Taiqiang Wu
BPDQ: Bit-Plane Decomposition Quantization on a Variable Grid for Large Language Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM) inference is often bounded by memory footprint and memory bandwidth in resource-constrained deployments, making quantization a fundamental technique for efficient serving. While post-training quantization (PTQ) maintains high fidelity at 4-bit, it deteriorates at 2-3 bits. Fundamentally, existing methods enforce a shape-invariant quantization grid (e.g., the fixed uniform intervals of UINT2) for each group, severely restricting the feasible set for error minimization. To address this, we propose Bit-Plane Decomposition Quantization (BPDQ), which constructs a variable quantization grid via bit-planes and scalar coefficients, and iteratively refines them using approximate second-order information while progressively compensating quantization errors to minimize output discrepancy. In the 2-bit regime, BPDQ enables serving Qwen2.5-72B on a single RTX 3090 with 83.85% GSM8K accuracy (vs. 90.83% at 16-bit). Moreover, we provide theoretical analysis showing that the variable grid expands the feasible set, and that the quantization process consistently aligns with the optimization objective in Hessian-induced geometry. Code: github.com/KingdalfGoodman/BPDQ.
LINA: Linear Autoregressive Image Generative Models with Continuous Tokens
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive models with continuous tokens form a promising paradigm for visual generation, especially for text-to-image (T2I) synthesis, but they suffer from high computational cost. We study how to design compute-efficient linear attention within this framework. Specifically, we conduct a systematic empirical analysis of scaling behavior with respect to parameter counts under different design choices, focusing on (1) normalization paradigms in linear attention (division-based vs. subtraction-based) and (2) depthwise convolution for locality augmentation. Our results show that although subtraction-based normalization is effective for image classification, division-based normalization scales better for linear generative transformers. In addition, incorporating convolution for locality modeling plays a crucial role in autoregressive generation, consistent with findings in diffusion models. We further extend gating mechanisms, commonly used in causal linear attention, to the bidirectional setting and propose a KV gate. By introducing data-independent learnable parameters to the key and value states, the KV gate assigns token-wise memory weights, enabling flexible memory management similar to forget gates in language models. Based on these findings, we present LINA, a simple and compute-efficient T2I model built entirely on linear attention, capable of generating high-fidelity 1024x1024 images from user instructions. LINA achieves competitive performance on both class-conditional and T2I benchmarks, obtaining 2.18 FID on ImageNet (about 1.4B parameters) and 0.74 on GenEval (about 1.5B parameters). A single linear attention module reduces FLOPs by about 61 percent compared to softmax attention. Code and models are available at: https://github.com/techmonsterwang/LINA.
ProFit: Leveraging High-Value Signals in SFT via Probability-Guided Token Selection
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) is a fundamental post-training strategy to align Large Language Models (LLMs) with human intent. However, traditional SFT often ignores the one-to-many nature of language by forcing alignment with a single reference answer, leading to the model overfitting to non-core expressions. Although our empirical analysis suggests that introducing multiple reference answers can mitigate this issue, the prohibitive data and computational costs necessitate a strategic shift: prioritizing the mitigation of single-reference overfitting over the costly pursuit of answer diversity. To achieve this, we reveal the intrinsic connection between token probability and semantic importance: high-probability tokens carry the core logical framework, while low-probability tokens are mostly replaceable expressions. Based on this insight, we propose ProFit, which selectively masks low-probability tokens to prevent surface-level overfitting. Extensive experiments confirm that ProFit consistently outperforms traditional SFT baselines on general reasoning and mathematical benchmarks.
MMFormalizer: Multimodal Autoformalization in the Wild
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Autoformalization, which translates natural language mathematics into formal statements to enable machine reasoning, faces fundamental challenges in the wild due to the multimodal nature of the physical world, where physics requires inferring hidden constraints (e.g., mass or energy) from visual elements. To address this, we propose MMFormalizer, which extends autoformalization beyond text by integrating adaptive grounding with entities from real-world mathematical and physical domains. MMFormalizer recursively constructs formal propositions from perceptually grounded primitives through recursive grounding and axiom composition, with adaptive recursive termination ensuring that every abstraction is supported by visual evidence and anchored in dimensional or axiomatic grounding. We evaluate MMFormalizer on a new benchmark, PhyX-AF, comprising 115 curated samples from MathVerse, PhyX, Synthetic Geometry, and Analytic Geometry, covering diverse multimodal autoformalization tasks. Results show that frontier models such as GPT-5 and Gemini-3-Pro achieve the highest compile and semantic accuracy, with GPT-5 excelling in physical reasoning, while geometry remains the most challenging domain. Overall, MMFormalizer provides a scalable framework for unified multimodal autoformalization, bridging perception and formal reasoning. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first multimodal autoformalization method capable of handling classical mechanics (derived from the Hamiltonian), as well as relativity, quantum mechanics, and thermodynamics. More details are available on our project page: MMFormalizer.github.io
QuadINR: Hardware-Efficient Implicit Neural Representations Through Quadratic Activation
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) encode discrete signals continuously while addressing spectral bias through activation functions (AFs). Previous approaches mitigate this bias by employing complex AFs, which often incur significant hardware overhead. To tackle this challenge, we introduce QuadINR, a hardware-efficient INR that utilizes piecewise quadratic AFs to achieve superior performance with dramatic reductions in hardware consumption. The quadratic functions encompass rich harmonic content in their Fourier series, delivering enhanced expressivity for high-frequency signals, as verified through Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK) analysis. We develop a unified $N$-stage pipeline framework that facilitates efficient hardware implementation of various AFs in INRs. We demonstrate FPGA implementations on the VCU128 platform and an ASIC implementation in a 28nm process. Experiments across images and videos show that QuadINR achieves up to 2.06dB PSNR improvement over prior work, with an area of only 1914$\mu$m$^2$ and a dynamic power of 6.14mW, reducing resource and power consumption by up to 97\% and improving latency by up to 93\% vs existing baselines.
SwingArena: Competitive Programming Arena for Long-context GitHub Issue Solving
May 29, 2025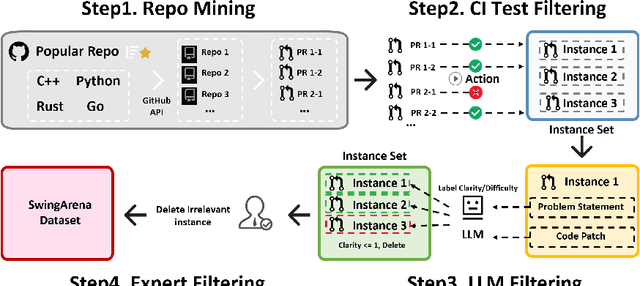
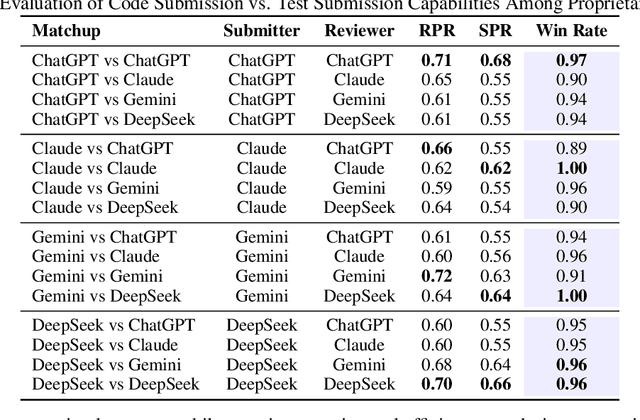
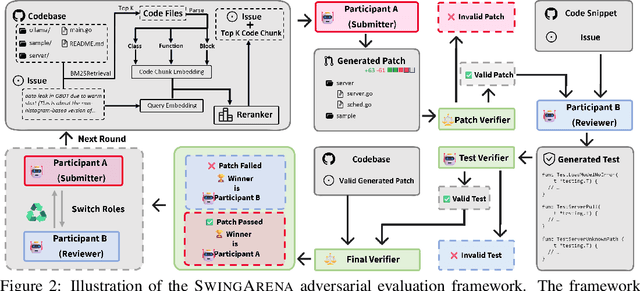
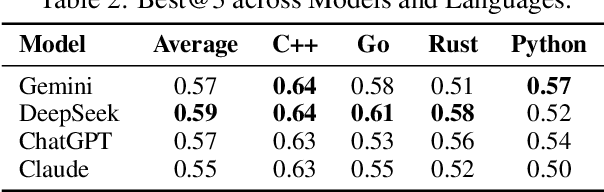
Abstract:We present SwingArena, a competitive evaluation framework for Large Language Models (LLMs) that closely mirrors real-world software development workflows. Unlike traditional static benchmarks, SwingArena models the collaborative process of software iteration by pairing LLMs as submitters, who generate patches, and reviewers, who create test cases and verify the patches through continuous integration (CI) pipelines. To support these interactive evaluations, we introduce a retrieval-augmented code generation (RACG) module that efficiently handles long-context challenges by providing syntactically and semantically relevant code snippets from large codebases, supporting multiple programming languages (C++, Python, Rust, and Go). This enables the framework to scale across diverse tasks and contexts while respecting token limitations. Our experiments, using over 400 high-quality real-world GitHub issues selected from a pool of 2,300 issues, show that models like GPT-4o excel at aggressive patch generation, whereas DeepSeek and Gemini prioritize correctness in CI validation. SwingArena presents a scalable and extensible methodology for evaluating LLMs in realistic, CI-driven software development settings. More details are available on our project page: swing-bench.github.io
PhyX: Does Your Model Have the "Wits" for Physical Reasoning?
May 21, 2025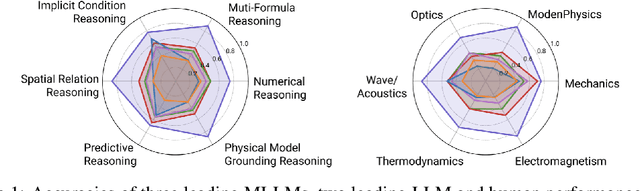
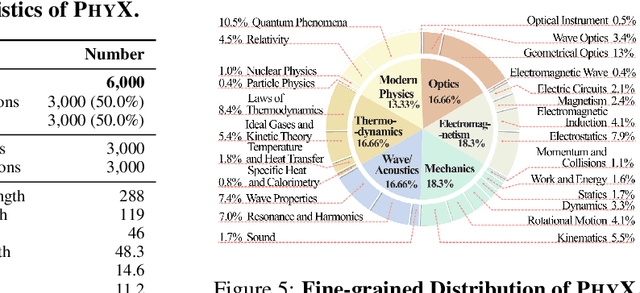
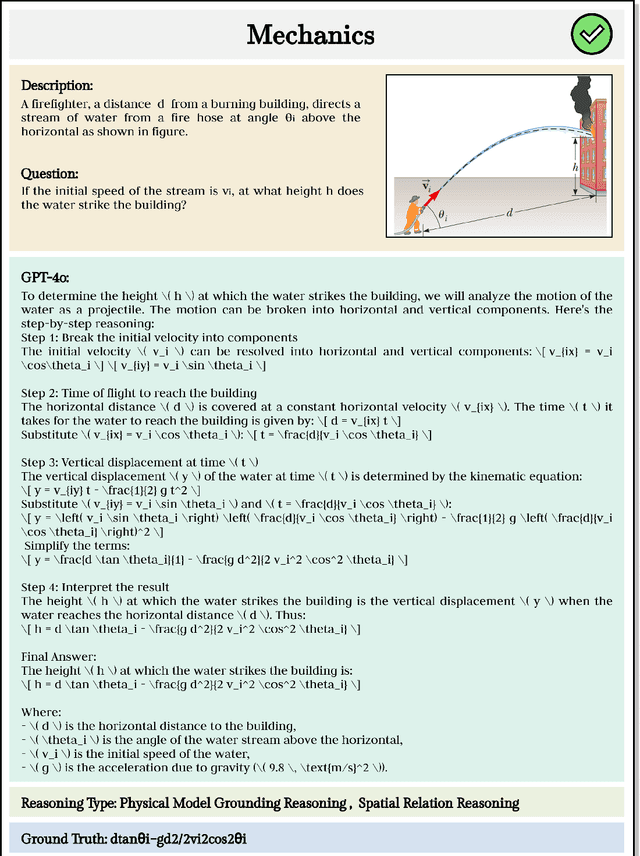
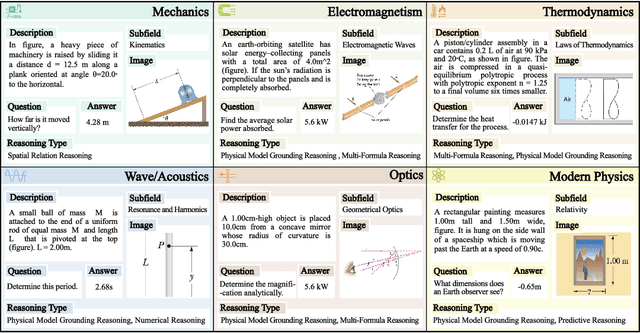
Abstract:Existing benchmarks fail to capture a crucial aspect of intelligence: physical reasoning, the integrated ability to combine domain knowledge, symbolic reasoning, and understanding of real-world constraints. To address this gap, we introduce PhyX: the first large-scale benchmark designed to assess models capacity for physics-grounded reasoning in visual scenarios. PhyX includes 3K meticulously curated multimodal questions spanning 6 reasoning types across 25 sub-domains and 6 core physics domains: thermodynamics, electromagnetism, mechanics, modern physics, optics, and wave\&acoustics. In our comprehensive evaluation, even state-of-the-art models struggle significantly with physical reasoning. GPT-4o, Claude3.7-Sonnet, and GPT-o4-mini achieve only 32.5\%, 42.2\%, and 45.8\% accuracy respectively-performance gaps exceeding 29\% compared to human experts. Our analysis exposes critical limitations in current models: over-reliance on memorized disciplinary knowledge, excessive dependence on mathematical formulations, and surface-level visual pattern matching rather than genuine physical understanding. We provide in-depth analysis through fine-grained statistics, detailed case studies, and multiple evaluation paradigms to thoroughly examine physical reasoning capabilities. To ensure reproducibility, we implement a compatible evaluation protocol based on widely-used toolkits such as VLMEvalKit, enabling one-click evaluation.
Shadow-FT: Tuning Instruct via Base
May 19, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) consistently benefit from further fine-tuning on various tasks. However, we observe that directly tuning the INSTRUCT (i.e., instruction tuned) models often leads to marginal improvements and even performance degeneration. Notably, paired BASE models, the foundation for these INSTRUCT variants, contain highly similar weight values (i.e., less than 2% on average for Llama 3.1 8B). Therefore, we propose a novel Shadow-FT framework to tune the INSTRUCT models by leveraging the corresponding BASE models. The key insight is to fine-tune the BASE model, and then directly graft the learned weight updates to the INSTRUCT model. Our proposed Shadow-FT introduces no additional parameters, is easy to implement, and significantly improves performance. We conduct extensive experiments on tuning mainstream LLMs, such as Qwen 3 and Llama 3 series, and evaluate them across 19 benchmarks covering coding, reasoning, and mathematical tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that Shadow-FT consistently outperforms conventional full-parameter and parameter-efficient tuning approaches. Further analyses indicate that Shadow-FT can be applied to multimodal large language models (MLLMs) and combined with direct preference optimization (DPO). Codes and weights are available at \href{https://github.com/wutaiqiang/Shadow-FT}{Github}.
HaLoRA: Hardware-aware Low-Rank Adaptation for Large Language Models Based on Hybrid Compute-in-Memory Architecture
Feb 27, 2025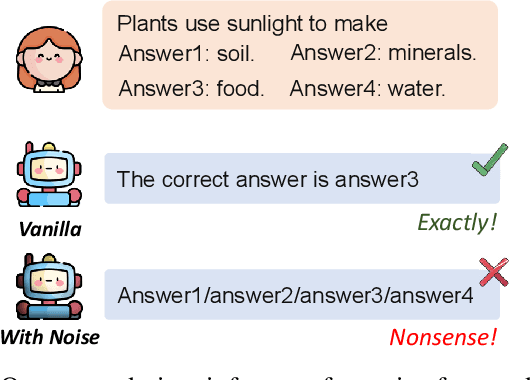
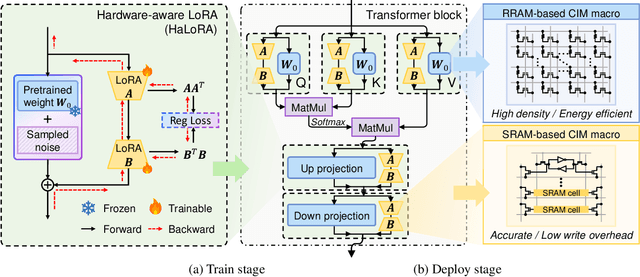
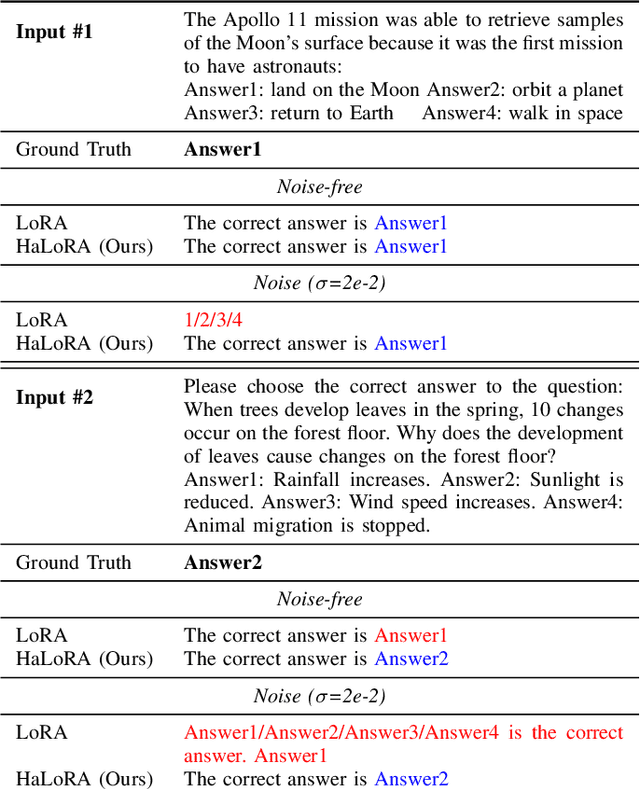
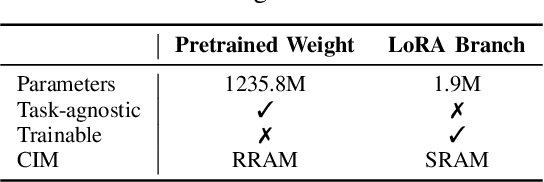
Abstract:Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) is a predominant parameter-efficient finetuning method to adapt large language models (LLMs) for downstream tasks. In this paper, we first propose to deploy the LoRA-finetuned LLMs on the hybrid compute-in-memory (CIM) architecture (i.e., pretrained weights onto RRAM and LoRA onto SRAM). To address performance degradation from RRAM's inherent noise, we design a novel Hardware-aware Low-rank Adaption (HaLoRA) method, aiming to train a LoRA branch that is both robust and accurate by aligning the training objectives under both ideal and noisy conditions. Experiments finetuning LLaMA 3.2 1B and 3B demonstrate HaLoRA's effectiveness across multiple reasoning tasks, achieving up to 22.7 improvement in average score while maintaining robustness at various noise levels.
LLM-Neo: Parameter Efficient Knowledge Distillation for Large Language Models
Nov 11, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel LLM-Neo framework that efficiently transfers knowledge from a large language model (LLM) teacher to a compact student. Initially, we revisit the knowledge distillation (KD) and low-rank adaption (LoRA), and argue that they share the same paradigm. Inspired by this observation, we explore the strategy that combines LoRA and KD to enhance the efficiency of knowledge transfer. We first summarize some guidelines for this design and further develop the LLM-Neo. Experimental results on compressing Llama 2 and Llama 3 show that LLM-Neo outperforms various baselines. Further analysis demonstrates the robustness of the proposed LLM-Neo on variants of LoRA. The trained models have been available at \href{https://huggingface.co/collections/yang31210999/llm-neo-66e3c882f5579b829ff57eba}{this repository}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge