FolkScope: Intention Knowledge Graph Construction for Discovering E-commerce Commonsense
Paper and Code
Nov 15, 2022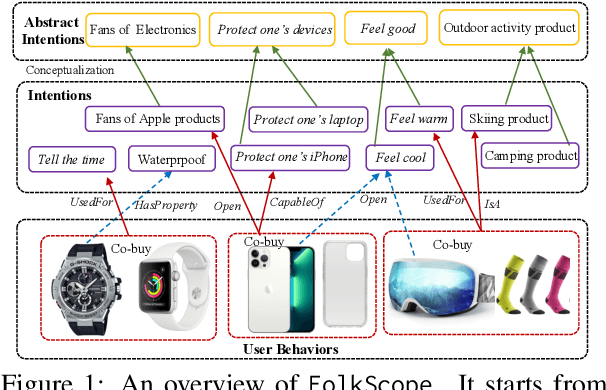
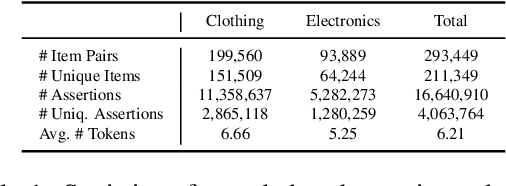
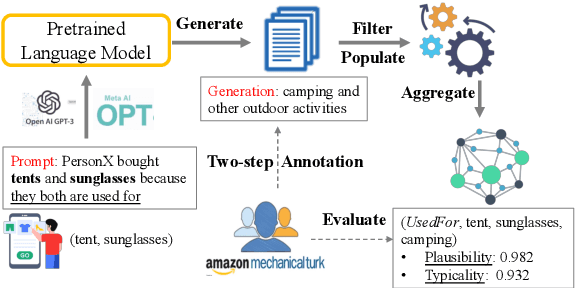
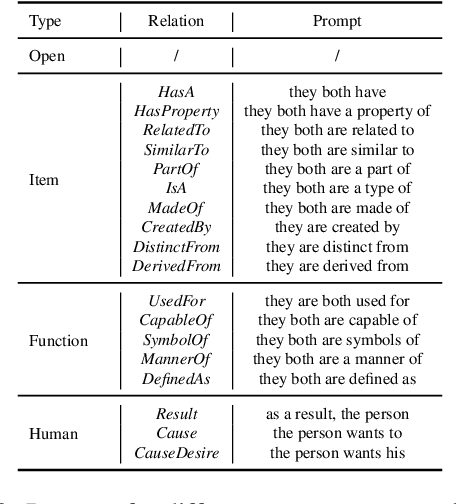
As stated by Oren Etzioni, ``commonsense is the dark matter of artificial intelligence''. In e-commerce, understanding users' needs or intentions requires substantial commonsense knowledge, e.g., ``A user bought an iPhone and a compatible case because the user wanted the phone to be protected''. In this paper, we present FolkScope, an intention knowledge graph construction framework, to reveal the structure of humans' minds about purchasing items on e-commerce platforms such as Amazon. As commonsense knowledge is usually ineffable and not expressed explicitly, it is challenging to perform any kind of information extraction. Thus, we propose a new approach that leverages the generation power of large-scale language models and human-in-the-loop annotations to semi-automatically construct the knowledge graph. We annotate a large amount of assertions for both plausibility and typicality of an intention that can explain a purchasing or co-purchasing behavior, where the intention can be an open reason or a predicate falling into one of 18 categories aligning with ConceptNet, e.g., IsA, MadeOf, UsedFor, etc. Then we populate the annotated information to all automatically generated ones, and further structurize the assertions using pattern mining and conceptualization to form more condensed and abstractive knowledge. We evaluate our knowledge graph using both intrinsic quality measures and a downstream application, i.e., recommendation. The comprehensive study shows that our knowledge graph can well model e-commerce commonsense knowledge and can have many potential applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge