Feng-Ju Chang
Alexa Machine Learning, Amazon, USA
A Simple Interpretable Transformer for Fine-Grained Image Classification and Analysis
Nov 07, 2023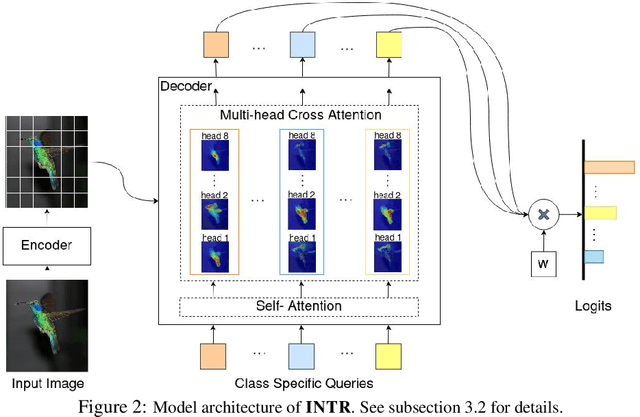
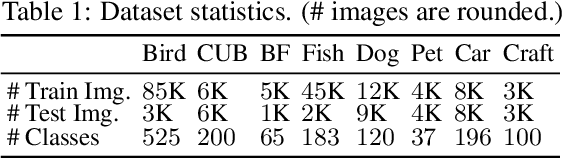
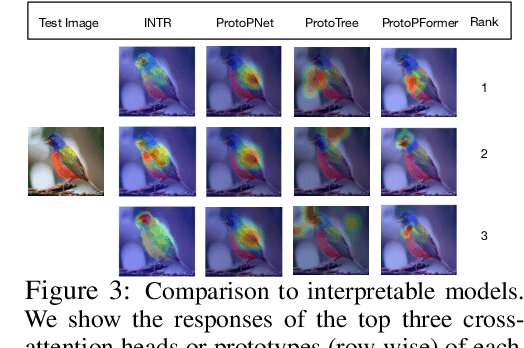
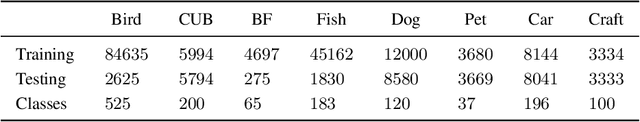
Abstract:We present a novel usage of Transformers to make image classification interpretable. Unlike mainstream classifiers that wait until the last fully-connected layer to incorporate class information to make predictions, we investigate a proactive approach, asking each class to search for itself in an image. We realize this idea via a Transformer encoder-decoder inspired by DEtection TRansformer (DETR). We learn ``class-specific'' queries (one for each class) as input to the decoder, enabling each class to localize its patterns in an image via cross-attention. We name our approach INterpretable TRansformer (INTR), which is fairly easy to implement and exhibits several compelling properties. We show that INTR intrinsically encourages each class to attend distinctively; the cross-attention weights thus provide a faithful interpretation of the prediction. Interestingly, via ``multi-head'' cross-attention, INTR could identify different ``attributes'' of a class, making it particularly suitable for fine-grained classification and analysis, which we demonstrate on eight datasets. Our code and pre-trained model are publicly accessible at https://github.com/Imageomics/INTR.
Dual-Attention Neural Transducers for Efficient Wake Word Spotting in Speech Recognition
Apr 05, 2023



Abstract:We present dual-attention neural biasing, an architecture designed to boost Wake Words (WW) recognition and improve inference time latency on speech recognition tasks. This architecture enables a dynamic switch for its runtime compute paths by exploiting WW spotting to select which branch of its attention networks to execute for an input audio frame. With this approach, we effectively improve WW spotting accuracy while saving runtime compute cost as defined by floating point operations (FLOPs). Using an in-house de-identified dataset, we demonstrate that the proposed dual-attention network can reduce the compute cost by $90\%$ for WW audio frames, with only $1\%$ increase in the number of parameters. This architecture improves WW F1 score by $16\%$ relative and improves generic rare word error rate by $3\%$ relative compared to the baselines.
Dialog act guided contextual adapter for personalized speech recognition
Mar 31, 2023
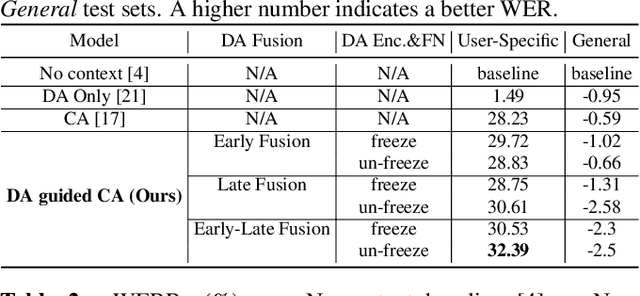
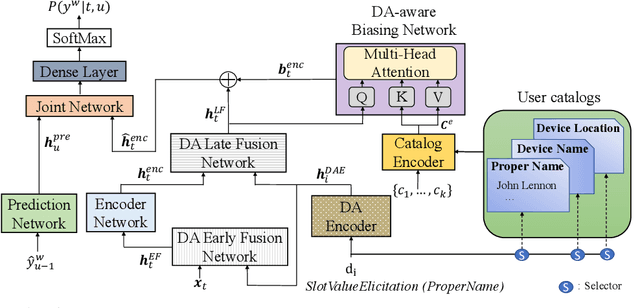
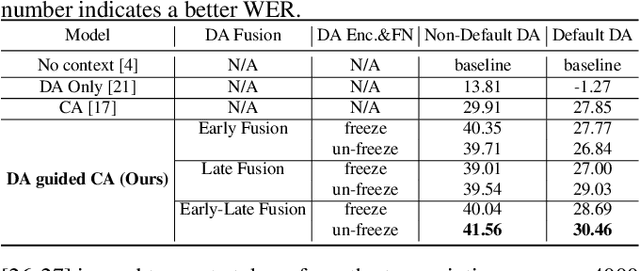
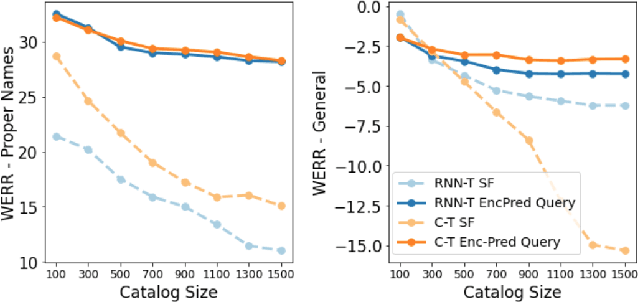
Abstract:Personalization in multi-turn dialogs has been a long standing challenge for end-to-end automatic speech recognition (E2E ASR) models. Recent work on contextual adapters has tackled rare word recognition using user catalogs. This adaptation, however, does not incorporate an important cue, the dialog act, which is available in a multi-turn dialog scenario. In this work, we propose a dialog act guided contextual adapter network. Specifically, it leverages dialog acts to select the most relevant user catalogs and creates queries based on both -- the audio as well as the semantic relationship between the carrier phrase and user catalogs to better guide the contextual biasing. On industrial voice assistant datasets, our model outperforms both the baselines - dialog act encoder-only model, and the contextual adaptation, leading to the most improvement over the no-context model: 58% average relative word error rate reduction (WERR) in the multi-turn dialog scenario, in comparison to the prior-art contextual adapter, which has achieved 39% WERR over the no-context model.
Leveraging Redundancy in Multiple Audio Signals for Far-Field Speech Recognition
Mar 01, 2023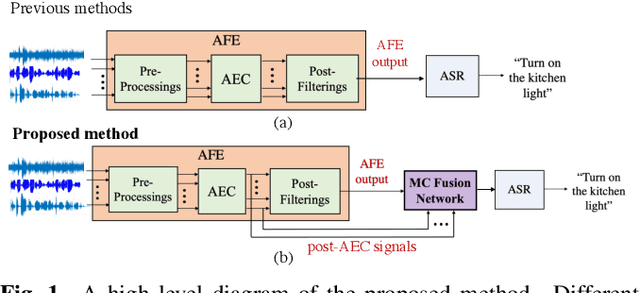

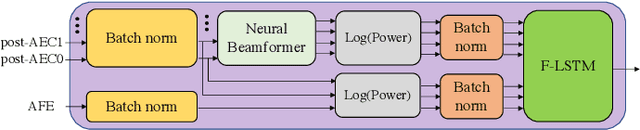
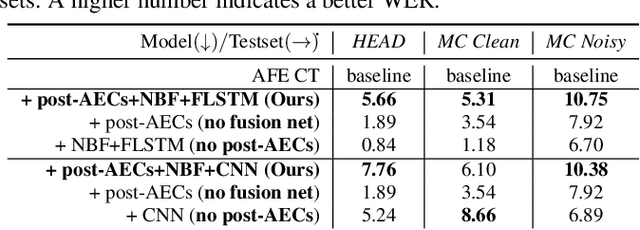
Abstract:To achieve robust far-field automatic speech recognition (ASR), existing techniques typically employ an acoustic front end (AFE) cascaded with a neural transducer (NT) ASR model. The AFE output, however, could be unreliable, as the beamforming output in AFE is steered to a wrong direction. A promising way to address this issue is to exploit the microphone signals before the beamforming stage and after the acoustic echo cancellation (post-AEC) in AFE. We argue that both, post-AEC and AFE outputs, are complementary and it is possible to leverage the redundancy between these signals to compensate for potential AFE processing errors. We present two fusion networks to explore this redundancy and aggregate these multi-channel (MC) signals: (1) Frequency-LSTM based, and (2) Convolutional Neural Network based fusion networks. We augment the MC fusion networks to a conformer transducer model and train it in an end-to-end fashion. Our experimental results on commercial virtual assistant tasks demonstrate that using the AFE output and two post-AEC signals with fusion networks offers up to 25.9% word error rate (WER) relative improvement over the model using the AFE output only, at the cost of <= 2% parameter increase.
ConvRNN-T: Convolutional Augmented Recurrent Neural Network Transducers for Streaming Speech Recognition
Sep 29, 2022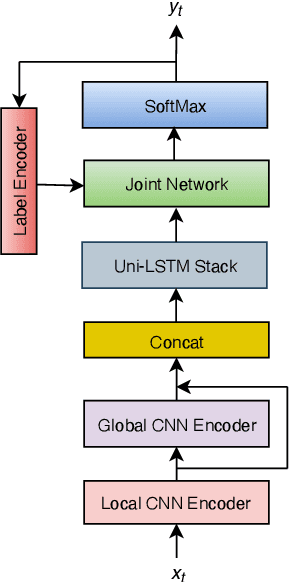
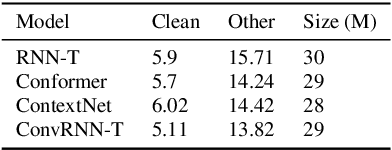
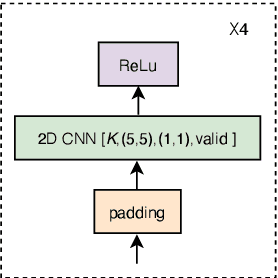
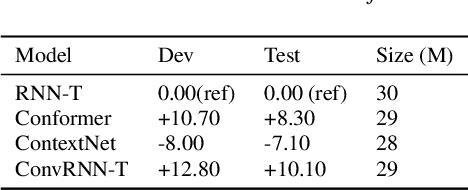
Abstract:The recurrent neural network transducer (RNN-T) is a prominent streaming end-to-end (E2E) ASR technology. In RNN-T, the acoustic encoder commonly consists of stacks of LSTMs. Very recently, as an alternative to LSTM layers, the Conformer architecture was introduced where the encoder of RNN-T is replaced with a modified Transformer encoder composed of convolutional layers at the frontend and between attention layers. In this paper, we introduce a new streaming ASR model, Convolutional Augmented Recurrent Neural Network Transducers (ConvRNN-T) in which we augment the LSTM-based RNN-T with a novel convolutional frontend consisting of local and global context CNN encoders. ConvRNN-T takes advantage of causal 1-D convolutional layers, squeeze-and-excitation, dilation, and residual blocks to provide both global and local audio context representation to LSTM layers. We show ConvRNN-T outperforms RNN-T, Conformer, and ContextNet on Librispeech and in-house data. In addition, ConvRNN-T offers less computational complexity compared to Conformer. ConvRNN-T's superior accuracy along with its low footprint make it a promising candidate for on-device streaming ASR technologies.
Compute Cost Amortized Transformer for Streaming ASR
Jul 05, 2022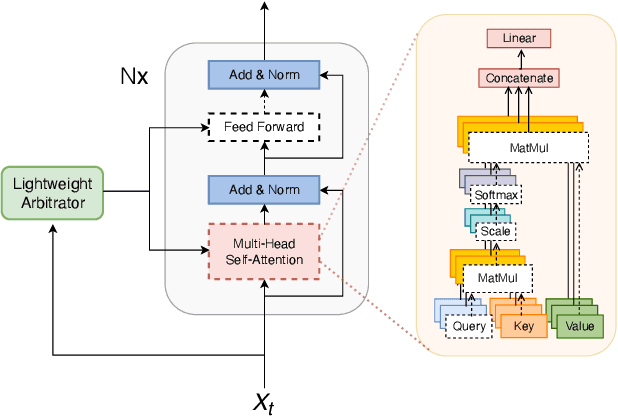
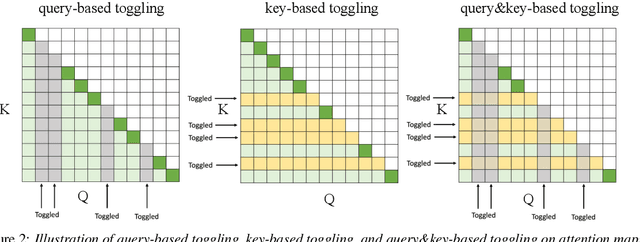
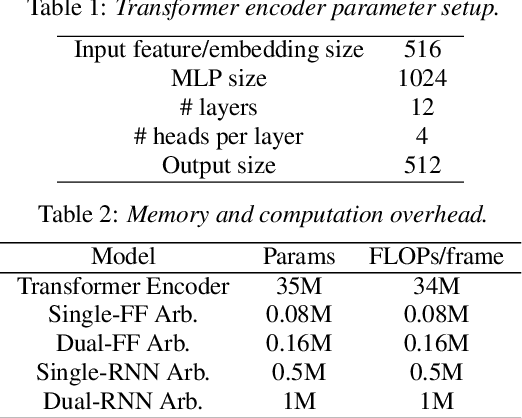
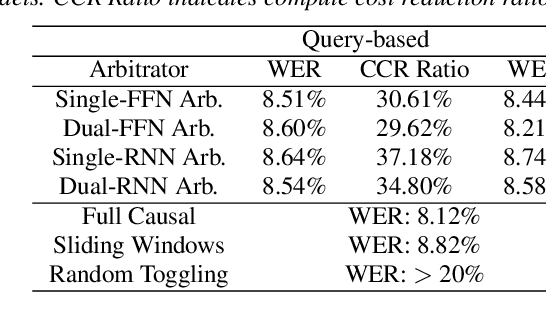
Abstract:We present a streaming, Transformer-based end-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR) architecture which achieves efficient neural inference through compute cost amortization. Our architecture creates sparse computation pathways dynamically at inference time, resulting in selective use of compute resources throughout decoding, enabling significant reductions in compute with minimal impact on accuracy. The fully differentiable architecture is trained end-to-end with an accompanying lightweight arbitrator mechanism operating at the frame-level to make dynamic decisions on each input while a tunable loss function is used to regularize the overall level of compute against predictive performance. We report empirical results from experiments using the compute amortized Transformer-Transducer (T-T) model conducted on LibriSpeech data. Our best model can achieve a 60% compute cost reduction with only a 3% relative word error rate (WER) increase.
Contextual Adapters for Personalized Speech Recognition in Neural Transducers
May 26, 2022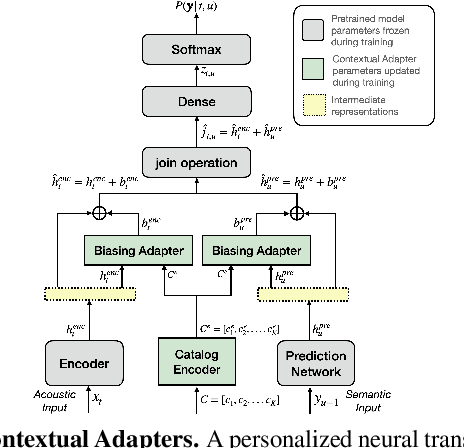
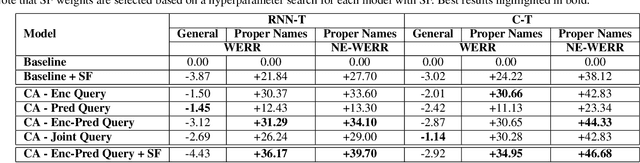
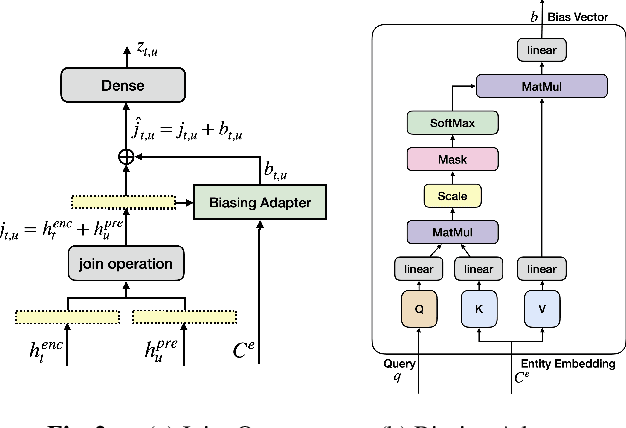
Abstract:Personal rare word recognition in end-to-end Automatic Speech Recognition (E2E ASR) models is a challenge due to the lack of training data. A standard way to address this issue is with shallow fusion methods at inference time. However, due to their dependence on external language models and the deterministic approach to weight boosting, their performance is limited. In this paper, we propose training neural contextual adapters for personalization in neural transducer based ASR models. Our approach can not only bias towards user-defined words, but also has the flexibility to work with pretrained ASR models. Using an in-house dataset, we demonstrate that contextual adapters can be applied to any general purpose pretrained ASR model to improve personalization. Our method outperforms shallow fusion, while retaining functionality of the pretrained models by not altering any of the model weights. We further show that the adapter style training is superior to full-fine-tuning of the ASR models on datasets with user-defined content.
Multi-task RNN-T with Semantic Decoder for Streamable Spoken Language Understanding
Apr 01, 2022
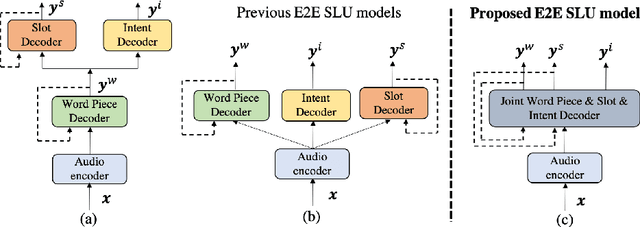
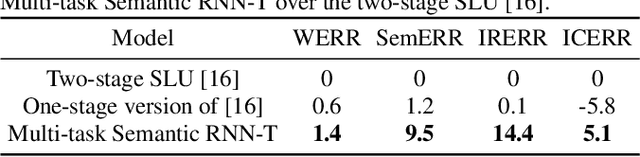
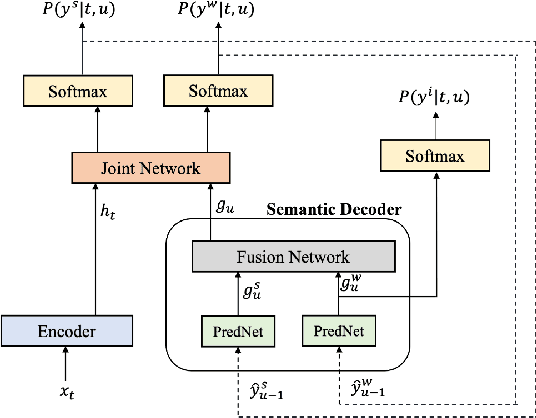
Abstract:End-to-end Spoken Language Understanding (E2E SLU) has attracted increasing interest due to its advantages of joint optimization and low latency when compared to traditionally cascaded pipelines. Existing E2E SLU models usually follow a two-stage configuration where an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) network first predicts a transcript which is then passed to a Natural Language Understanding (NLU) module through an interface to infer semantic labels, such as intent and slot tags. This design, however, does not consider the NLU posterior while making transcript predictions, nor correct the NLU prediction error immediately by considering the previously predicted word-pieces. In addition, the NLU model in the two-stage system is not streamable, as it must wait for the audio segments to complete processing, which ultimately impacts the latency of the SLU system. In this work, we propose a streamable multi-task semantic transducer model to address these considerations. Our proposed architecture predicts ASR and NLU labels auto-regressively and uses a semantic decoder to ingest both previously predicted word-pieces and slot tags while aggregating them through a fusion network. Using an industry scale SLU and a public FSC dataset, we show the proposed model outperforms the two-stage E2E SLU model for both ASR and NLU metrics.
Attentive Contextual Carryover for Multi-Turn End-to-End Spoken Language Understanding
Dec 13, 2021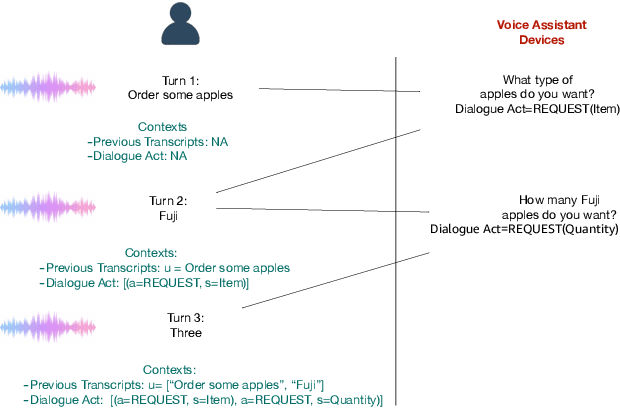
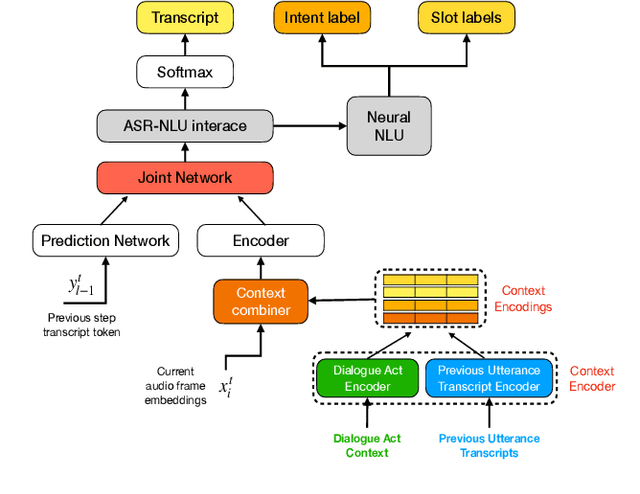
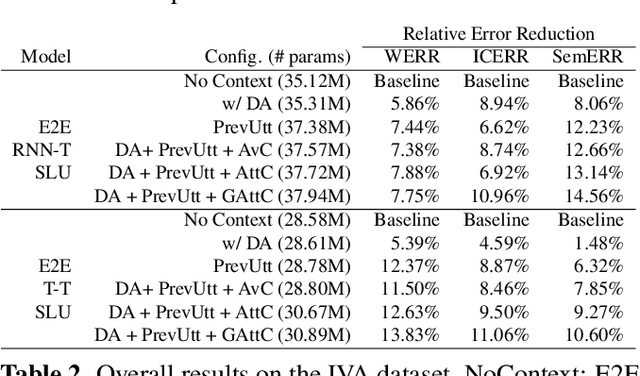
Abstract:Recent years have seen significant advances in end-to-end (E2E) spoken language understanding (SLU) systems, which directly predict intents and slots from spoken audio. While dialogue history has been exploited to improve conventional text-based natural language understanding systems, current E2E SLU approaches have not yet incorporated such critical contextual signals in multi-turn and task-oriented dialogues. In this work, we propose a contextual E2E SLU model architecture that uses a multi-head attention mechanism over encoded previous utterances and dialogue acts (actions taken by the voice assistant) of a multi-turn dialogue. We detail alternative methods to integrate these contexts into the state-ofthe-art recurrent and transformer-based models. When applied to a large de-identified dataset of utterances collected by a voice assistant, our method reduces average word and semantic error rates by 10.8% and 12.6%, respectively. We also present results on a publicly available dataset and show that our method significantly improves performance over a noncontextual baseline
Context-Aware Transformer Transducer for Speech Recognition
Nov 05, 2021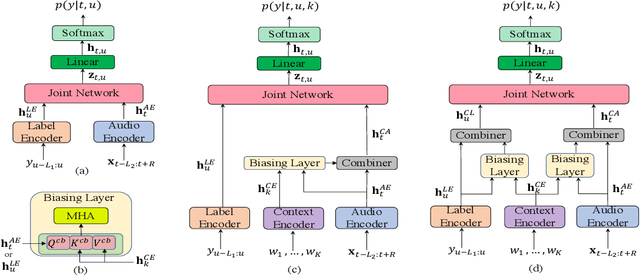
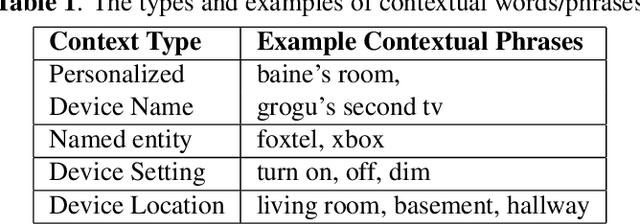

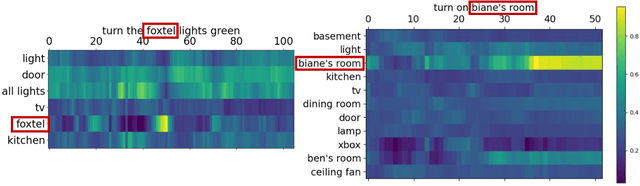
Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems often have difficulty recognizing uncommon words, that appear infrequently in the training data. One promising method, to improve the recognition accuracy on such rare words, is to latch onto personalized/contextual information at inference. In this work, we present a novel context-aware transformer transducer (CATT) network that improves the state-of-the-art transformer-based ASR system by taking advantage of such contextual signals. Specifically, we propose a multi-head attention-based context-biasing network, which is jointly trained with the rest of the ASR sub-networks. We explore different techniques to encode contextual data and to create the final attention context vectors. We also leverage both BLSTM and pretrained BERT based models to encode contextual data and guide the network training. Using an in-house far-field dataset, we show that CATT, using a BERT based context encoder, improves the word error rate of the baseline transformer transducer and outperforms an existing deep contextual model by 24.2% and 19.4% respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge