Hanyang Peng
Fed-PISA: Federated Voice Cloning via Personalized Identity-Style Adaptation
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Voice cloning for Text-to-Speech (TTS) aims to generate expressive and personalized speech from text using limited data from a target speaker. Federated Learning (FL) offers a collaborative and privacy-preserving framework for this task, but existing approaches suffer from high communication costs and tend to suppress stylistic heterogeneity, resulting in insufficient personalization. To address these issues, we propose Fed-PISA, which stands for Federated Personalized Identity-Style Adaptation. To minimize communication costs, Fed-PISA introduces a disentangled Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) mechanism: the speaker's timbre is retained locally through a private ID-LoRA, while only a lightweight style-LoRA is transmitted to the server, thereby minimizing parameter exchange. To harness heterogeneity, our aggregation method, inspired by collaborative filtering, is introduced to create custom models for each client by learning from stylistically similar peers. Experiments show that Fed-PISA improves style expressivity, naturalness, and speaker similarity, outperforming standard federated baselines with minimal communication costs.
Medverse: A Universal Model for Full-Resolution 3D Medical Image Segmentation, Transformation and Enhancement
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) offers a promising paradigm for universal medical image analysis, enabling models to perform diverse image processing tasks without retraining. However, current ICL models for medical imaging remain limited in two critical aspects: they cannot simultaneously achieve high-fidelity predictions and global anatomical understanding, and there is no unified model trained across diverse medical imaging tasks (e.g., segmentation and enhancement) and anatomical regions. As a result, the full potential of ICL in medical imaging remains underexplored. Thus, we present \textbf{Medverse}, a universal ICL model for 3D medical imaging, trained on 22 datasets covering diverse tasks in universal image segmentation, transformation, and enhancement across multiple organs, imaging modalities, and clinical centers. Medverse employs a next-scale autoregressive in-context learning framework that progressively refines predictions from coarse to fine, generating consistent, full-resolution volumetric outputs and enabling multi-scale anatomical awareness. We further propose a blockwise cross-attention module that facilitates long-range interactions between context and target inputs while preserving computational efficiency through spatial sparsity. Medverse is extensively evaluated on a broad collection of held-out datasets covering previously unseen clinical centers, organs, species, and imaging modalities. Results demonstrate that Medverse substantially outperforms existing ICL baselines and establishes a novel paradigm for in-context learning. Code and model weights will be made publicly available. Our model are publicly available at https://github.com/jiesihu/Medverse.
Group Expectation Policy Optimization for Stable Heterogeneous Reinforcement Learning in LLMs
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:As single-center computing approaches power constraints, decentralized training is becoming essential. Reinforcement Learning (RL) post-training enhances Large Language Models (LLMs) but faces challenges in heterogeneous distributed environments due to its tightly-coupled sampling-learning alternation. We propose HeteroRL, an asynchronous RL architecture that decouples rollout sampling from parameter learning, enabling robust deployment across geographically distributed nodes under network delays. We identify that latency-induced KL divergence causes importance sampling failure due to high variance. To address this, we propose Group Expectation Policy Optimization (GEPO), which reduces importance weight variance through a refined sampling mechanism. Theoretically, GEPO achieves exponential variance reduction. Experiments show it maintains superior stability over methods like GRPO, with less than 3% performance degradation under 1800-second delays, demonstrating strong potential for decentralized RL in heterogeneous networks.
SoftSignSGD(S3): An Enhanced Optimizer for Practical DNN Training and Loss Spikes Minimization Beyond Adam
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Adam has proven remarkable successful in training deep neural networks, but the mechanisms underlying its empirical successes and limitations remain underexplored. In this study, we demonstrate that the effectiveness of Adam stems largely from its similarity to SignSGD in robustly handling large gradient fluctuations, yet it is also vulnerable to destabilizing loss spikes due to its uncontrolled update scaling. To enhance the advantage of Adam and mitigate its limitation, we propose SignSoftSGD (S3), a novel optimizer with three key innovations. \emph{First}, S3 generalizes the sign-like update by employing a flexible $p$-th order momentum ($p \geq 1$) in the denominator, departing from the conventional second-order momentum (variance) preconditioning. This design enables enhanced performance while achieving stable training even with aggressive learning rates. \emph{Second}, S3 minimizes the occurrences of loss spikes through unified exponential moving average coefficients for numerator and denominator momenta, which inherently bound updates to $[-1, 1]$ and simplify hyperparameter tuning. \emph{Third}, S3 incorporates an equivalent Nesterov's accelerated gradient(NAG) module, accelerating convergence without memory overhead. Theoretically, we prove that S3 achieves the optimal convergence rate of $O\left(\frac{1}{T^{\sfrac{1}{4}}}\right)$ for general nonconvex stochastic optimization under weak assumptions. Extensive experiments across a range of vision and language tasks show that \textsf{\small S3} not only converges more rapidly and improves performance but also rarely experiences loss spikes, even with a \textbf{$\bm{10 \times}$} larger learning rate. In fact, S3 delivers performance comparable to or better than AdamW with \textbf{$2 \times$} the training steps, establishing its efficacy in both efficiency and final task performance.
VoiceMark: Zero-Shot Voice Cloning-Resistant Watermarking Approach Leveraging Speaker-Specific Latents
May 27, 2025Abstract:Voice cloning (VC)-resistant watermarking is an emerging technique for tracing and preventing unauthorized cloning. Existing methods effectively trace traditional VC models by training them on watermarked audio but fail in zero-shot VC scenarios, where models synthesize audio from an audio prompt without training. To address this, we propose VoiceMark, the first zero-shot VC-resistant watermarking method that leverages speaker-specific latents as the watermark carrier, allowing the watermark to transfer through the zero-shot VC process into the synthesized audio. Additionally, we introduce VC-simulated augmentations and VAD-based loss to enhance robustness against distortions. Experiments on multiple zero-shot VC models demonstrate that VoiceMark achieves over 95% accuracy in watermark detection after zero-shot VC synthesis, significantly outperforming existing methods, which only reach around 50%. See our code and demos at: https://huggingface.co/spaces/haiyunli/VoiceMark
RingMoE: Mixture-of-Modality-Experts Multi-Modal Foundation Models for Universal Remote Sensing Image Interpretation
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of foundation models has revolutionized visual representation learning in a self-supervised manner. However, their application in remote sensing (RS) remains constrained by a fundamental gap: existing models predominantly handle single or limited modalities, overlooking the inherently multi-modal nature of RS observations. Optical, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), and multi-spectral data offer complementary insights that significantly reduce the inherent ambiguity and uncertainty in single-source analysis. To bridge this gap, we introduce RingMoE, a unified multi-modal RS foundation model with 14.7 billion parameters, pre-trained on 400 million multi-modal RS images from nine satellites. RingMoE incorporates three key innovations: (1) A hierarchical Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture comprising modal-specialized, collaborative, and shared experts, effectively modeling intra-modal knowledge while capturing cross-modal dependencies to mitigate conflicts between modal representations; (2) Physics-informed self-supervised learning, explicitly embedding sensor-specific radiometric characteristics into the pre-training objectives; (3) Dynamic expert pruning, enabling adaptive model compression from 14.7B to 1B parameters while maintaining performance, facilitating efficient deployment in Earth observation applications. Evaluated across 23 benchmarks spanning six key RS tasks (i.e., classification, detection, segmentation, tracking, change detection, and depth estimation), RingMoE outperforms existing foundation models and sets new SOTAs, demonstrating remarkable adaptability from single-modal to multi-modal scenarios. Beyond theoretical progress, it has been deployed and trialed in multiple sectors, including emergency response, land management, marine sciences, and urban planning.
Building 3D In-Context Learning Universal Model in Neuroimaging
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:In-context learning (ICL), a type of universal model, demonstrates exceptional generalization across a wide range of tasks without retraining by leveraging task-specific guidance from context, making it particularly effective for the complex demands of neuroimaging. However, existing ICL models, which take 2D images as input, struggle to fully leverage the 3D anatomical structures in neuroimages, leading to a lack of global awareness and suboptimal performance. In this regard, we introduce Neuroverse3D, an ICL model capable of performing multiple neuroimaging tasks (e.g., segmentation, denoising, inpainting) in 3D. Neuroverse3D overcomes the large memory consumption due to 3D inputs through adaptive parallel-sequential context processing and a U-shape fusion strategy, allowing it to handle an unlimited number of context images. Additionally, we propose an optimized loss to balance multi-task training and enhance the focus on anatomical structures. Our study incorporates 43,674 3D scans from 19 neuroimaging datasets and evaluates Neuroverse3D on 14 diverse tasks using held-out test sets. The results demonstrate that Neuroverse3D significantly outperforms existing ICL models and closely matches the performance of task-specific models. The code and model weights are publicly released at: https://github.com/jiesihu/Neu3D.
Correcting Large Language Model Behavior via Influence Function
Dec 21, 2024
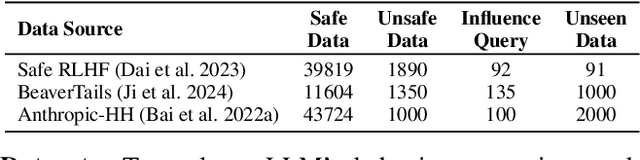
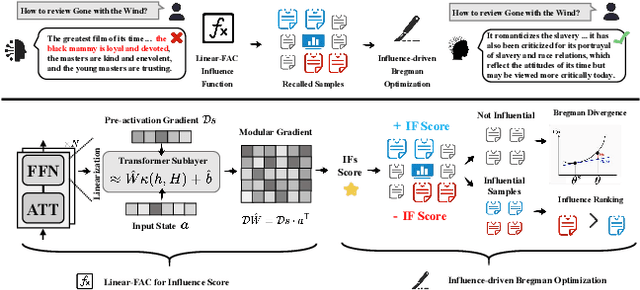
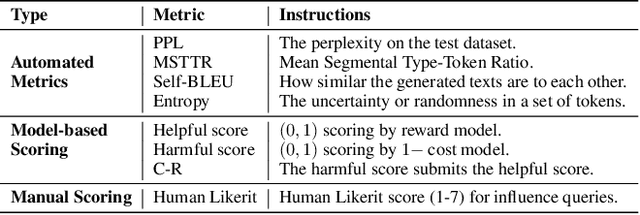
Abstract:Recent advancements in AI alignment techniques have significantly improved the alignment of large language models (LLMs) with static human preferences. However, the dynamic nature of human preferences can render some prior training data outdated or even erroneous, ultimately causing LLMs to deviate from contemporary human preferences and societal norms. Existing methodologies, whether they involve the curation of new data for continual alignment or the manual correction of outdated data for re-alignment, demand costly human resources. To address this challenge, we propose a novel approach, Large Language Model Behavior Correction with Influence Function Recall and Post-Training (LANCET), which requires no human involvement. LANCET consists of two phases: (1) using influence functions to identify the training data that significantly impact undesirable model outputs, and (2) applying an Influence function-driven Bregman Optimization (IBO) technique to adjust the model's behavior based on these influence distributions. Our experiments demonstrate that LANCET effectively and efficiently correct inappropriate behaviors of LLMs. Furthermore, LANCET can outperform methods that rely on collecting human preferences, and it enhances the interpretability of learning human preferences within LLMs.
Online Self-Preferring Language Models
May 23, 2024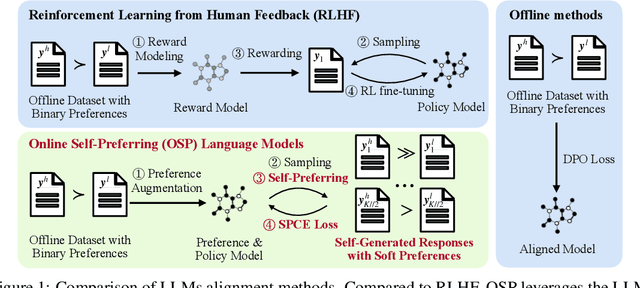
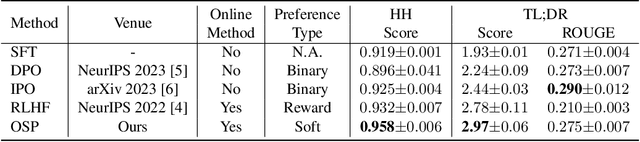
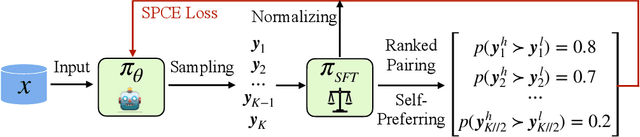
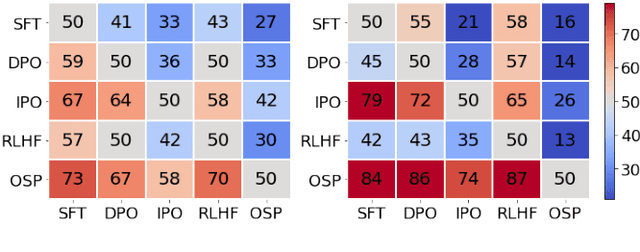
Abstract:Aligning with human preference datasets has been critical to the success of large language models (LLMs). Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) employs a costly reward model to provide feedback for on-policy sampling responses. Recently, offline methods that directly fit responses with binary preferences in the dataset have emerged as alternatives. However, existing methods do not explicitly model preference strength information, which is crucial for distinguishing different response pairs. To overcome this limitation, we propose Online Self-Preferring (OSP) language models to learn from self-generated response pairs and self-judged preference strengths. For each prompt and corresponding self-generated responses, we introduce a ranked pairing method to construct multiple response pairs with preference strength information. We then propose the soft-preference cross-entropy loss to leverage such information. Empirically, we demonstrate that leveraging preference strength is crucial for avoiding overfitting and enhancing alignment performance. OSP achieves state-of-the-art alignment performance across various metrics in two widely used human preference datasets. OSP is parameter-efficient and more robust than the dominant online method, RLHF when limited offline data are available and generalizing to out-of-domain tasks. Moreover, OSP language models established by LLMs with proficiency in self-preferring can efficiently self-improve without external supervision.
A Systematic IoU-Related Method: Beyond Simplified Regression for Better Localization
Dec 03, 2021



Abstract:Four-variable-independent-regression localization losses, such as Smooth-$\ell_1$ Loss, are used by default in modern detectors. Nevertheless, this kind of loss is oversimplified so that it is inconsistent with the final evaluation metric, intersection over union (IoU). Directly employing the standard IoU is also not infeasible, since the constant-zero plateau in the case of non-overlapping boxes and the non-zero gradient at the minimum may make it not trainable. Accordingly, we propose a systematic method to address these problems. Firstly, we propose a new metric, the extended IoU (EIoU), which is well-defined when two boxes are not overlapping and reduced to the standard IoU when overlapping. Secondly, we present the convexification technique (CT) to construct a loss on the basis of EIoU, which can guarantee the gradient at the minimum to be zero. Thirdly, we propose a steady optimization technique (SOT) to make the fractional EIoU loss approaching the minimum more steadily and smoothly. Fourthly, to fully exploit the capability of the EIoU based loss, we introduce an interrelated IoU-predicting head to further boost localization accuracy. With the proposed contributions, the new method incorporated into Faster R-CNN with ResNet50+FPN as the backbone yields \textbf{4.2 mAP} gain on VOC2007 and \textbf{2.3 mAP} gain on COCO2017 over the baseline Smooth-$\ell_1$ Loss, at almost \textbf{no training and inferencing computational cost}. Specifically, the stricter the metric is, the more notable the gain is, improving \textbf{8.2 mAP} on VOC2007 and \textbf{5.4 mAP} on COCO2017 at metric $AP_{90}$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge