Zhaoye Fei
WESR: Scaling and Evaluating Word-level Event-Speech Recognition
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Speech conveys not only linguistic information but also rich non-verbal vocal events such as laughing and crying. While semantic transcription is well-studied, the precise localization of non-verbal events remains a critical yet under-explored challenge. Current methods suffer from insufficient task definitions with limited category coverage and ambiguous temporal granularity. They also lack standardized evaluation frameworks, hindering the development of downstream applications. To bridge this gap, we first develop a refined taxonomy of 21 vocal events, with a new categorization into discrete (standalone) versus continuous (mixed with speech) types. Based on the refined taxonomy, we introduce WESR-Bench, an expert-annotated evaluation set (900+ utterances) with a novel position-aware protocol that disentangles ASR errors from event detection, enabling precise localization measurement for both discrete and continuous events. We also build a strong baseline by constructing a 1,700+ hour corpus, and train specialized models, surpassing both open-source audio-language models and commercial APIs while preserving ASR quality. We anticipate that WESR will serve as a foundational resource for future research in modeling rich, real-world auditory scenes.
MOSS Transcribe Diarize: Accurate Transcription with Speaker Diarization
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Speaker-Attributed, Time-Stamped Transcription (SATS) aims to transcribe what is said and to precisely determine the timing of each speaker, which is particularly valuable for meeting transcription. Existing SATS systems rarely adopt an end-to-end formulation and are further constrained by limited context windows, weak long-range speaker memory, and the inability to output timestamps. To address these limitations, we present MOSS Transcribe Diarize, a unified multimodal large language model that jointly performs Speaker-Attributed, Time-Stamped Transcription in an end-to-end paradigm. Trained on extensive real wild data and equipped with a 128k context window for up to 90-minute inputs, MOSS Transcribe Diarize scales well and generalizes robustly. Across comprehensive evaluations, it outperforms state-of-the-art commercial systems on multiple public and in-house benchmarks.
MOSS-Speech: Towards True Speech-to-Speech Models Without Text Guidance
Oct 02, 2025



Abstract:Spoken dialogue systems often rely on cascaded pipelines that transcribe, process, and resynthesize speech. While effective, this design discards paralinguistic cues and limits expressivity. Recent end-to-end methods reduce latency and better preserve these cues, yet still rely on text intermediates, creating a fundamental bottleneck. We present MOSS-Speech, a true speech-to-speech large language model that directly understands and generates speech without relying on text guidance. Our approach combines a modality-based layer-splitting architecture with a frozen pre-training strategy, preserving the reasoning and knowledge of pretrained text LLMs while adding native speech capabilities. Experiments show that our model achieves state-of-the-art results in spoken question answering and delivers comparable speech-to-speech performance relative to existing text-guided systems, while still maintaining competitive text performance. By narrowing the gap between text-guided and direct speech generation, our work establishes a new paradigm for expressive and efficient end-to-end speech interaction.
CodecBench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Acoustic and Semantic Evaluation
Aug 28, 2025



Abstract:With the rise of multimodal large language models (LLMs), audio codec plays an increasingly vital role in encoding audio into discrete tokens, enabling integration of audio into text-based LLMs. Current audio codec captures two types of information: acoustic and semantic. As audio codec is applied to diverse scenarios in speech language model , it needs to model increasingly complex information and adapt to varied contexts, such as scenarios with multiple speakers, background noise, or richer paralinguistic information. However, existing codec's own evaluation has been limited by simplistic metrics and scenarios, and existing benchmarks for audio codec are not designed for complex application scenarios, which limits the assessment performance on complex datasets for acoustic and semantic capabilities. We introduce CodecBench, a comprehensive evaluation dataset to assess audio codec performance from both acoustic and semantic perspectives across four data domains. Through this benchmark, we aim to identify current limitations, highlight future research directions, and foster advances in the development of audio codec. The codes are available at https://github.com/RayYuki/CodecBench.
VisuoThink: Empowering LVLM Reasoning with Multimodal Tree Search
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Vision-Language Models have showcased remarkable capabilities. However, they often falter when confronted with complex reasoning tasks that humans typically address through visual aids and deliberate, step-by-step thinking. While existing methods have explored text-based slow thinking or rudimentary visual assistance, they fall short of capturing the intricate, interleaved nature of human visual-verbal reasoning processes. To overcome these limitations and inspired by the mechanisms of slow thinking in human cognition, we introduce VisuoThink, a novel framework that seamlessly integrates visuospatial and linguistic domains. VisuoThink facilitates multimodal slow thinking by enabling progressive visual-textual reasoning and incorporates test-time scaling through look-ahead tree search. Extensive experiments demonstrate that VisuoThink significantly enhances reasoning capabilities via inference-time scaling, even without fine-tuning, achieving state-of-the-art performance in tasks involving geometry and spatial reasoning.
World Modeling Makes a Better Planner: Dual Preference Optimization for Embodied Task Planning
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large vision-language models (LVLMs) have shown promise for embodied task planning, yet they struggle with fundamental challenges like dependency constraints and efficiency. Existing approaches either solely optimize action selection or leverage world models during inference, overlooking the benefits of learning to model the world as a way to enhance planning capabilities. We propose Dual Preference Optimization (D$^2$PO), a new learning framework that jointly optimizes state prediction and action selection through preference learning, enabling LVLMs to understand environment dynamics for better planning. To automatically collect trajectories and stepwise preference data without human annotation, we introduce a tree search mechanism for extensive exploration via trial-and-error. Extensive experiments on VoTa-Bench demonstrate that our D$^2$PO-based method significantly outperforms existing methods and GPT-4o when applied to Qwen2-VL (7B), LLaVA-1.6 (7B), and LLaMA-3.2 (11B), achieving superior task success rates with more efficient execution paths.
How to Mitigate Overfitting in Weak-to-strong Generalization?
Mar 06, 2025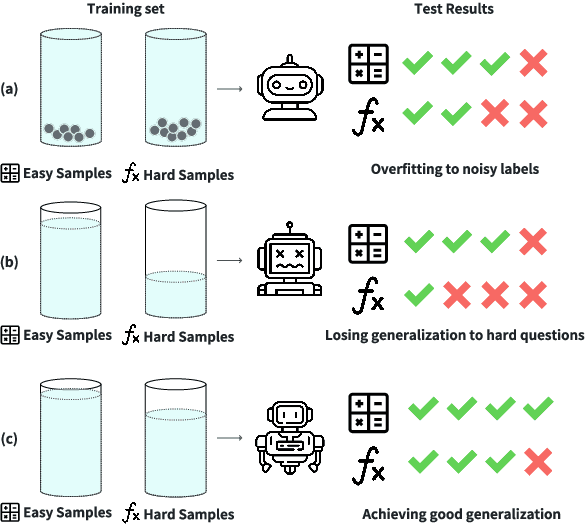
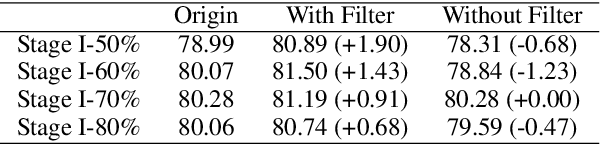
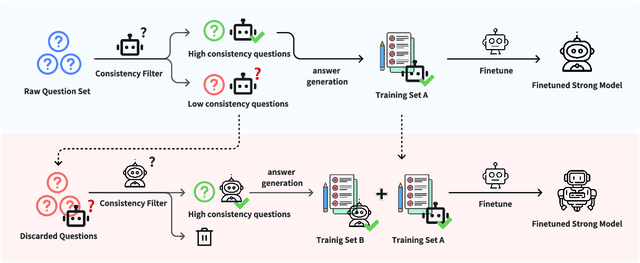
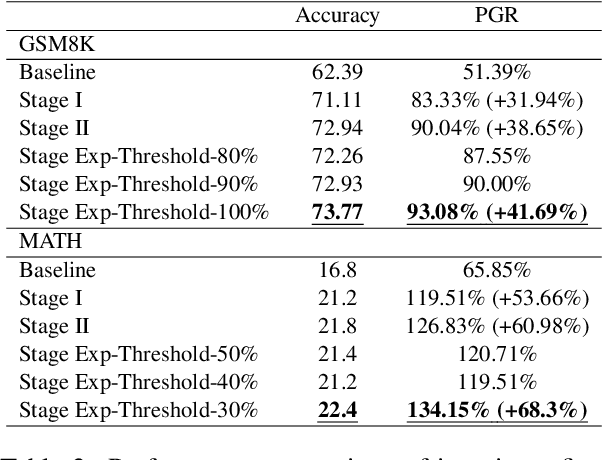
Abstract:Aligning powerful AI models on tasks that surpass human evaluation capabilities is the central problem of \textbf{superalignment}. To address this problem, weak-to-strong generalization aims to elicit the capabilities of strong models through weak supervisors and ensure that the behavior of strong models aligns with the intentions of weak supervisors without unsafe behaviors such as deception. Although weak-to-strong generalization exhibiting certain generalization capabilities, strong models exhibit significant overfitting in weak-to-strong generalization: Due to the strong fit ability of strong models, erroneous labels from weak supervisors may lead to overfitting in strong models. In addition, simply filtering out incorrect labels may lead to a degeneration in question quality, resulting in a weak generalization ability of strong models on hard questions. To mitigate overfitting in weak-to-strong generalization, we propose a two-stage framework that simultaneously improves the quality of supervision signals and the quality of input questions. Experimental results in three series of large language models and two mathematical benchmarks demonstrate that our framework significantly improves PGR compared to naive weak-to-strong generalization, even achieving up to 100\% PGR on some models.
VLABench: A Large-Scale Benchmark for Language-Conditioned Robotics Manipulation with Long-Horizon Reasoning Tasks
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:General-purposed embodied agents are designed to understand the users' natural instructions or intentions and act precisely to complete universal tasks. Recently, methods based on foundation models especially Vision-Language-Action models (VLAs) have shown a substantial potential to solve language-conditioned manipulation (LCM) tasks well. However, existing benchmarks do not adequately meet the needs of VLAs and relative algorithms. To better define such general-purpose tasks in the context of LLMs and advance the research in VLAs, we present VLABench, an open-source benchmark for evaluating universal LCM task learning. VLABench provides 100 carefully designed categories of tasks, with strong randomization in each category of task and a total of 2000+ objects. VLABench stands out from previous benchmarks in four key aspects: 1) tasks requiring world knowledge and common sense transfer, 2) natural language instructions with implicit human intentions rather than templates, 3) long-horizon tasks demanding multi-step reasoning, and 4) evaluation of both action policies and language model capabilities. The benchmark assesses multiple competencies including understanding of mesh\&texture, spatial relationship, semantic instruction, physical laws, knowledge transfer and reasoning, etc. To support the downstream finetuning, we provide high-quality training data collected via an automated framework incorporating heuristic skills and prior information. The experimental results indicate that both the current state-of-the-art pretrained VLAs and the workflow based on VLMs face challenges in our tasks.
InternLM2 Technical Report
Mar 26, 2024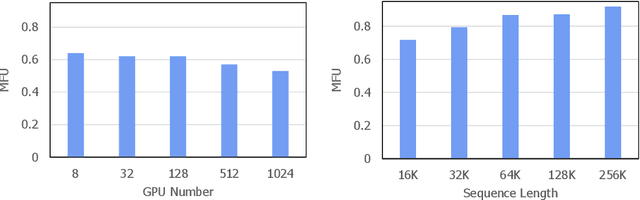

Abstract:The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and GPT-4 has sparked discussions on the advent of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). However, replicating such advancements in open-source models has been challenging. This paper introduces InternLM2, an open-source LLM that outperforms its predecessors in comprehensive evaluations across 6 dimensions and 30 benchmarks, long-context modeling, and open-ended subjective evaluations through innovative pre-training and optimization techniques. The pre-training process of InternLM2 is meticulously detailed, highlighting the preparation of diverse data types including text, code, and long-context data. InternLM2 efficiently captures long-term dependencies, initially trained on 4k tokens before advancing to 32k tokens in pre-training and fine-tuning stages, exhibiting remarkable performance on the 200k ``Needle-in-a-Haystack" test. InternLM2 is further aligned using Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and a novel Conditional Online Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (COOL RLHF) strategy that addresses conflicting human preferences and reward hacking. By releasing InternLM2 models in different training stages and model sizes, we provide the community with insights into the model's evolution.
WanJuan-CC: A Safe and High-Quality Open-sourced English Webtext Dataset
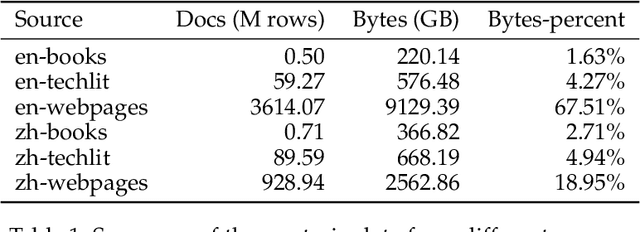
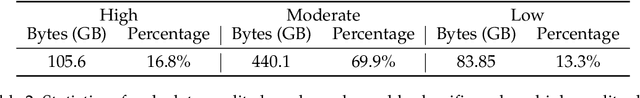
Mar 12, 2024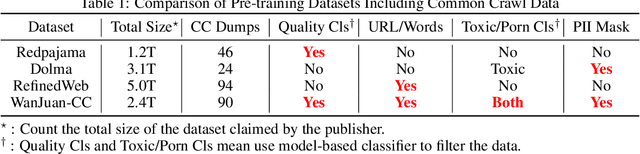
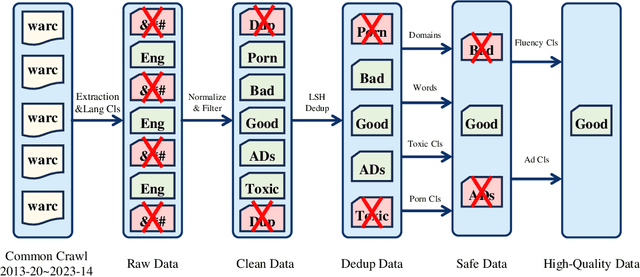
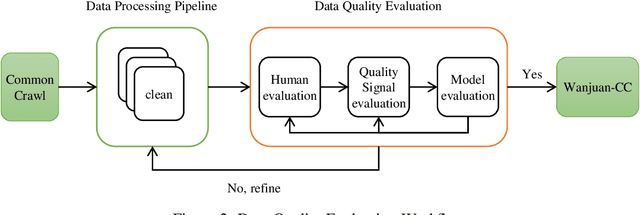

Abstract:This paper presents WanJuan-CC, a safe and high-quality open-sourced English webtext dataset derived from Common Crawl data. The study addresses the challenges of constructing large-scale pre-training datasets for language models, which require vast amounts of high-quality data. A comprehensive process was designed to handle Common Crawl data, including extraction, heuristic rule filtering, fuzzy deduplication, content safety filtering, and data quality filtering. From approximately 68 billion original English documents, we obtained 2.22T Tokens of safe data and selected 1.0T Tokens of high-quality data as part of WanJuan-CC. We have open-sourced 100B Tokens from this dataset. The paper also provides statistical information related to data quality, enabling users to select appropriate data according to their needs. To evaluate the quality and utility of the dataset, we trained 1B-parameter and 3B-parameter models using WanJuan-CC and another dataset, RefinedWeb. Results show that WanJuan-CC performs better on validation datasets and downstream tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge