Yaoxun Xu
LeVo: High-Quality Song Generation with Multi-Preference Alignment
Jun 09, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) and audio language models have significantly improved music generation, particularly in lyrics-to-song generation. However, existing approaches still struggle with the complex composition of songs and the scarcity of high-quality data, leading to limitations in sound quality, musicality, instruction following, and vocal-instrument harmony. To address these challenges, we introduce LeVo, an LM-based framework consisting of LeLM and a music codec. LeLM is capable of parallelly modeling two types of tokens: mixed tokens, which represent the combined audio of vocals and accompaniment to achieve vocal-instrument harmony, and dual-track tokens, which separately encode vocals and accompaniment for high-quality song generation. It employs two decoder-only transformers and a modular extension training strategy to prevent interference between different token types. To further enhance musicality and instruction following, we introduce a multi-preference alignment method based on Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). This method handles diverse human preferences through a semi-automatic data construction process and DPO post-training. Experimental results demonstrate that LeVo consistently outperforms existing methods on both objective and subjective metrics. Ablation studies further justify the effectiveness of our designs. Audio examples are available at https://levo-demo.github.io/.
WAKE: Watermarking Audio with Key Enrichment
Jun 06, 2025
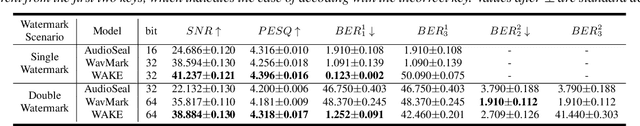
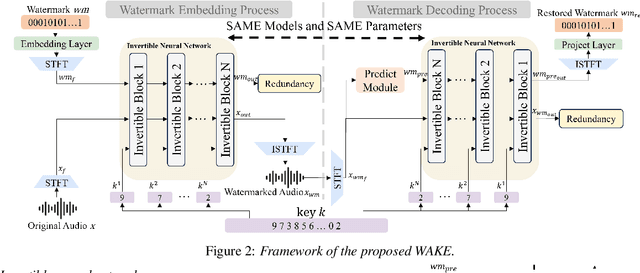
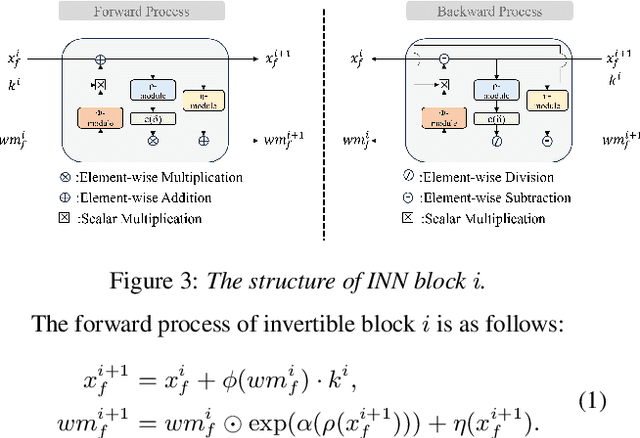
Abstract:As deep learning advances in audio generation, challenges in audio security and copyright protection highlight the need for robust audio watermarking. Recent neural network-based methods have made progress but still face three main issues: preventing unauthorized access, decoding initial watermarks after multiple embeddings, and embedding varying lengths of watermarks. To address these issues, we propose WAKE, the first key-controllable audio watermark framework. WAKE embeds watermarks using specific keys and recovers them with corresponding keys, enhancing security by making incorrect key decoding impossible. It also resolves the overwriting issue by allowing watermark decoding after multiple embeddings and supports variable-length watermark insertion. WAKE outperforms existing models in both watermarked audio quality and watermark detection accuracy. Code, more results, and demo page: https://thuhcsi.github.io/WAKE.
VoiceMark: Zero-Shot Voice Cloning-Resistant Watermarking Approach Leveraging Speaker-Specific Latents
May 27, 2025Abstract:Voice cloning (VC)-resistant watermarking is an emerging technique for tracing and preventing unauthorized cloning. Existing methods effectively trace traditional VC models by training them on watermarked audio but fail in zero-shot VC scenarios, where models synthesize audio from an audio prompt without training. To address this, we propose VoiceMark, the first zero-shot VC-resistant watermarking method that leverages speaker-specific latents as the watermark carrier, allowing the watermark to transfer through the zero-shot VC process into the synthesized audio. Additionally, we introduce VC-simulated augmentations and VAD-based loss to enhance robustness against distortions. Experiments on multiple zero-shot VC models demonstrate that VoiceMark achieves over 95% accuracy in watermark detection after zero-shot VC synthesis, significantly outperforming existing methods, which only reach around 50%. See our code and demos at: https://huggingface.co/spaces/haiyunli/VoiceMark
SongEditor: Adapting Zero-Shot Song Generation Language Model as a Multi-Task Editor
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The emergence of novel generative modeling paradigms, particularly audio language models, has significantly advanced the field of song generation. Although state-of-the-art models are capable of synthesizing both vocals and accompaniment tracks up to several minutes long concurrently, research about partial adjustments or editing of existing songs is still underexplored, which allows for more flexible and effective production. In this paper, we present SongEditor, the first song editing paradigm that introduces the editing capabilities into language-modeling song generation approaches, facilitating both segment-wise and track-wise modifications. SongEditor offers the flexibility to adjust lyrics, vocals, and accompaniments, as well as synthesizing songs from scratch. The core components of SongEditor include a music tokenizer, an autoregressive language model, and a diffusion generator, enabling generating an entire section, masked lyrics, or even separated vocals and background music. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SongEditor achieves exceptional performance in end-to-end song editing, as evidenced by both objective and subjective metrics. Audio samples are available in \url{https://cypress-yang.github.io/SongEditor_demo/}.
Comparing Discrete and Continuous Space LLMs for Speech Recognition
Sep 01, 2024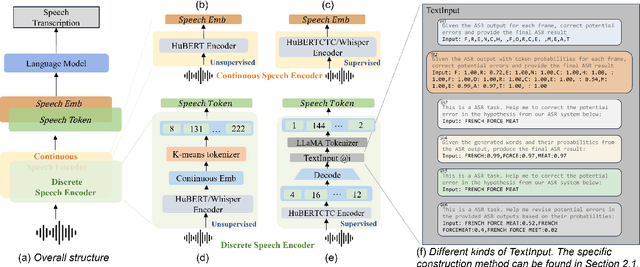
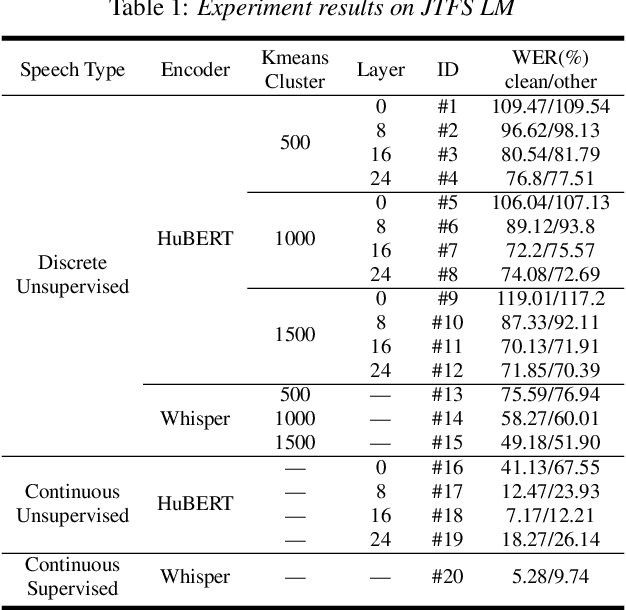
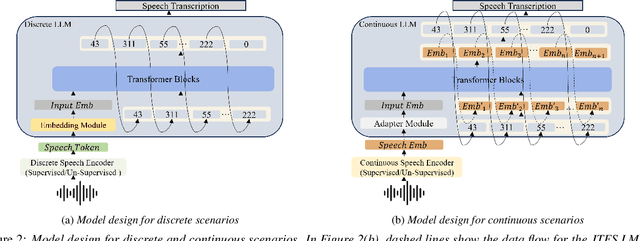
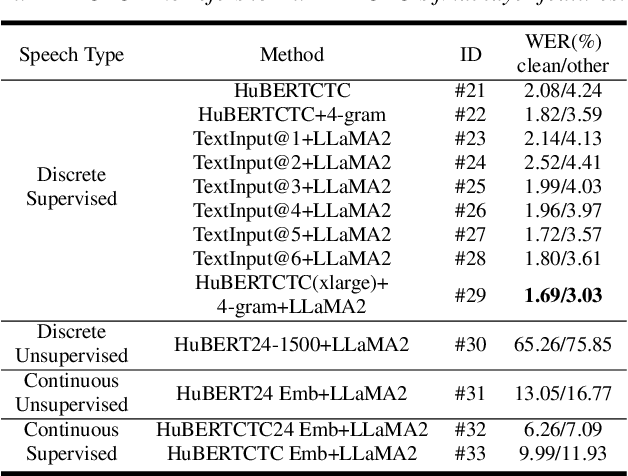
Abstract:This paper investigates discrete and continuous speech representations in Large Language Model (LLM)-based Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), organizing them by feature continuity and training approach into four categories: supervised and unsupervised for both discrete and continuous types. We further classify LLMs based on their input and autoregressive feedback into continuous and discrete-space models. Using specialized encoders and comparative analysis with a Joint-Training-From-Scratch Language Model (JTFS LM) and pre-trained LLaMA2-7b, we provide a detailed examination of their effectiveness. Our work marks the first extensive comparison of speech representations in LLM-based ASR and explores various modeling techniques. We present an open-sourced achievement of a state-of-the-art Word Error Rate (WER) of 1.69\% on LibriSpeech using a HuBERT encoder, offering valuable insights for advancing ASR and natural language processing (NLP) research.
Advancing Multi-talker ASR Performance with Large Language Models
Aug 30, 2024



Abstract:Recognizing overlapping speech from multiple speakers in conversational scenarios is one of the most challenging problem for automatic speech recognition (ASR). Serialized output training (SOT) is a classic method to address multi-talker ASR, with the idea of concatenating transcriptions from multiple speakers according to the emission times of their speech for training. However, SOT-style transcriptions, derived from concatenating multiple related utterances in a conversation, depend significantly on modeling long contexts. Therefore, compared to traditional methods that primarily emphasize encoder performance in attention-based encoder-decoder (AED) architectures, a novel approach utilizing large language models (LLMs) that leverages the capabilities of pre-trained decoders may be better suited for such complex and challenging scenarios. In this paper, we propose an LLM-based SOT approach for multi-talker ASR, leveraging pre-trained speech encoder and LLM, fine-tuning them on multi-talker dataset using appropriate strategies. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach surpasses traditional AED-based methods on the simulated dataset LibriMix and achieves state-of-the-art performance on the evaluation set of the real-world dataset AMI, outperforming the AED model trained with 1000 times more supervised data in previous works.
HydraFormer: One Encoder For All Subsampling Rates
Aug 08, 2024



Abstract:In automatic speech recognition, subsampling is essential for tackling diverse scenarios. However, the inadequacy of a single subsampling rate to address various real-world situations often necessitates training and deploying multiple models, consequently increasing associated costs. To address this issue, we propose HydraFormer, comprising HydraSub, a Conformer-based encoder, and a BiTransformer-based decoder. HydraSub encompasses multiple branches, each representing a distinct subsampling rate, allowing for the flexible selection of any branch during inference based on the specific use case. HydraFormer can efficiently manage different subsampling rates, significantly reducing training and deployment expenses. Experiments on AISHELL-1 and LibriSpeech datasets reveal that HydraFormer effectively adapts to various subsampling rates and languages while maintaining high recognition performance. Additionally, HydraFormer showcases exceptional stability, sustaining consistent performance under various initialization conditions, and exhibits robust transferability by learning from pretrained single subsampling rate automatic speech recognition models\footnote{Model code and scripts: https://github.com/HydraFormer/hydraformer}.
SECap: Speech Emotion Captioning with Large Language Model
Dec 23, 2023



Abstract:Speech emotions are crucial in human communication and are extensively used in fields like speech synthesis and natural language understanding. Most prior studies, such as speech emotion recognition, have categorized speech emotions into a fixed set of classes. Yet, emotions expressed in human speech are often complex, and categorizing them into predefined groups can be insufficient to adequately represent speech emotions. On the contrary, describing speech emotions directly by means of natural language may be a more effective approach. Regrettably, there are not many studies available that have focused on this direction. Therefore, this paper proposes a speech emotion captioning framework named SECap, aiming at effectively describing speech emotions using natural language. Owing to the impressive capabilities of large language models in language comprehension and text generation, SECap employs LLaMA as the text decoder to allow the production of coherent speech emotion captions. In addition, SECap leverages HuBERT as the audio encoder to extract general speech features and Q-Former as the Bridge-Net to provide LLaMA with emotion-related speech features. To accomplish this, Q-Former utilizes mutual information learning to disentangle emotion-related speech features and speech contents, while implementing contrastive learning to extract more emotion-related speech features. The results of objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that: 1) the SECap framework outperforms the HTSAT-BART baseline in all objective evaluations; 2) SECap can generate high-quality speech emotion captions that attain performance on par with human annotators in subjective mean opinion score tests.
Text-Only Domain Adaptation for End-to-End Speech Recognition through Down-Sampling Acoustic Representation
Sep 04, 2023



Abstract:Mapping two modalities, speech and text, into a shared representation space, is a research topic of using text-only data to improve end-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR) performance in new domains. However, the length of speech representation and text representation is inconsistent. Although the previous method up-samples the text representation to align with acoustic modality, it may not match the expected actual duration. In this paper, we proposed novel representations match strategy through down-sampling acoustic representation to align with text modality. By introducing a continuous integrate-and-fire (CIF) module generating acoustic representations consistent with token length, our ASR model can learn unified representations from both modalities better, allowing for domain adaptation using text-only data of the target domain. Experiment results of new domain data demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
CB-Conformer: Contextual biasing Conformer for biased word recognition
Apr 25, 2023
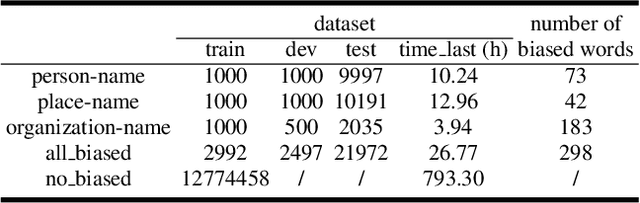
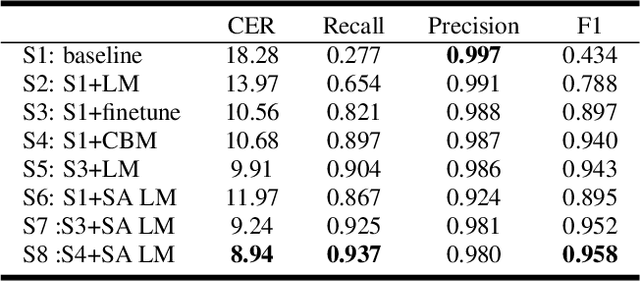
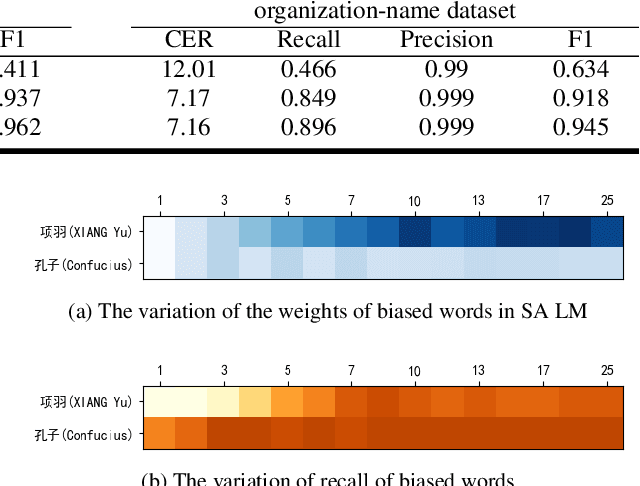
Abstract:Due to the mismatch between the source and target domains, how to better utilize the biased word information to improve the performance of the automatic speech recognition model in the target domain becomes a hot research topic. Previous approaches either decode with a fixed external language model or introduce a sizeable biasing module, which leads to poor adaptability and slow inference. In this work, we propose CB-Conformer to improve biased word recognition by introducing the Contextual Biasing Module and the Self-Adaptive Language Model to vanilla Conformer. The Contextual Biasing Module combines audio fragments and contextual information, with only 0.2% model parameters of the original Conformer. The Self-Adaptive Language Model modifies the internal weights of biased words based on their recall and precision, resulting in a greater focus on biased words and more successful integration with the automatic speech recognition model than the standard fixed language model. In addition, we construct and release an open-source Mandarin biased-word dataset based on WenetSpeech. Experiments indicate that our proposed method brings a 15.34% character error rate reduction, a 14.13% biased word recall increase, and a 6.80% biased word F1-score increase compared with the base Conformer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge