Jiliang Zhang
Ray-Based Characterization of the AMPLE Model from 0.85 to 5 GHz
Apr 12, 2025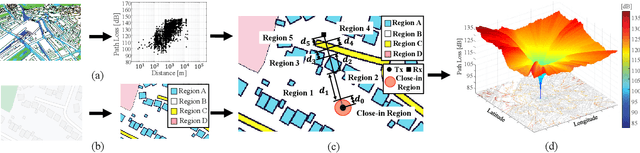
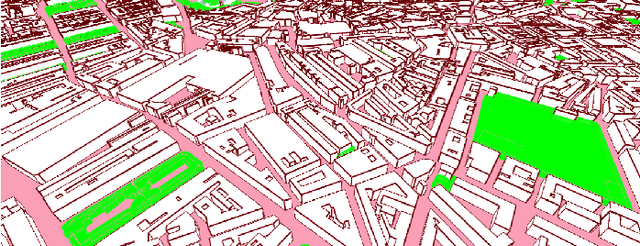
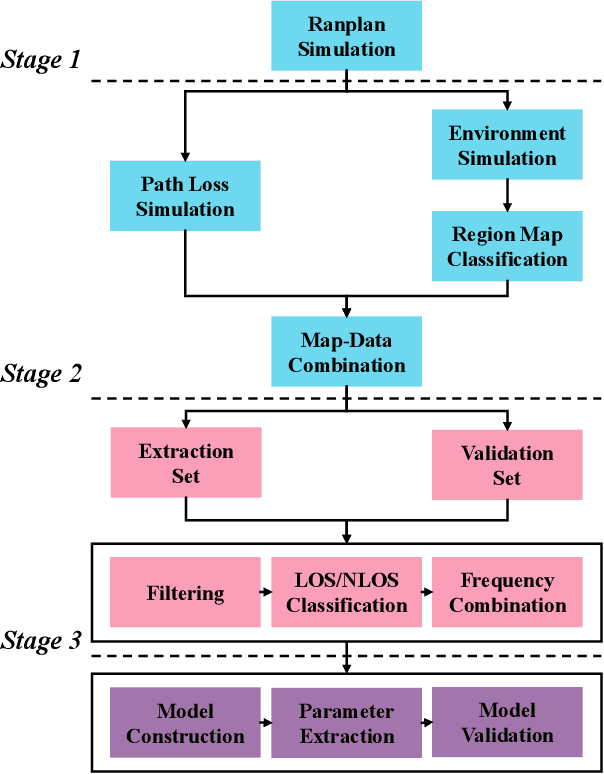
Abstract:In this paper, we characterize the adaptive multiple path loss exponent (AMPLE) radio propagation model under urban macrocell (UMa) and urban microcell (UMi) scenarios from 0.85-5 GHz using Ranplan Professional. We first enhance the original AMPLE model by introducing an additional frequency coefficient to support path loss prediction across multiple carrier frequencies. By using measurement-validated Ranplan Professional simulator, we simulate four cities and validate the simulations for further path loss model characterization. Specifically, we extract the close-in (CI) model parameters from the simulations and compare them with parameters extracted from measurements in other works. Under the ray-based model characterization, we compare the AMPLE model with the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) path loss model, the CI model, the alpha-beta-gamma (ABG) model, and those with simulation calibrations. In addition to standard performance metrics, we introduce the prediction-measurement difference error (PMDE) to assess overall prediction alignment with measurement, and mean simulation time per data point to evaluate model complexity. The results show that the AMPLE model outperforms existing models while maintaining similar model complexity.
Low Peak-to-Average Power Ratio FBMC-OQAM System based on Data Mapping and DFT Precoding
Sep 11, 2023



Abstract:Filter bank multicarrier with offset quadrature amplitude modulation (FBMC-OQAM) is an alternative to OFDM for enhanced spectrum flexible usage. To reduce the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR), DFT spreading is usually adopted in OFDM systems. However, in FBMC-OQAM systems, because the OQAM pre-processing splits the spread data into the real and imaginary parts, the DFT spreading can result in only marginal PAPR reduction. This letter proposes a novel map-DFT-spread FBMC-OQAM scheme. In this scheme, the transmitting data symbols are first mapped with a conjugate symmetry rule and then coded by the DFT. According to this method, the OQAM pre-processing can be avoided. Compared with the simple DFT-spread scheme, the proposed scheme achieves a better PAPR reduction. In addition, the effect of the prototype filter on the PAPR is studied via numerical simulation and a trade-off exists between the PAPR and out-of-band performances.
On the performance of an integrated communication and localization system: an analytical framework
Sep 08, 2023Abstract:Quantifying the performance bound of an integrated localization and communication (ILAC) system and the trade-off between communication and localization performance is critical. In this letter, we consider an ILAC system that can perform communication and localization via time-domain or frequency-domain resource allocation. We develop an analytical framework to derive the closed-form expression of the capacity loss versus localization Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRB) loss via time-domain and frequency-domain resource allocation. Simulation results validate the analytical model and demonstrate that frequency-domain resource allocation is preferable in scenarios with a smaller number of antennas at the next generation nodeB (gNB) and a larger distance between user equipment (UE) and gNB, while time-domain resource allocation is preferable in scenarios with a larger number of antennas and smaller distance between UE and the gNB.
Spatial Scattering Modulation with Multipath Component Aggregation Based on Antenna Arrays
Apr 05, 2023Abstract:In this paper, a multipath component aggregation (MCA) mechanism is introduced for spatial scattering modulation (SSM) to overcome the limitation in conventional SSM that the transmit antenna array steers the beam to a single multipath (MP) component at each instance. In the proposed MCA-SSM system, information bits are divided into two streams. One is mapped to an amplitude-phase-modulation (APM) constellation symbol, and the other is mapped to a beam vector symbol which steers multiple beams to selected strongest MP components via an MCA matrix. In comparison with the conventional SSM system, the proposed MCA-SSM enhances the bit error performance by avoiding both low receiving power due to steering the beam to a single weak MP component and inter-MP interference due to MP components with close values of angle of arrival (AoA) or angle of departure (AoD). For the proposed MCA-SSM, a union upper bound (UUB) on the average bit error probability (ABEP) with any MCA matrix is analytically derived and validated via Monte Carlo simulations. Based on the UUB, the MCA matrix is analytically optimized to minimize the ABEP of the MCA-SSM. Finally, numerical experiments are carried out, which show that the proposed MCA-SSM system remarkably outperforms the state-of-the-art SSM system in terms of ABEP under a typical indoor environment.
A Fast Path Loss Model for Wireless Channels Considering Environmental Factors
Mar 22, 2023Abstract:We present a path loss model that accurately predicts the path loss with low computational complexity considering environmental factors. In the proposed model, the entire area under consideration is recognized and divided into regions from a raster map, and each type of region is assigned with a path loss exponent (PLE) value. We then extract the model parameters via measurement in a suburban area to verify the proposed model. The results show that the root mean square error (RMSE) of the proposed model is 1.4 dB smaller than the widely used log-distance model.
A Distributed Machine Learning-Based Approach for IRS-Enhanced Cell-Free MIMO Networks
Jan 19, 2023



Abstract:In cell-free multiple input multiple output (MIMO) networks, multiple base stations (BSs) can collaborate to achieve high spectral efficiency. Nevertheless, high penetration loss due to large blockages in harsh propagation environments is often an issue that severely degrades communication performance. Considering that intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is capable of constructing digitally controllable reflection links in a low-cost manner, we investigate an IRS-enhanced downlink cell-free MIMO network in this paper. We aim to maximize the sum rate of all the users by jointly optimizing the transmit beamforming at the BSs and the reflection coefficients at the IRS. To address the optimization problem, we propose a fully distributed machine learning algorithm. Compared with the conventional iterative optimization algorithms that require a central processing at the central processing unit and large amount of channel state information and signaling exchange among the BSs, each BS can locally design its beamforming vector in the proposed algorithm. Meanwhile, the IRS reflection coefficients are determined by one of the BSs. Simulation results show that the deployment of IRS can significantly boost the sum user rate and that the proposed algorithm outperforms the benchmark methods.
Microwave QR Code: An IRS-Based Solution
Aug 05, 2022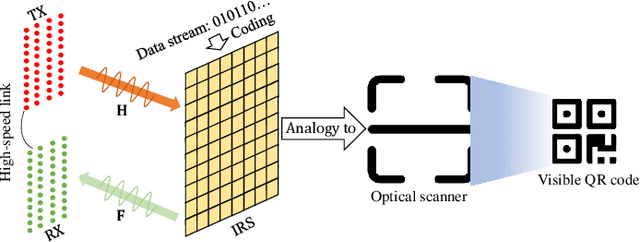
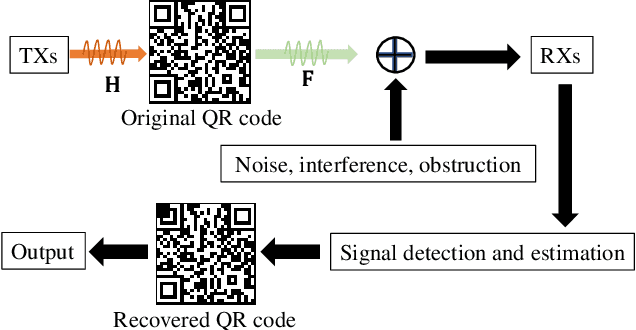
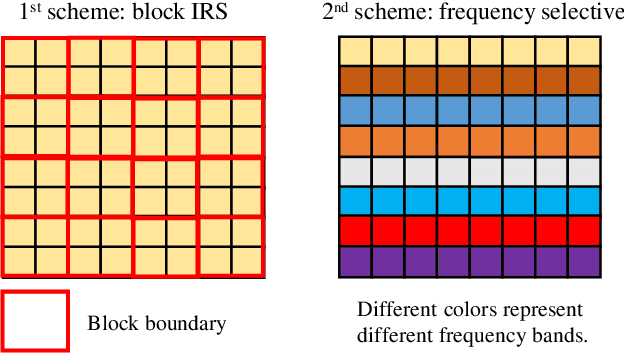
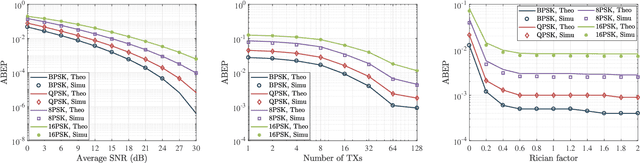
Abstract:This letter proposes to employ intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) as an information media to display a microwave quick response (QR) code for Internet-of-Things applications. To be specific, an IRS is used to form a dynamic bitmap image thanks to its tunable elements. With a QR code shown on the IRS, the transmitting and receiving antenna arrays are jointly designed to scan it by radiating electromagnetic wave as well as receiving and detecting the reflected signal. Based on such an idea, an IRS enabled information and communication system is modelled. Accordingly, some fundamental systematic operating mechanisms are investigated, involving derivation of average bit error probability for signal modulation, QR code implementation on an IRS, transmission design, detection, etc. The simulations are performed to show the achievable communication performance of system and confirm the feasibility of IRS-based microwave QR code.
An IRS Backscatter Enabled Integrated Sensing, Communication and Computation System
Jul 20, 2022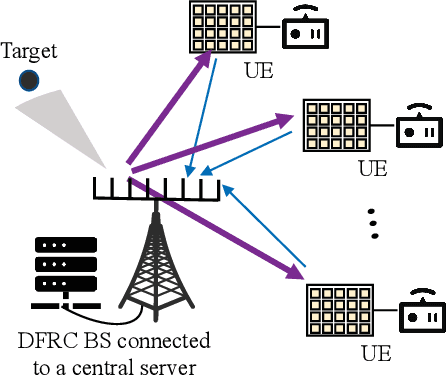
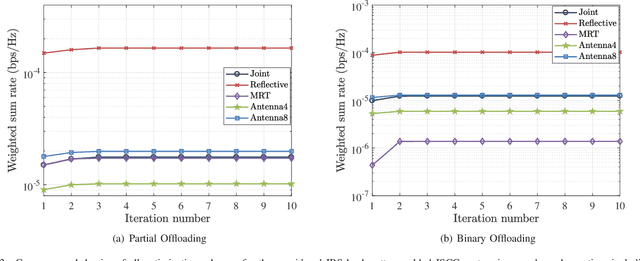
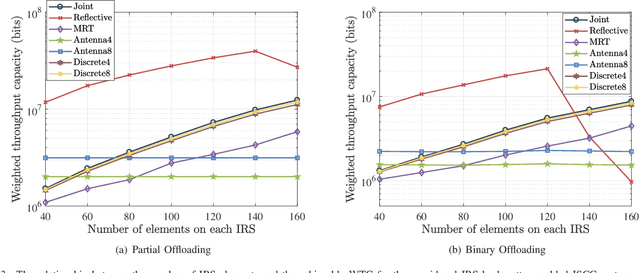
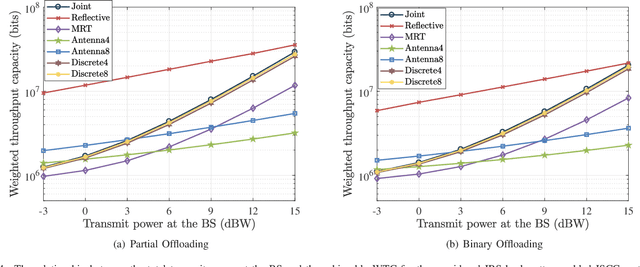
Abstract:This paper proposes to leverage intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) backscatter to realize radio-frequency-chain-free uplink-transmissions (RFCF-UT). In this communication paradigm, IRS works as an information carrier, whose elements are capable of adjusting their amplitudes and phases to collaboratively portray an electromagnetic image like a dynamic quick response (QR) code, rather than a familiar reflection device, while a full-duplex base station (BS) is used as a scanner to collect and recognize the information on IRS. To elaborate it, an integrated sensing, communication and computation system as an example is presented, in which a dual-functional radar-communication BS simultaneously detects the target and collects the data from user equipments each connected to an IRS. Based on the established model, partial and binary data offloading strategies are respectively considered. By defining a performance metric named weighted throughput capacity (WTC), two maximization problems of WTC are formulated. According to the coupling degree of optimization variables in the objective function and the constraints, each optimization problem is firstly decomposed into two subproblems. Then, the methods of linear programming, fractional programming, integer programming and alternative optimization are developed to solve the subproblems. The simulation results demonstrate the achievable WTC of the considered system, thereby validating RFCF-UT.
On the Performance of Data Compression in Clustered Fog Radio Access Networks
Jul 01, 2022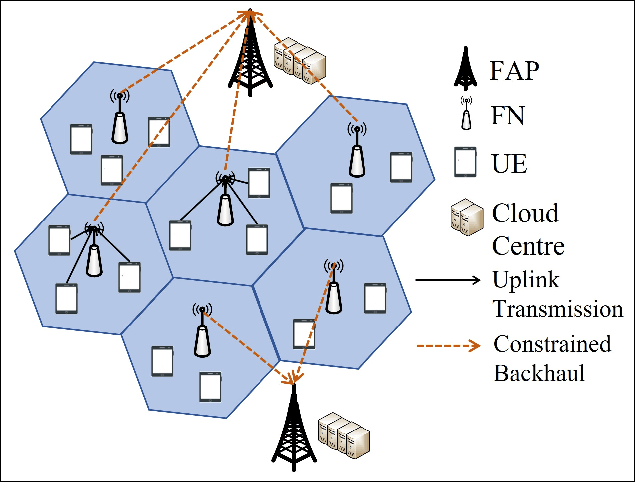
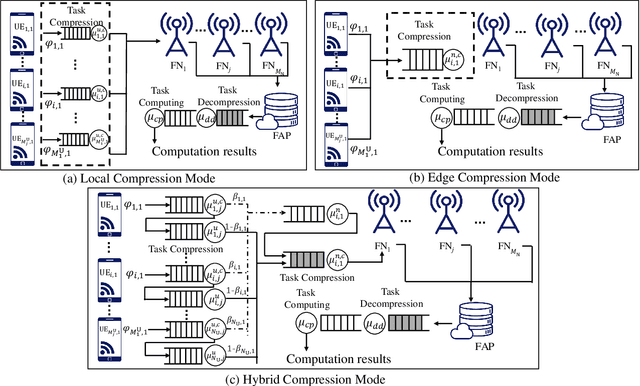
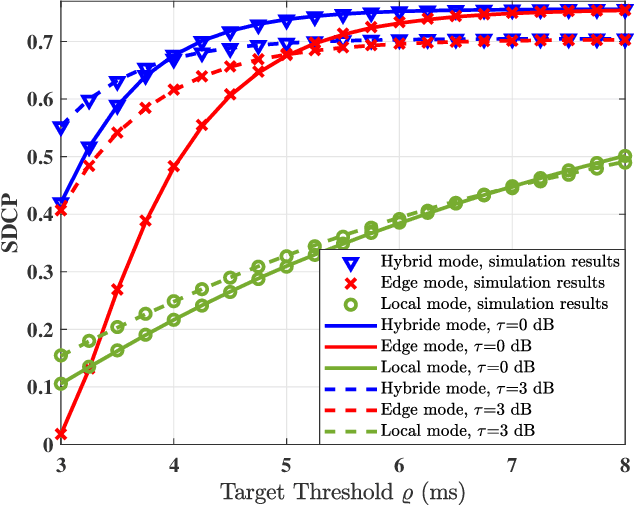
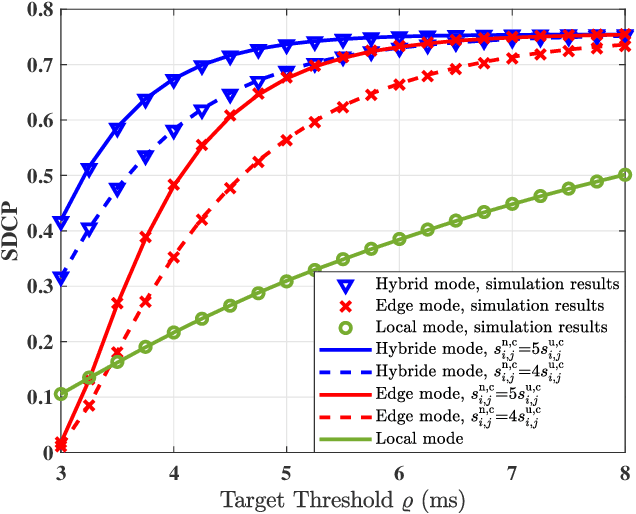
Abstract:The fog-radio-access-network (F-RAN) has been proposed to address the strict latency requirements, which offloads computation tasks generated in user equipments (UEs) to the edge to reduce the processing latency. However, it incorporates the task transmission latency, which may become the bottleneck of latency requirements. Data compression (DC) has been considered as one of the promising techniques to reduce the transmission latency. By compressing the computation tasks before transmitting, the transmission delay is reduced due to the shrink transmitted data size, and the original computing task can be retrieved by employing data decompressing (DD) at the edge nodes or the centre cloud. Nevertheless, the DC and DD incorporate extra processing latency, and the latency performance has not been investigated in the large-scale DC-enabled F-RAN. Therefore, in this work, the successful data compression probability (SDCP) is defined to analyse the latency performance of the F-RAN. Moreover, to analyse the effect of compression offloading ratio (COR), a novel hybrid compression mode is proposed based on the queueing theory. Based on this, the closed-form result of SDCP in the large-scale DC-enabled F-RAN is derived by combining the Matern cluster process and M/G/1 queueing model, and validated by Monte Carlo simulations. Based on the derived SDCP results, the effects of COR on the SDCP is analysed numerically. The results show that the SDCP with the optimal COR can be enhanced with a maximum value of 0.3 and 0.55 as compared with the cases of compressing all computing tasks at the edge and at the UE, respectively. Moreover, for the system requiring the minimal latency, the proposed hybrid compression mode can alleviate the requirement on the backhaul capacity.
Adaptive Modulation for Wobbling UAV Air-to-Ground Links in Millimeter-wave Bands
Apr 13, 2022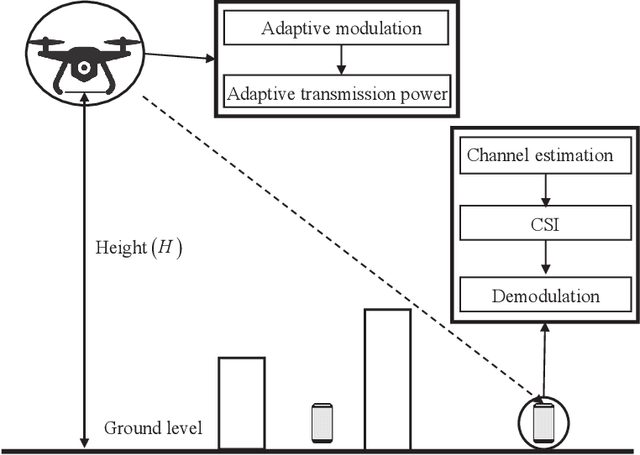
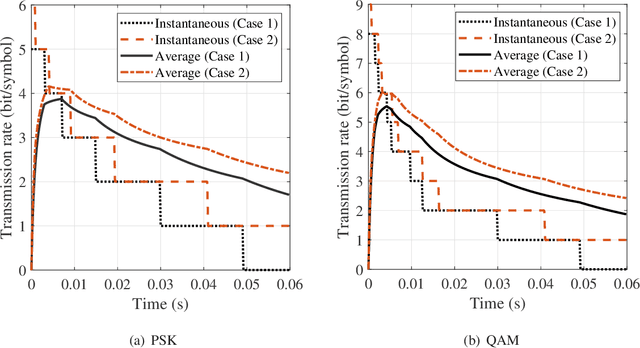
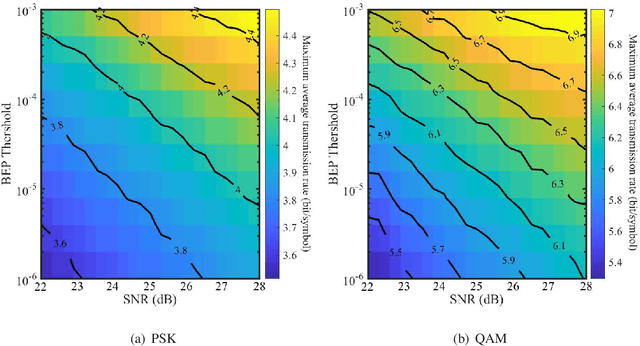
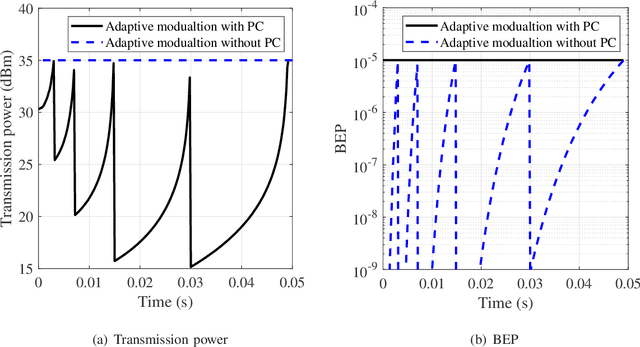
Abstract:The emerging millimeter-wave (mm-wave) unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) air-to-ground (A2G) communications are facing the Doppler effect problem that arises from the inevitable wobbling of the UAV. The fast time-varying channel for UAV A2G communications may lead to the outdated channel state information (CSI) from the channel estimation. In this paper, we introduce two detectors to demodulate the received signal and get the instantaneous bit error probability (BEP) of a mm-wave UAV A2G link under imperfect CSI. Based on the designed detectors, we propose an adaptive modulation scheme to maximize the average transmission rate under imperfect CSI by optimizing the data transmission time subject to the maximum tolerable BEP. A power control policy is in conjunction with adaptive modulation to minimize the transmission power while maintaining both the BEP under the threshold and the maximized average transmission rate. Numerical results show that the proposed adaptive modulation scheme in conjunction with the power control policy could maximize the temporally averaged transmission rate, while saves as much as 50\% energy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge