Jianghan Shen
OVD: On-policy Verbal Distillation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Knowledge distillation offers a promising path to transfer reasoning capabilities from large teacher models to efficient student models; however, existing token-level on-policy distillation methods require token-level alignment between the student and teacher models, which restricts the student model's exploration ability, prevent effective use of interactive environment feedback, and suffer from severe memory bottlenecks in reinforcement learning. We introduce On-policy Verbal Distillation (OVD), a memory-efficient framework that replaces token-level probability matching with trajectory matching using discrete verbal scores (0--9) from teacher models. OVD dramatically reduces memory consumption while enabling on-policy distillation from teacher models with verbal feedback, and avoids token-level alignment, allowing the student model to freely explore the output space. Extensive experiments on Web question answering and mathematical reasoning tasks show that OVD substantially outperforms existing methods, delivering up to +12.9% absolute improvement in average EM on Web Q&A tasks and a up to +25.7% gain on math benchmarks (when trained with only one random samples), while also exhibiting superior training efficiency. Our project page is available at https://OVD.github.io
ParallelComp: Parallel Long-Context Compressor for Length Extrapolation
Feb 20, 2025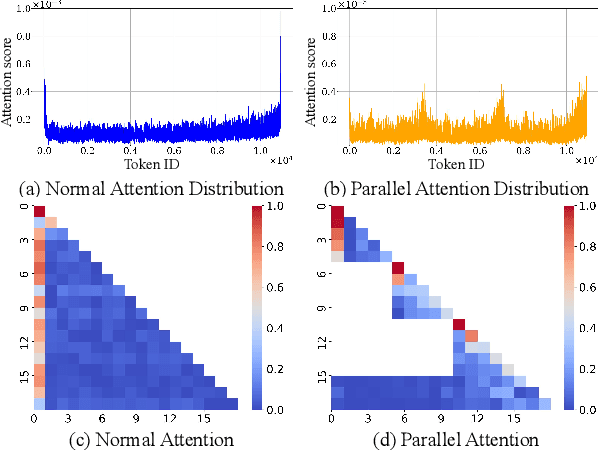
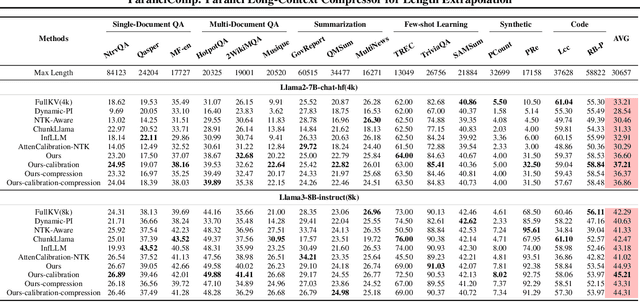
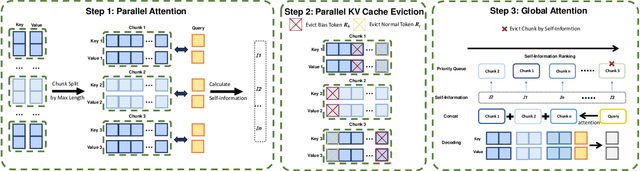
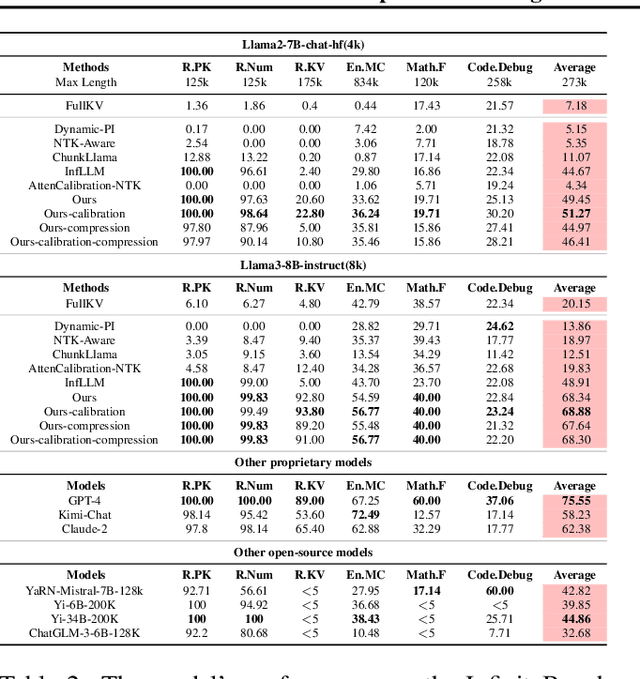
Abstract:Efficiently handling long contexts is crucial for large language models (LLMs). While rotary position embeddings (RoPEs) enhance length generalization, effective length extrapolation remains challenging and often requires costly fine-tuning. In contrast, recent training-free approaches suffer from the attention sink phenomenon, leading to severe performance degradation. In this paper, we introduce ParallelComp, a novel training-free method for long-context extrapolation that extends LLMs' context length from 4K to 128K while maintaining high throughput and preserving perplexity, and integrates seamlessly with Flash Attention. Our analysis offers new insights into attention biases in parallel attention mechanisms and provides practical solutions to tackle these challenges. To mitigate the attention sink issue, we propose an attention calibration strategy that reduces biases, ensuring more stable long-range attention. Additionally, we introduce a chunk eviction strategy to efficiently manage ultra-long contexts on a single A100 80GB GPU. To further enhance efficiency, we propose a parallel KV cache eviction technique, which improves chunk throughput by 1.76x, thereby achieving a 23.50x acceleration in the prefilling stage with negligible performance loss due to attention calibration. Furthermore, ParallelComp achieves 91.17% of GPT-4's performance on long-context tasks using an 8B model trained on 8K-length context, outperforming powerful closed-source models such as Claude-2 and Kimi-Chat.
UNComp: Uncertainty-Aware Long-Context Compressor for Efficient Large Language Model Inference
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Deploying large language models (LLMs) is challenging due to their high memory and computational demands, especially during long-context inference. While key-value (KV) caching accelerates inference by reusing previously computed keys and values, it also introduces significant memory overhead. Existing KV cache compression methods such as eviction and merging typically compress the KV cache after it is generated and overlook the eviction of hidden states, failing to improve the speed of the prefilling stage. Additionally, applying a uniform compression rate across different attention heads can harm crucial retrieval heads in needle-in-a-haystack tasks due to excessive compression. In this paper, we propose UNComp, an uncertainty-aware compression scheme that leverages matrix entropy to estimate model uncertainty across layers and heads at the token sequence level. By grouping layers and heads based on their uncertainty, UNComp adaptively compresses both the hidden states and the KV cache. Our method achieves a 1.6x speedup in the prefilling stage and reduces the KV cache to 4.74% of its original size, resulting in a 6.4x increase in throughput and a 1.4x speedup in inference with only a 1.41% performance loss. Remarkably, in needle-in-a-haystack tasks, UNComp outperforms the full-size KV cache even when compressed to 9.38% of its original size. Our approach offers an efficient, training-free Grouped-Query Attention paradigm that can be seamlessly integrated into existing KV cache schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge