Rongzhi Gu
MEPIC: Memory Efficient Position Independent Caching for LLM Serving
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Modern LLM applications such as deep-research assistants, coding agents, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems, repeatedly process long prompt histories containing shared document or code chunks, creating significant pressure on the Key Value (KV) cache, which must operate within limited memory while sustaining high throughput and low latency. Prefix caching partially alleviates some of these costs by reusing KV cache for previously processed tokens, but limited by strict prefix matching. Position-independent caching (PIC) enables chunk-level reuse at arbitrary positions, but requires selective recomputation and positional-encoding (PE) adjustments. However, because these operations vary across queries, KV for the same chunk diverges across requests. Moreover, without page alignment, chunk KV layouts diverge in memory, preventing page sharing. These issues result in only modest HBM savings even when many requests reuse the same content. We present MEPIC, a memory-efficient PIC system that enables chunk KV reuse across positions, requests, and batches. MEPIC aligns chunk KV to paged storage, shifts recomputation from token- to block-level so only the first block is request-specific, removes positional encodings via Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE) fusion in the attention kernel, and makes remaining blocks fully shareable. These techniques eliminate most duplicate chunk KV in HBM, reducing usage by up to 2x over state-of-the-art PIC at comparable latency and accuracy, and up to 5x for long prompts, without any model changes.
WAKE: Watermarking Audio with Key Enrichment
Jun 06, 2025
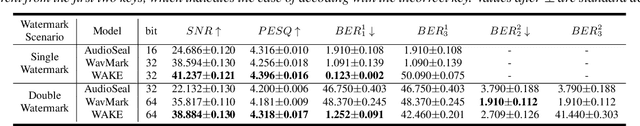
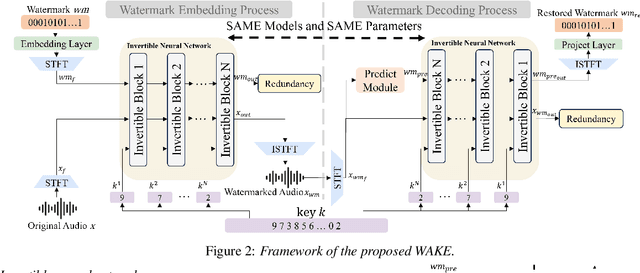
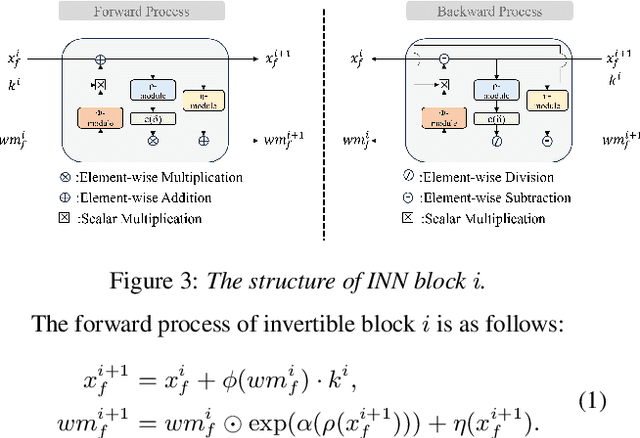
Abstract:As deep learning advances in audio generation, challenges in audio security and copyright protection highlight the need for robust audio watermarking. Recent neural network-based methods have made progress but still face three main issues: preventing unauthorized access, decoding initial watermarks after multiple embeddings, and embedding varying lengths of watermarks. To address these issues, we propose WAKE, the first key-controllable audio watermark framework. WAKE embeds watermarks using specific keys and recovers them with corresponding keys, enhancing security by making incorrect key decoding impossible. It also resolves the overwriting issue by allowing watermark decoding after multiple embeddings and supports variable-length watermark insertion. WAKE outperforms existing models in both watermarked audio quality and watermark detection accuracy. Code, more results, and demo page: https://thuhcsi.github.io/WAKE.
MuQ: Self-Supervised Music Representation Learning with Mel Residual Vector Quantization
Jan 03, 2025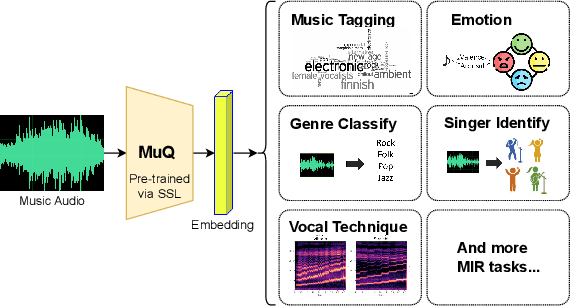



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the success of foundation models pre-trained with self-supervised learning (SSL) in various music informatics understanding tasks, including music tagging, instrument classification, key detection, and more. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised music representation learning model for music understanding. Distinguished from previous studies adopting random projection or existing neural codec, the proposed model, named MuQ, is trained to predict tokens generated by Mel Residual Vector Quantization (Mel-RVQ). Our Mel-RVQ utilizes residual linear projection structure for Mel spectrum quantization to enhance the stability and efficiency of target extraction and lead to better performance. Experiments in a large variety of downstream tasks demonstrate that MuQ outperforms previous self-supervised music representation models with only 0.9K hours of open-source pre-training data. Scaling up the data to over 160K hours and adopting iterative training consistently improve the model performance. To further validate the strength of our model, we present MuQ-MuLan, a joint music-text embedding model based on contrastive learning, which achieves state-of-the-art performance in the zero-shot music tagging task on the MagnaTagATune dataset. Code and checkpoints are open source in https://github.com/tencent-ailab/MuQ.
SongEditor: Adapting Zero-Shot Song Generation Language Model as a Multi-Task Editor
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The emergence of novel generative modeling paradigms, particularly audio language models, has significantly advanced the field of song generation. Although state-of-the-art models are capable of synthesizing both vocals and accompaniment tracks up to several minutes long concurrently, research about partial adjustments or editing of existing songs is still underexplored, which allows for more flexible and effective production. In this paper, we present SongEditor, the first song editing paradigm that introduces the editing capabilities into language-modeling song generation approaches, facilitating both segment-wise and track-wise modifications. SongEditor offers the flexibility to adjust lyrics, vocals, and accompaniments, as well as synthesizing songs from scratch. The core components of SongEditor include a music tokenizer, an autoregressive language model, and a diffusion generator, enabling generating an entire section, masked lyrics, or even separated vocals and background music. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SongEditor achieves exceptional performance in end-to-end song editing, as evidenced by both objective and subjective metrics. Audio samples are available in \url{https://cypress-yang.github.io/SongEditor_demo/}.
Gull: A Generative Multifunctional Audio Codec
Apr 07, 2024Abstract:We introduce Gull, a generative multifunctional audio codec. Gull is a general purpose neural audio compression and decompression model which can be applied to a wide range of tasks and applications such as real-time communication, audio super-resolution, and codec language models. The key components of Gull include (1) universal-sample-rate modeling via subband modeling schemes motivated by recent progress in audio source separation, (2) gain-shape representations motivated by traditional audio codecs, (3) improved residual vector quantization modules for simpler training, (4) elastic decoder network that enables user-defined model size and complexity during inference time, (5) built-in ability for audio super-resolution without the increase of bitrate. We compare Gull with existing traditional and neural audio codecs and show that Gull is able to achieve on par or better performance across various sample rates, bitrates and model complexities in both subjective and objective evaluation metrics.
SECap: Speech Emotion Captioning with Large Language Model
Dec 23, 2023



Abstract:Speech emotions are crucial in human communication and are extensively used in fields like speech synthesis and natural language understanding. Most prior studies, such as speech emotion recognition, have categorized speech emotions into a fixed set of classes. Yet, emotions expressed in human speech are often complex, and categorizing them into predefined groups can be insufficient to adequately represent speech emotions. On the contrary, describing speech emotions directly by means of natural language may be a more effective approach. Regrettably, there are not many studies available that have focused on this direction. Therefore, this paper proposes a speech emotion captioning framework named SECap, aiming at effectively describing speech emotions using natural language. Owing to the impressive capabilities of large language models in language comprehension and text generation, SECap employs LLaMA as the text decoder to allow the production of coherent speech emotion captions. In addition, SECap leverages HuBERT as the audio encoder to extract general speech features and Q-Former as the Bridge-Net to provide LLaMA with emotion-related speech features. To accomplish this, Q-Former utilizes mutual information learning to disentangle emotion-related speech features and speech contents, while implementing contrastive learning to extract more emotion-related speech features. The results of objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that: 1) the SECap framework outperforms the HTSAT-BART baseline in all objective evaluations; 2) SECap can generate high-quality speech emotion captions that attain performance on par with human annotators in subjective mean opinion score tests.
ReZero: Region-customizable Sound Extraction
Aug 31, 2023



Abstract:We introduce region-customizable sound extraction (ReZero), a general and flexible framework for the multi-channel region-wise sound extraction (R-SE) task. R-SE task aims at extracting all active target sounds (e.g., human speech) within a specific, user-defined spatial region, which is different from conventional and existing tasks where a blind separation or a fixed, predefined spatial region are typically assumed. The spatial region can be defined as an angular window, a sphere, a cone, or other geometric patterns. Being a solution to the R-SE task, the proposed ReZero framework includes (1) definitions of different types of spatial regions, (2) methods for region feature extraction and aggregation, and (3) a multi-channel extension of the band-split RNN (BSRNN) model specified for the R-SE task. We design experiments for different microphone array geometries, different types of spatial regions, and comprehensive ablation studies on different system configurations. Experimental results on both simulated and real-recorded data demonstrate the effectiveness of ReZero. Demos are available at https://innerselfm.github.io/rezero/.
Ultra Dual-Path Compression For Joint Echo Cancellation And Noise Suppression
Aug 21, 2023



Abstract:Echo cancellation and noise reduction are essential for full-duplex communication, yet most existing neural networks have high computational costs and are inflexible in tuning model complexity. In this paper, we introduce time-frequency dual-path compression to achieve a wide range of compression ratios on computational cost. Specifically, for frequency compression, trainable filters are used to replace manually designed filters for dimension reduction. For time compression, only using frame skipped prediction causes large performance degradation, which can be alleviated by a post-processing network with full sequence modeling. We have found that under fixed compression ratios, dual-path compression combining both the time and frequency methods will give further performance improvement, covering compression ratios from 4x to 32x with little model size change. Moreover, the proposed models show competitive performance compared with fast FullSubNet and DeepFilterNet. A demo page can be found at hangtingchen.github.io/ultra_dual_path_compression.github.io/.
The Sound Demixing Challenge 2023 $\unicode{x2013}$ Cinematic Demixing Track
Aug 14, 2023
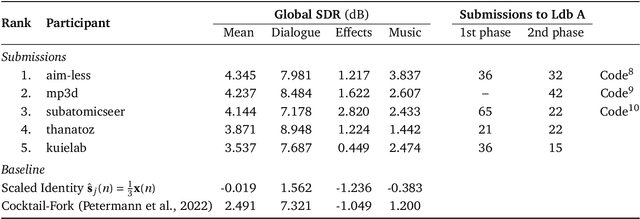


Abstract:This paper summarizes the cinematic demixing (CDX) track of the Sound Demixing Challenge 2023 (SDX'23). We provide a comprehensive summary of the challenge setup, detailing the structure of the competition and the datasets used. Especially, we detail CDXDB23, a new hidden dataset constructed from real movies that was used to rank the submissions. The paper also offers insights into the most successful approaches employed by participants. Compared to the cocktail-fork baseline, the best-performing system trained exclusively on the simulated Divide and Remaster (DnR) dataset achieved an improvement of 1.8dB in SDR whereas the top performing system on the open leaderboard, where any data could be used for training, saw a significant improvement of 5.7dB.
Fast Random Approximation of Multi-channel Room Impulse Response
Apr 17, 2023



Abstract:Modern neural-network-based speech processing systems are typically required to be robust against reverberation, and the training of such systems thus needs a large amount of reverberant data. During the training of the systems, on-the-fly simulation pipeline is nowadays preferred as it allows the model to train on infinite number of data samples without pre-generating and saving them on harddisk. An RIR simulation method thus needs to not only generate more realistic artificial room impulse response (RIR) filters, but also generate them in a fast way to accelerate the training process. Existing RIR simulation tools have proven effective in a wide range of speech processing tasks and neural network architectures, but their usage in on-the-fly simulation pipeline remains questionable due to their computational complexity or the quality of the generated RIR filters. In this paper, we propose FRAM-RIR, a fast random approximation method of the widely-used image-source method (ISM), to efficiently generate realistic multi-channel RIR filters. FRAM-RIR bypasses the explicit calculation of sound propagation paths in ISM-based algorithms by randomly sampling the location and number of reflections of each virtual sound source based on several heuristic assumptions, while still maintains accurate direction-of-arrival (DOA) information of all sound sources. Visualization of oracle beampatterns and directional features shows that FRAM-RIR can generate more realistic RIR filters than existing widely-used ISM-based tools, and experiment results on multi-channel noisy speech separation and dereverberation tasks with a wide range of neural network architectures show that models trained with FRAM-RIR can also achieve on par or better performance on real RIRs compared to other RIR simulation tools with a significantly accelerated training procedure. A Python implementation of FRAM-RIR is released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge