Sai Xu
Pinching-Antenna-Enabled Cognitive Radio Networks
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates a pinching-antenna (PA)-enabled cognitive radio network, where both the primary transmitter (PT) and secondary transmitter (ST) are equipped with a single waveguide and multiple PAs to facilitate simultaneous spectrum sharing. Under a general Ricean fading channel model, a closed-form analytical expression for the average spectral efficiency (SE) achieved by PAs is first derived. Based on this, a sum-SE maximization problem is formulated to jointly optimize the primary and secondary pinching beamforming, subject to system constraints on the transmission power budgets, minimum antenna separation requirements, and feasible PA deployment regions. To address this non-convex problem, a three-stage optimization algorithm is developed to sequentially optimize both the PT and ST pinching beamforming, and the ST power control. For the PT and ST pinching beamforming optimization, the coarse positions of PA are first determined at the waveguide-level. Then, wavelength-level refinements achieve constructive signal combination at the intended user and destructive superposition at the unintended user. For the ST power control, a closed-form solution is derived. Simulation results demonstrate that i) PAs can achieve significant SE improvements over conventional fixed-position antennas; ii) the proposed pinching beamforming design achieves effective interference suppression and superior performance for both even and odd numbers of PAs; and iii) the developed three-stage optimization algorithm enables nearly orthogonal transmission between the primary and secondary networks.
Fluid Antenna System-Assisted Self-Interference Cancellation for In-Band Full Duplex Communications
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:In-band full-duplex (IBFD) systems are expected to double the spectral efficiency compared to half-duplex systems, provided that loopback self-interference (SI) can be effectively suppressed. The inherent interference mitigation capabilities of the emerging fluid antenna system (FAS) technology make it a promising candidate for addressing the SI challenge in IBFD systems. This paper thus proposes a FAS-assisted self-interference cancellation (SIC) framework, which leverages a receiver-side FAS to dynamically select an interference-free port. Analytical results include a lower bound and an approximation of the residual SI (RSI) power, both derived for rich-scattering channels by considering the joint spatial correlation amongst the FAS ports. Simulations of RSI power and forward link rates validate the analysis, showing that the SIC performance improves with the number of FAS ports. Additionally, simulations under practical conditions, such as finite-scattering environments and wideband integrated access and backhaul (IAB) channels, reveal that the proposed approach offers superior SIC capability and significant forward rate gains over conventional IBFD SIC schemes.
GSM: A GNN-based Space-MIMO Framework for Direct-to-Cell Communications
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes a graph neural network (GNN)-based space multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) framework, named GSM, for direct-to-cell communications, aiming to achieve distributed coordinated beamforming for low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites. Firstly, a system model for LEO multi-satellite communications is established, where multiple LEO satellites collaborate to perform distributed beamforming and communicate with terrestrial user terminals coherently. Based on the system model, a weighted sum rate maximization problem is formulated. Secondly, a GNN-based method is developed to address the optimization problem. Particularly, the adopted neural network is composed of multiple identical GNNs, which are trained together and then deployed individually on each LEO satellite. Finally, the trained GNN is quantized and deployed on a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) to accelerate the inference by customizing the microarchitecture. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed GNN scheme outperforms the benchmark ones including maximum ratio transmission, zero forcing and minimum mean square error. Furthermore, experimental results show that the FPGA-based accelerator achieves remarkably low inference latency, ranging from 3.863 to 5.883 ms under a 10-ns target clock period with 8-bit fixed-point data representation.
Leveraging Inter-Chunk Interactions for Enhanced Retrieval in Large Language Model-Based Question Answering
Aug 06, 2024



Abstract:Retrieving external knowledge and prompting large language models with relevant information is an effective paradigm to enhance the performance of question-answering tasks. Previous research typically handles paragraphs from external documents in isolation, resulting in a lack of context and ambiguous references, particularly in multi-document and complex tasks. To overcome these challenges, we propose a new retrieval framework IIER, that leverages Inter-chunk Interactions to Enhance Retrieval. This framework captures the internal connections between document chunks by considering three types of interactions: structural, keyword, and semantic. We then construct a unified Chunk-Interaction Graph to represent all external documents comprehensively. Additionally, we design a graph-based evidence chain retriever that utilizes previous paths and chunk interactions to guide the retrieval process. It identifies multiple seed nodes based on the target question and iteratively searches for relevant chunks to gather supporting evidence. This retrieval process refines the context and reasoning chain, aiding the large language model in reasoning and answer generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that IIER outperforms strong baselines across four datasets, highlighting its effectiveness in improving retrieval and reasoning capabilities.
A Distributed Machine Learning-Based Approach for IRS-Enhanced Cell-Free MIMO Networks
Jan 19, 2023



Abstract:In cell-free multiple input multiple output (MIMO) networks, multiple base stations (BSs) can collaborate to achieve high spectral efficiency. Nevertheless, high penetration loss due to large blockages in harsh propagation environments is often an issue that severely degrades communication performance. Considering that intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is capable of constructing digitally controllable reflection links in a low-cost manner, we investigate an IRS-enhanced downlink cell-free MIMO network in this paper. We aim to maximize the sum rate of all the users by jointly optimizing the transmit beamforming at the BSs and the reflection coefficients at the IRS. To address the optimization problem, we propose a fully distributed machine learning algorithm. Compared with the conventional iterative optimization algorithms that require a central processing at the central processing unit and large amount of channel state information and signaling exchange among the BSs, each BS can locally design its beamforming vector in the proposed algorithm. Meanwhile, the IRS reflection coefficients are determined by one of the BSs. Simulation results show that the deployment of IRS can significantly boost the sum user rate and that the proposed algorithm outperforms the benchmark methods.
Microwave QR Code: An IRS-Based Solution
Aug 05, 2022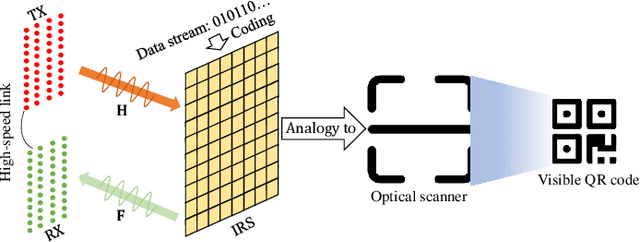
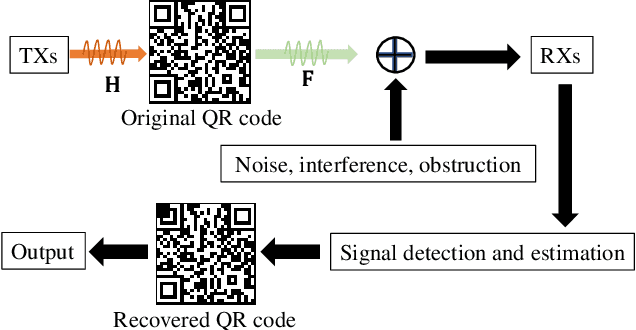
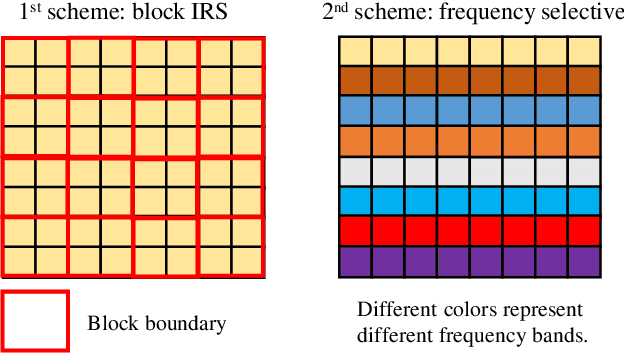
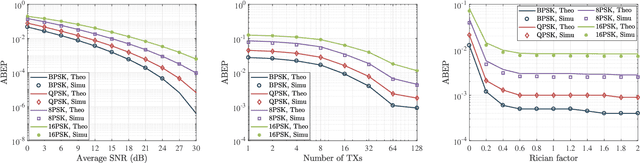
Abstract:This letter proposes to employ intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) as an information media to display a microwave quick response (QR) code for Internet-of-Things applications. To be specific, an IRS is used to form a dynamic bitmap image thanks to its tunable elements. With a QR code shown on the IRS, the transmitting and receiving antenna arrays are jointly designed to scan it by radiating electromagnetic wave as well as receiving and detecting the reflected signal. Based on such an idea, an IRS enabled information and communication system is modelled. Accordingly, some fundamental systematic operating mechanisms are investigated, involving derivation of average bit error probability for signal modulation, QR code implementation on an IRS, transmission design, detection, etc. The simulations are performed to show the achievable communication performance of system and confirm the feasibility of IRS-based microwave QR code.
An IRS Backscatter Enabled Integrated Sensing, Communication and Computation System
Jul 20, 2022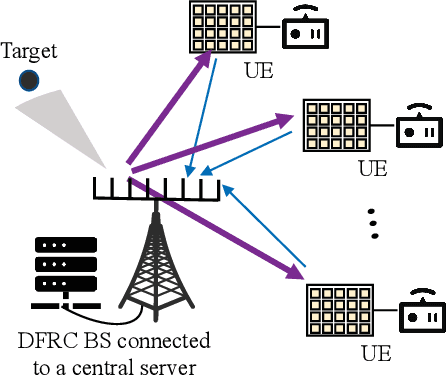
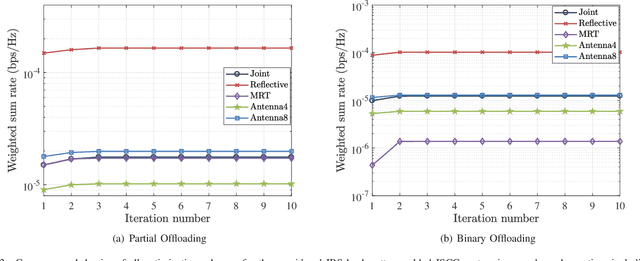
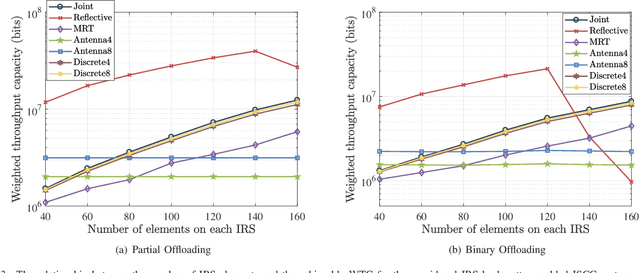
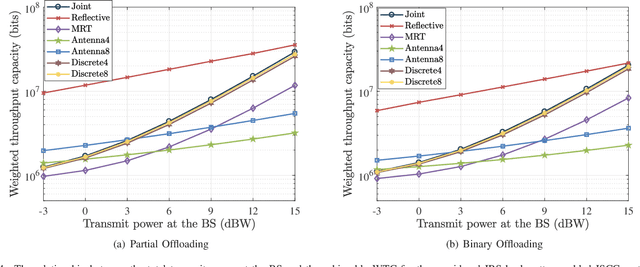
Abstract:This paper proposes to leverage intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) backscatter to realize radio-frequency-chain-free uplink-transmissions (RFCF-UT). In this communication paradigm, IRS works as an information carrier, whose elements are capable of adjusting their amplitudes and phases to collaboratively portray an electromagnetic image like a dynamic quick response (QR) code, rather than a familiar reflection device, while a full-duplex base station (BS) is used as a scanner to collect and recognize the information on IRS. To elaborate it, an integrated sensing, communication and computation system as an example is presented, in which a dual-functional radar-communication BS simultaneously detects the target and collects the data from user equipments each connected to an IRS. Based on the established model, partial and binary data offloading strategies are respectively considered. By defining a performance metric named weighted throughput capacity (WTC), two maximization problems of WTC are formulated. According to the coupling degree of optimization variables in the objective function and the constraints, each optimization problem is firstly decomposed into two subproblems. Then, the methods of linear programming, fractional programming, integer programming and alternative optimization are developed to solve the subproblems. The simulation results demonstrate the achievable WTC of the considered system, thereby validating RFCF-UT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge