Haifeng Chen
Multi-Agent Procedural Graph Extraction with Structural and Logical Refinement
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Automatically extracting workflows as procedural graphs from natural language is promising yet underexplored, demanding both structural validity and logical alignment. While recent large language models (LLMs) show potential for procedural graph extraction, they often produce ill-formed structures or misinterpret logical flows. We present \model{}, a multi-agent framework that formulates procedural graph extraction as a multi-round reasoning process with dedicated structural and logical refinement. The framework iterates through three stages: (1) a graph extraction phase with the graph builder agent, (2) a structural feedback phase in which a simulation agent diagnoses and explains structural defects, and (3) a logical feedback phase in which a semantic agent aligns semantics between flow logic and linguistic cues in the source text. Important feedback is prioritized and expressed in natural language, which is injected into subsequent prompts, enabling interpretable and controllable refinement. This modular design allows agents to target distinct error types without supervision or parameter updates. Experiments demonstrate that \model{} achieves substantial improvements in both structural correctness and logical consistency over strong baselines.
Multi-Agent Coordinated Rename Refactoring
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:The primary value of AI agents in software development lies in their ability to extend the developer's capacity for reasoning and action, not to supplant human involvement. To showcase how to use agents working in tandem with developers, we designed a novel approach for carrying out coordinated renaming. Coordinated renaming, where a single rename refactoring triggers refactorings in multiple, related identifiers, is a frequent yet challenging task. Developers must manually propagate these rename refactorings across numerous files and contexts, a process that is both tedious and highly error-prone. State-of-the-art heuristic-based approaches produce an overwhelming number of false positives, while vanilla Large Language Models (LLMs) provide incomplete suggestions due to their limited context and inability to interact with refactoring tools. This leaves developers with incomplete refactorings or burdens them with filtering too many false positives. Coordinated renaming is exactly the kind of repetitive task that agents can significantly reduce the developers' burden while keeping them in the driver's seat. We designed, implemented, and evaluated the first multi-agent framework that automates coordinated renaming. It operates on a key insight: a developer's initial refactoring is a clue to infer the scope of related refactorings. Our Scope Inference Agent first transforms this clue into an explicit, natural-language Declared Scope. The Planned Execution Agent then uses this as a strict plan to identify program elements that should undergo refactoring and safely executes the changes by invoking the IDE's own trusted refactoring APIs. Finally, the Replication Agent uses it to guide the project-wide search. We first conducted a formative study on the practice of coordinated renaming in 609K commits in 100 open-source projects and surveyed 205 developers ...
xTime: Extreme Event Prediction with Hierarchical Knowledge Distillation and Expert Fusion
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Extreme events frequently occur in real-world time series and often carry significant practical implications. In domains such as climate and healthcare, these events, such as floods, heatwaves, or acute medical episodes, can lead to serious consequences. Accurate forecasting of such events is therefore of substantial importance. Most existing time series forecasting models are optimized for overall performance within the prediction window, but often struggle to accurately predict extreme events, such as high temperatures or heart rate spikes. The main challenges are data imbalance and the neglect of valuable information contained in intermediate events that precede extreme events. In this paper, we propose xTime, a novel framework for extreme event forecasting in time series. xTime leverages knowledge distillation to transfer information from models trained on lower-rarity events, thereby improving prediction performance on rarer ones. In addition, we introduce a mixture of experts (MoE) mechanism that dynamically selects and fuses outputs from expert models across different rarity levels, which further improves the forecasting performance for extreme events. Experiments on multiple datasets show that xTime achieves consistent improvements, with forecasting accuracy on extreme events improving from 3% to 78%.
DeepSieve: Information Sieving via LLM-as-a-Knowledge-Router
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at many reasoning tasks but struggle with knowledge-intensive queries due to their inability to dynamically access up-to-date or domain-specific information. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a promising solution, enabling LLMs to ground their responses in external sources. However, existing RAG methods lack fine-grained control over both the query and source sides, often resulting in noisy retrieval and shallow reasoning. In this work, we introduce DeepSieve, an agentic RAG framework that incorporates information sieving via LLM-as-a-knowledge-router. DeepSieve decomposes complex queries into structured sub-questions and recursively routes each to the most suitable knowledge source, filtering irrelevant information through a multi-stage distillation process. Our design emphasizes modularity, transparency, and adaptability, leveraging recent advances in agentic system design. Experiments on multi-hop QA tasks across heterogeneous sources demonstrate improved reasoning depth, retrieval precision, and interpretability over conventional RAG approaches. Our codes are available at https://github.com/MinghoKwok/DeepSieve.
Supply Chain Optimization via Generative Simulation and Iterative Decision Policies
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:High responsiveness and economic efficiency are critical objectives in supply chain transportation, both of which are influenced by strategic decisions on shipping mode. An integrated framework combining an efficient simulator with an intelligent decision-making algorithm can provide an observable, low-risk environment for transportation strategy design. An ideal simulation-decision framework must (1) generalize effectively across various settings, (2) reflect fine-grained transportation dynamics, (3) integrate historical experience with predictive insights, and (4) maintain tight integration between simulation feedback and policy refinement. We propose Sim-to-Dec framework to satisfy these requirements. Specifically, Sim-to-Dec consists of a generative simulation module, which leverages autoregressive modeling to simulate continuous state changes, reducing dependence on handcrafted domain-specific rules and enhancing robustness against data fluctuations; and a history-future dual-aware decision model, refined iteratively through end-to-end optimization with simulator interactions. Extensive experiments conducted on three real-world datasets demonstrate that Sim-to-Dec significantly improves timely delivery rates and profit.
Multi-Modal View Enhanced Large Vision Models for Long-Term Time Series Forecasting
May 29, 2025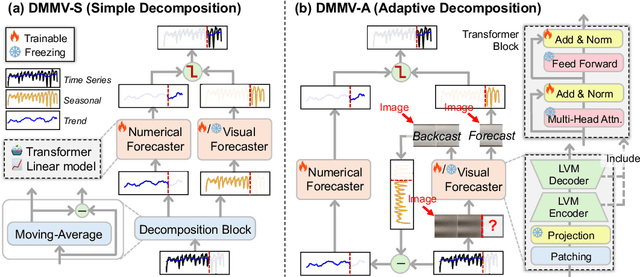
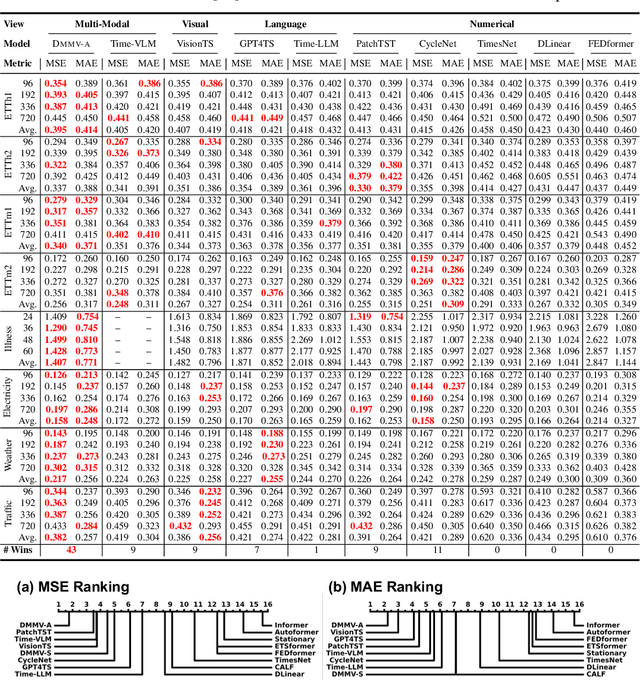
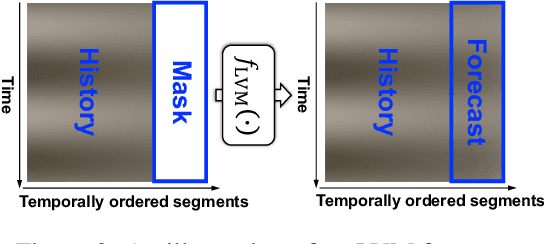
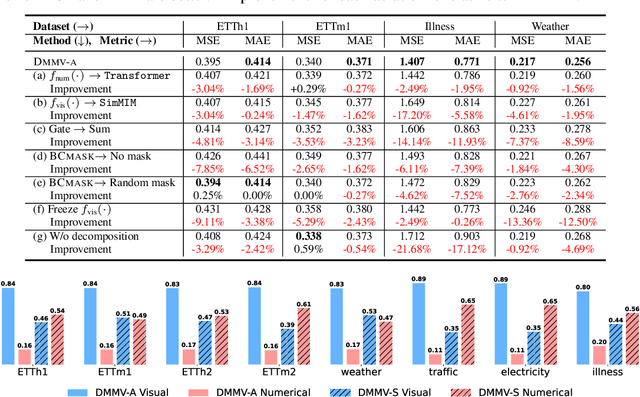
Abstract:Time series, typically represented as numerical sequences, can also be transformed into images and texts, offering multi-modal views (MMVs) of the same underlying signal. These MMVs can reveal complementary patterns and enable the use of powerful pre-trained large models, such as large vision models (LVMs), for long-term time series forecasting (LTSF). However, as we identified in this work, applying LVMs to LTSF poses an inductive bias towards "forecasting periods". To harness this bias, we propose DMMV, a novel decomposition-based multi-modal view framework that leverages trend-seasonal decomposition and a novel backcast residual based adaptive decomposition to integrate MMVs for LTSF. Comparative evaluations against 14 state-of-the-art (SOTA) models across diverse datasets show that DMMV outperforms single-view and existing multi-modal baselines, achieving the best mean squared error (MSE) on 6 out of 8 benchmark datasets.
Brownian Bridge Augmented Surrogate Simulation and Injection Planning for Geological CO$_2$ Storage
May 21, 2025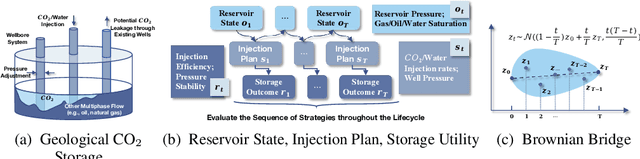
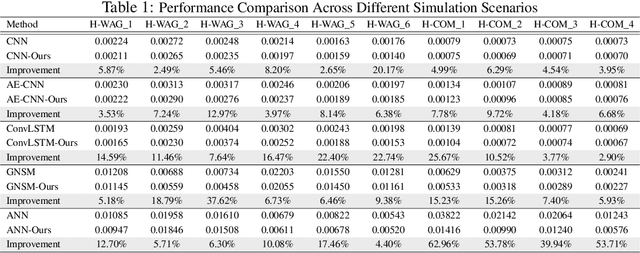
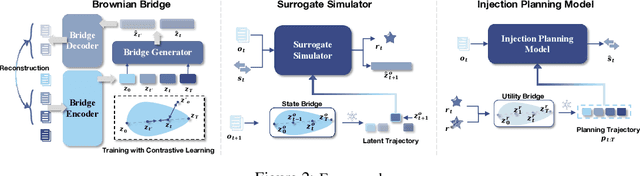
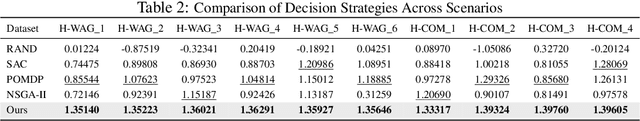
Abstract:Geological CO2 storage (GCS) involves injecting captured CO2 into deep subsurface formations to support climate goals. The effective management of GCS relies on adaptive injection planning to dynamically control injection rates and well pressures to balance both storage safety and efficiency. Prior literature, including numerical optimization methods and surrogate-optimization methods, is limited by real-world GCS requirements of smooth state transitions and goal-directed planning within limited time. To address these limitations, we propose a Brownian Bridge-augmented framework for surrogate simulation and injection planning in GCS and develop two insights: (i) Brownian bridge as a smooth state regularizer for better surrogate simulation; (ii) Brownian bridge as goal-time-conditioned planning guidance for improved injection planning. Our method has three stages: (i) learning deep Brownian bridge representations with contrastive and reconstructive losses from historical reservoir and utility trajectories, (ii) incorporating Brownian bridge-based next state interpolation for simulator regularization, and (iii) guiding injection planning with Brownian utility-conditioned trajectories to generate high-quality injection plans. Experimental results across multiple datasets collected from diverse GCS settings demonstrate that our framework consistently improves simulation fidelity and planning effectiveness while maintaining low computational overhead.
Bridging the Domain Gap in Equation Distillation with Reinforcement Feedback
May 21, 2025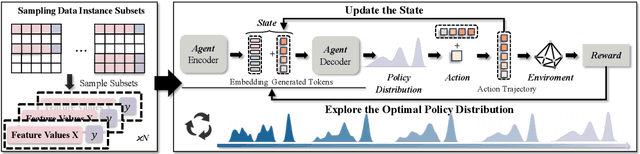
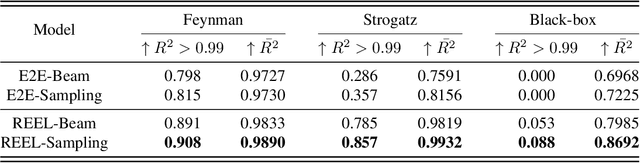
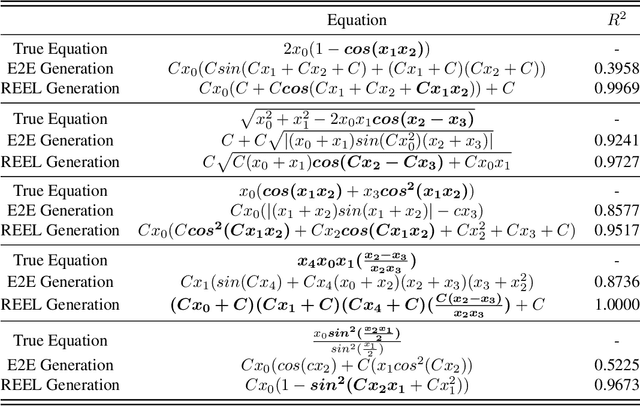
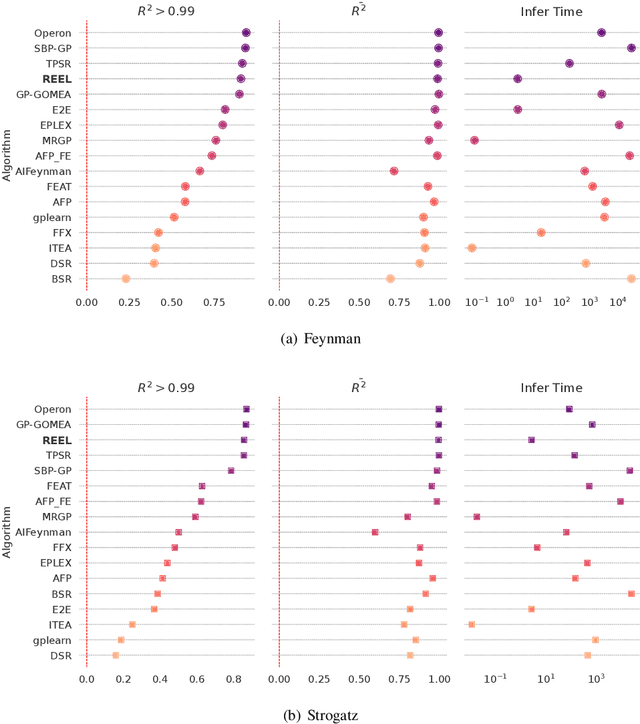
Abstract:The data-to-equation (Data2Eqn) task aims to discover interpretable mathematical equations that map observed values to labels, offering physical insights and broad applicability across academic and industrial domains. Genetic programming and traditional deep learning-based approaches suffer from search inefficiency and poor generalization on small task-specific datasets. Foundation models showed promise in this area, but existing approaches suffer from: 1) They are pretrained on general-purpose data distributions, making them less effective for domain-specific tasks; and 2) their training objectives focus on token-level alignment, overlooking mathematical semantics, which can lead to inaccurate equations. To address these issues, we aim to enhance the domain adaptability of foundation models for Data2Eqn tasks. In this work, we propose a reinforcement learning-based finetuning framework that directly optimizes the generation policy of a pretrained model through reward signals derived from downstream numerical fitness. Our method allows the model to adapt to specific and complex data distributions and generate mathematically meaningful equations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach improves both the accuracy and robustness of equation generation under complex distributions.
LM$^2$otifs : An Explainable Framework for Machine-Generated Texts Detection
May 18, 2025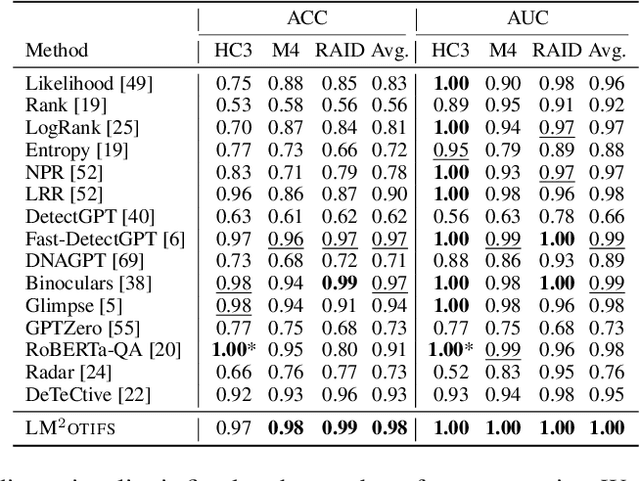
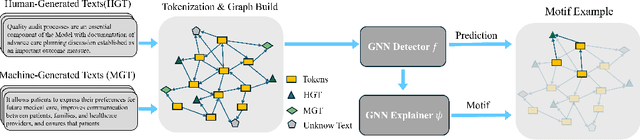
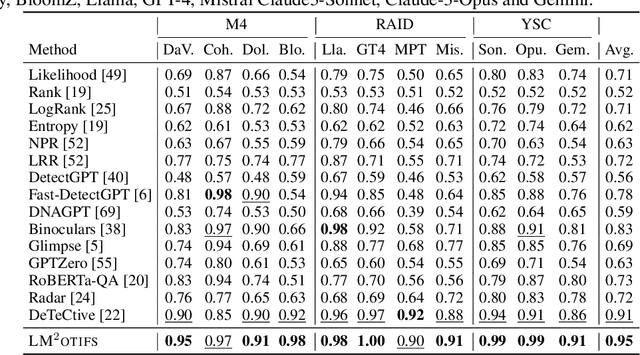
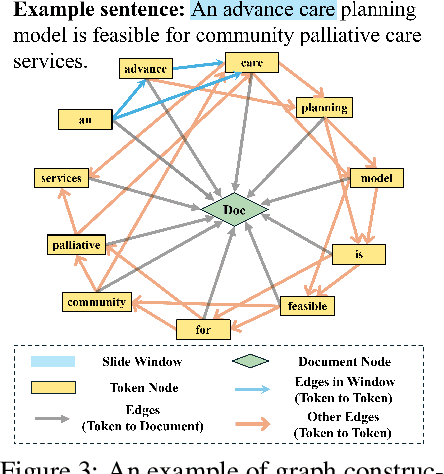
Abstract:The impressive ability of large language models to generate natural text across various tasks has led to critical challenges in authorship authentication. Although numerous detection methods have been developed to differentiate between machine-generated texts (MGT) and human-generated texts (HGT), the explainability of these methods remains a significant gap. Traditional explainability techniques often fall short in capturing the complex word relationships that distinguish HGT from MGT. To address this limitation, we present LM$^2$otifs, a novel explainable framework for MGT detection. Inspired by probabilistic graphical models, we provide a theoretical rationale for the effectiveness. LM$^2$otifs utilizes eXplainable Graph Neural Networks to achieve both accurate detection and interpretability. The LM$^2$otifs pipeline operates in three key stages: first, it transforms text into graphs based on word co-occurrence to represent lexical dependencies; second, graph neural networks are used for prediction; and third, a post-hoc explainability method extracts interpretable motifs, offering multi-level explanations from individual words to sentence structures. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate the comparable performance of LM$^2$otifs. The empirical evaluation of the extracted explainable motifs confirms their effectiveness in differentiating HGT and MGT. Furthermore, qualitative analysis reveals distinct and visible linguistic fingerprints characteristic of MGT.
Where's the liability in the Generative Era? Recovery-based Black-Box Detection of AI-Generated Content
May 02, 2025Abstract:The recent proliferation of photorealistic images created by generative models has sparked both excitement and concern, as these images are increasingly indistinguishable from real ones to the human eye. While offering new creative and commercial possibilities, the potential for misuse, such as in misinformation and fraud, highlights the need for effective detection methods. Current detection approaches often rely on access to model weights or require extensive collections of real image datasets, limiting their scalability and practical application in real world scenarios. In this work, we introduce a novel black box detection framework that requires only API access, sidestepping the need for model weights or large auxiliary datasets. Our approach leverages a corrupt and recover strategy: by masking part of an image and assessing the model ability to reconstruct it, we measure the likelihood that the image was generated by the model itself. For black-box models that do not support masked image inputs, we incorporate a cost efficient surrogate model trained to align with the target model distribution, enhancing detection capability. Our framework demonstrates strong performance, outperforming baseline methods by 4.31% in mean average precision across eight diffusion model variant datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge