Haina Zhu
Audio ControlNet for Fine-Grained Audio Generation and Editing
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:We study the fine-grained text-to-audio (T2A) generation task. While recent models can synthesize high-quality audio from text descriptions, they often lack precise control over attributes such as loudness, pitch, and sound events. Unlike prior approaches that retrain models for specific control types, we propose to train ControlNet models on top of pre-trained T2A backbones to achieve controllable generation over loudness, pitch, and event roll. We introduce two designs, T2A-ControlNet and T2A-Adapter, and show that the T2A-Adapter model offers a more efficient structure with strong control ability. With only 38M additional parameters, T2A-Adapter achieves state-of-the-art performance on the AudioSet-Strong in both event-level and segment-level F1 scores. We further extend this framework to audio editing, proposing T2A-Editor for removing and inserting audio events at time locations specified by instructions. Models, code, dataset pipelines, and benchmarks will be released to support future research on controllable audio generation and editing.
SLAM-LLM: A Modular, Open-Source Multimodal Large Language Model Framework and Best Practice for Speech, Language, Audio and Music Processing
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:The recent surge in open-source Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLM) frameworks, such as LLaVA, provides a convenient kickoff for artificial intelligence developers and researchers. However, most of the MLLM frameworks take vision as the main input modality, and provide limited in-depth support for the modality of speech, audio, and music. This situation hinders the development of audio-language models, and forces researchers to spend a lot of effort on code writing and hyperparameter tuning. We present SLAM-LLM, an open-source deep learning framework designed to train customized MLLMs, focused on speech, language, audio, and music processing. SLAM-LLM provides a modular configuration of different encoders, projectors, LLMs, and parameter-efficient fine-tuning plugins. SLAM-LLM also includes detailed training and inference recipes for mainstream tasks, along with high-performance checkpoints like LLM-based Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Automated Audio Captioning (AAC), and Music Captioning (MC). Some of these recipes have already reached or are nearing state-of-the-art performance, and some relevant techniques have also been accepted by academic papers. We hope SLAM-LLM will accelerate iteration, development, data engineering, and model training for researchers. We are committed to continually pushing forward audio-based MLLMs through this open-source framework, and call on the community to contribute to the LLM-based speech, audio and music processing.
LeVo: High-Quality Song Generation with Multi-Preference Alignment
Jun 09, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) and audio language models have significantly improved music generation, particularly in lyrics-to-song generation. However, existing approaches still struggle with the complex composition of songs and the scarcity of high-quality data, leading to limitations in sound quality, musicality, instruction following, and vocal-instrument harmony. To address these challenges, we introduce LeVo, an LM-based framework consisting of LeLM and a music codec. LeLM is capable of parallelly modeling two types of tokens: mixed tokens, which represent the combined audio of vocals and accompaniment to achieve vocal-instrument harmony, and dual-track tokens, which separately encode vocals and accompaniment for high-quality song generation. It employs two decoder-only transformers and a modular extension training strategy to prevent interference between different token types. To further enhance musicality and instruction following, we introduce a multi-preference alignment method based on Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). This method handles diverse human preferences through a semi-automatic data construction process and DPO post-training. Experimental results demonstrate that LeVo consistently outperforms existing methods on both objective and subjective metrics. Ablation studies further justify the effectiveness of our designs. Audio examples are available at https://levo-demo.github.io/.
Layer-wise Investigation of Large-Scale Self-Supervised Music Representation Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Recently, pre-trained models for music information retrieval based on self-supervised learning (SSL) are becoming popular, showing success in various downstream tasks. However, there is limited research on the specific meanings of the encoded information and their applicability. Exploring these aspects can help us better understand their capabilities and limitations, leading to more effective use in downstream tasks. In this study, we analyze the advanced music representation model MusicFM and the newly emerged SSL model MuQ. We focus on three main aspects: (i) validating the advantages of SSL models across multiple downstream tasks, (ii) exploring the specialization of layer-wise information for different tasks, and (iii) comparing performance differences when selecting specific layers. Through this analysis, we reveal insights into the structure and potential applications of SSL models in music information retrieval.
MMAR: A Challenging Benchmark for Deep Reasoning in Speech, Audio, Music, and Their Mix
May 19, 2025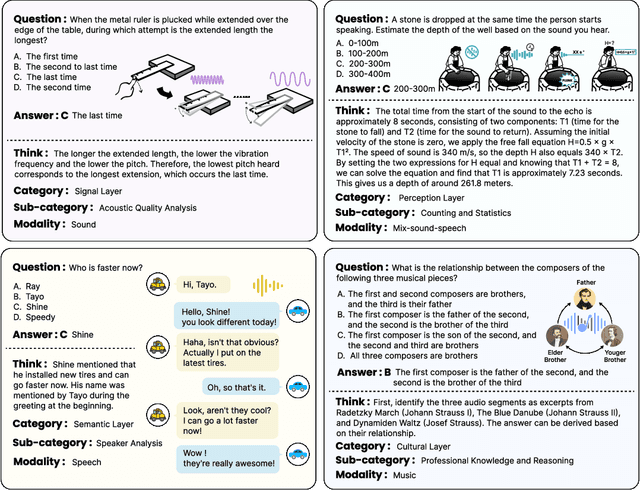
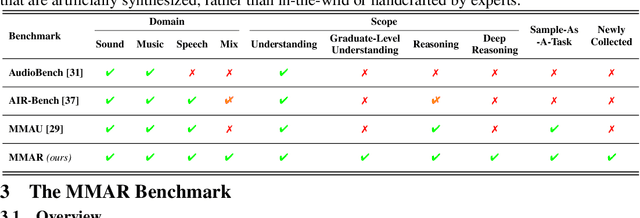
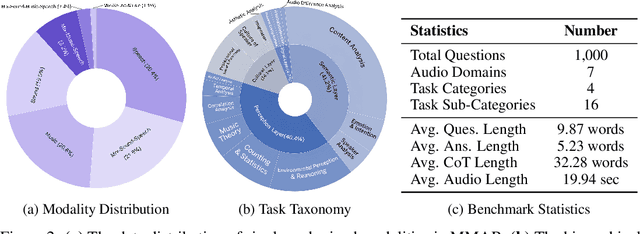
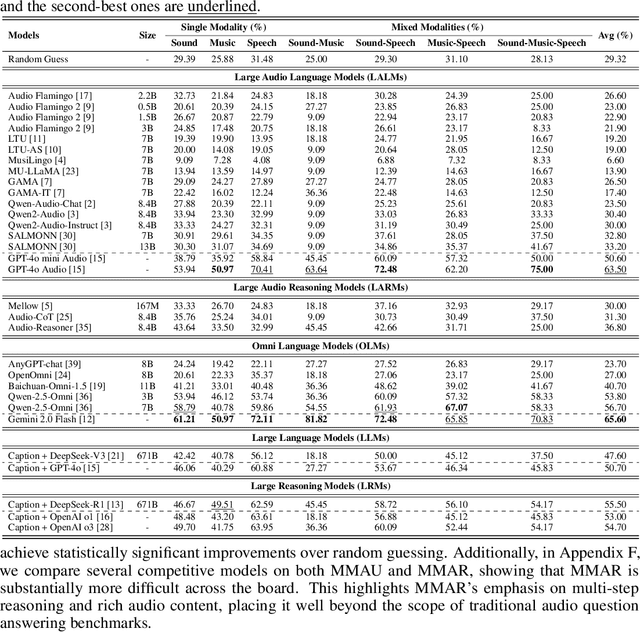
Abstract:We introduce MMAR, a new benchmark designed to evaluate the deep reasoning capabilities of Audio-Language Models (ALMs) across massive multi-disciplinary tasks. MMAR comprises 1,000 meticulously curated audio-question-answer triplets, collected from real-world internet videos and refined through iterative error corrections and quality checks to ensure high quality. Unlike existing benchmarks that are limited to specific domains of sound, music, or speech, MMAR extends them to a broad spectrum of real-world audio scenarios, including mixed-modality combinations of sound, music, and speech. Each question in MMAR is hierarchically categorized across four reasoning layers: Signal, Perception, Semantic, and Cultural, with additional sub-categories within each layer to reflect task diversity and complexity. To further foster research in this area, we annotate every question with a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) rationale to promote future advancements in audio reasoning. Each item in the benchmark demands multi-step deep reasoning beyond surface-level understanding. Moreover, a part of the questions requires graduate-level perceptual and domain-specific knowledge, elevating the benchmark's difficulty and depth. We evaluate MMAR using a broad set of models, including Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs), Large Audio Reasoning Models (LARMs), Omni Language Models (OLMs), Large Language Models (LLMs), and Large Reasoning Models (LRMs), with audio caption inputs. The performance of these models on MMAR highlights the benchmark's challenging nature, and our analysis further reveals critical limitations of understanding and reasoning capabilities among current models. We hope MMAR will serve as a catalyst for future advances in this important but little-explored area.
MuQ: Self-Supervised Music Representation Learning with Mel Residual Vector Quantization
Jan 03, 2025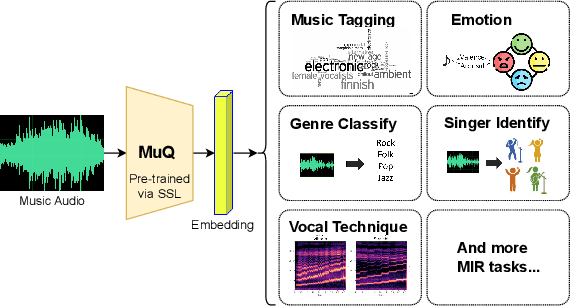



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the success of foundation models pre-trained with self-supervised learning (SSL) in various music informatics understanding tasks, including music tagging, instrument classification, key detection, and more. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised music representation learning model for music understanding. Distinguished from previous studies adopting random projection or existing neural codec, the proposed model, named MuQ, is trained to predict tokens generated by Mel Residual Vector Quantization (Mel-RVQ). Our Mel-RVQ utilizes residual linear projection structure for Mel spectrum quantization to enhance the stability and efficiency of target extraction and lead to better performance. Experiments in a large variety of downstream tasks demonstrate that MuQ outperforms previous self-supervised music representation models with only 0.9K hours of open-source pre-training data. Scaling up the data to over 160K hours and adopting iterative training consistently improve the model performance. To further validate the strength of our model, we present MuQ-MuLan, a joint music-text embedding model based on contrastive learning, which achieves state-of-the-art performance in the zero-shot music tagging task on the MagnaTagATune dataset. Code and checkpoints are open source in https://github.com/tencent-ailab/MuQ.
SongEditor: Adapting Zero-Shot Song Generation Language Model as a Multi-Task Editor
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The emergence of novel generative modeling paradigms, particularly audio language models, has significantly advanced the field of song generation. Although state-of-the-art models are capable of synthesizing both vocals and accompaniment tracks up to several minutes long concurrently, research about partial adjustments or editing of existing songs is still underexplored, which allows for more flexible and effective production. In this paper, we present SongEditor, the first song editing paradigm that introduces the editing capabilities into language-modeling song generation approaches, facilitating both segment-wise and track-wise modifications. SongEditor offers the flexibility to adjust lyrics, vocals, and accompaniments, as well as synthesizing songs from scratch. The core components of SongEditor include a music tokenizer, an autoregressive language model, and a diffusion generator, enabling generating an entire section, masked lyrics, or even separated vocals and background music. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SongEditor achieves exceptional performance in end-to-end song editing, as evidenced by both objective and subjective metrics. Audio samples are available in \url{https://cypress-yang.github.io/SongEditor_demo/}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge