Youjiang Xu
VITON-DiT: Learning In-the-Wild Video Try-On from Human Dance Videos via Diffusion Transformers
May 28, 2024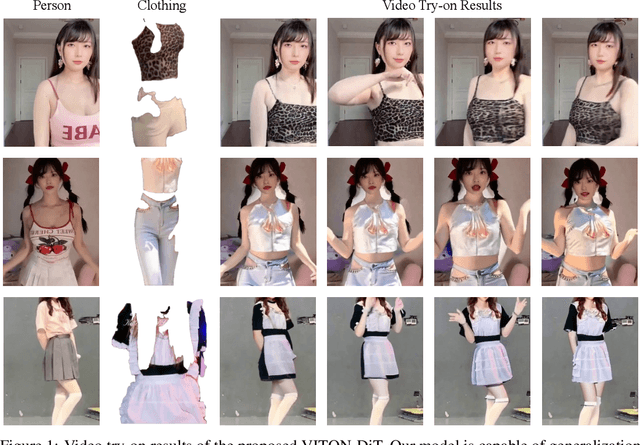
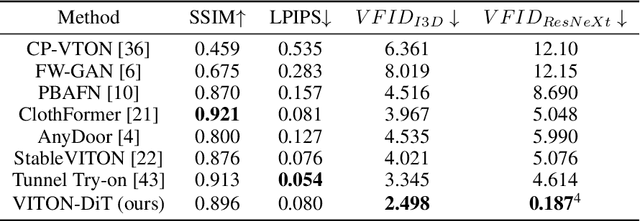
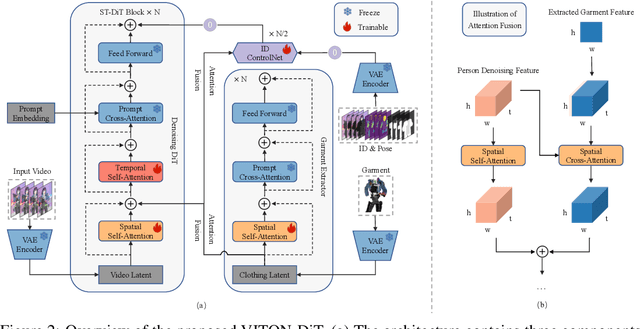
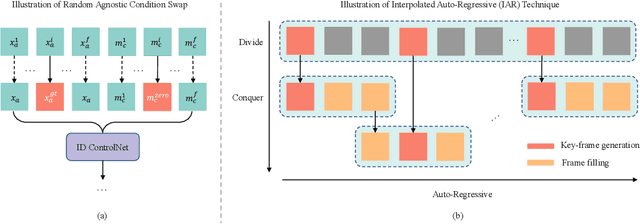
Abstract:Video try-on stands as a promising area for its tremendous real-world potential. Prior works are limited to transferring product clothing images onto person videos with simple poses and backgrounds, while underperforming on casually captured videos. Recently, Sora revealed the scalability of Diffusion Transformer (DiT) in generating lifelike videos featuring real-world scenarios. Inspired by this, we explore and propose the first DiT-based video try-on framework for practical in-the-wild applications, named VITON-DiT. Specifically, VITON-DiT consists of a garment extractor, a Spatial-Temporal denoising DiT, and an identity preservation ControlNet. To faithfully recover the clothing details, the extracted garment features are fused with the self-attention outputs of the denoising DiT and the ControlNet. We also introduce novel random selection strategies during training and an Interpolated Auto-Regressive (IAR) technique at inference to facilitate long video generation. Unlike existing attempts that require the laborious and restrictive construction of a paired training dataset, severely limiting their scalability, VITON-DiT alleviates this by relying solely on unpaired human dance videos and a carefully designed multi-stage training strategy. Furthermore, we curate a challenging benchmark dataset to evaluate the performance of casual video try-on. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of VITON-DiT in generating spatio-temporal consistent try-on results for in-the-wild videos with complicated human poses.
Faster Meta Update Strategy for Noise-Robust Deep Learning
Apr 30, 2021



Abstract:It has been shown that deep neural networks are prone to overfitting on biased training data. Towards addressing this issue, meta-learning employs a meta model for correcting the training bias. Despite the promising performances, super slow training is currently the bottleneck in the meta learning approaches. In this paper, we introduce a novel Faster Meta Update Strategy (FaMUS) to replace the most expensive step in the meta gradient computation with a faster layer-wise approximation. We empirically find that FaMUS yields not only a reasonably accurate but also a low-variance approximation of the meta gradient. We conduct extensive experiments to verify the proposed method on two tasks. We show our method is able to save two-thirds of the training time while still maintaining the comparable or achieving even better generalization performance. In particular, our method achieves the state-of-the-art performance on both synthetic and realistic noisy labels, and obtains promising performance on long-tailed recognition on standard benchmarks.
Geometry Normalization Networks for Accurate Scene Text Detection
Sep 02, 2019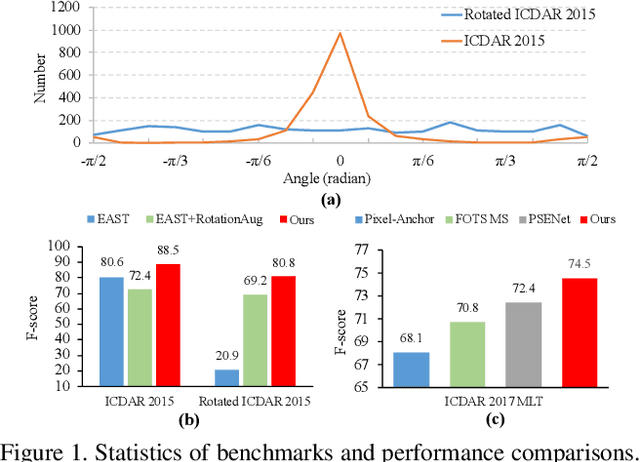
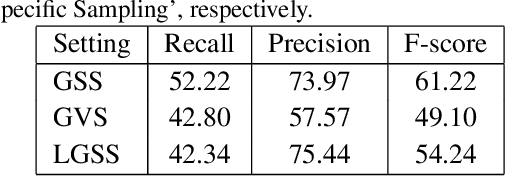
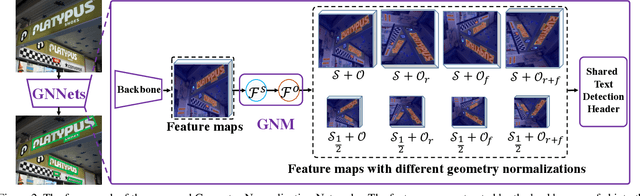
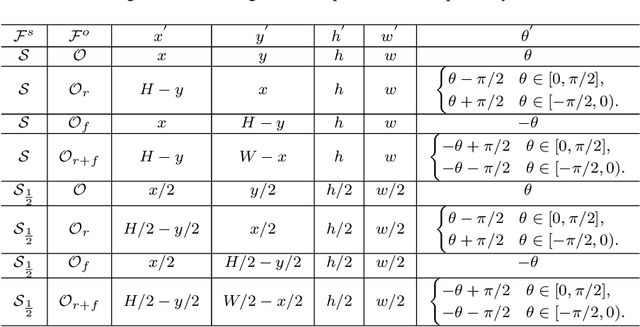
Abstract:Large geometry (e.g., orientation) variances are the key challenges in the scene text detection. In this work, we first conduct experiments to investigate the capacity of networks for learning geometry variances on detecting scene texts, and find that networks can handle only limited text geometry variances. Then, we put forward a novel Geometry Normalization Module (GNM) with multiple branches, each of which is composed of one Scale Normalization Unit and one Orientation Normalization Unit, to normalize each text instance to one desired canonical geometry range through at least one branch. The GNM is general and readily plugged into existing convolutional neural network based text detectors to construct end-to-end Geometry Normalization Networks (GNNets). Moreover, we propose a geometry-aware training scheme to effectively train the GNNets by sampling and augmenting text instances from a uniform geometry variance distribution. Finally, experiments on popular benchmarks of ICDAR 2015 and ICDAR 2017 MLT validate that our method outperforms all the state-of-the-art approaches remarkably by obtaining one-forward test F-scores of 88.52 and 74.54 respectively.
Movie Question Answering: Remembering the Textual Cues for Layered Visual Contents
Apr 25, 2018



Abstract:Movies provide us with a mass of visual content as well as attracting stories. Existing methods have illustrated that understanding movie stories through only visual content is still a hard problem. In this paper, for answering questions about movies, we put forward a Layered Memory Network (LMN) that represents frame-level and clip-level movie content by the Static Word Memory module and the Dynamic Subtitle Memory module, respectively. Particularly, we firstly extract words and sentences from the training movie subtitles. Then the hierarchically formed movie representations, which are learned from LMN, not only encode the correspondence between words and visual content inside frames, but also encode the temporal alignment between sentences and frames inside movie clips. We also extend our LMN model into three variant frameworks to illustrate the good extendable capabilities. We conduct extensive experiments on the MovieQA dataset. With only visual content as inputs, LMN with frame-level representation obtains a large performance improvement. When incorporating subtitles into LMN to form the clip-level representation, we achieve the state-of-the-art performance on the online evaluation task of 'Video+Subtitles'. The good performance successfully demonstrates that the proposed framework of LMN is effective and the hierarchically formed movie representations have good potential for the applications of movie question answering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge