Yiwen Shao
SpatialEmb: Extract and Encode Spatial Information for 1-Stage Multi-channel Multi-speaker ASR on Arbitrary Microphone Arrays
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Spatial information is a critical clue for multi-channel multi-speaker target speech recognition. Most state-of-the-art multi-channel Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems extract spatial features only during the speech separation stage, followed by standard single-channel ASR on the separated speech. This approach results in an inefficient, lengthy pipeline and sub-optimal ASR performance due to the accumulated errors from preprocessing modules. Furthermore, most spatial feature extraction methods depend on the knowledge of speaker positions and microphone topology, making the systems reliant on specific settings and challenging to adapt to new equipment. In this work, we propose a solution to these issues with a lightweight embedding module named SpatialEmb, which extracts and encodes spatial information directly for the ASR model, supporting both fixed and arbitrary microphone topology. We conduct comprehensive experiments on AliMeeting, a real meeting corpus, to determine the optimal model design for SpatialEmb in terms of both performance and efficiency. Our best model trained with 105 hours Train-Ali-far achieves 17.04% and 20.32% character error rates (CER) on the Eval and Test sets, establishing a new state-of-the-art result with the same training data.
Towards Comprehensive Semantic Speech Embeddings for Chinese Dialects
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Despite having hundreds of millions of speakers, Chinese dialects lag behind Mandarin in speech and language technologies. Most varieties are primarily spoken, making dialect-to-Mandarin speech-LLMs (large language models) more practical than dialect LLMs. Building dialect-to-Mandarin speech-LLMs requires speech representations with cross-dialect semantic alignment between Chinese dialects and Mandarin. In this paper, we achieve such a cross-dialect semantic alignment by training a speech encoder with ASR (automatic speech recognition)-only data, as demonstrated by speech-to-speech retrieval on a new benchmark of spoken Chinese varieties that we contribute. Our speech encoder further demonstrates state-of-the-art ASR performance on Chinese dialects. Together, our Chinese dialect benchmark, semantically aligned speech representations, and speech-to-speech retrieval evaluation lay the groundwork for future Chinese dialect speech-LLMs. We release the benchmark at https://github.com/kalvinchang/yubao.
TagSpeech: End-to-End Multi-Speaker ASR and Diarization with Fine-Grained Temporal Grounding
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:We present TagSpeech, a unified LLM-based framework that utilizes Temporal Anchor Grounding for joint multi-speaker ASR and diarization. The framework is built on two key designs: (1) decoupled semantic and speaker streams fine-tuned via Serialized Output Training (SOT) to learn turn-taking dynamics; and (2) an interleaved time anchor mechanism that not only supports fine-grained timestamp prediction but also acts as a synchronization signal between semantic understanding and speaker tracking. Compared to previous works that primarily focus on speaker-attributed ASR or implicit diarization, TagSpeech addresses the challenge of fine-grained speaker-content alignment and explicitly models "who spoke what and when" in an end-to-end manner. Experiments on AMI and AliMeeting benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves consistent improvements in Diarization Error Rate (DER) over strong end-to-end baselines, including Qwen-Omni and Gemini, particularly in handling complex speech overlaps. Moreover, TagSpeech employs a parameter-efficient training paradigm in which the LLM backbone is frozen and only lightweight projectors are trained, resulting in strong performance with low computational cost.
Auden-Voice: General-Purpose Voice Encoder for Speech and Language Understanding
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Human voice encodes both identity and paralinguistic cues, yet encoders in large audio-language models (LALMs) rarely balance both aspects. In this work, we present a study toward building a general-purpose voice encoder that captures nuanced voice cues. Through a comprehensive evaluation, we find that multi-task training yields the most balanced representations, whereas contrastive language-audio pretraining (CLAP) primarily improves retrieval without enhancing paralinguistic understanding. Our final encoder, Auden-Voice, also demonstrates strong performance when integrated with LLMs. The code and training recipes will be released with the audio understanding toolkit Auden.
TTA: Transcribe, Translate and Alignment for Cross-lingual Speech Representation
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Speech-LLM models have demonstrated great performance in multi-modal and multi-task speech understanding. A typical speech-LLM paradigm is integrating speech modality with a large language model (LLM). While the Whisper encoder was frequently adopted in previous studies for speech input, it shows limitations regarding input format, model scale, and semantic performance. To this end, we propose a lightweight TTA model specialized in speech semantics for more effective LLM integration. With large-scale training of 358k hours of speech data on multilingual speech recognition (ASR), speech translation (ST) and speech-text alignment tasks, TTA is capable of producing robust cross-lingual speech representations. Extensive evaluations across diverse benchmarks, including ASR/ST, speech retrieval, and ASR-LLM performance assessments, demonstrate TTA's superiority over Whisper. Furthermore, we rigorously validate the interplay between cross-lingual capabilities and ASR/ST performance. The model weights and training recipes of TTA will be released as part of an audio understanding toolkit Auden.
Taming the Chaos: Coordinated Autoscaling for Heterogeneous and Disaggregated LLM Inference
Aug 27, 2025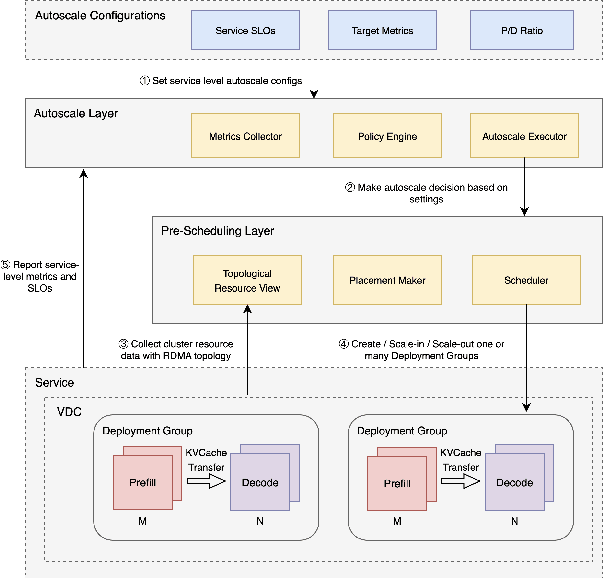
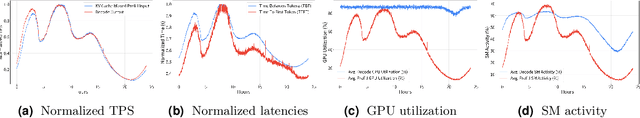
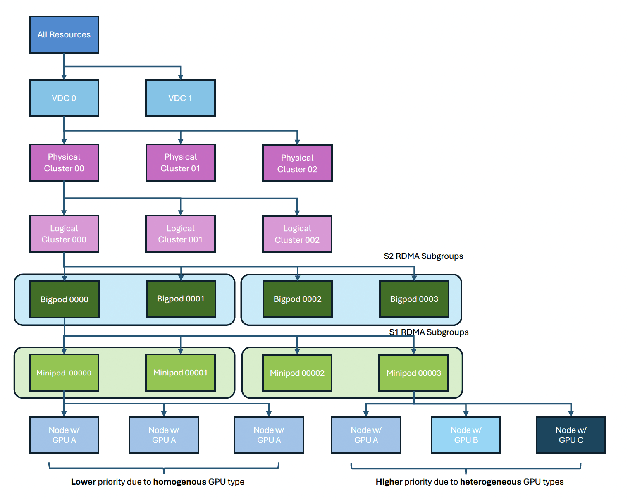
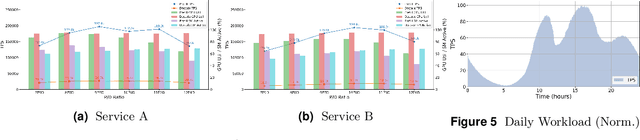
Abstract:Serving Large Language Models (LLMs) is a GPU-intensive task where traditional autoscalers fall short, particularly for modern Prefill-Decode (P/D) disaggregated architectures. This architectural shift, while powerful, introduces significant operational challenges, including inefficient use of heterogeneous hardware, network bottlenecks, and critical imbalances between prefill and decode stages. We introduce HeteroScale, a coordinated autoscaling framework that addresses the core challenges of P/D disaggregated serving. HeteroScale combines a topology-aware scheduler that adapts to heterogeneous hardware and network constraints with a novel metric-driven policy derived from the first large-scale empirical study of autoscaling signals in production. By leveraging a single, robust metric to jointly scale prefill and decode pools, HeteroScale maintains architectural balance while ensuring efficient, adaptive resource management. Deployed in a massive production environment on tens of thousands of GPUs, HeteroScale has proven its effectiveness, increasing average GPU utilization by a significant 26.6 percentage points and saving hundreds of thousands of GPU-hours daily, all while upholding stringent service level objectives.
DualSpeechLM: Towards Unified Speech Understanding and Generation via Dual Speech Token Modeling with Large Language Models
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Extending pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs)'s speech understanding or generation abilities by introducing various effective speech tokens has attracted great attention in the speech community. However, building a unified speech understanding and generation model still faces the following challenges: (1) Due to the huge modality gap between speech tokens and text tokens, extending text LLMs to unified speech LLMs relies on large-scale paired data for fine-tuning, and (2) Generation and understanding tasks prefer information at different levels, e.g., generation benefits from detailed acoustic features, while understanding favors high-level semantics. This divergence leads to difficult performance optimization in one unified model. To solve these challenges, in this paper, we present two key insights in speech tokenization and speech language modeling. Specifically, we first propose an Understanding-driven Speech Tokenizer (USTokenizer), which extracts high-level semantic information essential for accomplishing understanding tasks using text LLMs. In this way, USToken enjoys better modality commonality with text, which reduces the difficulty of modality alignment in adapting text LLMs to speech LLMs. Secondly, we present DualSpeechLM, a dual-token modeling framework that concurrently models USToken as input and acoustic token as output within a unified, end-to-end framework, seamlessly integrating speech understanding and generation capabilities. Furthermore, we propose a novel semantic supervision loss and a Chain-of-Condition (CoC) strategy to stabilize model training and enhance speech generation performance. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed approach effectively fosters a complementary relationship between understanding and generation tasks, highlighting the promising strategy of mutually enhancing both tasks in one unified model.
Efficient Scaling for LLM-based ASR
Aug 06, 2025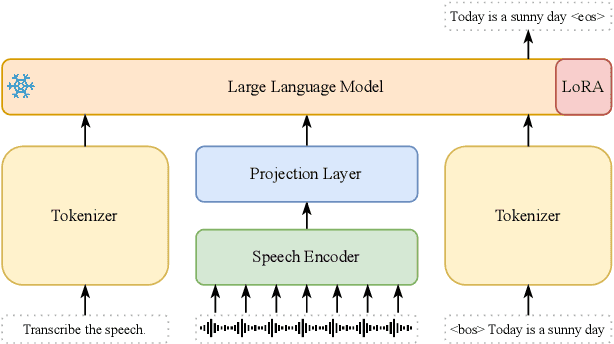
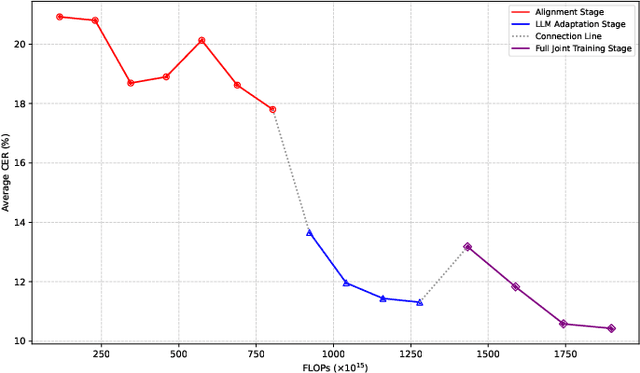
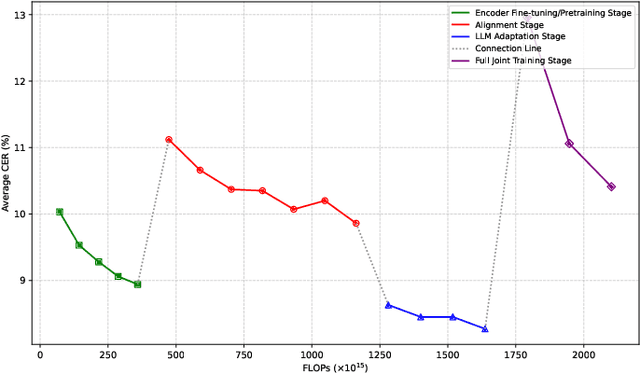
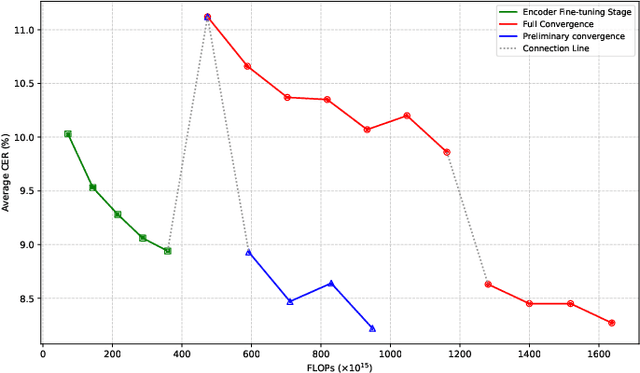
Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-based automatic speech recognition (ASR) achieves strong performance but often incurs high computational costs. This work investigates how to obtain the best LLM-ASR performance efficiently. Through comprehensive and controlled experiments, we find that pretraining the speech encoder before integrating it with the LLM leads to significantly better scaling efficiency than the standard practice of joint post-training of LLM-ASR. Based on this insight, we propose a new multi-stage LLM-ASR training strategy, EFIN: Encoder First Integration. Among all training strategies evaluated, EFIN consistently delivers better performance (relative to 21.1% CERR) with significantly lower computation budgets (49.9% FLOPs). Furthermore, we derive a scaling law that approximates ASR error rates as a computation function, providing practical guidance for LLM-ASR scaling.
Advancing Multi-talker ASR Performance with Large Language Models
Aug 30, 2024



Abstract:Recognizing overlapping speech from multiple speakers in conversational scenarios is one of the most challenging problem for automatic speech recognition (ASR). Serialized output training (SOT) is a classic method to address multi-talker ASR, with the idea of concatenating transcriptions from multiple speakers according to the emission times of their speech for training. However, SOT-style transcriptions, derived from concatenating multiple related utterances in a conversation, depend significantly on modeling long contexts. Therefore, compared to traditional methods that primarily emphasize encoder performance in attention-based encoder-decoder (AED) architectures, a novel approach utilizing large language models (LLMs) that leverages the capabilities of pre-trained decoders may be better suited for such complex and challenging scenarios. In this paper, we propose an LLM-based SOT approach for multi-talker ASR, leveraging pre-trained speech encoder and LLM, fine-tuning them on multi-talker dataset using appropriate strategies. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach surpasses traditional AED-based methods on the simulated dataset LibriMix and achieves state-of-the-art performance on the evaluation set of the real-world dataset AMI, outperforming the AED model trained with 1000 times more supervised data in previous works.
Multi-Channel Multi-Speaker ASR Using Target Speaker's Solo Segment
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:In the field of multi-channel, multi-speaker Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), the task of discerning and accurately transcribing a target speaker's speech within background noise remains a formidable challenge. Traditional approaches often rely on microphone array configurations and the information of the target speaker's location or voiceprint. This study introduces the Solo Spatial Feature (Solo-SF), an innovative method that utilizes a target speaker's isolated speech segment to enhance ASR performance, thereby circumventing the need for conventional inputs like microphone array layouts. We explore effective strategies for selecting optimal solo segments, a crucial aspect for Solo-SF's success. Through evaluations conducted on the AliMeeting dataset and AISHELL-1 simulations, Solo-SF demonstrates superior performance over existing techniques, significantly lowering Character Error Rates (CER) in various test conditions. Our findings highlight Solo-SF's potential as an effective solution for addressing the complexities of multi-channel, multi-speaker ASR tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge