Zhanghui Kuang
Uncertainty Estimation via Response Scaling for Pseudo-mask Noise Mitigation in Weakly-supervised Semantic Segmentation
Dec 14, 2021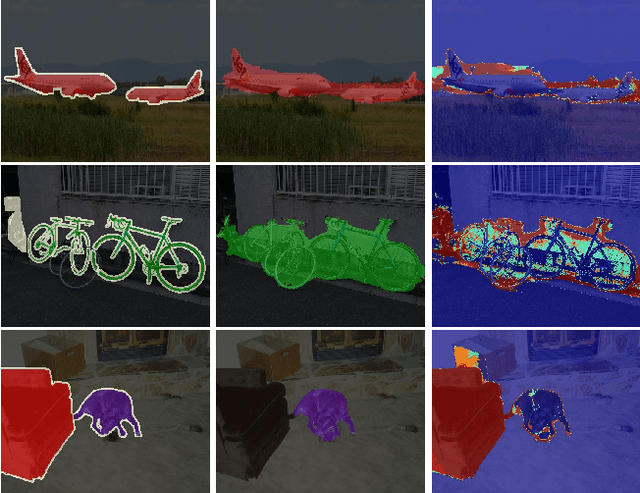
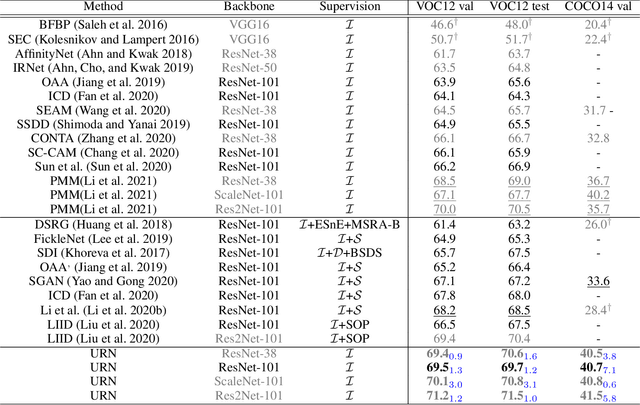

Abstract:Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) segments objects without a heavy burden of dense annotation. While as a price, generated pseudo-masks exist obvious noisy pixels, which result in sub-optimal segmentation models trained over these pseudo-masks. But rare studies notice or work on this problem, even these noisy pixels are inevitable after their improvements on pseudo-mask. So we try to improve WSSS in the aspect of noise mitigation. And we observe that many noisy pixels are of high confidence, especially when the response range is too wide or narrow, presenting an uncertain status. Thus, in this paper, we simulate noisy variations of response by scaling the prediction map multiple times for uncertainty estimation. The uncertainty is then used to weight the segmentation loss to mitigate noisy supervision signals. We call this method URN, abbreviated from Uncertainty estimation via Response scaling for Noise mitigation. Experiments validate the benefits of URN, and our method achieves state-of-the-art results at 71.2% and 41.5% on PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 respectively, without extra models like saliency detection. Code is available at https://github.com/XMed-Lab/URN.
Pseudo-mask Matters in Weakly-supervised Semantic Segmentation
Sep 07, 2021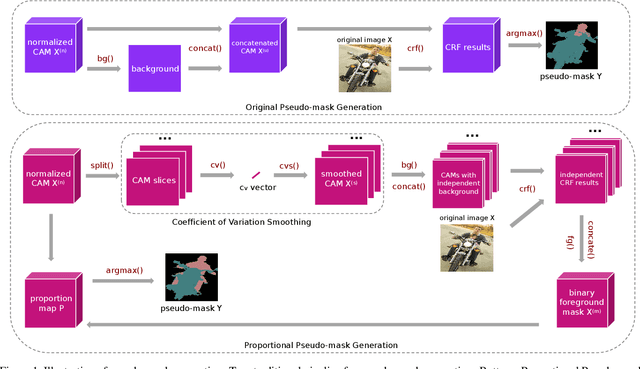

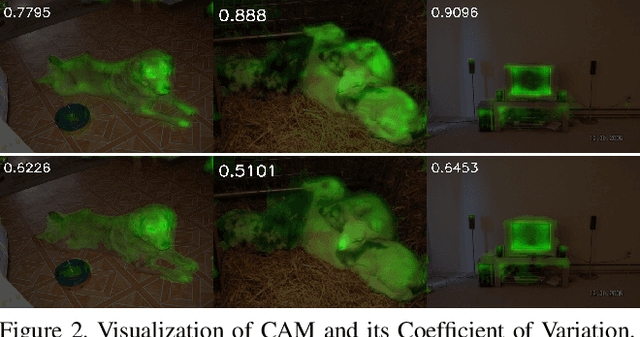

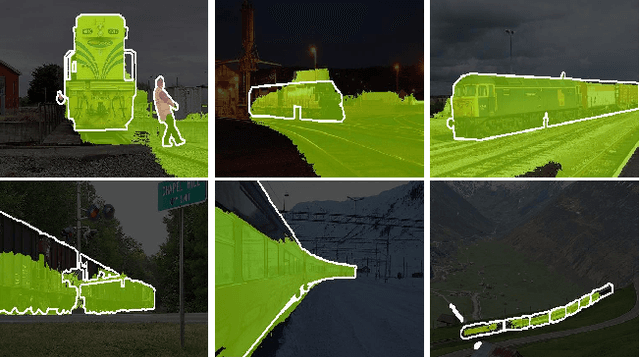
Abstract:Most weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) methods follow the pipeline that generates pseudo-masks initially and trains the segmentation model with the pseudo-masks in fully supervised manner after. However, we find some matters related to the pseudo-masks, including high quality pseudo-masks generation from class activation maps (CAMs), and training with noisy pseudo-mask supervision. For these matters, we propose the following designs to push the performance to new state-of-art: (i) Coefficient of Variation Smoothing to smooth the CAMs adaptively; (ii) Proportional Pseudo-mask Generation to project the expanded CAMs to pseudo-mask based on a new metric indicating the importance of each class on each location, instead of the scores trained from binary classifiers. (iii) Pretended Under-Fitting strategy to suppress the influence of noise in pseudo-mask; (iv) Cyclic Pseudo-mask to boost the pseudo-masks during training of fully supervised semantic segmentation (FSSS). Experiments based on our methods achieve new state-of-art results on two changeling weakly supervised semantic segmentation datasets, pushing the mIoU to 70.0% and 40.2% on PAS-CAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 respectively. Codes including segmentation framework are released at https://github.com/Eli-YiLi/PMM
MMOCR: A Comprehensive Toolbox for Text Detection, Recognition and Understanding
Aug 14, 2021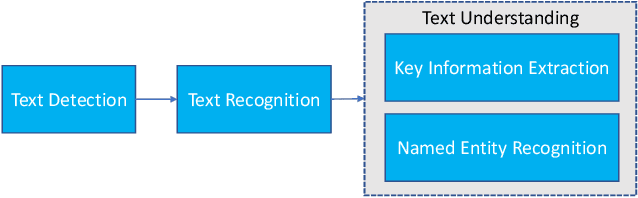
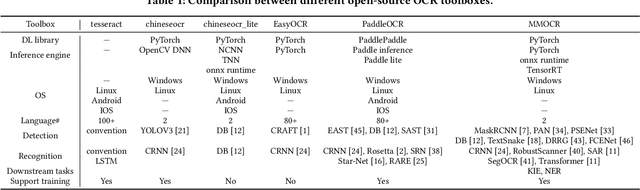
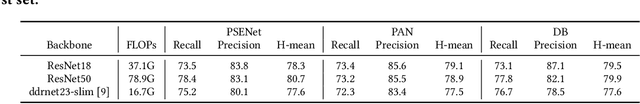
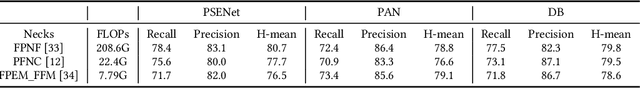
Abstract:We present MMOCR-an open-source toolbox which provides a comprehensive pipeline for text detection and recognition, as well as their downstream tasks such as named entity recognition and key information extraction. MMOCR implements 14 state-of-the-art algorithms, which is significantly more than all the existing open-source OCR projects we are aware of to date. To facilitate future research and industrial applications of text recognition-related problems, we also provide a large number of trained models and detailed benchmarks to give insights into the performance of text detection, recognition and understanding. MMOCR is publicly released at https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmocr.
Vision Transformer with Progressive Sampling
Aug 03, 2021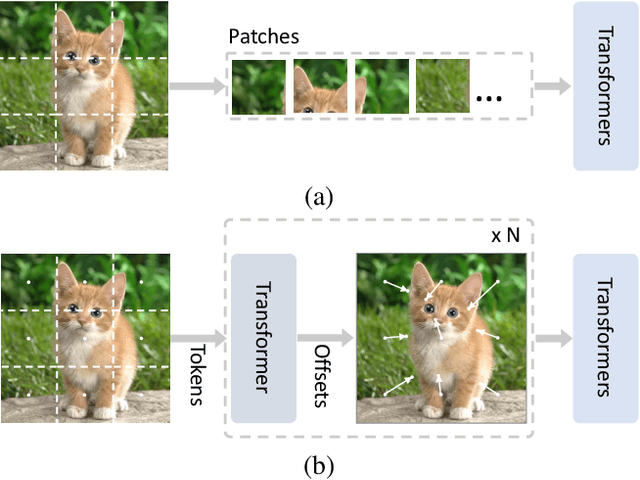



Abstract:Transformers with powerful global relation modeling abilities have been introduced to fundamental computer vision tasks recently. As a typical example, the Vision Transformer (ViT) directly applies a pure transformer architecture on image classification, by simply splitting images into tokens with a fixed length, and employing transformers to learn relations between these tokens. However, such naive tokenization could destruct object structures, assign grids to uninterested regions such as background, and introduce interference signals. To mitigate the above issues, in this paper, we propose an iterative and progressive sampling strategy to locate discriminative regions. At each iteration, embeddings of the current sampling step are fed into a transformer encoder layer, and a group of sampling offsets is predicted to update the sampling locations for the next step. The progressive sampling is differentiable. When combined with the Vision Transformer, the obtained PS-ViT network can adaptively learn where to look. The proposed PS-ViT is both effective and efficient. When trained from scratch on ImageNet, PS-ViT performs 3.8% higher than the vanilla ViT in terms of top-1 accuracy with about $4\times$ fewer parameters and $10\times$ fewer FLOPs. Code is available at https://github.com/yuexy/PS-ViT.
Group Fisher Pruning for Practical Network Compression
Aug 02, 2021



Abstract:Network compression has been widely studied since it is able to reduce the memory and computation cost during inference. However, previous methods seldom deal with complicated structures like residual connections, group/depth-wise convolution and feature pyramid network, where channels of multiple layers are coupled and need to be pruned simultaneously. In this paper, we present a general channel pruning approach that can be applied to various complicated structures. Particularly, we propose a layer grouping algorithm to find coupled channels automatically. Then we derive a unified metric based on Fisher information to evaluate the importance of a single channel and coupled channels. Moreover, we find that inference speedup on GPUs is more correlated with the reduction of memory rather than FLOPs, and thus we employ the memory reduction of each channel to normalize the importance. Our method can be used to prune any structures including those with coupled channels. We conduct extensive experiments on various backbones, including the classic ResNet and ResNeXt, mobile-friendly MobileNetV2, and the NAS-based RegNet, both on image classification and object detection which is under-explored. Experimental results validate that our method can effectively prune sophisticated networks, boosting inference speed without sacrificing accuracy.
Fourier Contour Embedding for Arbitrary-Shaped Text Detection
Apr 22, 2021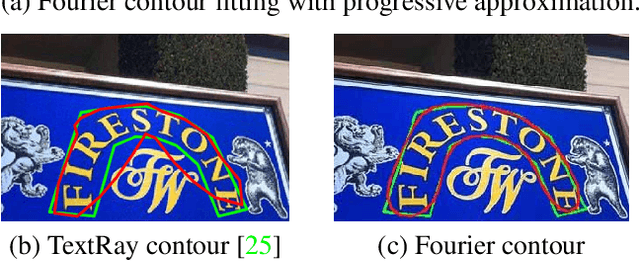
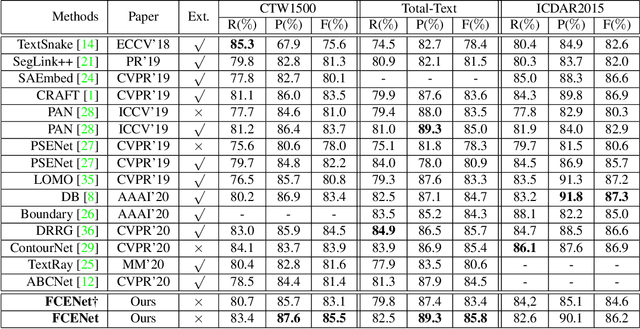
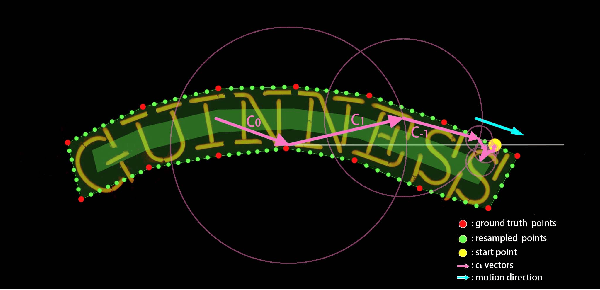
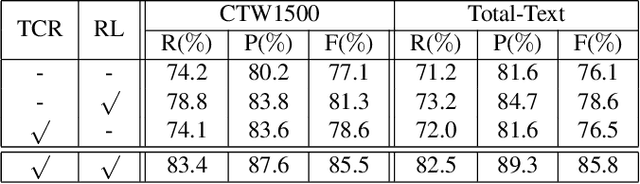
Abstract:One of the main challenges for arbitrary-shaped text detection is to design a good text instance representation that allows networks to learn diverse text geometry variances. Most of existing methods model text instances in image spatial domain via masks or contour point sequences in the Cartesian or the polar coordinate system. However, the mask representation might lead to expensive post-processing, while the point sequence one may have limited capability to model texts with highly-curved shapes. To tackle these problems, we model text instances in the Fourier domain and propose one novel Fourier Contour Embedding (FCE) method to represent arbitrary shaped text contours as compact signatures. We further construct FCENet with a backbone, feature pyramid networks (FPN) and a simple post-processing with the Inverse Fourier Transformation (IFT) and Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Different from previous methods, FCENet first predicts compact Fourier signatures of text instances, and then reconstructs text contours via IFT and NMS during test. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FCE is accurate and robust to fit contours of scene texts even with highly-curved shapes, and also validate the effectiveness and the good generalization of FCENet for arbitrary-shaped text detection. Furthermore, experimental results show that our FCENet is superior to the state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on CTW1500 and Total-Text, especially on challenging highly-curved text subset.
Spatial Dual-Modality Graph Reasoning for Key Information Extraction
Mar 26, 2021



Abstract:Key information extraction from document images is of paramount importance in office automation. Conventional template matching based approaches fail to generalize well to document images of unseen templates, and are not robust against text recognition errors. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end Spatial Dual-Modality Graph Reasoning method (SDMG-R) to extract key information from unstructured document images. We model document images as dual-modality graphs, nodes of which encode both the visual and textual features of detected text regions, and edges of which represent the spatial relations between neighboring text regions. The key information extraction is solved by iteratively propagating messages along graph edges and reasoning the categories of graph nodes. In order to roundly evaluate our proposed method as well as boost the future research, we release a new dataset named WildReceipt, which is collected and annotated tailored for the evaluation of key information extraction from document images of unseen templates in the wild. It contains 25 key information categories, a total of about 69000 text boxes, and is about 2 times larger than the existing public datasets. Extensive experiments validate that all information including visual features, textual features and spatial relations can benefit key information extraction. It has been shown that SDMG-R can effectively extract key information from document images of unseen templates, and obtain new state-of-the-art results on the recent popular benchmark SROIE and our WildReceipt. Our code and dataset will be publicly released.
Context-Aware RCNN: A Baseline for Action Detection in Videos
Jul 20, 2020
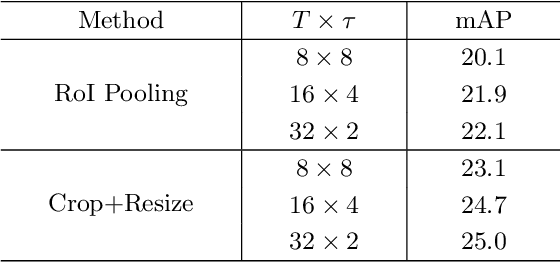
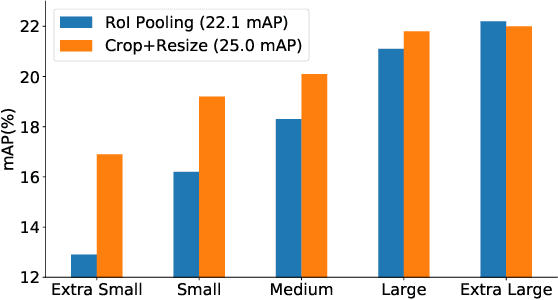

Abstract:Video action detection approaches usually conduct actor-centric action recognition over RoI-pooled features following the standard pipeline of Faster-RCNN. In this work, we first empirically find the recognition accuracy is highly correlated with the bounding box size of an actor, and thus higher resolution of actors contributes to better performance. However, video models require dense sampling in time to achieve accurate recognition. To fit in GPU memory, the frames to backbone network must be kept low-resolution, resulting in a coarse feature map in RoI-Pooling layer. Thus, we revisit RCNN for actor-centric action recognition via cropping and resizing image patches around actors before feature extraction with I3D deep network. Moreover, we found that expanding actor bounding boxes slightly and fusing the context features can further boost the performance. Consequently, we develop a surpringly effective baseline (Context-Aware RCNN) and it achieves new state-of-the-art results on two challenging action detection benchmarks of AVA and JHMDB. Our observations challenge the conventional wisdom of RoI-Pooling based pipeline and encourage researchers rethink the importance of resolution in actor-centric action recognition. Our approach can serve as a strong baseline for video action detection and is expected to inspire new ideas for this filed. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/MCG-NJU/CRCNN-Action}.
RobustScanner: Dynamically Enhancing Positional Clues for Robust Text Recognition
Jul 17, 2020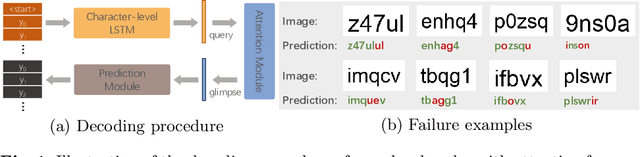


Abstract:The attention-based encoder-decoder framework has recently achieved impressive results for scene text recognition, and many variants have emerged with improvements in recognition quality. However, it performs poorly on contextless texts (e.g., random character sequences) which is unacceptable in most of real application scenarios. In this paper, we first deeply investigate the decoding process of the decoder. We empirically find that a representative character-level sequence decoder utilizes not only context information but also positional information. Contextual information, which the existing approaches heavily rely on, causes the problem of attention drift. To suppress such side-effect, we propose a novel position enhancement branch, and dynamically fuse its outputs with those of the decoder attention module for scene text recognition. Specifically, it contains a position aware module to enable the encoder to output feature vectors encoding their own spatial positions, and an attention module to estimate glimpses using the positional clue (i.e., the current decoding time step) only. The dynamic fusion is conducted for more robust feature via an element-wise gate mechanism. Theoretically, our proposed method, dubbed \emph{RobustScanner}, decodes individual characters with dynamic ratio between context and positional clues, and utilizes more positional ones when the decoding sequences with scarce context, and thus is robust and practical. Empirically, it has achieved new state-of-the-art results on popular regular and irregular text recognition benchmarks while without much performance drop on contextless benchmarks, validating its robustness in both contextual and contextless application scenarios.
Geometry Normalization Networks for Accurate Scene Text Detection
Sep 02, 2019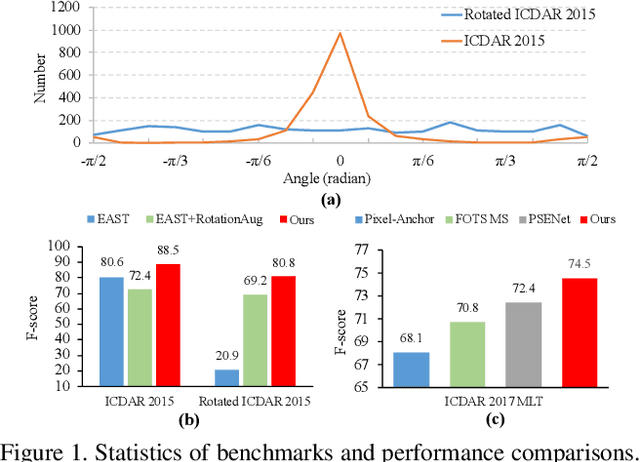
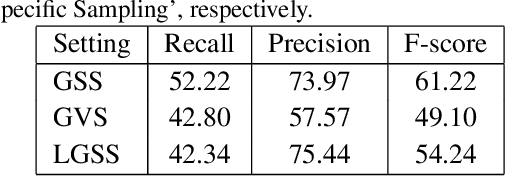
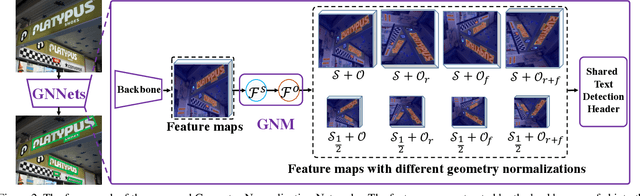
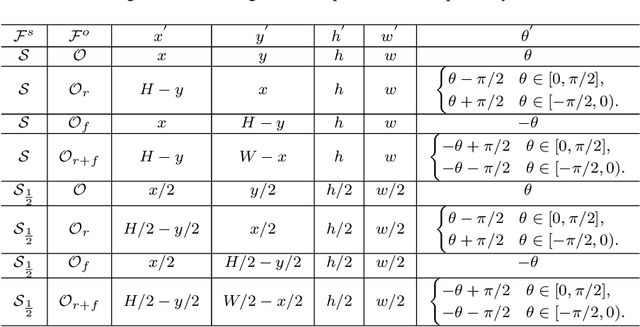
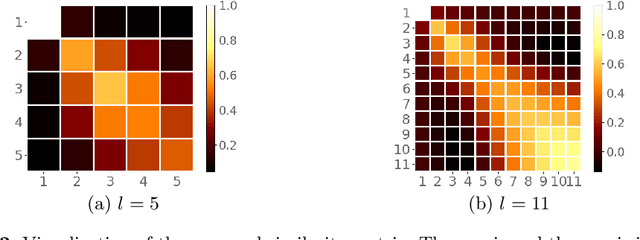
Abstract:Large geometry (e.g., orientation) variances are the key challenges in the scene text detection. In this work, we first conduct experiments to investigate the capacity of networks for learning geometry variances on detecting scene texts, and find that networks can handle only limited text geometry variances. Then, we put forward a novel Geometry Normalization Module (GNM) with multiple branches, each of which is composed of one Scale Normalization Unit and one Orientation Normalization Unit, to normalize each text instance to one desired canonical geometry range through at least one branch. The GNM is general and readily plugged into existing convolutional neural network based text detectors to construct end-to-end Geometry Normalization Networks (GNNets). Moreover, we propose a geometry-aware training scheme to effectively train the GNNets by sampling and augmenting text instances from a uniform geometry variance distribution. Finally, experiments on popular benchmarks of ICDAR 2015 and ICDAR 2017 MLT validate that our method outperforms all the state-of-the-art approaches remarkably by obtaining one-forward test F-scores of 88.52 and 74.54 respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge