Jingshan Pan
Predicting Satisfied User and Machine Ratio for Compressed Images: A Unified Approach
Dec 23, 2024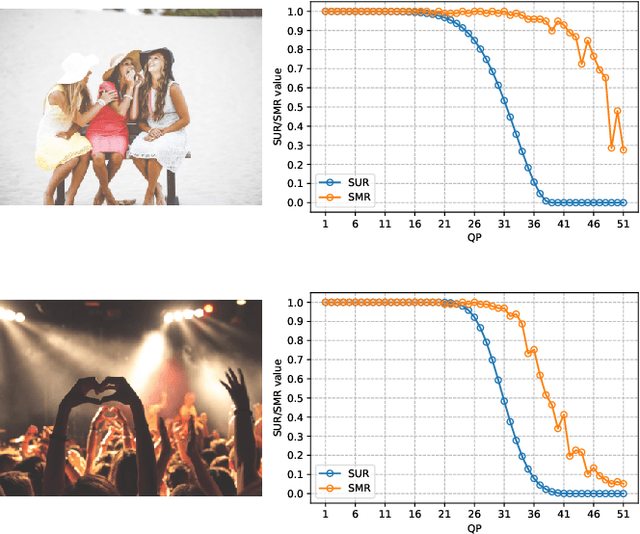
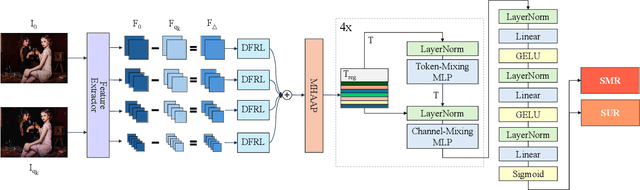
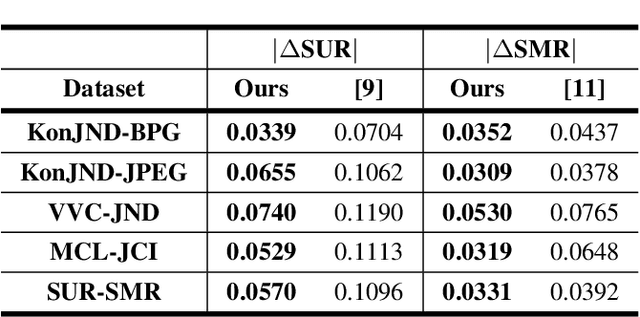
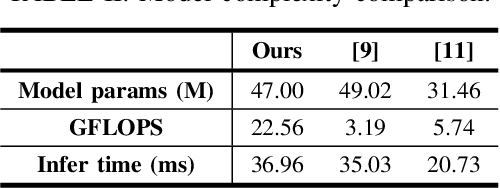
Abstract:Nowadays, high-quality images are pursued by both humans for better viewing experience and by machines for more accurate visual analysis. However, images are usually compressed before being consumed, decreasing their quality. It is meaningful to predict the perceptual quality of compressed images for both humans and machines, which guides the optimization for compression. In this paper, we propose a unified approach to address this. Specifically, we create a deep learning-based model to predict Satisfied User Ratio (SUR) and Satisfied Machine Ratio (SMR) of compressed images simultaneously. We first pre-train a feature extractor network on a large-scale SMR-annotated dataset with human perception-related quality labels generated by diverse image quality models, which simulates the acquisition of SUR labels. Then, we propose an MLP-Mixer-based network to predict SUR and SMR by leveraging and fusing the extracted multi-layer features. We introduce a Difference Feature Residual Learning (DFRL) module to learn more discriminative difference features. We further use a Multi-Head Attention Aggregation and Pooling (MHAAP) layer to aggregate difference features and reduce their redundancy. Experimental results indicate that the proposed model significantly outperforms state-of-the-art SUR and SMR prediction methods. Moreover, our joint learning scheme of human and machine perceptual quality prediction tasks is effective at improving the performance of both.
SMR: Satisfied Machine Ratio Modeling for Machine Recognition-Oriented Image and Video Compression
Nov 13, 2022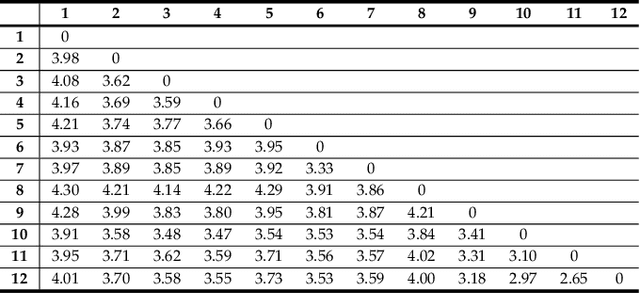
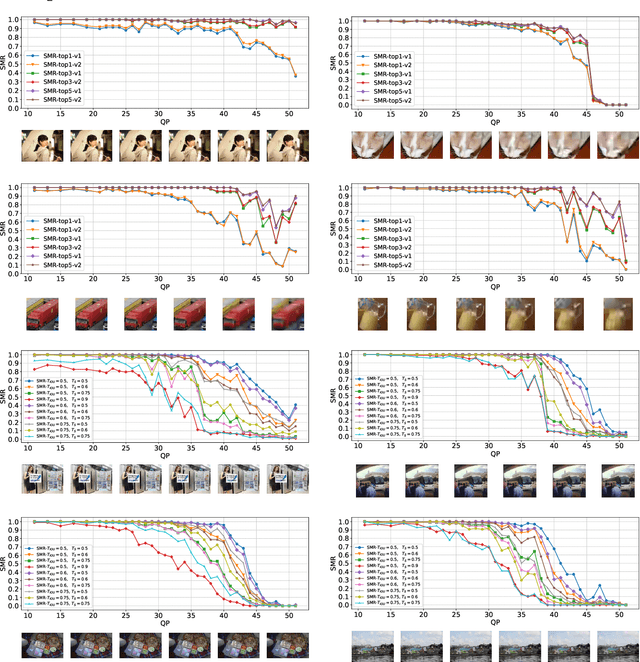
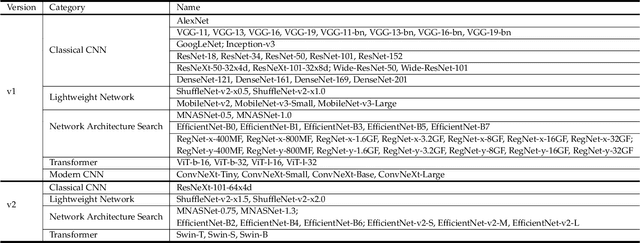
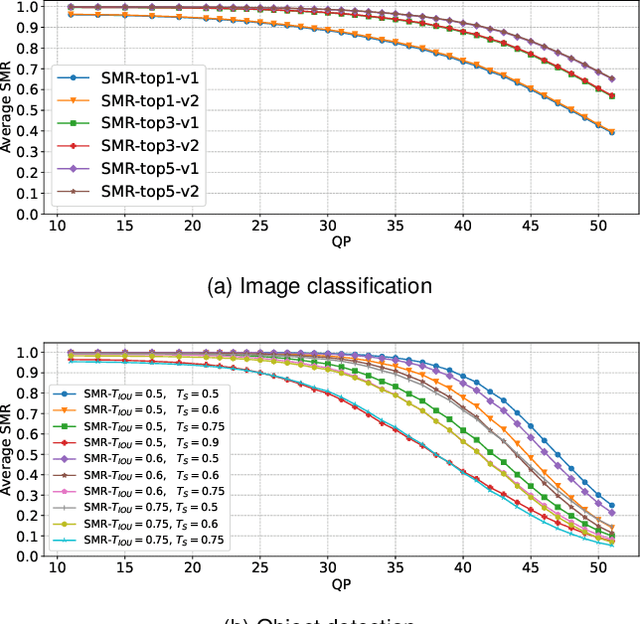
Abstract:Tons of images and videos are fed into machines for visual recognition all the time. Like human vision system (HVS), machine vision system (MVS) is sensitive to image quality, as quality degradation leads to information loss and recognition failure. In recent years, MVS-targeted image processing, particularly image and video compression, has emerged. However, existing methods only target an individual machine rather than the general machine community, thus cannot satisfy every type of machine. Moreover, the MVS characteristics are not well leveraged, which limits compression efficiency. In this paper, we introduce a new concept, Satisfied Machine Ratio (SMR), to address these issues. SMR statistically measures the image quality from the machine's perspective by collecting and combining satisfaction scores from a large quantity and variety of machine subjects, where such scores are obtained with MVS characteristics considered properly. We create the first large-scale SMR dataset that contains over 22 million annotated images for SMR studies. Furthermore, a deep learning-based model is proposed to predict the SMR for any given compressed image or video frame. Extensive experiments show that using the SMR model can significantly improve the performance of machine recognition-oriented image and video compression. And the SMR model generalizes well to unseen machines, compression frameworks, and datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge