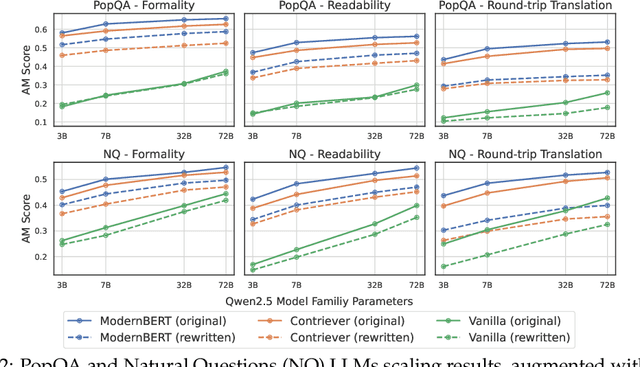
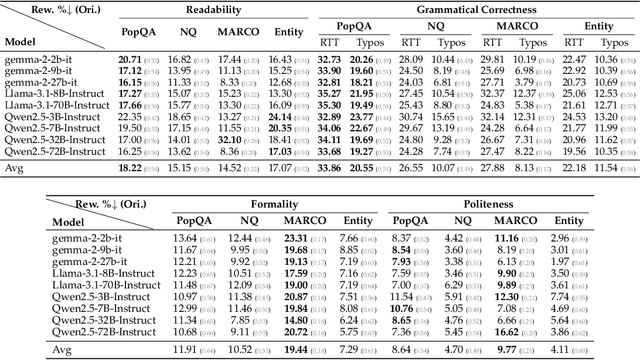
Abstract:Despite the impressive performance of Retrieval-augmented Generation (RAG) systems across various NLP benchmarks, their robustness in handling real-world user-LLM interaction queries remains largely underexplored. This presents a critical gap for practical deployment, where user queries exhibit greater linguistic variations and can trigger cascading errors across interdependent RAG components. In this work, we systematically analyze how varying four linguistic dimensions (formality, readability, politeness, and grammatical correctness) impact RAG performance. We evaluate two retrieval models and nine LLMs, ranging from 3 to 72 billion parameters, across four information-seeking Question Answering (QA) datasets. Our results reveal that linguistic reformulations significantly impact both retrieval and generation stages, leading to a relative performance drop of up to 40.41% in Recall@5 scores for less formal queries and 38.86% in answer match scores for queries containing grammatical errors. Notably, RAG systems exhibit greater sensitivity to such variations compared to LLM-only generations, highlighting their vulnerability to error propagation due to linguistic shifts. These findings highlight the need for improved robustness techniques to enhance reliability in diverse user interactions.
DCatalyst: A Unified Accelerated Framework for Decentralized Optimization
Jan 30, 2025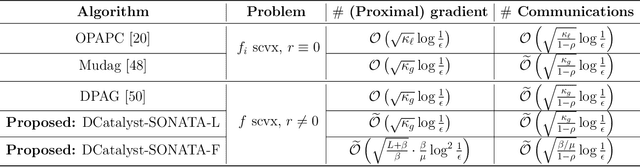
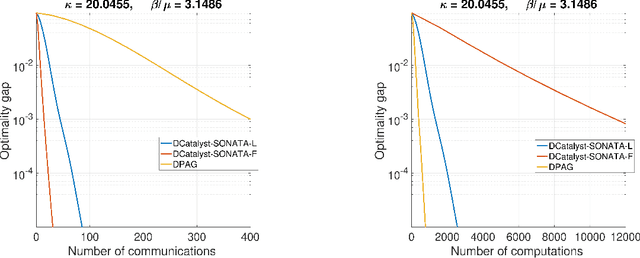
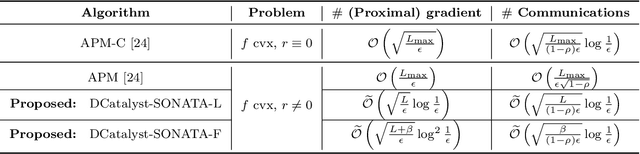
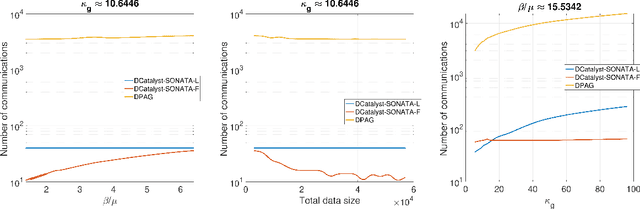
Abstract:We study decentralized optimization over a network of agents, modeled as graphs, with no central server. The goal is to minimize $f+r$, where $f$ represents a (strongly) convex function averaging the local agents' losses, and $r$ is a convex, extended-value function. We introduce DCatalyst, a unified black-box framework that integrates Nesterov acceleration into decentralized optimization algorithms. %, enhancing their performance. At its core, DCatalyst operates as an \textit{inexact}, \textit{momentum-accelerated} proximal method (forming the outer loop) that seamlessly incorporates any selected decentralized algorithm (as the inner loop). We demonstrate that DCatalyst achieves optimal communication and computational complexity (up to log-factors) across various decentralized algorithms and problem instances. Notably, it extends acceleration capabilities to problem classes previously lacking accelerated solution methods, thereby broadening the effectiveness of decentralized methods. On the technical side, our framework introduce the {\it inexact estimating sequences}--a novel extension of the well-known Nesterov's estimating sequences, tailored for the minimization of composite losses in decentralized settings. This method adeptly handles consensus errors and inexact solutions of agents' subproblems, challenges not addressed by existing models.
Enhancing Convergence of Decentralized Gradient Tracking under the KL Property
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:We study decentralized multiagent optimization over networks, modeled as undirected graphs. The optimization problem consists of minimizing a nonconvex smooth function plus a convex extended-value function, which enforces constraints or extra structure on the solution (e.g., sparsity, low-rank). We further assume that the objective function satisfies the Kurdyka-{\L}ojasiewicz (KL) property, with given exponent $\theta\in [0,1)$. The KL property is satisfied by several (nonconvex) functions of practical interest, e.g., arising from machine learning applications; in the centralized setting, it permits to achieve strong convergence guarantees. Here we establish convergence of the same type for the notorious decentralized gradient-tracking-based algorithm SONATA. Specifically, $\textbf{(i)}$ when $\theta\in (0,1/2]$, the sequence generated by SONATA converges to a stationary solution of the problem at R-linear rate;$ \textbf{(ii)} $when $\theta\in (1/2,1)$, sublinear rate is certified; and finally $\textbf{(iii)}$ when $\theta=0$, the iterates will either converge in a finite number of steps or converges at R-linear rate. This matches the convergence behavior of centralized proximal-gradient algorithms except when $\theta=0$. Numerical results validate our theoretical findings.
Shopping MMLU: A Massive Multi-Task Online Shopping Benchmark for Large Language Models
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Online shopping is a complex multi-task, few-shot learning problem with a wide and evolving range of entities, relations, and tasks. However, existing models and benchmarks are commonly tailored to specific tasks, falling short of capturing the full complexity of online shopping. Large Language Models (LLMs), with their multi-task and few-shot learning abilities, have the potential to profoundly transform online shopping by alleviating task-specific engineering efforts and by providing users with interactive conversations. Despite the potential, LLMs face unique challenges in online shopping, such as domain-specific concepts, implicit knowledge, and heterogeneous user behaviors. Motivated by the potential and challenges, we propose Shopping MMLU, a diverse multi-task online shopping benchmark derived from real-world Amazon data. Shopping MMLU consists of 57 tasks covering 4 major shopping skills: concept understanding, knowledge reasoning, user behavior alignment, and multi-linguality, and can thus comprehensively evaluate the abilities of LLMs as general shop assistants. With Shopping MMLU, we benchmark over 20 existing LLMs and uncover valuable insights about practices and prospects of building versatile LLM-based shop assistants. Shopping MMLU can be publicly accessed at https://github.com/KL4805/ShoppingMMLU. In addition, with Shopping MMLU, we host a competition in KDD Cup 2024 with over 500 participating teams. The winning solutions and the associated workshop can be accessed at our website https://amazon-kddcup24.github.io/.
Con4m: Context-aware Consistency Learning Framework for Segmented Time Series Classification
Jul 31, 2024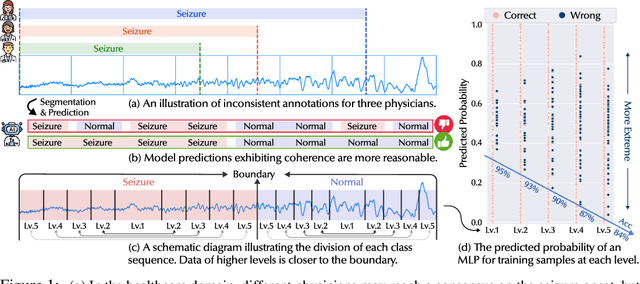
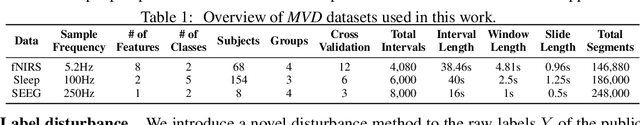
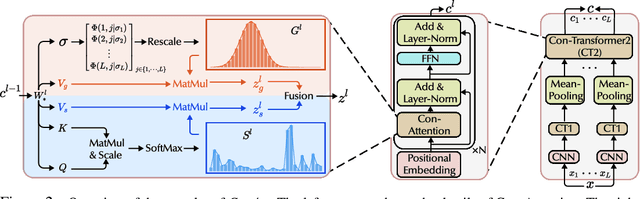
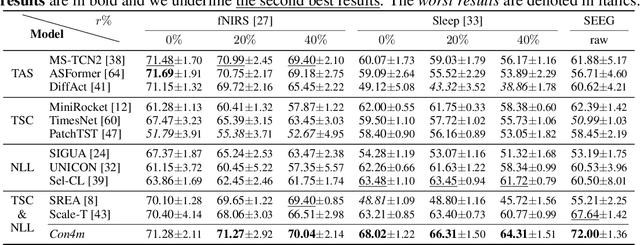
Abstract:Time Series Classification (TSC) encompasses two settings: classifying entire sequences or classifying segmented subsequences. The raw time series for segmented TSC usually contain Multiple classes with Varying Duration of each class (MVD). Therefore, the characteristics of MVD pose unique challenges for segmented TSC, yet have been largely overlooked by existing works. Specifically, there exists a natural temporal dependency between consecutive instances (segments) to be classified within MVD. However, mainstream TSC models rely on the assumption of independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.), focusing on independently modeling each segment. Additionally, annotators with varying expertise may provide inconsistent boundary labels, leading to unstable performance of noise-free TSC models. To address these challenges, we first formally demonstrate that valuable contextual information enhances the discriminative power of classification instances. Leveraging the contextual priors of MVD at both the data and label levels, we propose a novel consistency learning framework Con4m, which effectively utilizes contextual information more conducive to discriminating consecutive segments in segmented TSC tasks, while harmonizing inconsistent boundary labels for training. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets validate the effectiveness of Con4m in handling segmented TSC tasks on MVD.
Characterizing Multimodal Long-form Summarization: A Case Study on Financial Reports
Apr 09, 2024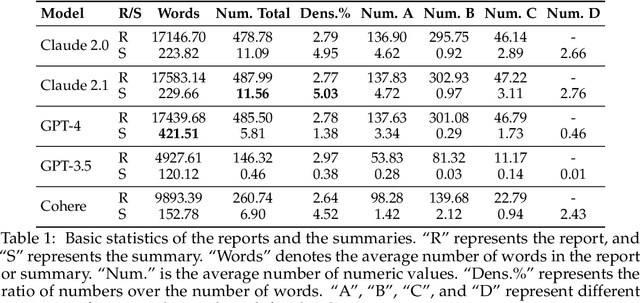
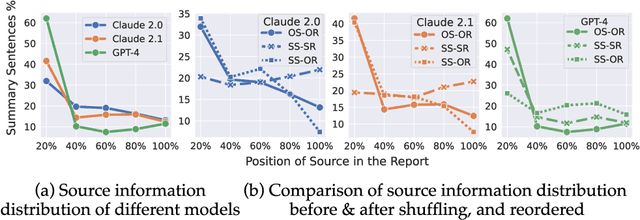
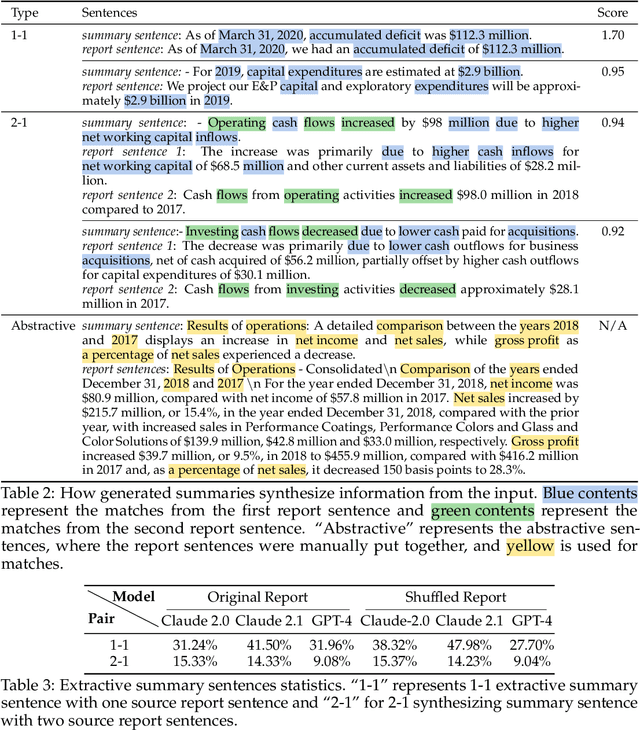

Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) expand the power of natural language processing to handle long inputs, rigorous and systematic analyses are necessary to understand their abilities and behavior. A salient application is summarization, due to its ubiquity and controversy (e.g., researchers have declared the death of summarization). In this paper, we use financial report summarization as a case study because financial reports not only are long but also use numbers and tables extensively. We propose a computational framework for characterizing multimodal long-form summarization and investigate the behavior of Claude 2.0/2.1, GPT-4/3.5, and Command. We find that GPT-3.5 and Command fail to perform this summarization task meaningfully. For Claude 2 and GPT-4, we analyze the extractiveness of the summary and identify a position bias in LLMs. This position bias disappears after shuffling the input for Claude, which suggests that Claude has the ability to recognize important information. We also conduct a comprehensive investigation on the use of numeric data in LLM-generated summaries and offer a taxonomy of numeric hallucination. We employ prompt engineering to improve GPT-4's use of numbers with limited success. Overall, our analyses highlight the strong capability of Claude 2 in handling long multimodal inputs compared to GPT-4.
Enhancing User Intent Capture in Session-Based Recommendation with Attribute Patterns
Dec 23, 2023Abstract:The goal of session-based recommendation in E-commerce is to predict the next item that an anonymous user will purchase based on the browsing and purchase history. However, constructing global or local transition graphs to supplement session data can lead to noisy correlations and user intent vanishing. In this work, we propose the Frequent Attribute Pattern Augmented Transformer (FAPAT) that characterizes user intents by building attribute transition graphs and matching attribute patterns. Specifically, the frequent and compact attribute patterns are served as memory to augment session representations, followed by a gate and a transformer block to fuse the whole session information. Through extensive experiments on two public benchmarks and 100 million industrial data in three domains, we demonstrate that FAPAT consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods by an average of 4.5% across various evaluation metrics (Hits, NDCG, MRR). Besides evaluating the next-item prediction, we estimate the models' capabilities to capture user intents via predicting items' attributes and period-item recommendations.
Mutually-paced Knowledge Distillation for Cross-lingual Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning
Mar 27, 2023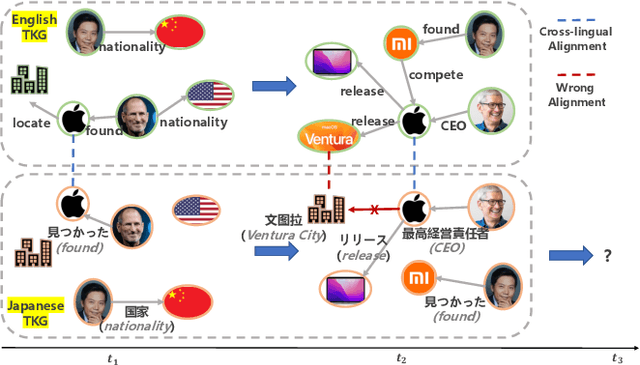
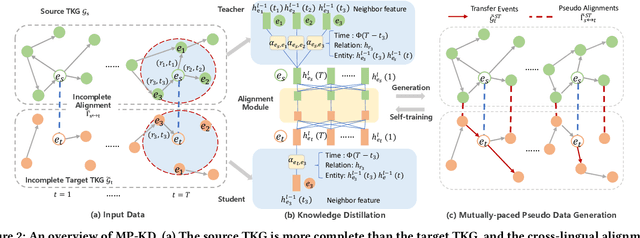
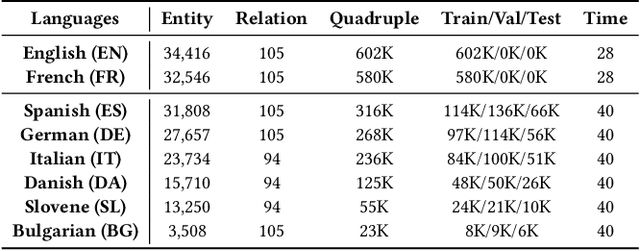
Abstract:This paper investigates cross-lingual temporal knowledge graph reasoning problem, which aims to facilitate reasoning on Temporal Knowledge Graphs (TKGs) in low-resource languages by transfering knowledge from TKGs in high-resource ones. The cross-lingual distillation ability across TKGs becomes increasingly crucial, in light of the unsatisfying performance of existing reasoning methods on those severely incomplete TKGs, especially in low-resource languages. However, it poses tremendous challenges in two aspects. First, the cross-lingual alignments, which serve as bridges for knowledge transfer, are usually too scarce to transfer sufficient knowledge between two TKGs. Second, temporal knowledge discrepancy of the aligned entities, especially when alignments are unreliable, can mislead the knowledge distillation process. We correspondingly propose a mutually-paced knowledge distillation model MP-KD, where a teacher network trained on a source TKG can guide the training of a student network on target TKGs with an alignment module. Concretely, to deal with the scarcity issue, MP-KD generates pseudo alignments between TKGs based on the temporal information extracted by our representation module. To maximize the efficacy of knowledge transfer and control the noise caused by the temporal knowledge discrepancy, we enhance MP-KD with a temporal cross-lingual attention mechanism to dynamically estimate the alignment strength. The two procedures are mutually paced along with model training. Extensive experiments on twelve cross-lingual TKG transfer tasks in the EventKG benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed MP-KD method.
FolkScope: Intention Knowledge Graph Construction for Discovering E-commerce Commonsense
Nov 15, 2022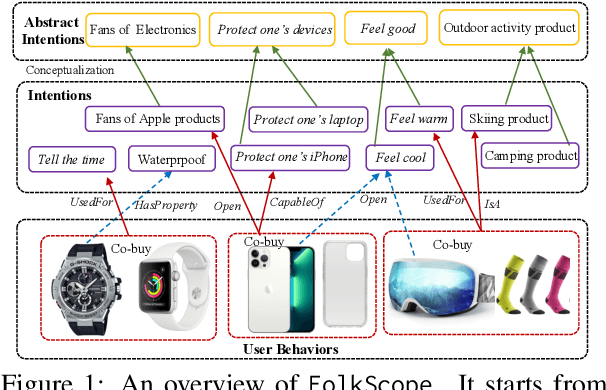
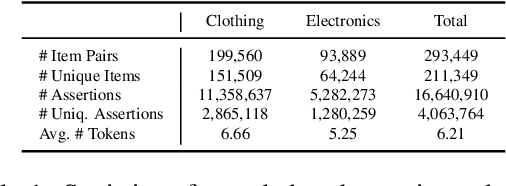
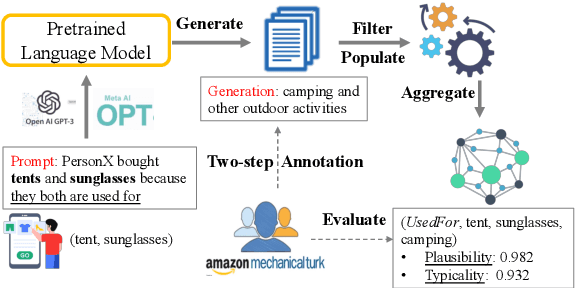
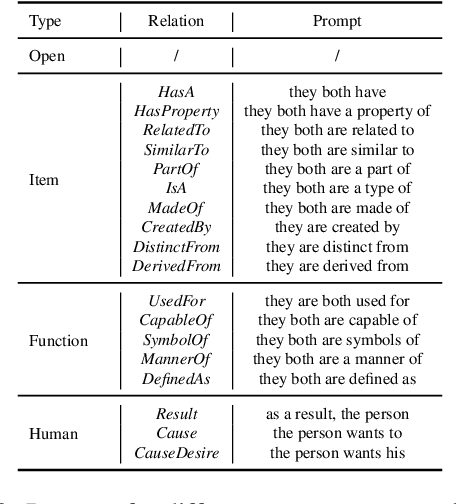
Abstract:As stated by Oren Etzioni, ``commonsense is the dark matter of artificial intelligence''. In e-commerce, understanding users' needs or intentions requires substantial commonsense knowledge, e.g., ``A user bought an iPhone and a compatible case because the user wanted the phone to be protected''. In this paper, we present FolkScope, an intention knowledge graph construction framework, to reveal the structure of humans' minds about purchasing items on e-commerce platforms such as Amazon. As commonsense knowledge is usually ineffable and not expressed explicitly, it is challenging to perform any kind of information extraction. Thus, we propose a new approach that leverages the generation power of large-scale language models and human-in-the-loop annotations to semi-automatically construct the knowledge graph. We annotate a large amount of assertions for both plausibility and typicality of an intention that can explain a purchasing or co-purchasing behavior, where the intention can be an open reason or a predicate falling into one of 18 categories aligning with ConceptNet, e.g., IsA, MadeOf, UsedFor, etc. Then we populate the annotated information to all automatically generated ones, and further structurize the assertions using pattern mining and conceptualization to form more condensed and abstractive knowledge. We evaluate our knowledge graph using both intrinsic quality measures and a downstream application, i.e., recommendation. The comprehensive study shows that our knowledge graph can well model e-commerce commonsense knowledge and can have many potential applications.
Short Text Pre-training with Extended Token Classification for E-commerce Query Understanding
Oct 08, 2022
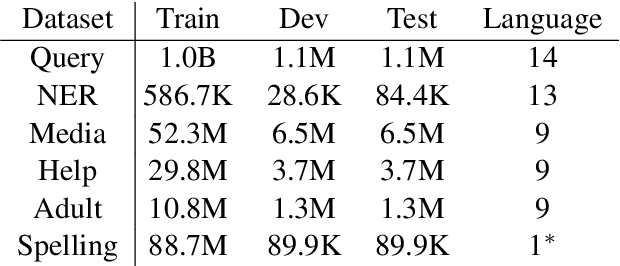
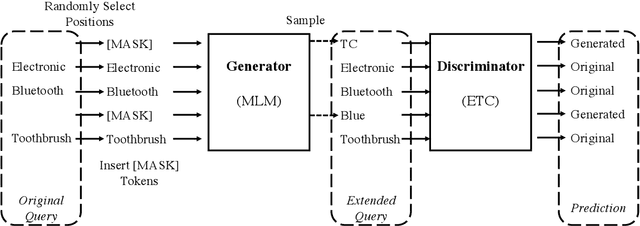
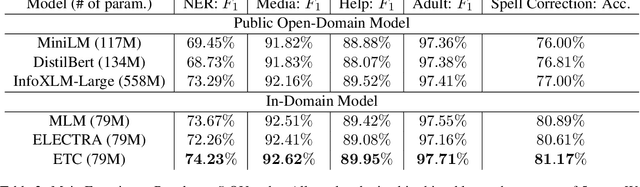
Abstract:E-commerce query understanding is the process of inferring the shopping intent of customers by extracting semantic meaning from their search queries. The recent progress of pre-trained masked language models (MLM) in natural language processing is extremely attractive for developing effective query understanding models. Specifically, MLM learns contextual text embedding via recovering the masked tokens in the sentences. Such a pre-training process relies on the sufficient contextual information. It is, however, less effective for search queries, which are usually short text. When applying masking to short search queries, most contextual information is lost and the intent of the search queries may be changed. To mitigate the above issues for MLM pre-training on search queries, we propose a novel pre-training task specifically designed for short text, called Extended Token Classification (ETC). Instead of masking the input text, our approach extends the input by inserting tokens via a generator network, and trains a discriminator to identify which tokens are inserted in the extended input. We conduct experiments in an E-commerce store to demonstrate the effectiveness of ETC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge