Fanghua Ye
The Script is All You Need: An Agentic Framework for Long-Horizon Dialogue-to-Cinematic Video Generation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in video generation have produced models capable of synthesizing stunning visual content from simple text prompts. However, these models struggle to generate long-form, coherent narratives from high-level concepts like dialogue, revealing a ``semantic gap'' between a creative idea and its cinematic execution. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel, end-to-end agentic framework for dialogue-to-cinematic-video generation. Central to our framework is ScripterAgent, a model trained to translate coarse dialogue into a fine-grained, executable cinematic script. To enable this, we construct ScriptBench, a new large-scale benchmark with rich multimodal context, annotated via an expert-guided pipeline. The generated script then guides DirectorAgent, which orchestrates state-of-the-art video models using a cross-scene continuous generation strategy to ensure long-horizon coherence. Our comprehensive evaluation, featuring an AI-powered CriticAgent and a new Visual-Script Alignment (VSA) metric, shows our framework significantly improves script faithfulness and temporal fidelity across all tested video models. Furthermore, our analysis uncovers a crucial trade-off in current SOTA models between visual spectacle and strict script adherence, providing valuable insights for the future of automated filmmaking.
From LLMs to LRMs: Rethinking Pruning for Reasoning-Centric Models
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly costly to deploy, motivating extensive research on model pruning. However, most existing studies focus on instruction-following LLMs, leaving it unclear whether established pruning strategies transfer to reasoning-augmented models that explicitly generate long intermediate reasoning traces. In this work, we conduct a controlled study of pruning for both instruction-following ($\textbf{LLM-instruct}$) and reasoning-augmented ($\textbf{LLM-think}$) models. To isolate the effects of pruning, we align pruning calibration and post-pruning recovery data with each model's original training distribution, which we show yields more stable and reliable pruning behavior. We evaluate static depth pruning, static width pruning, and dynamic pruning across 17 tasks spanning classification, generation, and reasoning. Our results reveal clear paradigm-dependent differences: depth pruning outperforms width pruning on classification tasks, while width pruning is more robust for generation and reasoning. Moreover, static pruning better preserves reasoning performance, whereas dynamic pruning excels on classification and generation but remains challenging for long-chain reasoning. These findings underscore the need for pruning strategies that explicitly account for the distinct characteristics of reasoning-augmented LLMs. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/EIT-NLP/LRM-Pruning.
Too Good to be Bad: On the Failure of LLMs to Role-Play Villains
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly tasked with creative generation, including the simulation of fictional characters. However, their ability to portray non-prosocial, antagonistic personas remains largely unexamined. We hypothesize that the safety alignment of modern LLMs creates a fundamental conflict with the task of authentically role-playing morally ambiguous or villainous characters. To investigate this, we introduce the Moral RolePlay benchmark, a new dataset featuring a four-level moral alignment scale and a balanced test set for rigorous evaluation. We task state-of-the-art LLMs with role-playing characters from moral paragons to pure villains. Our large-scale evaluation reveals a consistent, monotonic decline in role-playing fidelity as character morality decreases. We find that models struggle most with traits directly antithetical to safety principles, such as ``Deceitful'' and ``Manipulative'', often substituting nuanced malevolence with superficial aggression. Furthermore, we demonstrate that general chatbot proficiency is a poor predictor of villain role-playing ability, with highly safety-aligned models performing particularly poorly. Our work provides the first systematic evidence of this critical limitation, highlighting a key tension between model safety and creative fidelity. Our benchmark and findings pave the way for developing more nuanced, context-aware alignment methods.
BatonVoice: An Operationalist Framework for Enhancing Controllable Speech Synthesis with Linguistic Intelligence from LLMs
Sep 30, 2025Abstract:The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) is reshaping multimodel models, with speech synthesis being a prominent application. However, existing approaches often underutilize the linguistic intelligence of these models, typically failing to leverage their powerful instruction-following capabilities. This limitation hinders the model's ability to follow text instructions for controllable Text-to-Speech~(TTS). To address this, we propose a new paradigm inspired by ``operationalism'' that decouples instruction understanding from speech generation. We introduce BatonVoice, a framework where an LLM acts as a ``conductor'', understanding user instructions and generating a textual ``plan'' -- explicit vocal features (e.g., pitch, energy). A separate TTS model, the ``orchestra'', then generates the speech from these features. To realize this component, we develop BatonTTS, a TTS model trained specifically for this task. Our experiments demonstrate that BatonVoice achieves strong performance in controllable and emotional speech synthesis, outperforming strong open- and closed-source baselines. Notably, our approach enables remarkable zero-shot cross-lingual generalization, accurately applying feature control abilities to languages unseen during post-training. This demonstrates that objectifying speech into textual vocal features can more effectively unlock the linguistic intelligence of LLMs.
A1: Asynchronous Test-Time Scaling via Conformal Prediction
Sep 18, 2025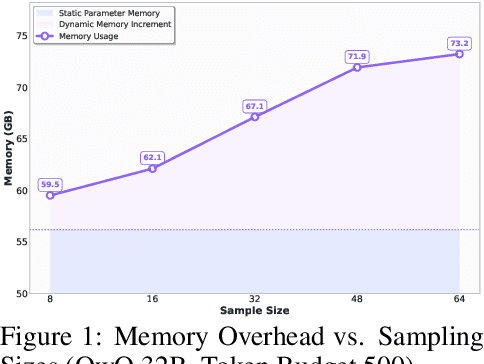
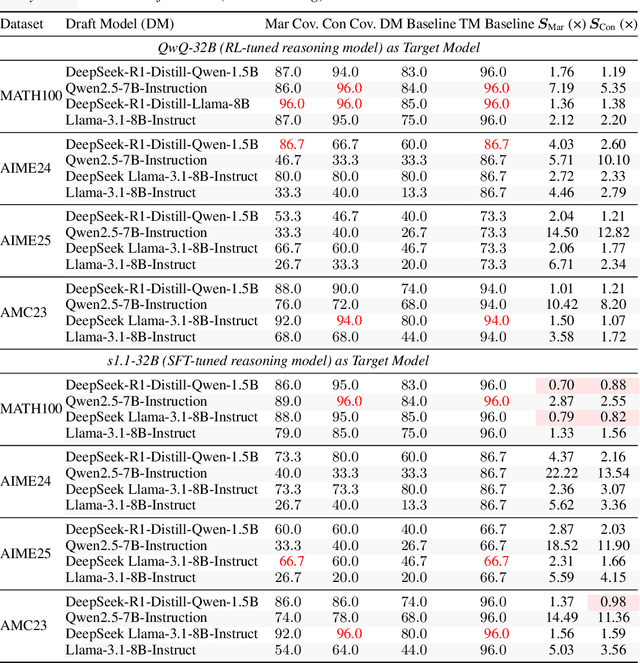
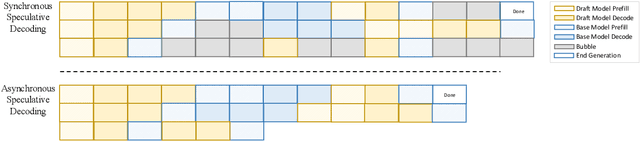
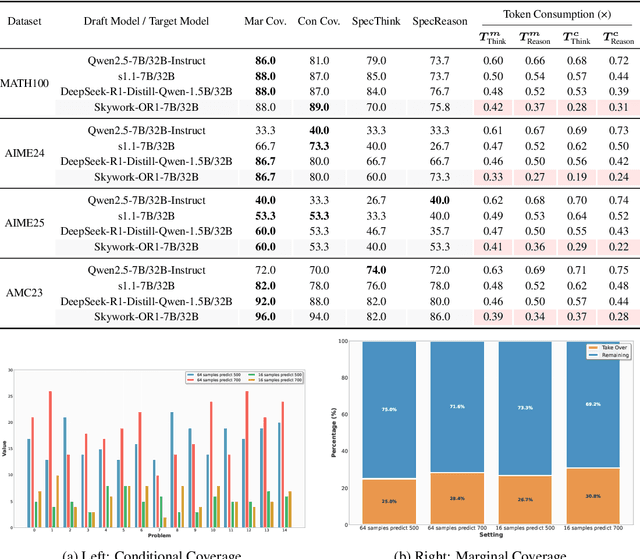
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) benefit from test-time scaling, but existing methods face significant challenges, including severe synchronization overhead, memory bottlenecks, and latency, especially during speculative decoding with long reasoning chains. We introduce A1 (Asynchronous Test-Time Scaling), a statistically guaranteed adaptive inference framework that addresses these challenges. A1 refines arithmetic intensity to identify synchronization as the dominant bottleneck, proposes an online calibration strategy to enable asynchronous inference, and designs a three-stage rejection sampling pipeline that supports both sequential and parallel scaling. Through experiments on the MATH, AMC23, AIME24, and AIME25 datasets, across various draft-target model families, we demonstrate that A1 achieves a remarkable 56.7x speedup in test-time scaling and a 4.14x improvement in throughput, all while maintaining accurate rejection-rate control, reducing latency and memory overhead, and no accuracy loss compared to using target model scaling alone. These results position A1 as an efficient and principled solution for scalable LLM inference. We have released the code at https://github.com/menik1126/asynchronous-test-time-scaling.
CogDual: Enhancing Dual Cognition of LLMs via Reinforcement Learning with Implicit Rule-Based Rewards
Jul 23, 2025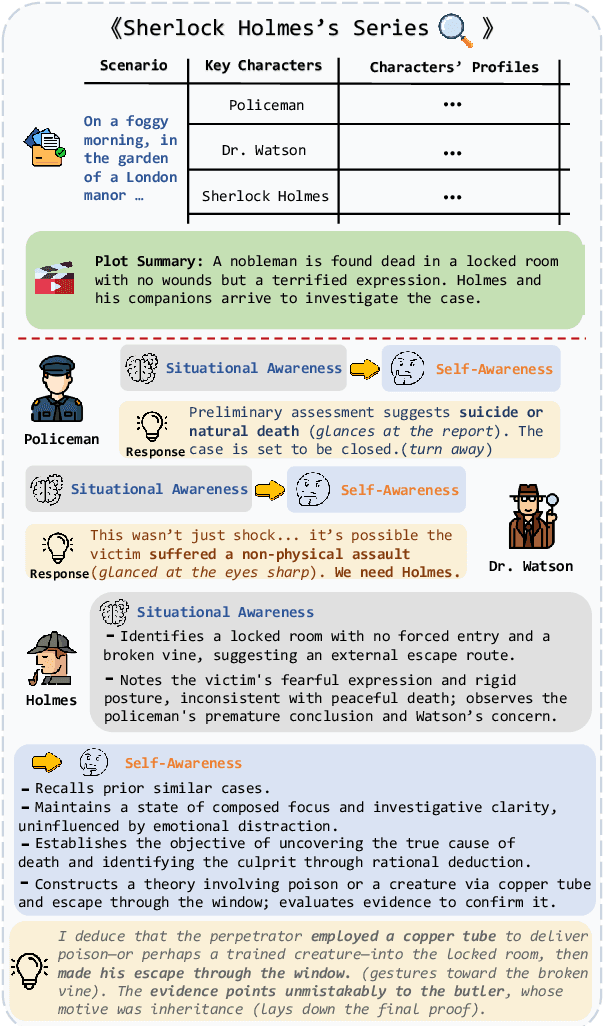
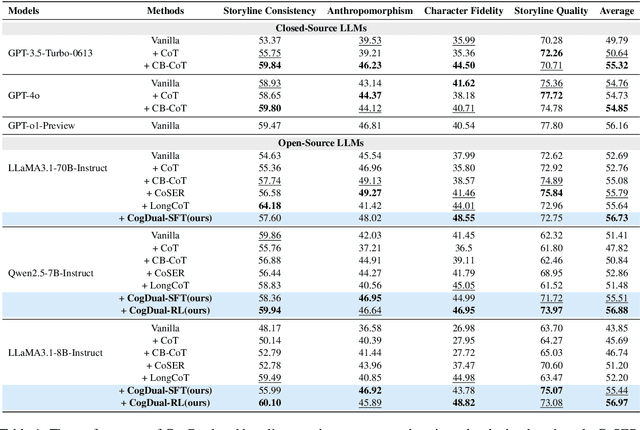
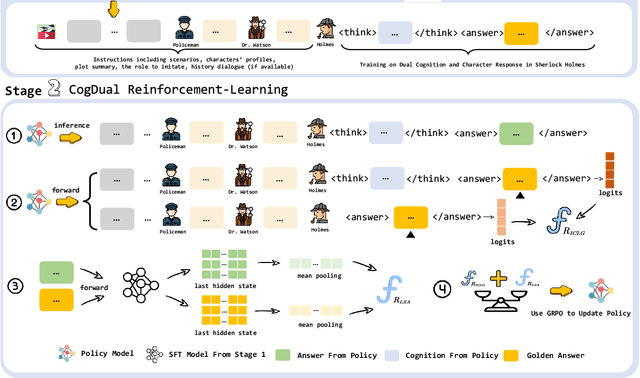
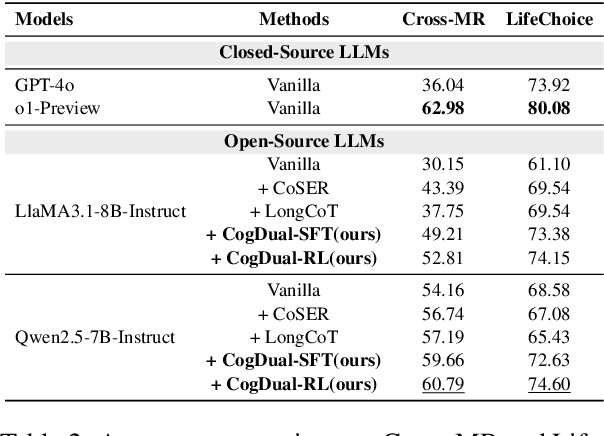
Abstract:Role-Playing Language Agents (RPLAs) have emerged as a significant application direction for Large Language Models (LLMs). Existing approaches typically rely on prompt engineering or supervised fine-tuning to enable models to imitate character behaviors in specific scenarios, but often neglect the underlying \emph{cognitive} mechanisms driving these behaviors. Inspired by cognitive psychology, we introduce \textbf{CogDual}, a novel RPLA adopting a \textit{cognize-then-respond } reasoning paradigm. By jointly modeling external situational awareness and internal self-awareness, CogDual generates responses with improved character consistency and contextual alignment. To further optimize the performance, we employ reinforcement learning with two general-purpose reward schemes designed for open-domain text generation. Extensive experiments on the CoSER benchmark, as well as Cross-MR and LifeChoice, demonstrate that CogDual consistently outperforms existing baselines and generalizes effectively across diverse role-playing tasks.
SkipGPT: Dynamic Layer Pruning Reinvented with Token Awareness and Module Decoupling
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) achieve remarkable performance across tasks but incur substantial computational costs due to their deep, multi-layered architectures. Layer pruning has emerged as a strategy to alleviate these inefficiencies, but conventional static pruning methods overlook two critical dynamics inherent to LLM inference: (1) horizontal dynamics, where token-level heterogeneity demands context-aware pruning decisions, and (2) vertical dynamics, where the distinct functional roles of MLP and self-attention layers necessitate component-specific pruning policies. We introduce SkipGPT, a dynamic layer pruning framework designed to optimize computational resource allocation through two core innovations: (1) global token-aware routing to prioritize critical tokens, and (2) decoupled pruning policies for MLP and self-attention components. To mitigate training instability, we propose a two-stage optimization paradigm: first, a disentangled training phase that learns routing strategies via soft parameterization to avoid premature pruning decisions, followed by parameter-efficient LoRA fine-tuning to restore performance impacted by layer removal. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SkipGPT reduces over 40% of model parameters while matching or exceeding the performance of the original dense model across benchmarks. By harmonizing dynamic efficiency with preserved expressivity, SkipGPT advances the practical deployment of scalable, resource-aware LLMs. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/EIT-NLP/SkipGPT.
Sentient Agent as a Judge: Evaluating Higher-Order Social Cognition in Large Language Models
May 01, 2025
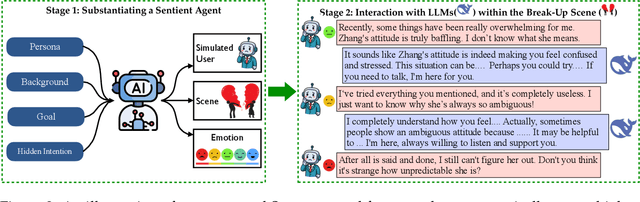
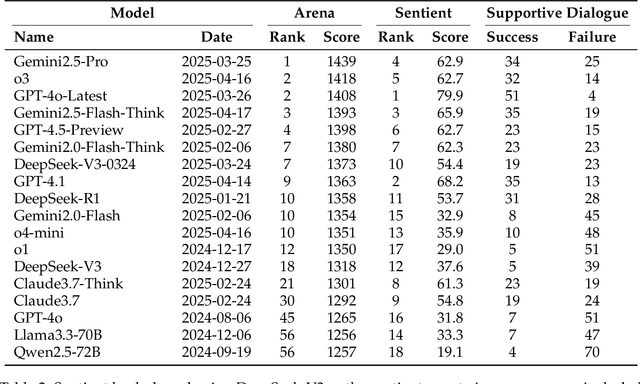
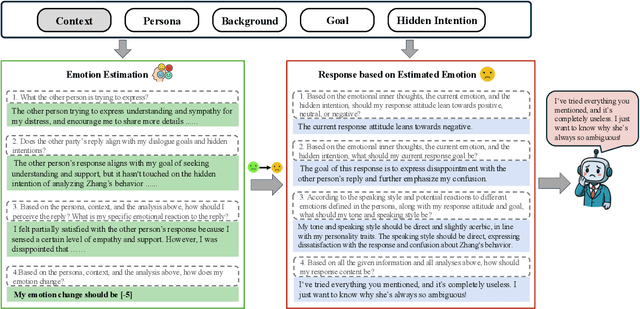
Abstract:Assessing how well a large language model (LLM) understands human, rather than merely text, remains an open challenge. To bridge the gap, we introduce Sentient Agent as a Judge (SAGE), an automated evaluation framework that measures an LLM's higher-order social cognition. SAGE instantiates a Sentient Agent that simulates human-like emotional changes and inner thoughts during interaction, providing a more realistic evaluation of the tested model in multi-turn conversations. At every turn, the agent reasons about (i) how its emotion changes, (ii) how it feels, and (iii) how it should reply, yielding a numerical emotion trajectory and interpretable inner thoughts. Experiments on 100 supportive-dialogue scenarios show that the final Sentient emotion score correlates strongly with Barrett-Lennard Relationship Inventory (BLRI) ratings and utterance-level empathy metrics, validating psychological fidelity. We also build a public Sentient Leaderboard covering 18 commercial and open-source models that uncovers substantial gaps (up to 4x) between frontier systems (GPT-4o-Latest, Gemini2.5-Pro) and earlier baselines, gaps not reflected in conventional leaderboards (e.g., Arena). SAGE thus provides a principled, scalable and interpretable tool for tracking progress toward genuinely empathetic and socially adept language agents.
The Lighthouse of Language: Enhancing LLM Agents via Critique-Guided Improvement
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have recently transformed from text-based assistants to autonomous agents capable of planning, reasoning, and iteratively improving their actions. While numerical reward signals and verifiers can effectively rank candidate actions, they often provide limited contextual guidance. In contrast, natural language feedback better aligns with the generative capabilities of LLMs, providing richer and more actionable suggestions. However, parsing and implementing this feedback effectively can be challenging for LLM-based agents. In this work, we introduce Critique-Guided Improvement (CGI), a novel two-player framework, comprising an actor model that explores an environment and a critic model that generates detailed nature language feedback. By training the critic to produce fine-grained assessments and actionable revisions, and the actor to utilize these critiques, our approach promotes more robust exploration of alternative strategies while avoiding local optima. Experiments in three interactive environments show that CGI outperforms existing baselines by a substantial margin. Notably, even a small critic model surpasses GPT-4 in feedback quality. The resulting actor achieves state-of-the-art performance, demonstrating the power of explicit iterative guidance to enhance decision-making in LLM-based agents.
ParallelComp: Parallel Long-Context Compressor for Length Extrapolation
Feb 20, 2025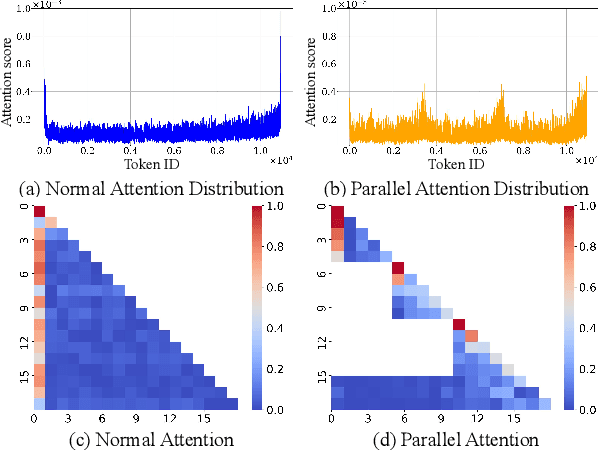
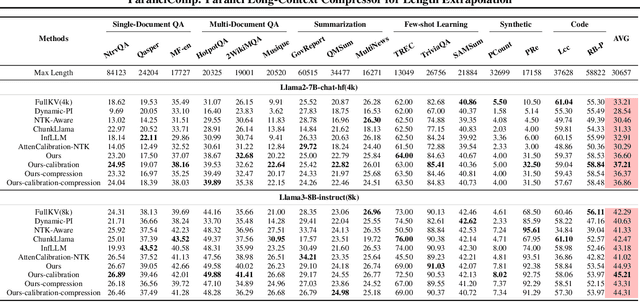
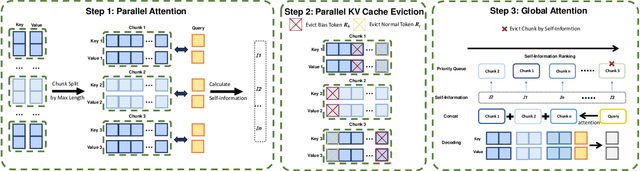
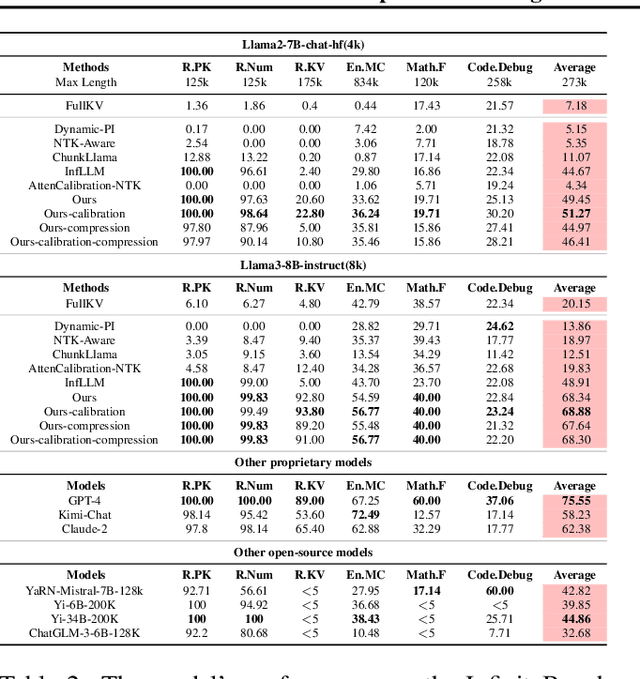
Abstract:Efficiently handling long contexts is crucial for large language models (LLMs). While rotary position embeddings (RoPEs) enhance length generalization, effective length extrapolation remains challenging and often requires costly fine-tuning. In contrast, recent training-free approaches suffer from the attention sink phenomenon, leading to severe performance degradation. In this paper, we introduce ParallelComp, a novel training-free method for long-context extrapolation that extends LLMs' context length from 4K to 128K while maintaining high throughput and preserving perplexity, and integrates seamlessly with Flash Attention. Our analysis offers new insights into attention biases in parallel attention mechanisms and provides practical solutions to tackle these challenges. To mitigate the attention sink issue, we propose an attention calibration strategy that reduces biases, ensuring more stable long-range attention. Additionally, we introduce a chunk eviction strategy to efficiently manage ultra-long contexts on a single A100 80GB GPU. To further enhance efficiency, we propose a parallel KV cache eviction technique, which improves chunk throughput by 1.76x, thereby achieving a 23.50x acceleration in the prefilling stage with negligible performance loss due to attention calibration. Furthermore, ParallelComp achieves 91.17% of GPT-4's performance on long-context tasks using an 8B model trained on 8K-length context, outperforming powerful closed-source models such as Claude-2 and Kimi-Chat.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge