Jinlan Fu
HERMES: KV Cache as Hierarchical Memory for Efficient Streaming Video Understanding
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated significant improvement in offline video understanding. However, extending these capabilities to streaming video inputs, remains challenging, as existing models struggle to simultaneously maintain stable understanding performance, real-time responses, and low GPU memory overhead. To address this challenge, we propose HERMES, a novel training-free architecture for real-time and accurate understanding of video streams. Based on a mechanistic attention investigation, we conceptualize KV cache as a hierarchical memory framework that encapsulates video information across multiple granularities. During inference, HERMES reuses a compact KV cache, enabling efficient streaming understanding under resource constraints. Notably, HERMES requires no auxiliary computations upon the arrival of user queries, thereby guaranteeing real-time responses for continuous video stream interactions, which achieves 10$\times$ faster TTFT compared to prior SOTA. Even when reducing video tokens by up to 68% compared with uniform sampling, HERMES achieves superior or comparable accuracy across all benchmarks, with up to 11.4% gains on streaming datasets.
FutureOmni: Evaluating Future Forecasting from Omni-Modal Context for Multimodal LLMs
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Although Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate strong omni-modal perception, their ability to forecast future events from audio-visual cues remains largely unexplored, as existing benchmarks focus mainly on retrospective understanding. To bridge this gap, we introduce FutureOmni, the first benchmark designed to evaluate omni-modal future forecasting from audio-visual environments. The evaluated models are required to perform cross-modal causal and temporal reasoning, as well as effectively leverage internal knowledge to predict future events. FutureOmni is constructed via a scalable LLM-assisted, human-in-the-loop pipeline and contains 919 videos and 1,034 multiple-choice QA pairs across 8 primary domains. Evaluations on 13 omni-modal and 7 video-only models show that current systems struggle with audio-visual future prediction, particularly in speech-heavy scenarios, with the best accuracy of 64.8% achieved by Gemini 3 Flash. To mitigate this limitation, we curate a 7K-sample instruction-tuning dataset and propose an Omni-Modal Future Forecasting (OFF) training strategy. Evaluations on FutureOmni and popular audio-visual and video-only benchmarks demonstrate that OFF enhances future forecasting and generalization. We publicly release all code (https://github.com/OpenMOSS/FutureOmni) and datasets (https://huggingface.co/datasets/OpenMOSS-Team/FutureOmni).
Analyzing Reasoning Consistency in Large Multimodal Models under Cross-Modal Conflicts
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in video reasoning via Chain-of-Thought (CoT). However, the robustness of their reasoning chains remains questionable. In this paper, we identify a critical failure mode termed textual inertia, where once a textual hallucination occurs in the thinking process, models tend to blindly adhere to the erroneous text while neglecting conflicting visual evidence. To systematically investigate this, we propose the LogicGraph Perturbation Protocol that structurally injects perturbations into the reasoning chains of diverse LMMs spanning both native reasoning architectures and prompt-driven paradigms to evaluate their self-reflection capabilities. The results reveal that models successfully self-correct in less than 10% of cases and predominantly succumb to blind textual error propagation. To mitigate this, we introduce Active Visual-Context Refinement, a training-free inference paradigm which orchestrates an active visual re-grounding mechanism to enforce fine-grained verification coupled with an adaptive context refinement strategy to summarize and denoise the reasoning history. Experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly stifles hallucination propagation and enhances reasoning robustness.
AI Meets Brain: Memory Systems from Cognitive Neuroscience to Autonomous Agents
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Memory serves as the pivotal nexus bridging past and future, providing both humans and AI systems with invaluable concepts and experience to navigate complex tasks. Recent research on autonomous agents has increasingly focused on designing efficient memory workflows by drawing on cognitive neuroscience. However, constrained by interdisciplinary barriers, existing works struggle to assimilate the essence of human memory mechanisms. To bridge this gap, we systematically synthesizes interdisciplinary knowledge of memory, connecting insights from cognitive neuroscience with LLM-driven agents. Specifically, we first elucidate the definition and function of memory along a progressive trajectory from cognitive neuroscience through LLMs to agents. We then provide a comparative analysis of memory taxonomy, storage mechanisms, and the complete management lifecycle from both biological and artificial perspectives. Subsequently, we review the mainstream benchmarks for evaluating agent memory. Additionally, we explore memory security from dual perspectives of attack and defense. Finally, we envision future research directions, with a focus on multimodal memory systems and skill acquisition.
MCM-DPO: Multifaceted Cross-Modal Direct Preference Optimization for Alt-text Generation
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:The alt-text generation task produces concise, context-relevant descriptions of images, enabling blind and low-vision users to access online images. Despite the capabilities of large vision-language models, alt-text generation performance remains limited due to noisy user annotations, inconsistent standards, and MLLMs' insensitivity to contextual information. Previous efforts to fine-tune MLLMs using supervised fine-tuning (SFT) have struggled, as SFT relies on accurate target annotations, which are often flawed in user-generated alt-text. To address this, we propose Multi-faceted Cross-modal Direct Preference Optimization (MCM-DPO), which improves alt-text generation by learning to identify better options in preference pairs without requiring precise annotations. MCM-DPO optimizes preferences across single, paired, and multi-preference dimensions, covering textual, visual, and cross-modal factors. In light of the scarcity of high-quality annotated and preference-labeled datasets for alt-text, we constructed two large-scale, high-quality datasets named TAlt and PAlt, sourced from Twitter and Pinterest. These datasets include 202k annotated alt-text samples and 18k preference pairs that cover diverse preference dimensions, aiming to support further research in this domain. Experimental results show that our proposed MCM-DPO method consistently outperforms both DPO and SFT, establishing a new state of the art in alt-text generation. We release the code and data here: https://github.com/LVUGAI/MCM-DPO
LLM as Effective Streaming Processor: Bridging Streaming-Batch Mismatches with Group Position Encoding
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are primarily designed for batch processing. Existing methods for adapting LLMs to streaming rely either on expensive re-encoding or specialized architectures with limited scalability. This work identifies three key mismatches in adapting batch-oriented LLMs to streaming: (1) input-attention, (2) output-attention, and (3) position-ID mismatches. While it is commonly assumed that the latter two mismatches require frequent re-encoding, our analysis reveals that only the input-attention mismatch significantly impacts performance, indicating re-encoding outputs is largely unnecessary. To better understand this discrepancy with the common assumption, we provide the first comprehensive analysis of the impact of position encoding on LLMs in streaming, showing that preserving relative positions within source and target contexts is more critical than maintaining absolute order. Motivated by the above analysis, we introduce a group position encoding paradigm built on batch architectures to enhance consistency between streaming and batch modes. Extensive experiments on cross-lingual and cross-modal tasks demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches. Our method requires no architectural modifications, exhibits strong generalization in both streaming and batch modes. The code is available at repository https://github.com/EIT-NLP/StreamingLLM.
Investigating and Enhancing the Robustness of Large Multimodal Models Against Temporal Inconsistency
May 20, 2025Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have recently demonstrated impressive performance on general video comprehension benchmarks. Nevertheless, for broader applications, the robustness of their temporal analysis capability needs to be thoroughly investigated yet predominantly ignored. Motivated by this, we propose a novel temporal robustness benchmark (TemRobBench), which introduces temporal inconsistency perturbations separately at the visual and textual modalities to assess the robustness of models. We evaluate 16 mainstream LMMs and find that they exhibit over-reliance on prior knowledge and textual context in adversarial environments, while ignoring the actual temporal dynamics in the video. To mitigate this issue, we design panoramic direct preference optimization (PanoDPO), which encourages LMMs to incorporate both visual and linguistic feature preferences simultaneously. Experimental results show that PanoDPO can effectively enhance the model's robustness and reliability in temporal analysis.
Rethinking Visual Layer Selection in Multimodal LLMs
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved impressive performance across a wide range of tasks, typically using CLIP-ViT as their visual encoder due to its strong text-image alignment capabilities. While prior studies suggest that different CLIP-ViT layers capture different types of information, with shallower layers focusing on fine visual details and deeper layers aligning more closely with textual semantics, most MLLMs still select visual features based on empirical heuristics rather than systematic analysis. In this work, we propose a Layer-wise Representation Similarity approach to group CLIP-ViT layers with similar behaviors into {shallow, middle, and deep} categories and assess their impact on MLLM performance. Building on this foundation, we revisit the visual layer selection problem in MLLMs at scale, training LLaVA-style models ranging from 1.4B to 7B parameters. Through extensive experiments across 10 datasets and 4 tasks, we find that: (1) deep layers are essential for OCR tasks; (2) shallow and middle layers substantially outperform deep layers on reasoning tasks involving counting, positioning, and object localization; (3) a lightweight fusion of features across shallow, middle, and deep layers consistently outperforms specialized fusion baselines and single-layer selections, achieving gains on 9 out of 10 datasets. Our work offers the first principled study of visual layer selection in MLLMs, laying the groundwork for deeper investigations into visual representation learning for MLLMs.
VistaDPO: Video Hierarchical Spatial-Temporal Direct Preference Optimization for Large Video Models
Apr 17, 2025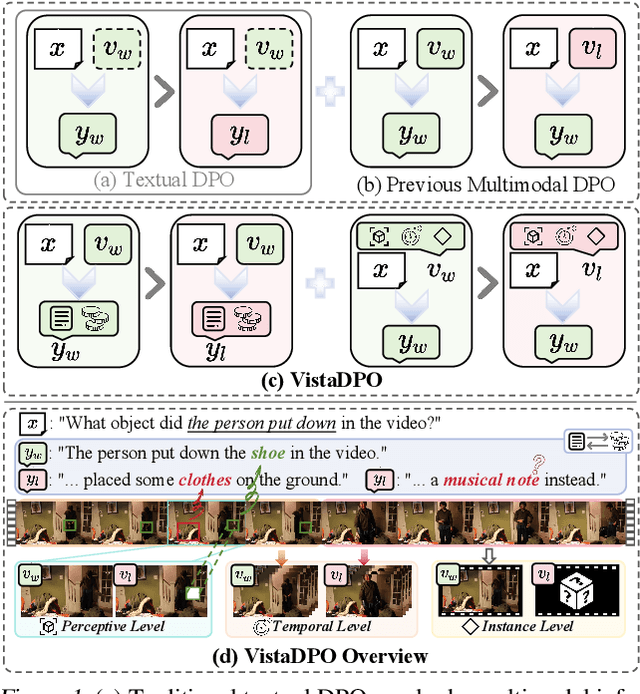
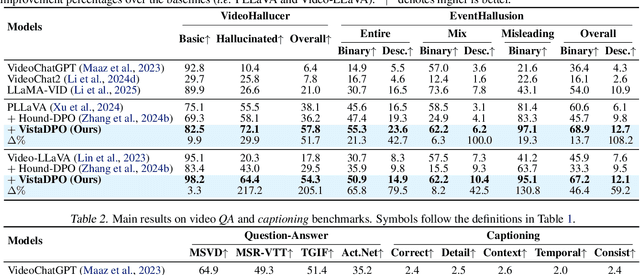
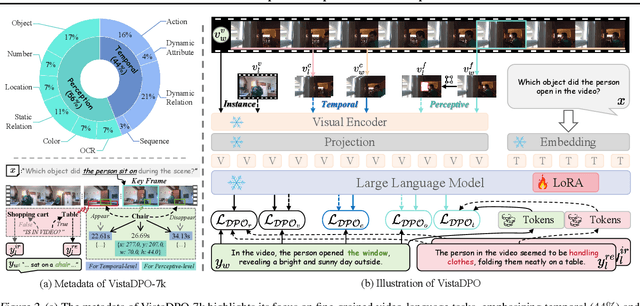
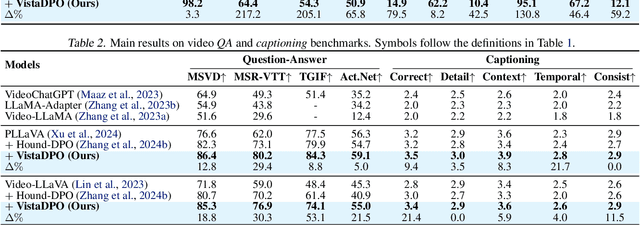
Abstract:Large Video Models (LVMs) built upon Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in video understanding but often suffer from misalignment with human intuition and video hallucination issues. To address these challenges, we introduce VistaDPO, a novel framework for Video Hierarchical Spatial-Temporal Direct Preference Optimization. VistaDPO enhances text-video preference alignment across three hierarchical levels: i) Instance Level, aligning overall video content with responses; ii) Temporal Level, aligning video temporal semantics with event descriptions; and iii) Perceptive Level, aligning spatial objects with language tokens. Given the lack of datasets for fine-grained video-language preference alignment, we construct VistaDPO-7k, a dataset of 7.2K QA pairs annotated with chosen and rejected responses, along with spatial-temporal grounding information such as timestamps, keyframes, and bounding boxes. Extensive experiments on benchmarks such as Video Hallucination, Video QA, and Captioning performance tasks demonstrate that VistaDPO significantly improves the performance of existing LVMs, effectively mitigating video-language misalignment and hallucination. The code and data are available at https://github.com/HaroldChen19/VistaDPO.
World Modeling Makes a Better Planner: Dual Preference Optimization for Embodied Task Planning
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large vision-language models (LVLMs) have shown promise for embodied task planning, yet they struggle with fundamental challenges like dependency constraints and efficiency. Existing approaches either solely optimize action selection or leverage world models during inference, overlooking the benefits of learning to model the world as a way to enhance planning capabilities. We propose Dual Preference Optimization (D$^2$PO), a new learning framework that jointly optimizes state prediction and action selection through preference learning, enabling LVLMs to understand environment dynamics for better planning. To automatically collect trajectories and stepwise preference data without human annotation, we introduce a tree search mechanism for extensive exploration via trial-and-error. Extensive experiments on VoTa-Bench demonstrate that our D$^2$PO-based method significantly outperforms existing methods and GPT-4o when applied to Qwen2-VL (7B), LLaVA-1.6 (7B), and LLaMA-3.2 (11B), achieving superior task success rates with more efficient execution paths.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge