Ross McGowan
Robust Acoustic and Semantic Contextual Biasing in Neural Transducers for Speech Recognition
May 09, 2023Abstract:Attention-based contextual biasing approaches have shown significant improvements in the recognition of generic and/or personal rare-words in End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition (E2E ASR) systems like neural transducers. These approaches employ cross-attention to bias the model towards specific contextual entities injected as bias-phrases to the model. Prior approaches typically relied on subword encoders for encoding the bias phrases. However, subword tokenizations are coarse and fail to capture granular pronunciation information which is crucial for biasing based on acoustic similarity. In this work, we propose to use lightweight character representations to encode fine-grained pronunciation features to improve contextual biasing guided by acoustic similarity between the audio and the contextual entities (termed acoustic biasing). We further integrate pretrained neural language model (NLM) based encoders to encode the utterance's semantic context along with contextual entities to perform biasing informed by the utterance's semantic context (termed semantic biasing). Experiments using a Conformer Transducer model on the Librispeech dataset show a 4.62% - 9.26% relative WER improvement on different biasing list sizes over the baseline contextual model when incorporating our proposed acoustic and semantic biasing approach. On a large-scale in-house dataset, we observe 7.91% relative WER improvement compared to our baseline model. On tail utterances, the improvements are even more pronounced with 36.80% and 23.40% relative WER improvements on Librispeech rare words and an in-house testset respectively.
Dual-Attention Neural Transducers for Efficient Wake Word Spotting in Speech Recognition
Apr 05, 2023



Abstract:We present dual-attention neural biasing, an architecture designed to boost Wake Words (WW) recognition and improve inference time latency on speech recognition tasks. This architecture enables a dynamic switch for its runtime compute paths by exploiting WW spotting to select which branch of its attention networks to execute for an input audio frame. With this approach, we effectively improve WW spotting accuracy while saving runtime compute cost as defined by floating point operations (FLOPs). Using an in-house de-identified dataset, we demonstrate that the proposed dual-attention network can reduce the compute cost by $90\%$ for WW audio frames, with only $1\%$ increase in the number of parameters. This architecture improves WW F1 score by $16\%$ relative and improves generic rare word error rate by $3\%$ relative compared to the baselines.
Dialog act guided contextual adapter for personalized speech recognition
Mar 31, 2023
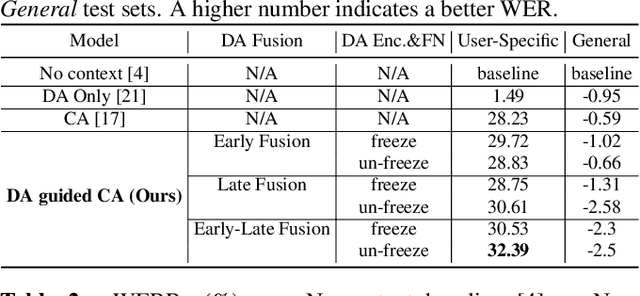
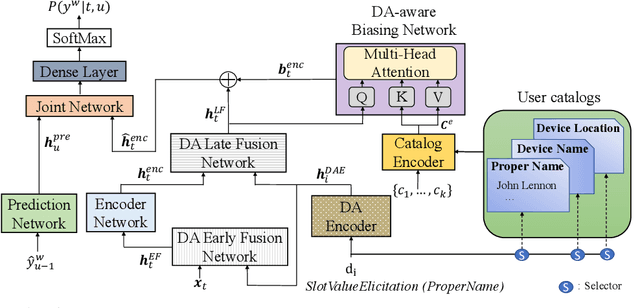
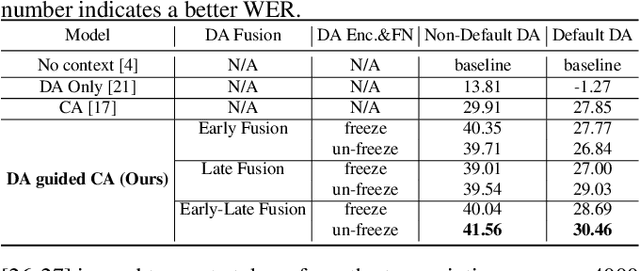
Abstract:Personalization in multi-turn dialogs has been a long standing challenge for end-to-end automatic speech recognition (E2E ASR) models. Recent work on contextual adapters has tackled rare word recognition using user catalogs. This adaptation, however, does not incorporate an important cue, the dialog act, which is available in a multi-turn dialog scenario. In this work, we propose a dialog act guided contextual adapter network. Specifically, it leverages dialog acts to select the most relevant user catalogs and creates queries based on both -- the audio as well as the semantic relationship between the carrier phrase and user catalogs to better guide the contextual biasing. On industrial voice assistant datasets, our model outperforms both the baselines - dialog act encoder-only model, and the contextual adaptation, leading to the most improvement over the no-context model: 58% average relative word error rate reduction (WERR) in the multi-turn dialog scenario, in comparison to the prior-art contextual adapter, which has achieved 39% WERR over the no-context model.
Attentive Contextual Carryover for Multi-Turn End-to-End Spoken Language Understanding
Dec 13, 2021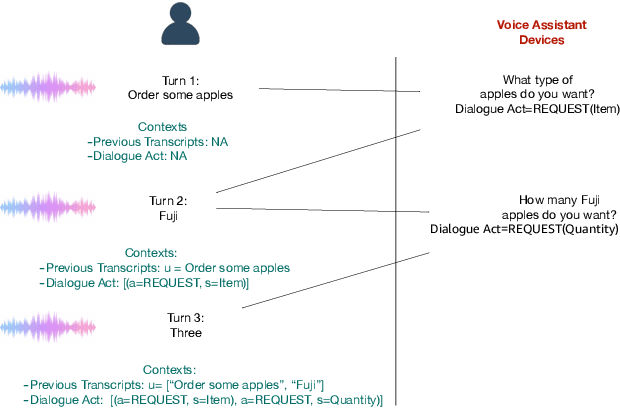
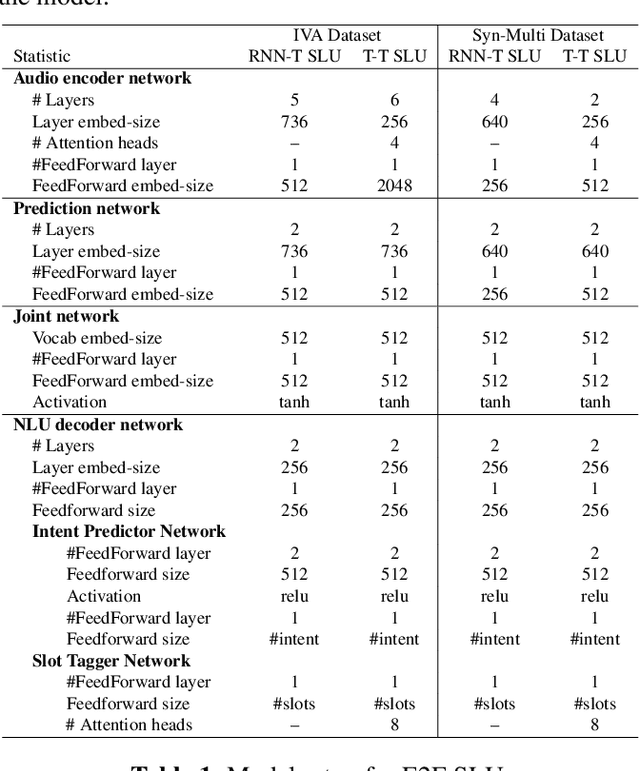
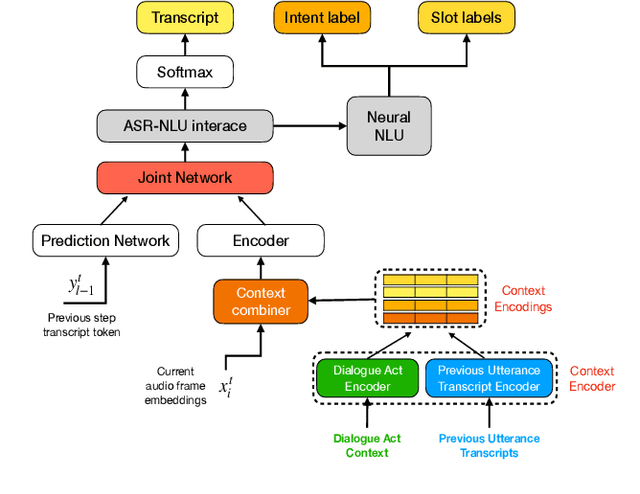
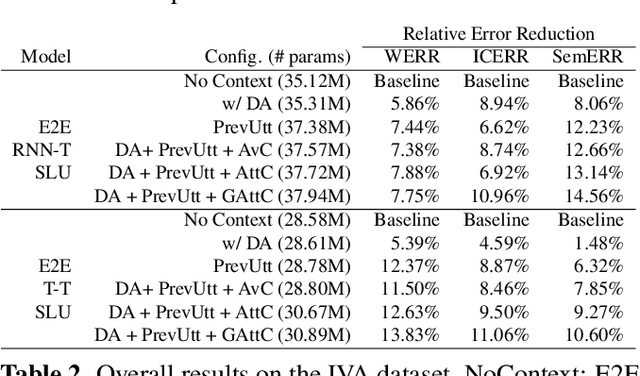
Abstract:Recent years have seen significant advances in end-to-end (E2E) spoken language understanding (SLU) systems, which directly predict intents and slots from spoken audio. While dialogue history has been exploited to improve conventional text-based natural language understanding systems, current E2E SLU approaches have not yet incorporated such critical contextual signals in multi-turn and task-oriented dialogues. In this work, we propose a contextual E2E SLU model architecture that uses a multi-head attention mechanism over encoded previous utterances and dialogue acts (actions taken by the voice assistant) of a multi-turn dialogue. We detail alternative methods to integrate these contexts into the state-ofthe-art recurrent and transformer-based models. When applied to a large de-identified dataset of utterances collected by a voice assistant, our method reduces average word and semantic error rates by 10.8% and 12.6%, respectively. We also present results on a publicly available dataset and show that our method significantly improves performance over a noncontextual baseline
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge