Zhengqing Zang
A Syllogistic Probe: Tracing the Evolution of Logic Reasoning in Large Language Models
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Human logic has gradually shifted from intuition-driven inference to rigorous formal systems. Motivated by recent advances in large language models (LLMs), we explore whether LLMs exhibit a similar evolution in the underlying logical framework. Using existential import as a probe, we for evaluate syllogism under traditional and modern logic. Through extensive experiments of testing SOTA LLMs on a new syllogism dataset, we have some interesting findings: (i) Model size scaling promotes the shift toward modern logic; (ii) Thinking serves as an efficient accelerator beyond parameter scaling; (iii) the Base model plays a crucial role in determining how easily and stably this shift can emerge. Beyond these core factors, we conduct additional experiments for in-depth analysis of properties of current LLMs on syllogistic reasoning.
Parallelism and Generation Order in Masked Diffusion Language Models: Limits Today, Potential Tomorrow
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Masked Diffusion Language Models (MDLMs) promise parallel token generation and arbitrary-order decoding, yet it remains unclear to what extent current models truly realize these capabilities. We characterize MDLM behavior along two dimensions -- parallelism strength and generation order -- using Average Finalization Parallelism (AFP) and Kendall's tau. We evaluate eight mainstream MDLMs (up to 100B parameters) on 58 benchmarks spanning knowledge, reasoning, and programming. The results show that MDLMs still lag behind comparably sized autoregressive models, mainly because parallel probabilistic modeling weakens inter-token dependencies. Meanwhile, MDLMs exhibit adaptive decoding behavior: their parallelism and generation order vary significantly with the task domain, the stage of reasoning, and whether the output is correct. On tasks that require "backward information" (e.g., Sudoku), MDLMs adopt a solution order that tends to fill easier Sudoku blanks first, highlighting their advantages. Finally, we provide theoretical motivation and design insights supporting a Generate-then-Edit paradigm, which mitigates dependency loss while retaining the efficiency of parallel decoding.
Dual Prompt Learning for Adapting Vision-Language Models to Downstream Image-Text Retrieval
Aug 06, 2025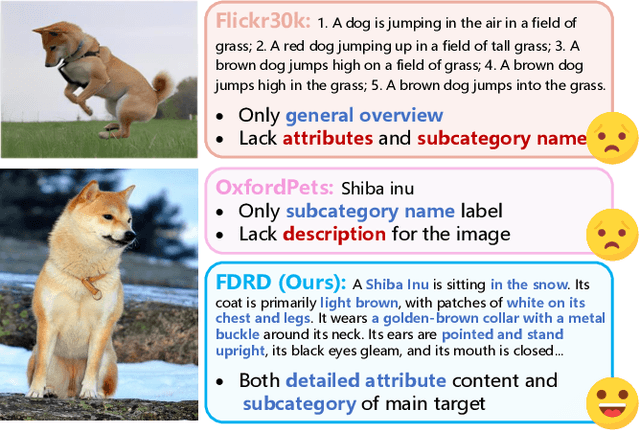
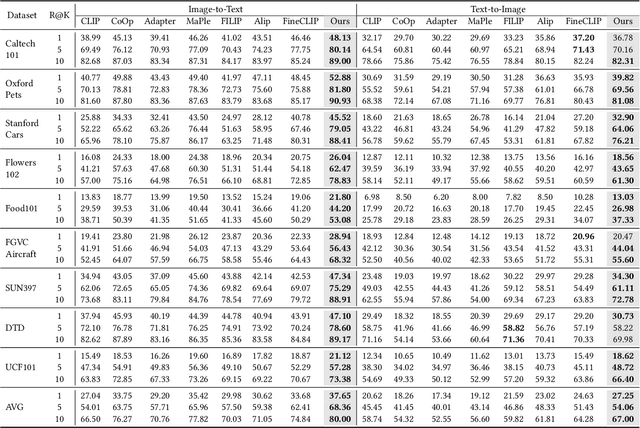
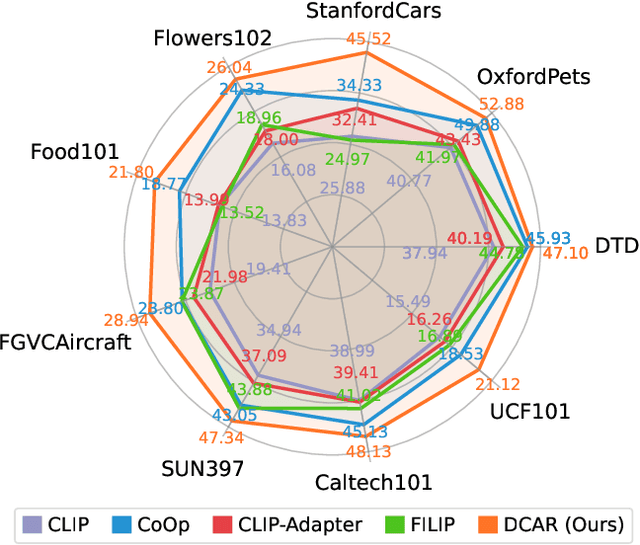
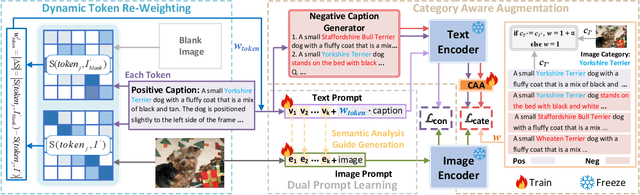
Abstract:Recently, prompt learning has demonstrated remarkable success in adapting pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to various downstream tasks such as image classification. However, its application to the downstream Image-Text Retrieval (ITR) task is more challenging. We find that the challenge lies in discriminating both fine-grained attributes and similar subcategories of the downstream data. To address this challenge, we propose Dual prompt Learning with Joint Category-Attribute Reweighting (DCAR), a novel dual-prompt learning framework to achieve precise image-text matching. The framework dynamically adjusts prompt vectors from both semantic and visual dimensions to improve the performance of CLIP on the downstream ITR task. Based on the prompt paradigm, DCAR jointly optimizes attribute and class features to enhance fine-grained representation learning. Specifically, (1) at the attribute level, it dynamically updates the weights of attribute descriptions based on text-image mutual information correlation; (2) at the category level, it introduces negative samples from multiple perspectives with category-matching weighting to learn subcategory distinctions. To validate our method, we construct the Fine-class Described Retrieval Dataset (FDRD), which serves as a challenging benchmark for ITR in downstream data domains. It covers over 1,500 downstream fine categories and 230,000 image-caption pairs with detailed attribute annotations. Extensive experiments on FDRD demonstrate that DCAR achieves state-of-the-art performance over existing baselines.
Zero-Shot Aerial Object Detection with Visual Description Regularization
Mar 01, 2024



Abstract:Existing object detection models are mainly trained on large-scale labeled datasets. However, annotating data for novel aerial object classes is expensive since it is time-consuming and may require expert knowledge. Thus, it is desirable to study label-efficient object detection methods on aerial images. In this work, we propose a zero-shot method for aerial object detection named visual Description Regularization, or DescReg. Concretely, we identify the weak semantic-visual correlation of the aerial objects and aim to address the challenge with prior descriptions of their visual appearance. Instead of directly encoding the descriptions into class embedding space which suffers from the representation gap problem, we propose to infuse the prior inter-class visual similarity conveyed in the descriptions into the embedding learning. The infusion process is accomplished with a newly designed similarity-aware triplet loss which incorporates structured regularization on the representation space. We conduct extensive experiments with three challenging aerial object detection datasets, including DIOR, xView, and DOTA. The results demonstrate that DescReg significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art ZSD methods with complex projection designs and generative frameworks, e.g., DescReg outperforms best reported ZSD method on DIOR by 4.5 mAP on unseen classes and 8.1 in HM. We further show the generalizability of DescReg by integrating it into generative ZSD methods as well as varying the detection architecture.
VCL Challenges 2023 at ICCV 2023 Technical Report: Bi-level Adaptation Method for Test-time Adaptive Object Detection
Oct 13, 2023Abstract:This report outlines our team's participation in VCL Challenges B Continual Test_time Adaptation, focusing on the technical details of our approach. Our primary focus is Testtime Adaptation using bi_level adaptations, encompassing image_level and detector_level adaptations. At the image level, we employ adjustable parameterbased image filters, while at the detector level, we leverage adjustable parameterbased mean teacher modules. Ultimately, through the utilization of these bi_level adaptations, we have achieved a remarkable 38.3% mAP on the target domain of the test set within VCL Challenges B. It is worth noting that the minimal drop in mAP, is mearly 4.2%, and the overall performance is 32.5% mAP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge