Yong Liang
BioVFM-21M: Benchmarking and Scaling Self-Supervised Vision Foundation Models for Biomedical Image Analysis
May 14, 2025Abstract:Scaling up model and data size have demonstrated impressive performance improvement over a wide range of tasks. Despite extensive studies on scaling behaviors for general-purpose tasks, medical images exhibit substantial differences from natural data. It remains unclear the key factors in developing medical vision foundation models at scale due to the absence of an extensive understanding of scaling behavior in the medical domain. In this paper, we explored the scaling behavior across model sizes, training algorithms, data sizes, and imaging modalities in developing scalable medical vision foundation models by self-supervised learning. To support scalable pretraining, we introduce BioVFM-21M, a large-scale biomedical image dataset encompassing a wide range of biomedical image modalities and anatomies. We observed that scaling up does provide benefits but varies across tasks. Additional analysis reveals several factors correlated with scaling benefits. Finally, we propose BioVFM, a large-scale medical vision foundation model pretrained on 21 million biomedical images, which outperforms the previous state-of-the-art foundation models across 12 medical benchmarks. Our results highlight that while scaling up is beneficial for pursuing better performance, task characteristics, data diversity, pretraining methods, and computational efficiency remain critical considerations for developing scalable medical foundation models.
SMPR: A structure-enhanced multimodal drug-disease prediction model for drug repositioning and cold start
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Repositioning drug-disease relationships has always been a hot field of research. However, actual cases of biologically validated drug relocation remain very limited, and existing models have not yet fully utilized the structural information of the drug. Furthermore, most repositioning models are only used to complete the relationship matrix, and their practicality is poor when dealing with drug cold start problems. This paper proposes a structure-enhanced multimodal relationship prediction model (SMRP). SMPR is based on the SMILE structure of the drug, using the Mol2VEC method to generate drug embedded representations, and learn disease embedded representations through heterogeneous network graph neural networks. Ultimately, a drug-disease relationship matrix is constructed. In addition, to reduce the difficulty of users' use, SMPR also provides a cold start interface based on structural similarity based on reposition results to simply and quickly predict drug-related diseases. The repositioning ability and cold start capability of the model are verified from multiple perspectives. While the AUC and ACUPR scores of repositioning reach 99% and 61% respectively, the AUC of cold start achieve 80%. In particular, the cold start Recall indicator can reach more than 70%, which means that SMPR is more sensitive to positive samples. Finally, case analysis is used to verify the practical value of the model and visual analysis directly demonstrates the improvement of the structure to the model. For quick use, we also provide local deployment of the model and package it into an executable program.
Spatial-Angular Representation Learning for High-Fidelity Continuous Super-Resolution in Diffusion MRI
Jan 27, 2025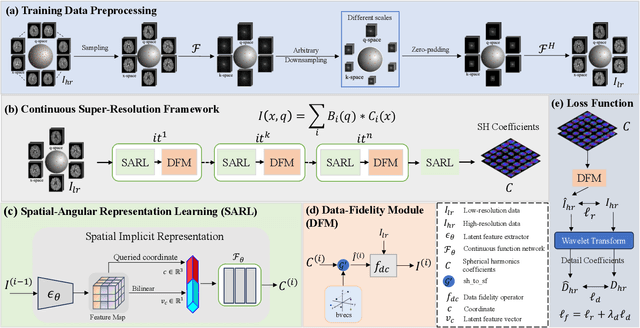
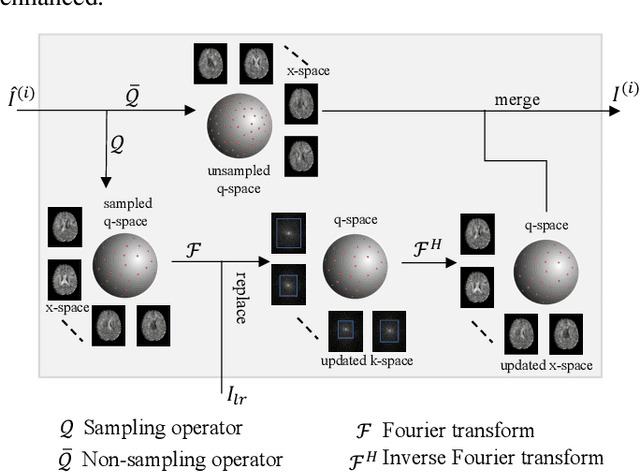
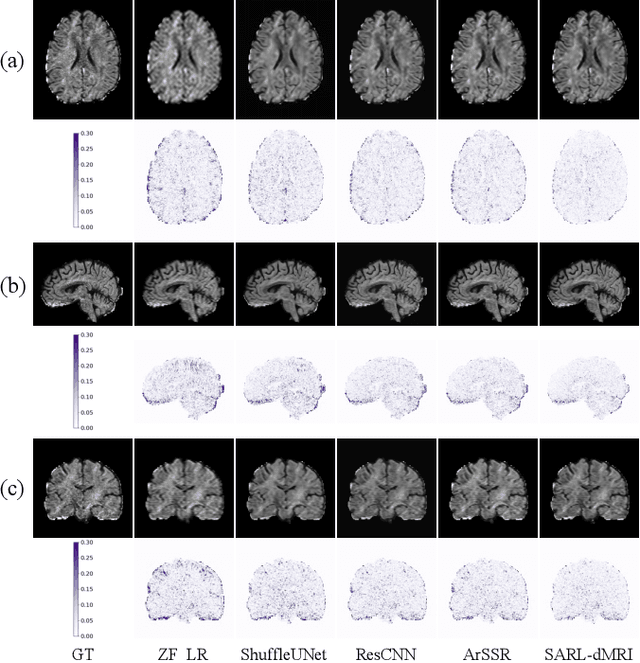
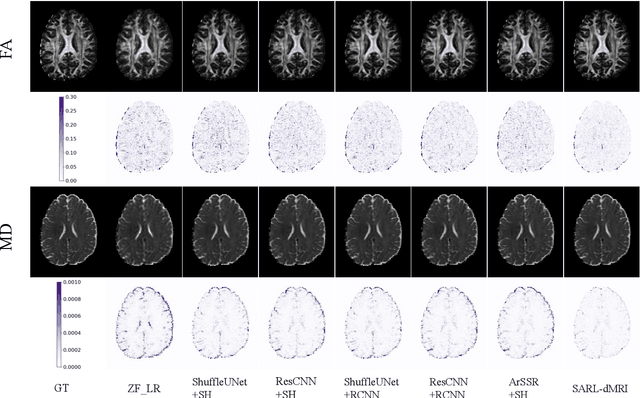
Abstract:Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) often suffers from low spatial and angular resolution due to inherent limitations in imaging hardware and system noise, adversely affecting the accurate estimation of microstructural parameters with fine anatomical details. Deep learning-based super-resolution techniques have shown promise in enhancing dMRI resolution without increasing acquisition time. However, most existing methods are confined to either spatial or angular super-resolution, limiting their effectiveness in capturing detailed microstructural features. Furthermore, traditional pixel-wise loss functions struggle to recover intricate image details essential for high-resolution reconstruction. To address these challenges, we propose SARL-dMRI, a novel Spatial-Angular Representation Learning framework for high-fidelity, continuous super-resolution in dMRI. SARL-dMRI explores implicit neural representations and spherical harmonics to model continuous spatial and angular representations, simultaneously enhancing both spatial and angular resolution while improving microstructural parameter estimation accuracy. To further preserve image fidelity, a data-fidelity module and wavelet-based frequency loss are introduced, ensuring the super-resolved images remain consistent with the original input and retain fine details. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, compared to five other state-of-the-art methods, our method significantly enhances dMRI data resolution, improves the accuracy of microstructural parameter estimation, and provides better generalization capabilities. It maintains stable performance even under a 45$\times$ downsampling factor.
Hengqin-RA-v1: Advanced Large Language Model for Diagnosis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Dataset based Traditional Chinese Medicine
Jan 05, 2025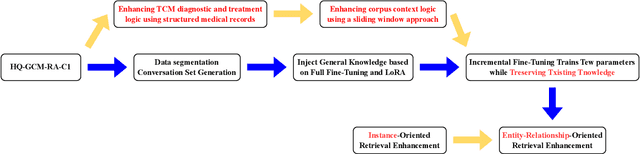
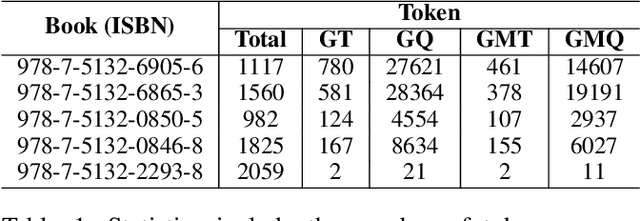
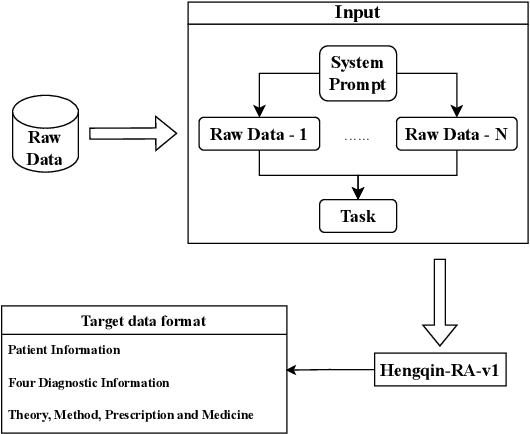
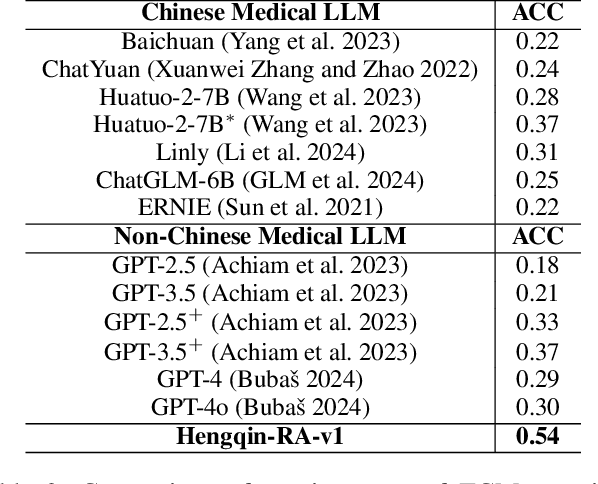
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) primarily trained on English texts, often face biases and inaccuracies in Chinese contexts. Their limitations are pronounced in fields like Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), where cultural and clinical subtleties are vital, further hindered by a lack of domain-specific data, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA). To address these issues, this paper introduces Hengqin-RA-v1, the first large language model specifically tailored for TCM with a focus on diagnosing and treating RA. We also present HQ-GCM-RA-C1, a comprehensive RA-specific dataset curated from ancient Chinese medical literature, classical texts, and modern clinical studies. This dataset empowers Hengqin-RA-v1 to deliver accurate and culturally informed responses, effectively bridging the gaps left by general-purpose models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Hengqin-RA-v1 outperforms state-of-the-art models, even surpassing the diagnostic accuracy of TCM practitioners in certain cases.
Swin-UMamba: Mamba-based UNet with ImageNet-based pretraining
Feb 05, 2024



Abstract:Accurate medical image segmentation demands the integration of multi-scale information, spanning from local features to global dependencies. However, it is challenging for existing methods to model long-range global information, where convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are constrained by their local receptive fields, and vision transformers (ViTs) suffer from high quadratic complexity of their attention mechanism. Recently, Mamba-based models have gained great attention for their impressive ability in long sequence modeling. Several studies have demonstrated that these models can outperform popular vision models in various tasks, offering higher accuracy, lower memory consumption, and less computational burden. However, existing Mamba-based models are mostly trained from scratch and do not explore the power of pretraining, which has been proven to be quite effective for data-efficient medical image analysis. This paper introduces a novel Mamba-based model, Swin-UMamba, designed specifically for medical image segmentation tasks, leveraging the advantages of ImageNet-based pretraining. Our experimental results reveal the vital role of ImageNet-based training in enhancing the performance of Mamba-based models. Swin-UMamba demonstrates superior performance with a large margin compared to CNNs, ViTs, and latest Mamba-based models. Notably, on AbdomenMRI, Encoscopy, and Microscopy datasets, Swin-UMamba outperforms its closest counterpart U-Mamba by an average score of 3.58%. The code and models of Swin-UMamba are publicly available at: https://github.com/JiarunLiu/Swin-UMamba
Enhancing the medical foundation model with multi-scale and cross-modality feature learning
Jan 03, 2024



Abstract:The development of multi-modal medical foundation models has attracted significant attention in the field of medicine and healthcare due to their promising prospects in various clinical applications. One area of focus in this research direction is the extractions of features at different scales. While previous studies have explored feature learning at individual scales, investigation on integrating the diverse scales and modalities of information is lacking, which may hinder the potential for mutual reinforcement among these features. This paper aims to bridge this gap by proposing a method that effectively exploits multi-scale and cross-modality information to enhance the performance of medical foundation models. The proposed method simultaneously exploit features at the local, instance, modality and global aspects, facilitating comprehensive representation learning within the models. We evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method on six open-source datasets across different clinical tasks, demonstrating its ability to enhance the performance of medical foundation models.
MLIP: Medical Language-Image Pre-training with Masked Local Representation Learning
Jan 03, 2024



Abstract:Existing contrastive language-image pre-training aims to learn a joint representation by matching abundant image-text pairs. However, the number of image-text pairs in medical datasets is usually orders of magnitude smaller than that in natural datasets. Besides, medical image-text pairs often involve numerous complex fine-grained correspondences. This paper aims to enhance the data efficiency by introducing multiple-to-multiple local relationship modeling to capture denser supervisions. More specifically, we propose a Medical Language-Image Pre-training (MLIP) framework, which exploits the limited image-text medical data more efficiently through patch-sentence matching. Furthermore, we introduce a masked contrastive learning strategy with semantic integrity estimation to reduce redundancy in images while preserving the underlying semantics. Our evaluation results show that MLIP outperforms previous work in zero/few-shot classification and few-shot segmentation tasks by a large margin.
Multimodal self-supervised learning for lesion localization
Jan 03, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal deep learning utilizing imaging and diagnostic reports has made impressive progress in the field of medical imaging diagnostics, demonstrating a particularly strong capability for auxiliary diagnosis in cases where sufficient annotation information is lacking. Nonetheless, localizing diseases accurately without detailed positional annotations remains a challenge. Although existing methods have attempted to utilize local information to achieve fine-grained semantic alignment, their capability in extracting the fine-grained semantics of the comprehensive contextual within reports is limited. To solve this problem, we introduce a new method that takes full sentences from textual reports as the basic units for local semantic alignment. Our approach combines chest X-ray images with their corresponding textual reports, performing contrastive learning at both global and local levels. The leading results obtained by our method on multiple datasets confirm its efficacy in the task of lesion localization.
Online Joint Assortment-Inventory Optimization under MNL Choices
Apr 04, 2023



Abstract:We study an online joint assortment-inventory optimization problem, in which we assume that the choice behavior of each customer follows the Multinomial Logit (MNL) choice model, and the attraction parameters are unknown a priori. The retailer makes periodic assortment and inventory decisions to dynamically learn from the realized demands about the attraction parameters while maximizing the expected total profit over time. In this paper, we propose a novel algorithm that can effectively balance the exploration and exploitation in the online decision-making of assortment and inventory. Our algorithm builds on a new estimator for the MNL attraction parameters, a novel approach to incentivize exploration by adaptively tuning certain known and unknown parameters, and an optimization oracle to static single-cycle assortment-inventory planning problems with given parameters. We establish a regret upper bound for our algorithm and a lower bound for the online joint assortment-inventory optimization problem, suggesting that our algorithm achieves nearly optimal regret rate, provided that the static optimization oracle is exact. Then we incorporate more practical approximate static optimization oracles into our algorithm, and bound from above the impact of static optimization errors on the regret of our algorithm. At last, we perform numerical studies to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed algorithm.
RCDNet: An Interpretable Rain Convolutional Dictionary Network for Single Image Deraining
Jul 14, 2021



Abstract:As a common weather, rain streaks adversely degrade the image quality. Hence, removing rains from an image has become an important issue in the field. To handle such an ill-posed single image deraining task, in this paper, we specifically build a novel deep architecture, called rain convolutional dictionary network (RCDNet), which embeds the intrinsic priors of rain streaks and has clear interpretability. In specific, we first establish a RCD model for representing rain streaks and utilize the proximal gradient descent technique to design an iterative algorithm only containing simple operators for solving the model. By unfolding it, we then build the RCDNet in which every network module has clear physical meanings and corresponds to each operation involved in the algorithm. This good interpretability greatly facilitates an easy visualization and analysis on what happens inside the network and why it works well in inference process. Moreover, taking into account the domain gap issue in real scenarios, we further design a novel dynamic RCDNet, where the rain kernels can be dynamically inferred corresponding to input rainy images and then help shrink the space for rain layer estimation with few rain maps so as to ensure a fine generalization performance in the inconsistent scenarios of rain types between training and testing data. By end-to-end training such an interpretable network, all involved rain kernels and proximal operators can be automatically extracted, faithfully characterizing the features of both rain and clean background layers, and thus naturally lead to better deraining performance. Comprehensive experiments substantiate the superiority of our method, especially on its well generality to diverse testing scenarios and good interpretability for all its modules. Code is available in \emph{\url{https://github.com/hongwang01/DRCDNet}}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge