Zheng Yuan
Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Italy, Università di Ferrara, Italy
ErrorLLM: Modeling SQL Errors for Text-to-SQL Refinement
Mar 04, 2026Abstract:Despite the remarkable performance of large language models (LLMs) in text-to-SQL (SQL generation), correctly producing SQL queries remains challenging during initial generation. The SQL refinement task is subsequently introduced to correct syntactic and semantic errors in generated SQL queries. However, existing paradigms face two major limitations: (i) self-debugging becomes increasingly ineffective as modern LLMs rarely produce explicit execution errors that can trigger debugging signals; (ii) self-correction exhibits low detection precision due to the lack of explicit error modeling grounded in the question and schema, and suffers from severe hallucination that frequently corrupts correct SQLs. In this paper, we propose ErrorLLM, a framework that explicitly models text-to-SQL Errors within a dedicated LLM for text-to-SQL refinement. Specifically, we represent the user question and database schema as structural features, employ static detection to identify execution failures and surface mismatches, and extend ErrorLLM's semantic space with dedicated error tokens that capture categorized implicit semantic error types. Through a well-designed training strategy, we explicitly model these errors with structural representations, enabling the LLM to detect complex implicit errors by predicting dedicated error tokens. Guided by the detected errors, we perform error-guided refinement on the SQL structure by prompting LLMs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ErrorLLM achieves the most significant improvements over backbone initial generation. Further analysis reveals that detection quality directly determines refinement effectiveness, and ErrorLLM addresses both sides by high detection F1 score while maintain refinement effectiveness.
Graph-based Agent Memory: Taxonomy, Techniques, and Applications
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Memory emerges as the core module in the Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents for long-horizon complex tasks (e.g., multi-turn dialogue, game playing, scientific discovery), where memory can enable knowledge accumulation, iterative reasoning and self-evolution. Among diverse paradigms, graph stands out as a powerful structure for agent memory due to the intrinsic capabilities to model relational dependencies, organize hierarchical information, and support efficient retrieval. This survey presents a comprehensive review of agent memory from the graph-based perspective. First, we introduce a taxonomy of agent memory, including short-term vs. long-term memory, knowledge vs. experience memory, non-structural vs. structural memory, with an implementation view of graph-based memory. Second, according to the life cycle of agent memory, we systematically analyze the key techniques in graph-based agent memory, covering memory extraction for transforming the data into the contents, storage for organizing the data efficiently, retrieval for retrieving the relevant contents from memory to support reasoning, and evolution for updating the contents in the memory. Third, we summarize the open-sourced libraries and benchmarks that support the development and evaluation of self-evolving agent memory. We also explore diverse application scenarios. Finally, we identify critical challenges and future research directions. This survey aims to offer actionable insights to advance the development of more efficient and reliable graph-based agent memory systems. All the related resources, including research papers, open-source data, and projects, are collected for the community in https://github.com/DEEP-PolyU/Awesome-GraphMemory.
T2VAttack: Adversarial Attack on Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:The rapid evolution of Text-to-Video (T2V) diffusion models has driven remarkable advancements in generating high-quality, temporally coherent videos from natural language descriptions. Despite these achievements, their vulnerability to adversarial attacks remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we introduce T2VAttack, a comprehensive study of adversarial attacks on T2V diffusion models from both semantic and temporal perspectives. Considering the inherently dynamic nature of video data, we propose two distinct attack objectives: a semantic objective to evaluate video-text alignment and a temporal objective to assess the temporal dynamics. To achieve an effective and efficient attack process, we propose two adversarial attack methods: (i) T2VAttack-S, which identifies semantically or temporally critical words in prompts and replaces them with synonyms via greedy search, and (ii) T2VAttack-I, which iteratively inserts optimized words with minimal perturbation to the prompt. By combining these objectives and strategies, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation on the adversarial robustness of several state-of-the-art T2V models, including ModelScope, CogVideoX, Open-Sora, and HunyuanVideo. Our experiments reveal that even minor prompt modifications, such as the substitution or insertion of a single word, can cause substantial degradation in semantic fidelity and temporal dynamics, highlighting critical vulnerabilities in current T2V diffusion models.
SegMo: Segment-aligned Text to 3D Human Motion Generation
Dec 24, 2025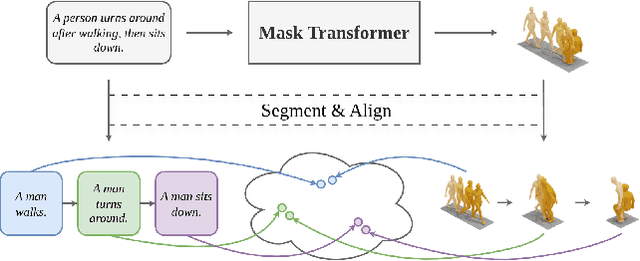
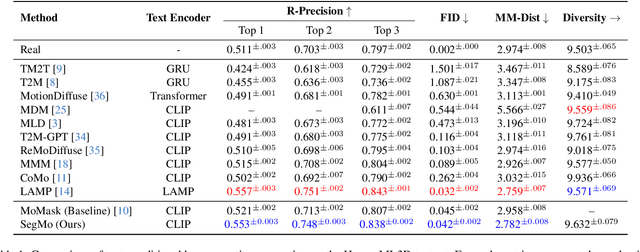
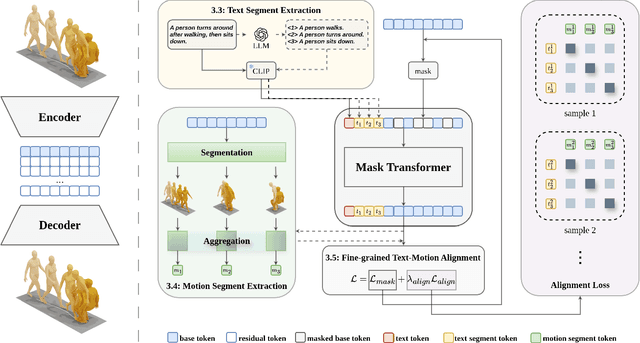
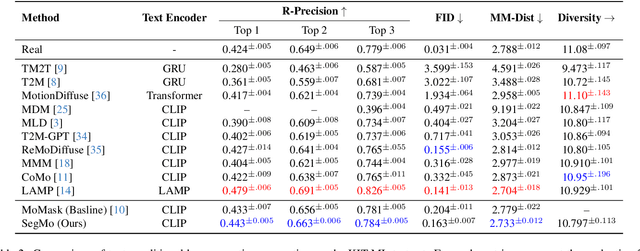
Abstract:Generating 3D human motions from textual descriptions is an important research problem with broad applications in video games, virtual reality, and augmented reality. Recent methods align the textual description with human motion at the sequence level, neglecting the internal semantic structure of modalities. However, both motion descriptions and motion sequences can be naturally decomposed into smaller and semantically coherent segments, which can serve as atomic alignment units to achieve finer-grained correspondence. Motivated by this, we propose SegMo, a novel Segment-aligned text-conditioned human Motion generation framework to achieve fine-grained text-motion alignment. Our framework consists of three modules: (1) Text Segment Extraction, which decomposes complex textual descriptions into temporally ordered phrases, each representing a simple atomic action; (2) Motion Segment Extraction, which partitions complete motion sequences into corresponding motion segments; and (3) Fine-grained Text-Motion Alignment, which aligns text and motion segments with contrastive learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SegMo improves the strong baseline on two widely used datasets, achieving an improved TOP 1 score of 0.553 on the HumanML3D test set. Moreover, thanks to the learned shared embedding space for text and motion segments, SegMo can also be applied to retrieval-style tasks such as motion grounding and motion-to-text retrieval.
Seed-Prover 1.5: Mastering Undergraduate-Level Theorem Proving via Learning from Experience
Dec 19, 2025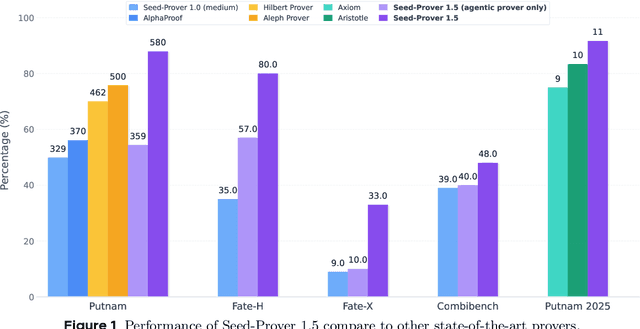

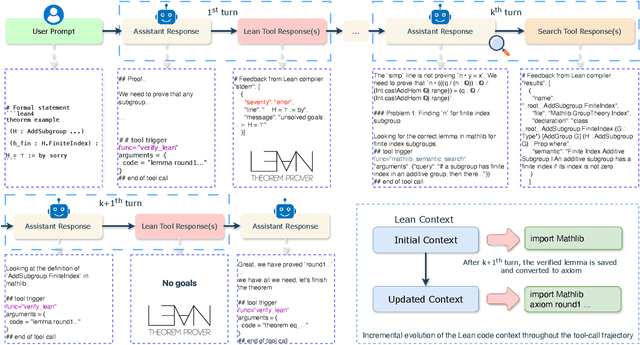
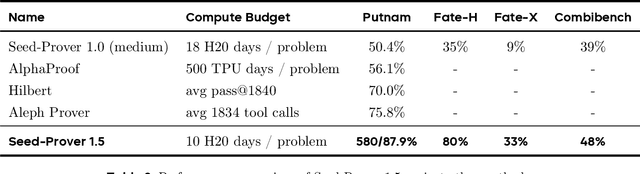
Abstract:Large language models have recently made significant progress to generate rigorous mathematical proofs. In contrast, utilizing LLMs for theorem proving in formal languages (such as Lean) remains challenging and computationally expensive, particularly when addressing problems at the undergraduate level and beyond. In this work, we present \textbf{Seed-Prover 1.5}, a formal theorem-proving model trained via large-scale agentic reinforcement learning, alongside an efficient test-time scaling (TTS) workflow. Through extensive interactions with Lean and other tools, the model continuously accumulates experience during the RL process, substantially enhancing the capability and efficiency of formal theorem proving. Furthermore, leveraging recent advancements in natural language proving, our TTS workflow efficiently bridges the gap between natural and formal languages. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, Seed-Prover 1.5 achieves superior performance with a smaller compute budget. It solves \textbf{88\% of PutnamBench} (undergraduate-level), \textbf{80\% of Fate-H} (graduate-level), and \textbf{33\% of Fate-X} (PhD-level) problems. Notably, using our system, we solved \textbf{11 out of 12 problems} from Putnam 2025 within 9 hours. Our findings suggest that scaling learning from experience, driven by high-quality formal feedback, holds immense potential for the future of formal mathematical reasoning.
KidsArtBench: Multi-Dimensional Children's Art Evaluation with Attribute-Aware MLLMs
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) show remarkable progress across many visual-language tasks; however, their capacity to evaluate artistic expression remains limited. Aesthetic concepts are inherently abstract and open-ended, and multimodal artwork annotations are scarce. We introduce KidsArtBench, a new benchmark of over 1k children's artworks (ages 5-15) annotated by 12 expert educators across 9 rubric-aligned dimensions, together with expert comments for feedback. Unlike prior aesthetic datasets that provide single scalar scores on adult imagery, KidsArtBench targets children's artwork and pairs multi-dimensional annotations with comment supervision to enable both ordinal assessment and formative feedback. Building on this resource, we propose an attribute-specific multi-LoRA approach, where each attribute corresponds to a distinct evaluation dimension (e.g., Realism, Imagination) in the scoring rubric, with Regression-Aware Fine-Tuning (RAFT) to align predictions with ordinal scales. On Qwen2.5-VL-7B, our method increases correlation from 0.468 to 0.653, with the largest gains on perceptual dimensions and narrowed gaps on higher-order attributes. These results show that educator-aligned supervision and attribute-aware training yield pedagogically meaningful evaluations and establish a rigorous testbed for sustained progress in educational AI. We release data and code with ethics documentation.
Teacher Demonstrations in a BabyLM's Zone of Proximal Development for Contingent Multi-Turn Interaction
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Multi-turn dialogues between a child and a caregiver are characterized by a property called contingency - that is, prompt, direct, and meaningful exchanges between interlocutors. We introduce ContingentChat, a teacher-student framework that benchmarks and improves multi-turn contingency in a BabyLM trained on 100M words. Using a novel alignment dataset for post-training, BabyLM generates responses that are more grammatical and cohesive. Experiments with adaptive teacher decoding strategies show limited additional gains. ContingentChat demonstrates the benefits of targeted post-training for dialogue quality and indicates that contingency remains a challenging goal for BabyLMs.
Probing Latent Knowledge Conflict for Faithful Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful paradigm to enhance the factuality of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, existing RAG systems often suffer from an unfaithfulness issue, where the model's response contradicts evidence from the retrieved context. Existing approaches to improving contextual faithfulness largely rely on external interventions, such as prompt engineering, decoding constraints, or reward-based fine-tuning. These works treat the LLM as a black box and overlook a crucial question: how does the LLM internally integrate retrieved evidence with its parametric memory, particularly under knowledge conflicts? To address this gap, we conduct a probing-based analysis of hidden-state representations in LLMs and observe three findings: knowledge integration occurs hierarchically, conflicts manifest as latent signals at the sentence level, and irrelevant context is often amplified when aligned with parametric knowledge. Building on these findings, we propose CLEAR (Conflict-Localized and Enhanced Attention for RAG), a framework that (i) decomposes context into fine-grained sentence-level knowledge, (ii) employs hidden-state probing to localize conflicting knowledge, and (iii) introduces conflict-aware fine-tuning to guide the model to accurately integrate retrieved evidence. Extensive experiments across three benchmarks demonstrate that CLEAR substantially improves both accuracy and contextual faithfulness, consistently outperforming strong baselines under diverse conflict conditions. The related resources are available at https://github.com/LinfengGao/CLEAR.
GenQuest: An LLM-based Text Adventure Game for Language Learners
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:GenQuest is a generative text adventure game that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to facilitate second language learning through immersive, interactive storytelling. The system engages English as a Foreign Language (EFL) learners in a collaborative "choose-your-own-adventure" style narrative, dynamically generated in response to learner choices. Game mechanics such as branching decision points and story milestones are incorporated to maintain narrative coherence while allowing learner-driven plot development. Key pedagogical features include content generation tailored to each learner's proficiency level, and a vocabulary assistant that provides in-context explanations of learner-queried text strings, ranging from words and phrases to sentences. Findings from a pilot study with university EFL students in China indicate promising vocabulary gains and positive user perceptions. Also discussed are suggestions from participants regarding the narrative length and quality, and the request for multi-modal content such as illustrations.
Beyond the Score: Uncertainty-Calibrated LLMs for Automated Essay Assessment
Sep 19, 2025
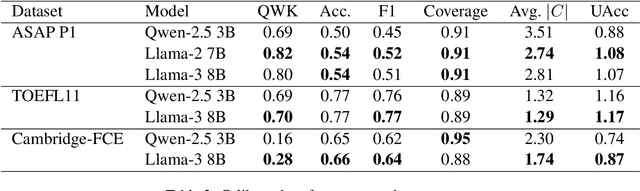
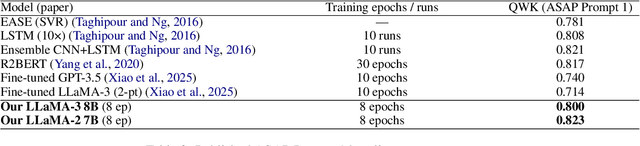
Abstract:Automated Essay Scoring (AES) systems now reach near human agreement on some public benchmarks, yet real-world adoption, especially in high-stakes examinations, remains limited. A principal obstacle is that most models output a single score without any accompanying measure of confidence or explanation. We address this gap with conformal prediction, a distribution-free wrapper that equips any classifier with set-valued outputs and formal coverage guarantees. Two open-source large language models (Llama-3 8B and Qwen-2.5 3B) are fine-tuned on three diverse corpora (ASAP, TOEFL11, Cambridge-FCE) and calibrated at a 90 percent risk level. Reliability is assessed with UAcc, an uncertainty-aware accuracy that rewards models for being both correct and concise. To our knowledge, this is the first work to combine conformal prediction and UAcc for essay scoring. The calibrated models consistently meet the coverage target while keeping prediction sets compact, indicating that open-source, mid-sized LLMs can already support teacher-in-the-loop AES; we discuss scaling and broader user studies as future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge