Ngai Wong
BPDQ: Bit-Plane Decomposition Quantization on a Variable Grid for Large Language Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM) inference is often bounded by memory footprint and memory bandwidth in resource-constrained deployments, making quantization a fundamental technique for efficient serving. While post-training quantization (PTQ) maintains high fidelity at 4-bit, it deteriorates at 2-3 bits. Fundamentally, existing methods enforce a shape-invariant quantization grid (e.g., the fixed uniform intervals of UINT2) for each group, severely restricting the feasible set for error minimization. To address this, we propose Bit-Plane Decomposition Quantization (BPDQ), which constructs a variable quantization grid via bit-planes and scalar coefficients, and iteratively refines them using approximate second-order information while progressively compensating quantization errors to minimize output discrepancy. In the 2-bit regime, BPDQ enables serving Qwen2.5-72B on a single RTX 3090 with 83.85% GSM8K accuracy (vs. 90.83% at 16-bit). Moreover, we provide theoretical analysis showing that the variable grid expands the feasible set, and that the quantization process consistently aligns with the optimization objective in Hessian-induced geometry. Code: github.com/KingdalfGoodman/BPDQ.
Residual Decoding: Mitigating Hallucinations in Large Vision-Language Models via History-Aware Residual Guidance
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) can reason effectively from image-text inputs and perform well in various multimodal tasks. Despite this success, they are affected by language priors and often produce hallucinations. Hallucinations denote generated content that is grammatically and syntactically coherent, yet bears no match or direct relevance to actual visual input. To address this problem, we propose Residual Decoding (ResDec). It is a novel training-free method that uses historical information to aid decoding. The method relies on the internal implicit reasoning mechanism and token logits evolution mechanism of LVLMs to correct biases. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ResDec effectively suppresses hallucinations induced by language priors, significantly improves visual grounding, and reduces object hallucinations. In addition to mitigating hallucinations, ResDec also performs exceptionally well on comprehensive LVLM benchmarks, highlighting its broad applicability.
OVD: On-policy Verbal Distillation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Knowledge distillation offers a promising path to transfer reasoning capabilities from large teacher models to efficient student models; however, existing token-level on-policy distillation methods require token-level alignment between the student and teacher models, which restricts the student model's exploration ability, prevent effective use of interactive environment feedback, and suffer from severe memory bottlenecks in reinforcement learning. We introduce On-policy Verbal Distillation (OVD), a memory-efficient framework that replaces token-level probability matching with trajectory matching using discrete verbal scores (0--9) from teacher models. OVD dramatically reduces memory consumption while enabling on-policy distillation from teacher models with verbal feedback, and avoids token-level alignment, allowing the student model to freely explore the output space. Extensive experiments on Web question answering and mathematical reasoning tasks show that OVD substantially outperforms existing methods, delivering up to +12.9% absolute improvement in average EM on Web Q&A tasks and a up to +25.7% gain on math benchmarks (when trained with only one random samples), while also exhibiting superior training efficiency. Our project page is available at https://OVD.github.io
Locate, Steer, and Improve: A Practical Survey of Actionable Mechanistic Interpretability in Large Language Models
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Mechanistic Interpretability (MI) has emerged as a vital approach to demystify the opaque decision-making of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, existing reviews primarily treat MI as an observational science, summarizing analytical insights while lacking a systematic framework for actionable intervention. To bridge this gap, we present a practical survey structured around the pipeline: "Locate, Steer, and Improve." We formally categorize Localizing (diagnosis) and Steering (intervention) methods based on specific Interpretable Objects to establish a rigorous intervention protocol. Furthermore, we demonstrate how this framework enables tangible improvements in Alignment, Capability, and Efficiency, effectively operationalizing MI as an actionable methodology for model optimization. The curated paper list of this work is available at https://github.com/rattlesnakey/Awesome-Actionable-MI-Survey.
MMFormalizer: Multimodal Autoformalization in the Wild
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Autoformalization, which translates natural language mathematics into formal statements to enable machine reasoning, faces fundamental challenges in the wild due to the multimodal nature of the physical world, where physics requires inferring hidden constraints (e.g., mass or energy) from visual elements. To address this, we propose MMFormalizer, which extends autoformalization beyond text by integrating adaptive grounding with entities from real-world mathematical and physical domains. MMFormalizer recursively constructs formal propositions from perceptually grounded primitives through recursive grounding and axiom composition, with adaptive recursive termination ensuring that every abstraction is supported by visual evidence and anchored in dimensional or axiomatic grounding. We evaluate MMFormalizer on a new benchmark, PhyX-AF, comprising 115 curated samples from MathVerse, PhyX, Synthetic Geometry, and Analytic Geometry, covering diverse multimodal autoformalization tasks. Results show that frontier models such as GPT-5 and Gemini-3-Pro achieve the highest compile and semantic accuracy, with GPT-5 excelling in physical reasoning, while geometry remains the most challenging domain. Overall, MMFormalizer provides a scalable framework for unified multimodal autoformalization, bridging perception and formal reasoning. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first multimodal autoformalization method capable of handling classical mechanics (derived from the Hamiltonian), as well as relativity, quantum mechanics, and thermodynamics. More details are available on our project page: MMFormalizer.github.io
XStreamVGGT: Extremely Memory-Efficient Streaming Vision Geometry Grounded Transformer with KV Cache Compression
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Learning-based 3D visual geometry models have benefited substantially from large-scale transformers. Among these, StreamVGGT leverages frame-wise causal attention for strong streaming reconstruction, but suffers from unbounded KV cache growth, leading to escalating memory consumption and inference latency as input frames accumulate. We propose XStreamVGGT, a tuning-free approach that systematically compresses the KV cache through joint pruning and quantization, enabling extremely memory-efficient streaming inference. Specifically, redundant KVs originating from multi-view inputs are pruned through efficient token importance identification, enabling a fixed memory budget. Leveraging the unique distribution of KV tensors, we incorporate KV quantization to further reduce memory consumption. Extensive evaluations show that XStreamVGGT achieves mostly negligible performance degradation while substantially reducing memory usage by 4.42$\times$ and accelerating inference by 5.48$\times$, enabling scalable and practical streaming 3D applications. The code is available at https://github.com/ywh187/XStreamVGGT/.
NTK-Guided Implicit Neural Teaching
Nov 19, 2025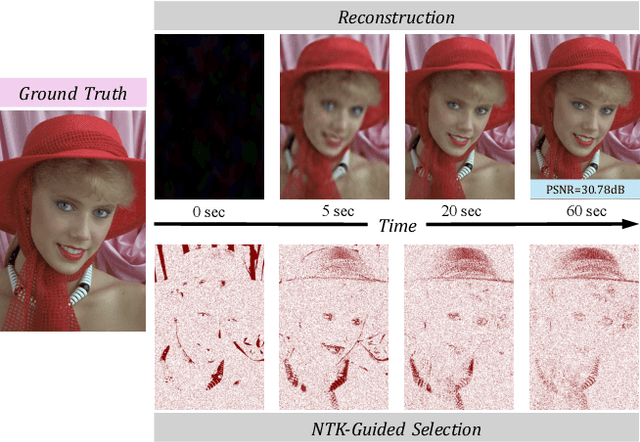
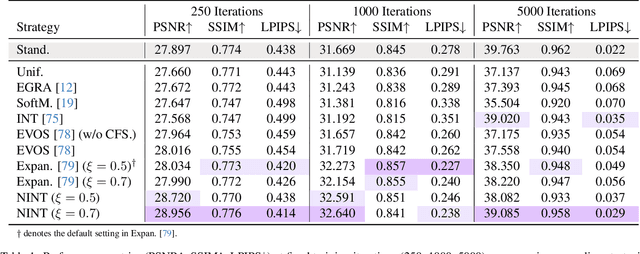
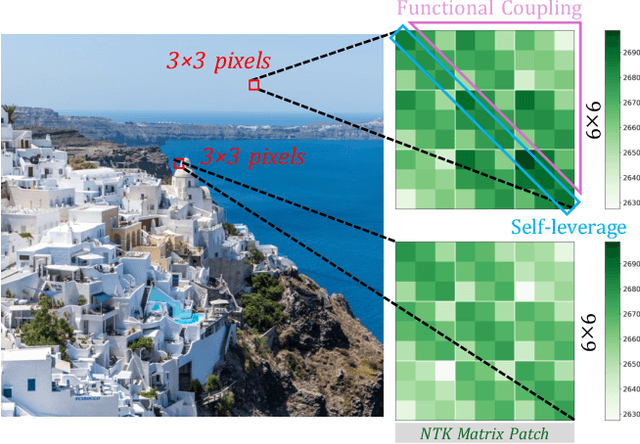
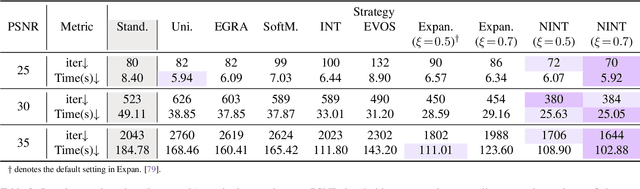
Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) parameterize continuous signals via multilayer perceptrons (MLPs), enabling compact, resolution-independent modeling for tasks like image, audio, and 3D reconstruction. However, fitting high-resolution signals demands optimizing over millions of coordinates, incurring prohibitive computational costs. To address it, we propose NTK-Guided Implicit Neural Teaching (NINT), which accelerates training by dynamically selecting coordinates that maximize global functional updates. Leveraging the Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK), NINT scores examples by the norm of their NTK-augmented loss gradients, capturing both fitting errors and heterogeneous leverage (self-influence and cross-coordinate coupling). This dual consideration enables faster convergence compared to existing methods. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that NINT significantly reduces training time by nearly half while maintaining or improving representation quality, establishing state-of-the-art acceleration among recent sampling-based strategies.
DoPE: Denoising Rotary Position Embedding
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE) in Transformer models has inherent limits that weaken length extrapolation. We reinterpret the attention map with positional encoding as a noisy feature map, and propose Denoising Positional Encoding (DoPE), a training-free method based on truncated matrix entropy to detect outlier frequency bands in the feature map. Leveraging the noise characteristics of the feature map, we further reparameterize it with a parameter-free Gaussian distribution to achieve robust extrapolation. Our method theoretically reveals the underlying cause of the attention sink phenomenon and its connection to truncated matrix entropy. Experiments on needle-in-a-haystack and many-shot in-context learning tasks demonstrate that DoPE significantly improves retrieval accuracy and reasoning stability across extended contexts (up to 64K tokens). The results show that the denoising strategy for positional embeddings effectively mitigates attention sinks and restores balanced attention patterns, providing a simple yet powerful solution for improving length generalization. Our project page is Project: https://The-physical-picture-of-LLMs.github.io
A1: Asynchronous Test-Time Scaling via Conformal Prediction
Sep 18, 2025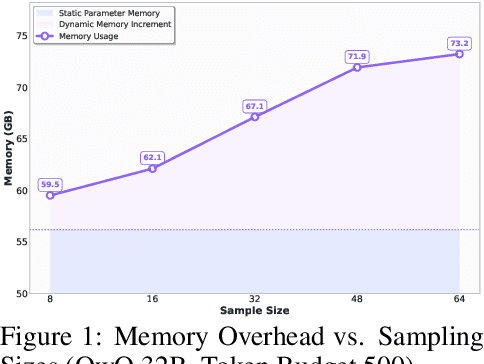
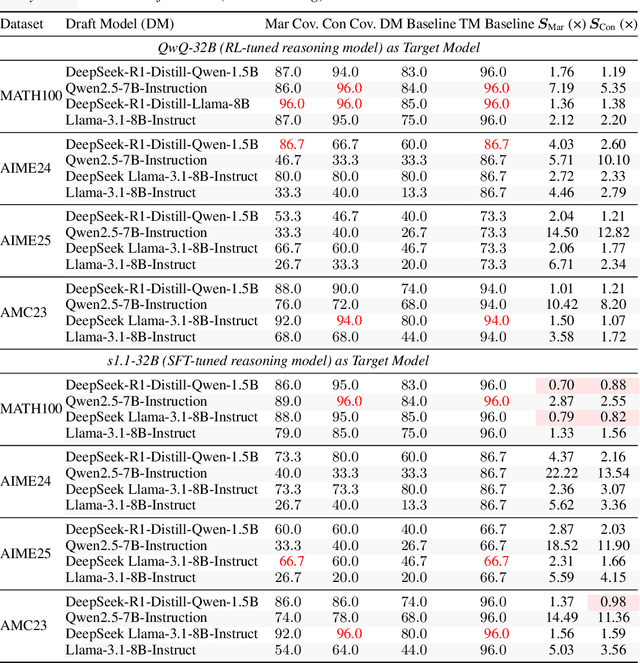
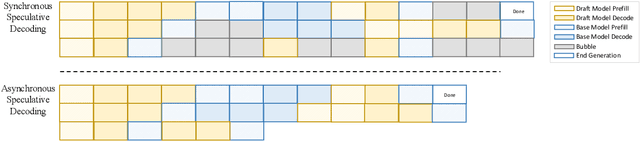
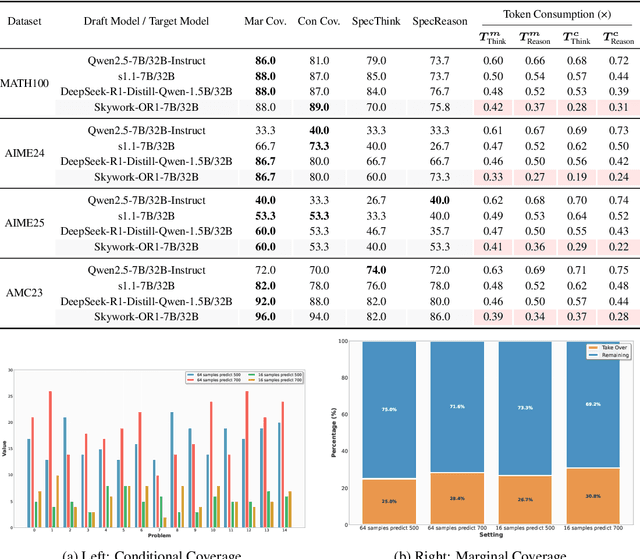
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) benefit from test-time scaling, but existing methods face significant challenges, including severe synchronization overhead, memory bottlenecks, and latency, especially during speculative decoding with long reasoning chains. We introduce A1 (Asynchronous Test-Time Scaling), a statistically guaranteed adaptive inference framework that addresses these challenges. A1 refines arithmetic intensity to identify synchronization as the dominant bottleneck, proposes an online calibration strategy to enable asynchronous inference, and designs a three-stage rejection sampling pipeline that supports both sequential and parallel scaling. Through experiments on the MATH, AMC23, AIME24, and AIME25 datasets, across various draft-target model families, we demonstrate that A1 achieves a remarkable 56.7x speedup in test-time scaling and a 4.14x improvement in throughput, all while maintaining accurate rejection-rate control, reducing latency and memory overhead, and no accuracy loss compared to using target model scaling alone. These results position A1 as an efficient and principled solution for scalable LLM inference. We have released the code at https://github.com/menik1126/asynchronous-test-time-scaling.
LongEmotion: Measuring Emotional Intelligence of Large Language Models in Long-Context Interaction
Sep 09, 2025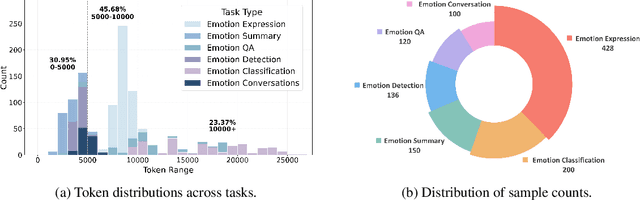
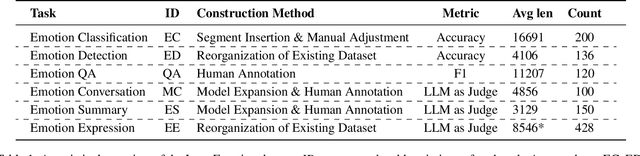
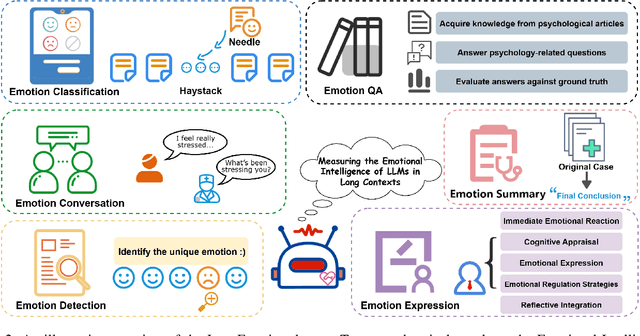
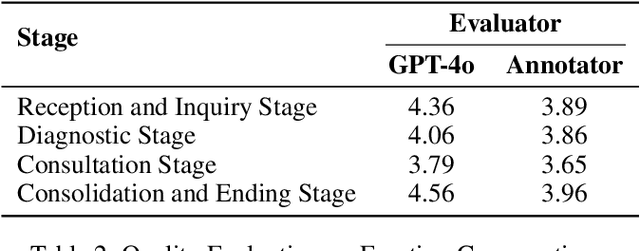
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) make significant progress in Emotional Intelligence (EI) and long-context understanding. However, existing benchmarks tend to overlook certain aspects of EI in long-context scenarios, especially under realistic, practical settings where interactions are lengthy, diverse, and often noisy. To move towards such realistic settings, we present LongEmotion, a benchmark specifically designed for long-context EI tasks. It covers a diverse set of tasks, including Emotion Classification, Emotion Detection, Emotion QA, Emotion Conversation, Emotion Summary, and Emotion Expression. On average, the input length for these tasks reaches 8,777 tokens, with long-form generation required for Emotion Expression. To enhance performance under realistic constraints, we incorporate Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Collaborative Emotional Modeling (CoEM), and compare them with standard prompt-based methods. Unlike conventional approaches, our RAG method leverages both the conversation context and the large language model itself as retrieval sources, avoiding reliance on external knowledge bases. The CoEM method further improves performance by decomposing the task into five stages, integrating both retrieval augmentation and limited knowledge injection. Experimental results show that both RAG and CoEM consistently enhance EI-related performance across most long-context tasks, advancing LLMs toward more practical and real-world EI applications. Furthermore, we conducted a comparative case study experiment on the GPT series to demonstrate the differences among various models in terms of EI. Code is available on GitHub at https://github.com/LongEmotion/LongEmotion, and the project page can be found at https://longemotion.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge