Weigang Guo
Recouple Event Field via Probabilistic Bias for Event Extraction
May 19, 2023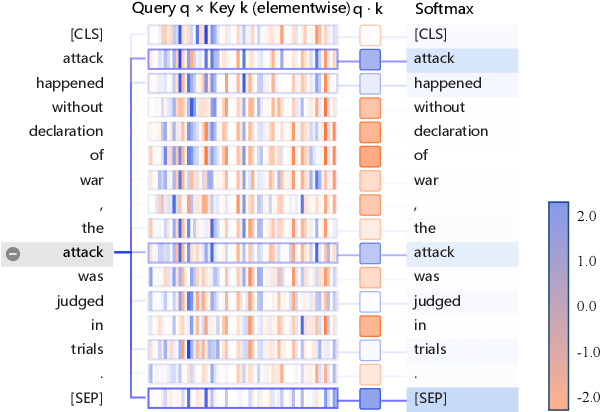
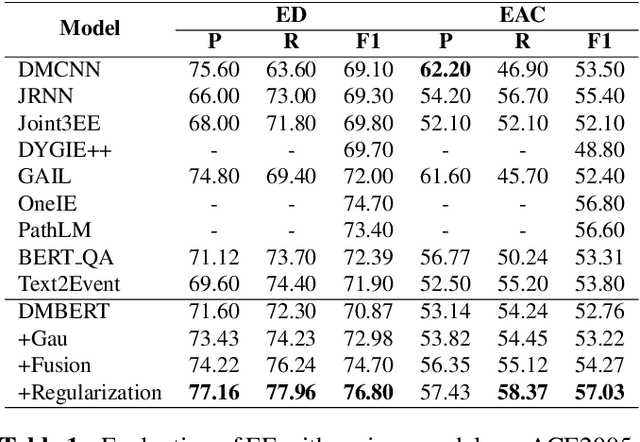
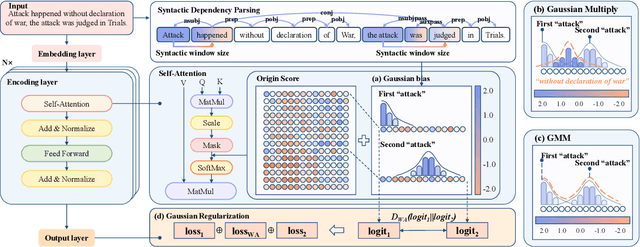
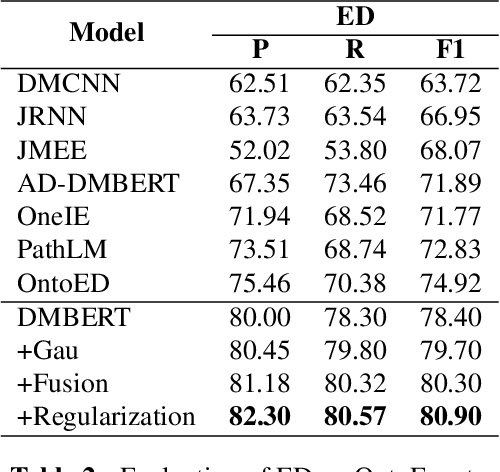
Abstract:Event Extraction (EE), aiming to identify and classify event triggers and arguments from event mentions, has benefited from pre-trained language models (PLMs). However, existing PLM-based methods ignore the information of trigger/argument fields, which is crucial for understanding event schemas. To this end, we propose a Probabilistic reCoupling model enhanced Event extraction framework (ProCE). Specifically, we first model the syntactic-related event fields as probabilistic biases, to clarify the event fields from ambiguous entanglement. Furthermore, considering multiple occurrences of the same triggers/arguments in EE, we explore probabilistic interaction strategies among multiple fields of the same triggers/arguments, to recouple the corresponding clarified distributions and capture more latent information fields. Experiments on EE datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of our proposed approach.
TencentPretrain: A Scalable and Flexible Toolkit for Pre-training Models of Different Modalities
Dec 13, 2022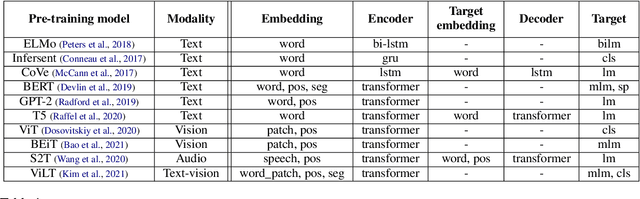
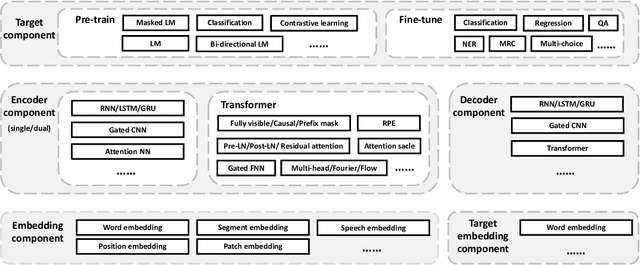
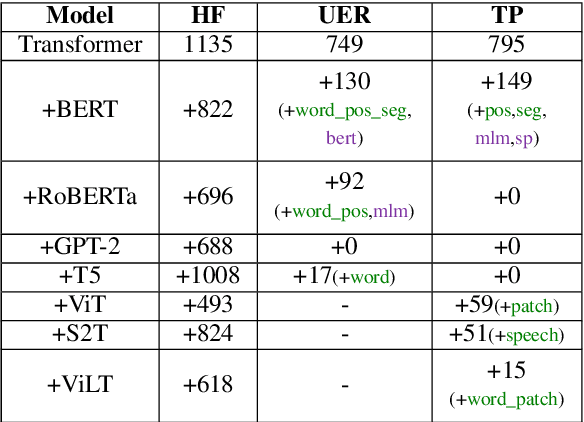
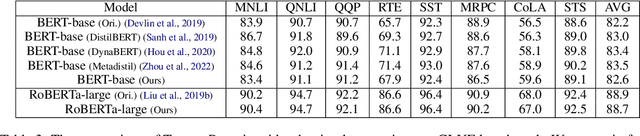
Abstract:Recently, the success of pre-training in text domain has been fully extended to vision, audio, and cross-modal scenarios. The proposed pre-training models of different modalities are showing a rising trend of homogeneity in their model structures, which brings the opportunity to implement different pre-training models within a uniform framework. In this paper, we present TencentPretrain, a toolkit supporting pre-training models of different modalities. The core feature of TencentPretrain is the modular design. The toolkit uniformly divides pre-training models into 5 components: embedding, encoder, target embedding, decoder, and target. As almost all of common modules are provided in each component, users can choose the desired modules from different components to build a complete pre-training model. The modular design enables users to efficiently reproduce existing pre-training models or build brand-new one. We test the toolkit on text, vision, and audio benchmarks and show that it can match the performance of the original implementations.
Modeling Fine-grained Information via Knowledge-aware Hierarchical Graph for Zero-shot Entity Retrieval
Nov 20, 2022Abstract:Zero-shot entity retrieval, aiming to link mentions to candidate entities under the zero-shot setting, is vital for many tasks in Natural Language Processing. Most existing methods represent mentions/entities via the sentence embeddings of corresponding context from the Pre-trained Language Model. However, we argue that such coarse-grained sentence embeddings can not fully model the mentions/entities, especially when the attention scores towards mentions/entities are relatively low. In this work, we propose GER, a \textbf{G}raph enhanced \textbf{E}ntity \textbf{R}etrieval framework, to capture more fine-grained information as complementary to sentence embeddings. We extract the knowledge units from the corresponding context and then construct a mention/entity centralized graph. Hence, we can learn the fine-grained information about mention/entity by aggregating information from these knowledge units. To avoid the graph information bottleneck for the central mention/entity node, we construct a hierarchical graph and design a novel Hierarchical Graph Attention Network~(HGAN). Experimental results on popular benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed GER framework performs better than previous state-of-the-art models. The code has been available at https://github.com/wutaiqiang/GER-WSDM2023.
* 9 pages, 5 figures
Semantic Matching from Different Perspectives
Feb 14, 2022
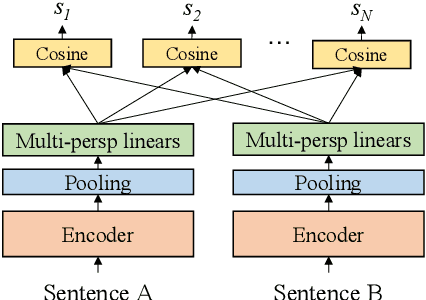
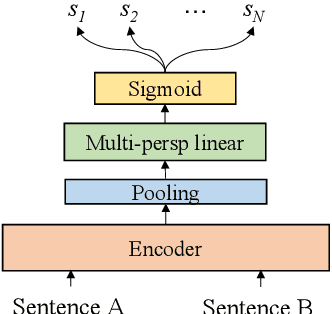

Abstract:In this paper, we pay attention to the issue which is usually overlooked, i.e., \textit{similarity should be determined from different perspectives}. To explore this issue, we release a Multi-Perspective Text Similarity (MPTS) dataset, in which sentence similarities are labeled from twelve perspectives. Furthermore, we conduct a series of experimental analysis on this task by retrofitting some famous text matching models. Finally, we obtain several conclusions and baseline models, laying the foundation for the following investigation of this issue. The dataset and code are publicly available at Github\footnote{\url{https://github.com/autoliuweijie/MPTS}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge